Flutter for OpenHarmony 进阶实战:打造 60FPS 流畅的物理切水果游戏
摘要: 在上一篇文章中,我们实现了一个基础的切水果原型。今天,我们将对其进行"硬核"升级。我们将引入物理模拟,让水果飞溅、切开后产生碎片并受重力影响下落,同时优化渲染循环以确保在
Trae 环境及真机上都能保持 60FPS 的流畅体验。本文将深入讲解如何在 Flutter 中构建简单的物理引擎和粒子系统。
成功运行效果
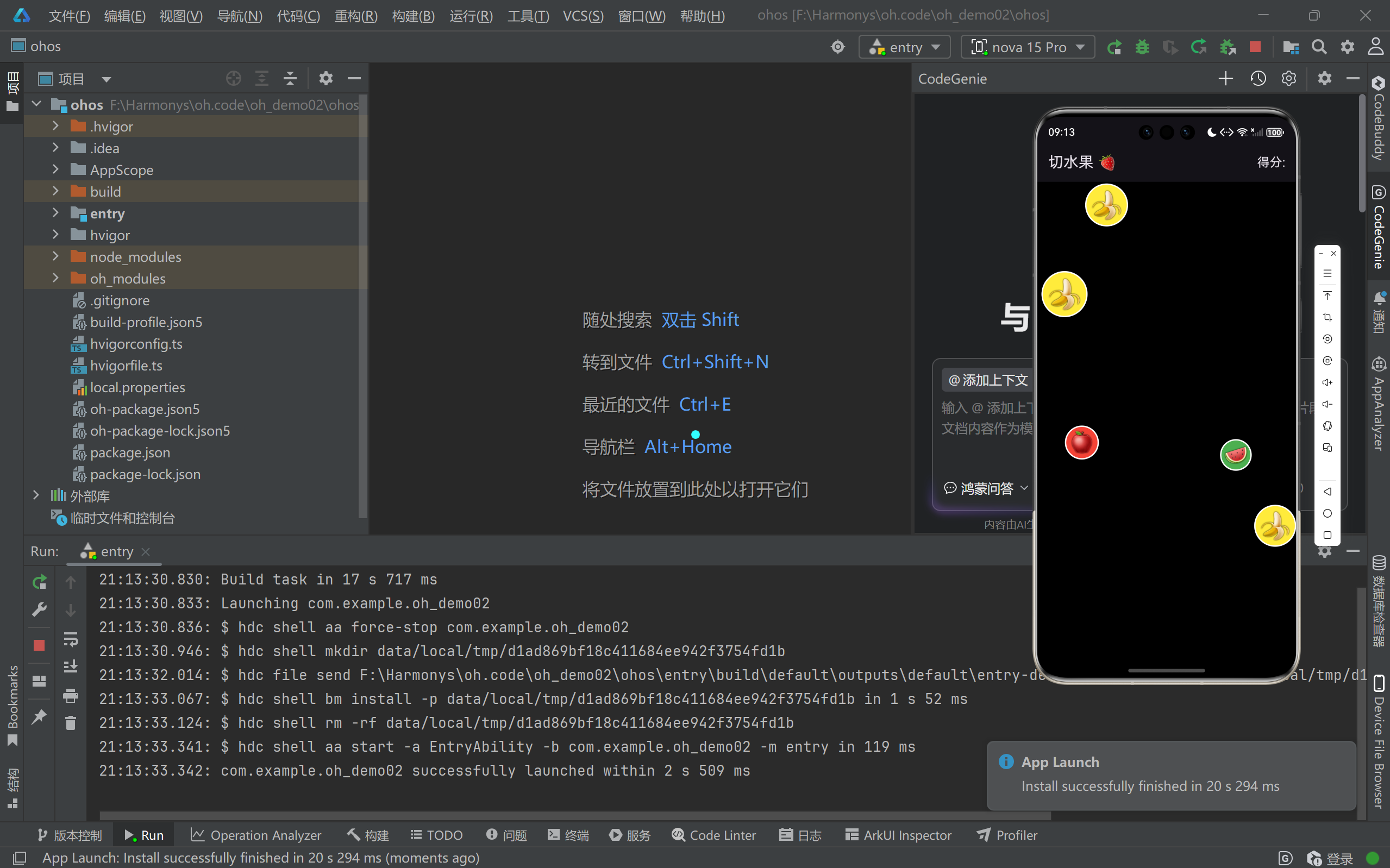
完整效果展示
完整代码展示
dart
import 'dart:math';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: '切水果游戏',
theme: ThemeData.dark().copyWith(
scaffoldBackgroundColor: Colors.black,
),
home: const FruitNinjaGame(),
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
);
}
}
class FruitNinjaGame extends StatefulWidget {
const FruitNinjaGame({super.key});
@override
State<FruitNinjaGame> createState() => _FruitNinjaGameState();
}
class _FruitNinjaGameState extends State<FruitNinjaGame>
with TickerProviderStateMixin {
// 水果列表,存储当前屏幕上所有的水果
final List<Fruit> _fruits = [];
// 刀光轨迹点
final List<Offset> _swordPoints = [];
// 分数
int _score = 0;
late AnimationController _controller;
// 重力加速度
static const double _gravity = 0.2;
// 下坠动画列表
final List<FallingPart> _fallingParts = [];
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_controller = AnimationController(
vsync: this, duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 16))
..repeat(); // 每秒约60帧
// 开始生成水果
_startSpawning();
// 启动物理更新循环
_controller.addListener(_updatePhysics);
}
@override
void dispose() {
_controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
// 生成水果的定时器
void _startSpawning() {
Future.delayed(const Duration(milliseconds: 300), () {
if (mounted) {
_spawnFruit();
// 递归调用,实现循环生成
_startSpawning();
}
});
}
// 生成多个水果
void _spawnFruit() {
final random = Random();
// 每次生成1-3个水果
final fruitCount = 1 + random.nextInt(3);
for (int i = 0; i < fruitCount; i++) {
// 随机从底部或顶部出现
final bool fromBottom = random.nextBool();
