文章目录
- 0.个人感悟
- [1. 概念](#1. 概念)
- [2. 适配场景](#2. 适配场景)
-
- [2.1 适合的场景](#2.1 适合的场景)
- [2.2 常见场景举例](#2.2 常见场景举例)
- [3. 实现方法](#3. 实现方法)
-
- [3.1 实现思路](#3.1 实现思路)
- [3.2 UML类图](#3.2 UML类图)
- [3.3 代码示例](#3.3 代码示例)
- [4. 优缺点](#4. 优缺点)
-
- [4.1 优点](#4.1 优点)
- [4.2 缺点](#4.2 缺点)
0.个人感悟
- 中介者模式核心是解耦,抽取一个中间层中介对象,让原来相关耦合的对象(多对对)都只与中介对象交互(一对多),由中介对象维护关系和交互
- 优缺点很明显,最明显优点是解耦,对象关系变得清晰;最明显缺点是对象的交互都由中介完成,容易导致代码杂乱膨胀。看了很多示例,中介者的逻辑都很复杂,比如智能家居,会设置多个模式,然后很多if else
- 建议实际使用时,对于中介者这块结合业务做好设计和实现
1. 概念
英文定义(《设计模式:可复用面向对象软件的基础》)
Define an object that encapsulates how a set of objects interact. Mediator promotes loose coupling by keeping objects from referring to each other explicitly, and it lets you vary their interaction independently.
中文翻译
定义一个中介对象来封装一系列对象之间的交互。中介者使各对象不需要显式地相互引用,从而使其耦合松散,而且可以独立地改变它们之间的交互。
理解
- 中介者模式的核心思想是集中控制多个对象之间的交互逻辑
- 将原本对象间的直接通信转为通过中介者间接通信
- 对象之间不再相互持有引用,只依赖中介者
- 交互逻辑从中介者的"同事类"中抽离,集中到中介者中管理
- 本质上是一种"多个对象通信的解耦"模式
2. 适配场景
2.1 适合的场景
- 复杂网状交互:当多个对象间存在复杂的网状引用关系,交互逻辑混乱时
- 通信协议统一化:需要定义一组对象间的通信协议,且这组协议可能变化时
- 行为可复用性差:由于对象间强耦合导致行为难以复用
2.2 常见场景举例
- 航空管制系统:飞机、塔台、跑道之间的通信通过空中交通管制中心协调
- 聊天室应用:多个用户通过聊天服务器中转消息,而不是直接P2P通信
- MVC架构:Controller作为Model和View之间的中介者
- GUI对话框:对话框中的各种控件(按钮、输入框、复选框)通过对话框协调
3. 实现方法
3.1 实现思路
- 识别交互群体:找出需要解耦的相互通信对象集合
- 定义中介者接口:声明协调各对象交互的方法
- 创建具体中介者:实现中介者接口,持有所有"同事"对象的引用
- 定义同事接口:声明同事对象的基本行为,包含中介者引用
- 重构同事类 :
- 移除与其他同事的直接引用
- 添加中介者引用
- 将原本直接调用改为通过中介者转发
- 客户端配置:创建中介者并注册所有同事对象
3.2 UML类图
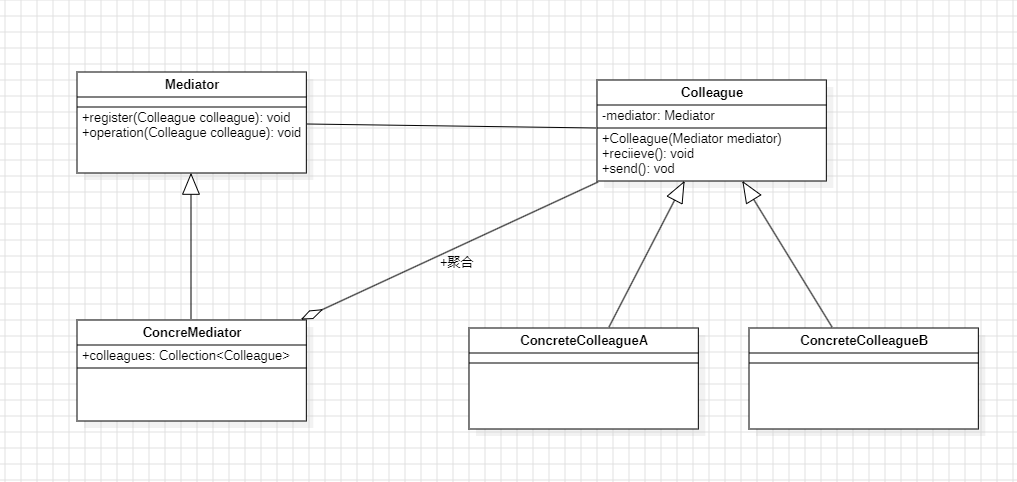
角色说明:
- Mediator(中介者接口):定义同事对象通信的接口
- ConcreteMediator(具体中介者):实现中介者接口,协调各同事对象的交互,知道所有同事
- Colleague(同事接口):定义同事类的接口,持有中介者引用
- ConcreteColleague(具体同事):实现同事接口,每个同事只知道中介者,不知道其他同事
3.3 代码示例
背景:以租房中介为例,简化一下流程
- 租客和房东互不依赖,都只与中介打交道
- 租客行为简化为 浏览房源、请求看房、接受消息
- 房东行为简化为发布房源、接受消息
设计
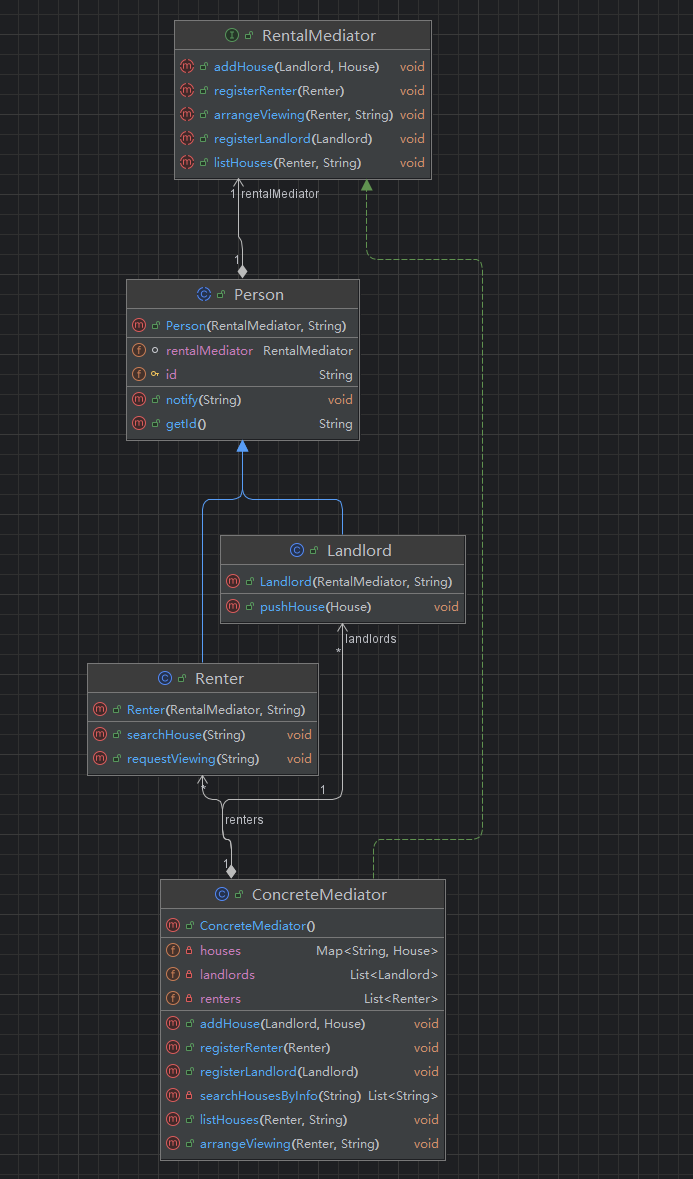
中介接口
- 定义租客和房东诉求
java
public interface RentalMediator {
/**
* @param renter 租客
* @description 租客注册
* @author bigHao
* @date 2026/1/26
**/
void registerRenter(Renter renter);