final double startX =
random.nextDouble() * MediaQuery.of(context).size.width;
// 随机水果类型
final FruitType type =
FruitType.values[random.nextInt(FruitType.values.length)];
// 随机速度
final double speed = 2 + random.nextDouble() * 3;
setState(() {
_fruits.add(
Fruit(
position: Offset(
startX, fromBottom ? MediaQuery.of(context).size.height : 0),
velocity: Offset(0, fromBottom ? -speed : speed),
type: type,
size: 40 + random.nextDouble() * 30,
),
);
});
}
}
// 切割逻辑
void _checkCut(Offset point) {
setState(() {
// 添加刀光点
_swordPoints.add(point);
// 限制刀光点数量,防止内存溢出
if (_swordPoints.length > 10) {
_swordPoints.removeAt(0);
}
// 遍历所有水果,检查是否被切中
for (int i = _fruits.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final fruit = _fruits[i];
// 计算刀光点到水果中心的距离
for (var swordPoint in _swordPoints) {
final double distance = (swordPoint - fruit.position).distance;
// 如果距离小于水果半径,则判定为切中
if (distance < fruit.size / 2) {
_score += 10;
// 创建下坠碎片效果
_createFallingParts(fruit);
// 从列表中移除该水果
_fruits.removeAt(i);
break;
}
}
}
});
}
// 创建下坠的碎片
void _createFallingParts(Fruit fruit) {
final random = Random();
// 创建4-6个碎片
final partCount = 4 + random.nextInt(3);
for (int i = 0; i < partCount; i++) {
final angle = (2 * pi / partCount) * i + random.nextDouble() * 0.5;
final speed = 2 + random.nextDouble() * 3;
_fallingParts.add(FallingPart(
position: fruit.position,
velocity: Offset(
cos(angle) * speed,
sin(angle) * speed - 2, // 稍微向上抛出
),
color: fruit.type.color,
icon: fruit.type.icon,
size: fruit.size * (0.3 + random.nextDouble() * 0.4),
rotation: random.nextDouble() * 2 * pi,
rotationSpeed: (random.nextDouble() - 0.5) * 0.3,
));
}
}
// 更新物理状态
void _updatePhysics() {
if (!mounted) return;
setState(() {
// 更新水果位置(未切割的)
for (var fruit in _fruits) {
// 应用重力加速度,使水果具有下坠效果
fruit.velocity =
Offset(fruit.velocity.dx, fruit.velocity.dy + _gravity);
fruit.position += fruit.velocity;
}
// 更新下坠碎片
for (int i = _fallingParts.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final part = _fallingParts[i];
part.velocity = Offset(part.velocity.dx, part.velocity.dy + _gravity);
part.position += part.velocity;
part.rotation += part.rotationSpeed;
// 移除超出屏幕的碎片
if (part.position.dy > MediaQuery.of(context).size.height + 100) {
_fallingParts.removeAt(i);
}
}
// 移除超出屏幕的水果
for (int i = _fruits.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final fruit = _fruits[i];
if (fruit.position.dy > MediaQuery.of(context).size.height + 100 ||
fruit.position.dy < -100 ||
fruit.position.dx > MediaQuery.of(context).size.width + 100 ||
fruit.position.dx < -100) {
_fruits.removeAt(i);
}
}
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('切水果 🍓'),
actions: [
Text('得分: ', style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 18)),
],
),
body: Stack(
children: [
// --- 水果绘制区 ---
..._fruits.map((fruit) {
return Positioned(
left: fruit.position.dx - fruit.size / 2,
top: fruit.position.dy - fruit.size / 2,
child: Container(
width: fruit.size,
height: fruit.size,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
shape: BoxShape.circle,
color: fruit.type.color,
border: Border.all(color: Colors.white, width: 2),
),
child: Center(
child: Text(
fruit.type.icon,
style: TextStyle(fontSize: fruit.size * 0.6, shadows: [
const Shadow(
blurRadius: 5,
color: Colors.black,
offset: Offset(0, 0))
]),
),
),
),
);
}).toList(),
// --- 下坠碎片绘制区 ---
..._fallingParts.map((part) {
return Positioned(
left: part.position.dx - part.size / 2,
top: part.position.dy - part.size / 2,
child: Transform.rotate(