/**
* @param landlord 房东
* @description 房东注册
* @author bigHao
* @date 2026/1/26
**/
void registerLandlord(Landlord landlord);
/**
* @param renter 租客
* @param request 请求信息
* @description 查看房源列表
* @author bigHao
* @date 2026/1/26
**/
void listHouses(Renter renter, String request);
/**
* @param landlord 房东
* @param house 房子信息
* @description 添加房源
* @author bigHao
* @date 2026/1/26
**/
void addHouse(Landlord landlord, House house);
/**
* @param renter 租客
* @param houseId 房子id
* @description 预约看房
* @author bigHao
* @date 2026/1/26
**/
void arrangeViewing(Renter renter, String houseId);
}同事接口和实现
- 这里抽象出父类person,公共属性为id和中介者,接受通知方法简化成只打印信息,不区分细节
- 租客类定义租客行为,都调用中介方法
- 房东类定义房东行为,都调用中介方法
java
public abstract class Person {
RentalMediator rentalMediator;
protected String id;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public Person(RentalMediator rentalMediator, String id) {
this.rentalMediator = rentalMediator;
this.id = id;
}
/**
* @param info 通知信息
* @description 通知
* @author bigHao
* @date 2026/1/26
**/
public void notify(String info) {
System.out.println(STR."\{id} 收到消息: \{info}");
}
}
public class Renter extends Person {
public Renter(RentalMediator rentalMediator, String id) {
super(rentalMediator, id);
rentalMediator.registerRenter(this);
}
/**
* @param request 请求
* @description 搜索房源
* @author bigHao
* @date 2026/1/26
**/ public void searchHouse(String request) {
rentalMediator.listHouses(this, request);
}
/**
* @param houseId 房子id
* @description 请求看房
* @author bigHao
* @date 2026/1/26
**/ public void requestViewing(String houseId) {
rentalMediator.arrangeViewing(this, houseId);
}
}
public class Landlord extends Person {
public Landlord(RentalMediator rentalMediator, String id) {
super(rentalMediator, id);
rentalMediator.registerLandlord(this);
}
/**
* @param house 房子
* @description 发布房源
* @author bigHao
* @date 2026/1/26