angle: part.rotation,
child: Container(
width: part.size,
height: part.size,
decoration: BoxDecoration(
shape: BoxShape.circle,
color: part.color,
border: Border.all(color: Colors.white, width: 1),
),
child: Center(
child: Text(
part.icon,
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: part.size * 0.6,
shadows: const [
Shadow(
blurRadius: 3,
color: Colors.black,
offset: Offset(0, 0),
),
],
),
),
),
),
),
);
}).toList(),
// --- 刀光绘制区 ---
if (_swordPoints.isNotEmpty)
CustomPaint(
size: Size.infinite,
painter: SwordTrailPainter(_swordPoints),
),
// --- 手势检测蒙版 ---
// 放在最上层以拦截所有触摸事件
GestureDetector(
onPanUpdate: (details) {
// 将全局坐标转换为逻辑坐标
_checkCut(details.localPosition);
},
onPanEnd: (_) {
// 刀光轨迹清空
_swordPoints.clear();
},
child: Container(color: Colors.transparent),
),
],
),
);
}
}
// 水果数据模型
class Fruit {
Offset position;
Offset velocity;
final FruitType type;
final double size;
bool isSliced;
List<Offset>? sliceParticles;
Fruit({
required this.position,
required this.velocity,
required this.type,
required this.size,
this.isSliced = false,
this.sliceParticles,
});
}
// 水果类型枚举
enum FruitType {
apple('🍎', Colors.red),
banana('🍌', Colors.yellow),
strawberry('🍓', Colors.pink),
watermelon('🍉', Colors.green);
const FruitType(this.icon, this.color);
final String icon;
final Color color;
}
// 刀光轨迹绘制器
class SwordTrailPainter extends CustomPainter {
final List<Offset> points;
SwordTrailPainter(this.points);
@override
void paint(Canvas canvas, Size size) {
if (points.length < 2) return;
final paint = Paint()
..color = Colors.white.withOpacity(0.8)
..strokeWidth = 5
..strokeCap = StrokeCap.round
..style = PaintingStyle.stroke;
final path = Path();
path.moveTo(points[0].dx, points[0].dy);
for (int i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
path.lineTo(points[i].dx, points[i].dy);
}
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
}
@override
bool shouldRepaint(covariant CustomPainter oldDelegate) => true;
}
// 下坠碎片类
class FallingPart {
Offset position;
Offset velocity;
final Color color;
final String icon;
final double size;
double rotation;
final double rotationSpeed;
FallingPart({
required this.position,
required this.velocity,
required this.color,
required this.icon,
required this.size,
required this.rotation,
required this.rotationSpeed,
});
}一、 引言:从"幻灯片"到"物理世界"
在上一版的切水果游戏中,我们使用了简单的 Future.delayed 来生成水果,并通过线性速度移动它们。虽然功能可用,但存在两个主要问题:
- 帧率不可控:水果生成和移动的频率取决于 CPU 性能,可能导致卡顿或过快。
- 缺乏真实感:切开后水果直接消失,没有物理反馈。
为了解决这些问题,我们将重构代码,利用 AnimationController 驱动游戏主循环,并引入重力加速度公式,让游戏世界拥有真实的物理规则。
二、 项目架构与核心状态管理
我们的游戏状态管理类 _FruitNinjaGameState 是整个游戏的心脏。在这个版本中,我们不仅管理水果列表,还增加了碎片列表 和物理更新逻辑。
核心状态变量解析:
| 变量名 | 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
_fruits |
List<Fruit> |
存储当前屏幕上所有正在飞行的完整水果。 |
_fallingParts |
List<FallingPart> |
存储切开后产生的碎片,它们拥有独立的物理属性。 |
_swordPoints |
List<Offset> |
记录用户手指轨迹,用于绘制刀光。 |
_score |
int |
记录当前得分。 |
_controller |
AnimationController |
游戏的"节拍器",驱动物理更新。 |
_gravity |
double |
全局重力加速度常量。 |
三、 游戏主循环:基于 AnimationController 的驱动机制
在 Flutter 游戏开发中,使用 Timer 或 Future 进行循环更新并不是最佳实践,因为它们与屏幕的刷新率(VSync)不同步,容易导致掉帧。
代码亮点:基于 VSync 的物理更新
在 initState 中,我们创建了一个特殊的 AnimationController:
dart
_controller = AnimationController(
vsync: this,
duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 16)) // 1000ms / 60 ≈ 16ms
..repeat(); // 永久循环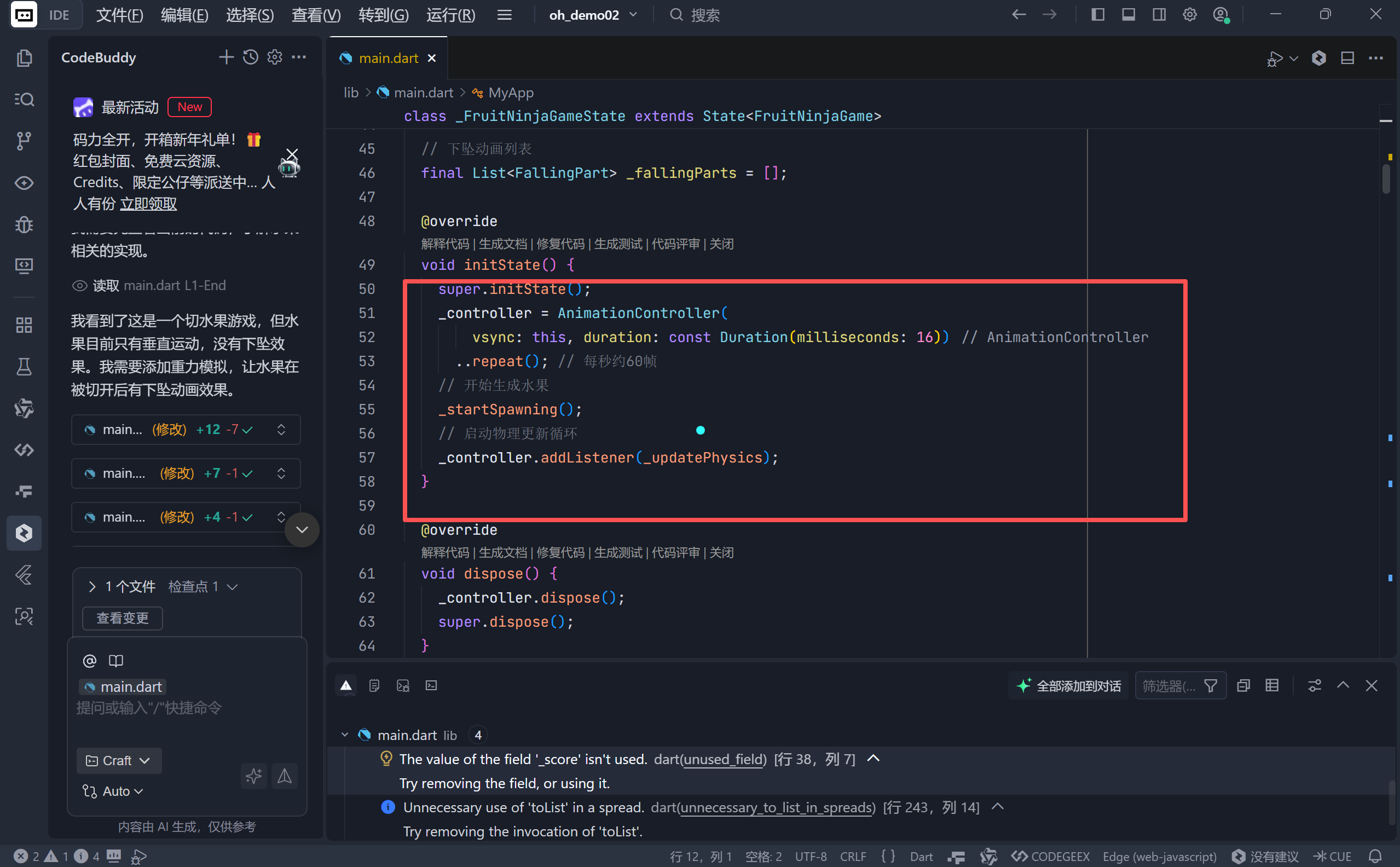
关键点解析:
- VSync 同步 :
vsync: this确保了动画与屏幕刷新率同步,避免画面撕裂。- 16ms 帧间隔 :我们将 Duration 设为 16 毫秒(约等于 60FPS),虽然
AnimationController通常用于 UI 动画,但在这里我们将其用作游戏循环的触发器。- 监听器绑定 :
_controller.addListener(_updatePhysics)。每一帧(每 16ms),_updatePhysics函数都会被调用,负责计算所有物体的新位置。
四、 物理引擎核心:重力与运动
为了让水果的运动看起来更自然,我们不能只给它一个恒定的速度。在真实世界中,抛射物体受到重力影响,垂直速度会不断变化。
1. 重力常量定义
我们在类中定义了一个静态常量:
dart
static const double _gravity = 0.2;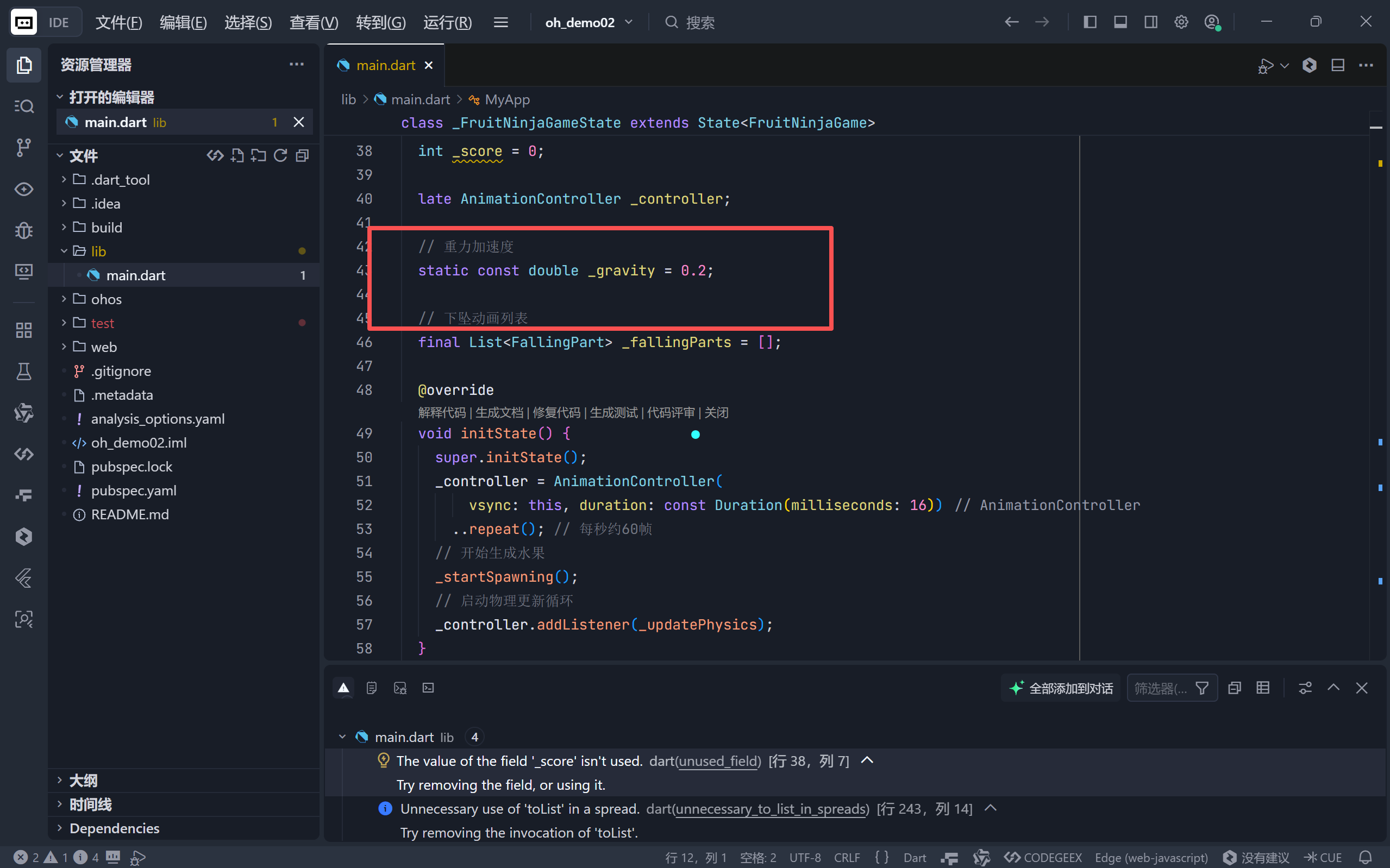
这个数值是经过调试的,太大会导致水果瞬间掉落,太小则像在月球上。
2. 物理更新逻辑 (_updatePhysics)
这是游戏最核心的数学部分:
dart
void _updatePhysics() {
if (!mounted) return;
setState(() {
// 1. 更新水果位置
for (var fruit in _fruits) {
// 核心物理公式:v = v0 + at (速度 = 初始速度 + 重力加速度)
fruit.velocity = Offset(
fruit.velocity.dx,
fruit.velocity.dy + _gravity
);
// 位置更新:s = s0 + v (位置 = 旧位置 + 速度)
fruit.position += fruit.velocity;
}
// 2. 更新碎片位置(包含旋转)
for (int i = _fallingParts.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final part = _fallingParts[i];
part.velocity = Offset(part.velocity.dx, part.velocity.dy + _gravity);
part.position += part.velocity;
part.rotation += part.rotationSpeed; // 更新旋转角度
// 移除屏幕外的碎片
if (part.position.dy > screenHeight + 100) _fallingParts.removeAt(i);
}
// 3. 移除屏幕外的水果
_fruits.removeWhere((fruit) =>
fruit.position.dy > screenHeight + 100 ||
fruit.position.offScreen);
});
}
物理模拟流程图解:
- 每一帧 :读取当前速度 -> 加上重力 -> 计算新位置 -> 渲染。
- 结果:水果飞出的轨迹不再是直线,而是优美的抛物线。
五、 视觉反馈:刀光与碰撞检测
1. 刀光轨迹 (SwordTrailPainter)
为了提供切割的手感,我们需要绘制用户的手指轨迹。
- 数据结构 :使用
List<Offset>存储最近的几个触摸点。 - 绘制原理 :在
CustomPaint中,将这些点用Path连接起来,形成一条白色的光带。 - 优化:代码中限制了点的数量(10个),防止列表无限增长导致内存溢出。
2. 碰撞检测逻辑 (_checkCut)
检测逻辑非常直观,采用圆形碰撞检测:
- 原理:计算手指点(刀光)与水果中心点的距离。
- 公式 :
distance = (pointA - pointB).distance- 判定 :如果
distance < fruit.radius,则判定为切中。
dart
final double distance = (swordPoint - fruit.position).distance;
if (distance < fruit.size / 2) {
// 触发切开效果
}六、 粒子系统:水果切开的爆炸效果
这是本版本最酷炫的部分。当水果被切中时,它不会直接消失,而是分裂成多个碎片(Particles)。
1. 碎片生成算法 (_createFallingParts)
我们不生成新的水果,而是生成 FallingPart 对象。
- 数量:随机生成 4-6 个碎片。
- 方向 :使用三角函数
cos和sin计算环绕中心点的发射角度。 - 初始速度 :给碎片一个向外飞溅的速度,并给予一个向上的初速度(
-2)以模拟被"切飞"的感觉。
dart
// 计算发射角度
final angle = (2 * pi / partCount) * i + randomOffset;
// 计算 X, Y 分量速度
final speed = 2 + random.nextDouble() * 3;
Offset velocity = Offset(
cos(angle) * speed,
sin(angle) * speed - 2
);2. 碎片属性
每个 FallingPart 拥有自己的:
- 位置与速度:独立于主水果,受重力影响。
- 旋转 (Rotation):碎片在下落时会自转,增加了视觉混乱感和真实感。
- 大小:碎片比原水果小(0.3-0.7倍)。
七、 UI 组件与数据模型
为了保持代码的整洁,我们使用了枚举和数据类来管理资源。
1. 水果类型枚举 (FruitType)
使用枚举来管理水果的外观,这是一种非常优雅的做法:
dart
enum FruitType {
apple('🍎', Colors.red),
banana('🍌', Colors.yellow);
const FruitType(this.icon, this.color);
final String icon;
final Color color;
}
这样,当我们需要增加新水果(如蓝莓)时,只需在枚举中添加一行,无需修改逻辑代码。
2. 状态管理 (Fruit & FallingPart)
注意 Fruit 类中的属性是 var 而不是 final。
- 原因 :因为在
_updatePhysics中,我们需要直接修改fruit.position和fruit.velocity。如果声明为final,我们无法在不重建对象的情况下修改其位置,这会导致大量的对象创建和销毁(GC 压力),影响性能。
八、 性能优化与边界处理
在无限循环的游戏中,内存管理至关重要。
- 对象回收 :无论是
_fruits还是_fallingParts,一旦它们飞出屏幕边界(position.y > screenHeight + 100),我们立即从列表中移除。这防止了列表无限膨胀拖慢游戏。 - Widget 复用 :在
build方法中,我们使用了..._fruits.map。虽然这在水果数量少时没问题,但如果水果过多,建议使用ListView.builder或者CustomMultiChildLayout来优化构建性能。 - 资源释放 :在
dispose中正确释放了_controller,防止内存泄漏。
九、 总结与扩展
通过这篇文章,我们完成了一个具备基本物理特性的切水果游戏。我们学习了:
- 如何利用
AnimationController实现游戏主循环。 - 基础的物理运动学公式(加速度、速度、位移)在代码中的实现。
- 粒子系统的简单构建(发射、重力、销毁)。
- 圆形碰撞检测算法。
后续扩展建议:
- 音效 :在切割和得分时加入音效(使用
audioplayers包)。 - 炸弹机制:引入炸弹水果,切中扣分。
- 连击系统:检测短时间内连续切中水果,增加连击分数。
- 更真实的切开动画 :使用
CustomClipper实现水果被切开的两半分离动画,而不仅仅是变成碎片。
这个项目展示了 Flutter 不仅适合开发传统的业务应用,也能胜任轻量级的 2D 游戏开发。希望你能通过这个项目,更深入地理解 Flutter 的渲染机制和状态管理。
🌐 加入社区
欢迎加入 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区 ,获取最新资源与技术支持:
技术因分享而进步,生态因共建而繁荣 。
------ 晚霞的不甘 · 与您共赴鸿蒙跨平台开发之旅