**/ public void pushHouse(House house) {
rentalMediator.addHouse(this, house);
}
}
// 参数类
public class House {
// 房东id
private String landlordId;
// 房子id
private String houseId;
// 信息
private String info;
public House(String landlordId, String houseId, String info) {
this.landlordId = landlordId;
this.houseId = houseId;
this.info = info;
}
public String getLandlordId() {
return landlordId;
}
public void setLandlordId(String landlordId) {
this.landlordId = landlordId;
}
public String getHouseId() {
return houseId;
}
public void setHouseId(String houseId) {
this.houseId = houseId;
}
public String getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(String info) {
this.info = info;
}
}具体中介者
- 持有房东和租客列表
- 简化房东-房子映射,house map 的key为房子id,vlue为房子信息,里面包含房东id
- 简化匹配房源逻辑,简单用contains来判断
java
public class ConcreteMediator implements RentalMediator {
private List<Renter> renters = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Landlord> landlords = new ArrayList<>();
private Map<String, House> houses = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void registerRenter(Renter renter) {
System.out.println(STR."\{renter.getId()} 注册成为租客");
renters.add(renter);
}
@Override
public void registerLandlord(Landlord landlord) {
System.out.println(STR."\{landlord.getId()} 注册成为房东");
landlords.add(landlord);
}
@Override
public void listHouses(Renter renter, String request) {
System.out.println(STR."\{renter.getId()} 找房");
// 匹配
List<String> housesIds = searchHousesByInfo(request);
// 发送返回结果给租客
String join = String.join(",", housesIds);
renter.notify("请求结果列表: " + join);
}
@Override
public void addHouse(Landlord landlord, House house) {
System.out.println(STR."\{house.getLandlordId()} 发布房子 \{house.getInfo()}");
houses.put(house.getHouseId(), house);
}
@Override
public void arrangeViewing(Renter renter, String houseId) {
System.out.println(STR."\{renter.getId()} 请求看房 \{houseId}");
String landlordId = houses.get(houseId).getLandlordId();
// 查找房东
Landlord landlord = landlords.stream().filter(item -> item.getId().equals(landlordId)).findFirst().get();
String msg = STR."明天15:00 一起看房";
// 给租客发消息
renter.notify(msg);
// 给房东发消息
landlord.notify(msg);
}
private List<String> searchHousesByInfo(String request) {
return houses.values().stream()
.filter(house -> house.getInfo() != null && house.getInfo().contains(request))
.map(House::getHouseId)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}测试
java
public class Client {
static void main() {
// 注册
RentalMediator rentalMediator = new ConcreteMediator();
System.out.println("===注册===");
Renter renter = new Renter(rentalMediator, "租客张三");
Landlord landlord = new Landlord(rentalMediator, "房东李四");
// 房源发布
System.out.println("===发布房源===");
House house1 = new House("房东李四", "房子001", "房租1000 拎包入住");
House house2 = new House("房东李四", "房子002", "房租2000 临近地铁18号线");
House house3 = new House("房东李四", "房子003", "房租2000 学区附近");
House house4 = new House("房东李四", "房子004", "房租5000 面朝大海");
landlord.pushHouse(house1);
landlord.pushHouse(house2);
landlord.pushHouse(house3);
landlord.pushHouse(house4);
// 查房
System.out.println("===查看房源===");
renter.searchHouse("2000");
// 看房
System.out.println("===看房===");
renter.requestViewing("房子002");
}
}输出
===注册===
租客张三 注册成为租客
房东李四 注册成为房东
===发布房源===
房东李四 发布房子 房租1000 拎包入住
房东李四 发布房子 房租2000 临近地铁18号线
房东李四 发布房子 房租2000 学区附近
房东李四 发布房子 房租5000 面朝大海
===查看房源===
租客张三 找房
租客张三 收到消息: 请求结果列表: 房子003,房子002
===看房===
租客张三 请求看房 房子002
租客张三 收到消息: 明天15:00 一起看房
房东李四 收到消息: 明天15:00 一起看房4. 优缺点
4.1 优点
-
高内聚低耦合(核心原则):
- 符合迪米特法则:对象只与中介者通信,减少对象间的直接依赖
- 降低耦合度:将网状依赖变为星型结构,对象间耦合度显著降低
-
可维护性:
- 集中控制:交互逻辑集中在中介者中,易于理解和维护
- 简化协议:将多对多交互简化为一对多交互
-
可扩展性:
- 新增同事类时,只需修改中介者,不影响其他同事
- 可以复用同事类,因为它们不直接依赖其他具体类
-
稳定性:
- 单个同事类的修改不会波及其他同事
- 交互逻辑变化只需修改中介者
4.2 缺点
-
中介者可能成为"上帝对象":
- 中介者可能承担过多职责,变得庞大复杂
- 可能违反单一职责原则
-
性能影响:
- 所有通信都经过中介者,可能成为性能瓶颈
- 增加了一层间接调用,略微影响性能
-
设计复杂性:
- 需要精心设计中介者接口,否则可能限制灵活性
- 过度使用可能导致系统结构不清晰
参考: