目录
最小栈
解法:栈
栈stack的类型为pair,第一个int是当前元素;第二个int是以当前位置为结尾的最小值,这个最小值的获取:push到栈顶之前,去栈顶元素的最小值与当前要插入的新元素去min即可
cpp
class MinStack
{
private:
stack<pair<int, int>> st; // <元素,当前位置为结尾的最小值>
public:
MinStack() {}
void push(int val)
{
if (st.empty())
st.push({val, val});
else
st.push({val, min(st.top().second, val)});
}
void pop()
{
st.pop();
}
int top()
{
return st.top().first;
}
int getMin()
{
return st.top().second;
}
};逆波兰表达式
解法:栈
使用栈收集数字字符,遇到+-*/时就继续计算
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string> &tokens)
{
stack<string> st;
for (auto &token : tokens)
{
// if(st.size()>=2)
//{
if (token == "+")
{
int a = stoi(st.top());
st.pop();
int b = stoi(st.top());
st.pop();
st.push(to_string(a + b));
}
else if (token == "-")
{
int a = stoi(st.top());
st.pop();
int b = stoi(st.top());
st.pop();
st.push(to_string(b - a));
}
else if (token == "*")
{
int a = stoi(st.top());
st.pop();
int b = stoi(st.top());
st.pop();
st.push(to_string(a * b));
}
else if (token == "/")
{
int a = stoi(st.top());
st.pop();
int b = stoi(st.top());
st.pop();
st.push(to_string(b / a));
}
else
st.push(token);
cout << st.top() << endl;
}
return stoi(st.top());
}
};但是if else感觉很累赘,可以使用C++11的包装器来处理变得简洁
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
map<string,function<int(int,int)>> oper =
{ {"+",[](int a,int b) {return a + b;}},
{"-",[](int a,int b) {return a - b;}},
{"*",[](int a,int b) {return a * b;}},
{"/",[](int a,int b) {return a / b;}}
};
stack<int> st;
for(int i=0;i < tokens.size();i++)
{
if(tokens[i] == "+" || tokens[i] == "-" || tokens[i] == "*" || tokens[i] == "/")
{
string op = tokens[i];
int b = st.top();st.pop();
int a = st.top();st.pop();
int result = oper[op](a,b);
st.push(result);
}
else
{
st.push(stoi(tokens[i]));
}
}
return st.top();
}
};基本计算器
解法:栈
使用两个栈,一个收集数字num,一个收集符号pos按照以下情况进行处理
- 遇到' '时,跳过
- 遇到'('时,pos收集
- 遇到')'时,拿一个符号和两个数字进行计算(前提栈不为空),把结果放到num中...
- 遇到数字时,定义变量sum=0,采用 sum*10 + 数字的方式收集,放到num中
但是要处理 **"+1-( -2)"**的特殊情况,所以:
- 先把所有空格先处理掉
- 开始枚举前在num中加入0;+或者-前面时'('时num也加入0保证结果正确
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int calculate(string s)
{
string tmp;
for (auto &ch : s)
{
if (ch != ' ')
tmp += ch;
}
s = tmp;
stack<long long> num;
stack<char> pos;
// 特殊处理
num.push(0);
int n = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// 处理特殊例子 "+1-( -2)" -> "0+1-(0-2)"
// if(s[i]==' ') continue;
if (s[i] == '(')
pos.push(s[i]);
else if (s[i] == ')')
{
cal(num, pos);
pos.pop();
}
else if (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9')
{
long long sum = 0, j = i;
while (j < n && s[j] >= '0' && s[j] <= '9')
{
sum = sum * 10 + (s[j++] - '0');
}
num.push(sum);
i = j - 1;
}
else
{
// 特殊处理
if (i - 1 >= 0 && s[i - 1] == '(')
num.push(0);
cal(num, pos);
pos.push(s[i]);
}
}
cal(num, pos);
return num.top();
}
void cal(stack<long long> &num, stack<char> &pos)
{
while (num.size() >= 2 && !pos.empty() && pos.top() != '(')
{
long long two = num.top();
num.pop();
long long one = num.top();
num.pop();
char p = pos.top();
pos.pop();
if (p == '+')
num.push(one + two);
else if (p == '-')
num.push(one - two);
}
}
};如果有 * / 需要考虑优先级呢?
那就使用 map 来储存优先级,进行计算之前先判断栈顶优先级是否大于等于当前s[i]的优先级,是的话才进行计算,否则就把 * 或者 / 加入到pos中,后面再计算
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
// */时添加优先级标记
map<char, int> PosToPriority = {{'+', 0}, {'-', 0}, {'*', 1}, {'/', 1}};
int calculate(string s)
{
string tmp;
for (auto &ch : s)
{
if (ch != ' ')
tmp += ch;
}
s = tmp;
stack<long long> num;
stack<char> pos;
num.push(0);
int n = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// 处理特殊例子 "+1-( -2)" -> "0+1-(0-2)"
// if(s[i]==' ') continue;
if (s[i] == '(')
pos.push(s[i]);
else if (s[i] == ')')
{
// 这里不用再进行优先级判断了,因为else已经处理了
while (!pos.empty() && pos.top() != '(')
cal(num, pos);
pos.pop();
}
else if (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9')
{
long long sum = 0, j = i;
while (j < n && s[j] >= '0' && s[j] <= '9')
{
sum = sum * 10 + (s[j++] - '0');
}
num.push(sum);
i = j - 1;
}
else
{
if (i - 1 >= 0 && s[i - 1] == '(')
num.push(0);
// 优先级判断是否要计算
while (!pos.empty() && pos.top() != '(' && PosToPriority[pos.top()] >= PosToPriority[s[i]])
cal(num, pos);
pos.push(s[i]);
}
}
while (!pos.empty())
cal(num, pos);
return num.top();
}
void cal(stack<long long> &num, stack<char> &pos)
{
if (num.size() < 2 || pos.top() == '(')
return;
long long two = num.top();
num.pop();
long long one = num.top();
num.pop();
char p = pos.top();
pos.pop();
if (p == '+')
num.push(one + two);
else if (p == '-')
num.push(one - two);
else if (p == '*')
num.push(one * two);
else
num.push(one / two);
}
};环形链表
解法:快慢双指针
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head)
{
ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
return true;
}
return false;
}
};两数相加
解法:模拟
模拟数学加法的方法来实现
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *addTwoNumbers(ListNode *l1, ListNode *l2)
{
ListNode *head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *tail = head;
int tmp = 0;
while (l1 || l2 || tmp)
{
int sum = tmp;
if (l1)
{
sum += l1->val;
l1 = l1->next;
}
if (l2)
{
sum += l2->val;
l2 = l2->next;
}
tail->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
tail = tail->next;
tmp = sum / 10;
}
ListNode *ret = head->next;
delete head;
return ret;
}
};随机链表的复制
解法:模拟
复制(new)相同的节点放在原节点后面
这样复制节点的random就是原节点random的next
再把new的节点提取出来,同时恢复原链表
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
Node *copyRandomList(Node *head)
{
if (head == nullptr)
return head;
// 每个节点后面复制一份
Node *tmp = head;
while (tmp)
{
Node *Next = tmp->next;
tmp->next = new Node(tmp->val);
tmp->next->next = Next;
tmp = Next;
}
// 处理 random
tmp = head;
while (tmp)
{
if (tmp->random != nullptr)
tmp->next->random = tmp->random->next;
else
tmp->random = nullptr;
tmp = tmp->next->next;
}
// 新节点取出来,同时保持原链表不变
Node *prev = head;
tmp = head->next;
Node *ret = new Node(-1);
Node *tail = ret;
while (prev)
{
Node *Next = tmp->next;
tail->next = tmp;
prev->next = Next;
tail = tail->next;
prev = Next;
if (prev)
tmp = prev->next;
}
return ret->next;
}
};反转链表二
解法:模拟
把要反转的链表头begin和尾end提取出来,同时保存beginPrev和endNext
把要反转的链表进行反转(头插或递归)
进行链接放回
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *reverse(ListNode *left, ListNode *right)
{
if (left == right)
return left;
ListNode *tmp = reverse(left->next, right);
tmp->next = left;
left->next = nullptr;
return left;
}
ListNode *reverseBetween(ListNode *head, int left, int right)
{
ListNode *begin = head, *end = head;
ListNode *leftPrev = nullptr, *rightNext = begin->next;
for (int i = 0; i < left - 1; i++)
{
leftPrev = begin;
begin = begin->next;
}
for (int i = 0; i < right - 1; i++)
{
end = rightNext;
rightNext = end->next;
}
ListNode *newEnd = reverse(begin, end);
ListNode *newBegin = end;
if (leftPrev)
leftPrev->next = newBegin;
newEnd->next = rightNext;
if (leftPrev == nullptr)
return newBegin;
else
return head;
}
};K个一组翻转链表
解法:模拟
找出要翻转链表的起始与结束位置
进行链表的反转操作
使用新链表保存反转后的链表
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *ret = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *retCur = ret;
ListNode *Reverse(ListNode *begin, ListNode *end)
{
if (begin == end)
return begin;
ListNode *head = Reverse(begin->next, end);
begin->next->next = begin;
begin->next = nullptr;
return head;
}
ListNode *reverseKGroup(ListNode *head, int k)
{
while (head)
{
ListNode *cur = head;
int tmp = k - 1;
while (cur && (tmp--))
cur = cur->next;
// cur为空说明链表不够k个,结束循环
if (cur == nullptr)
break;
// 先记录下一个链表的起始位置,不然后面找不到了
ListNode *nextListBegin = cur->next;
// 再继续反转
ListNode *begin = Reverse(head, cur);
retCur->next = begin;
// 更新位置
retCur = head;
cur = nextListBegin;
head = cur;
}
retCur->next = head;
ListNode *ans = ret->next;
delete ret;
return ans;
}
};删除链表的倒数第N个结点
解法:双指针
链表加个哨兵节点(处理 n == 链表总节点个数)
定义两个指针,一个指向哨兵节点left,另一个从哨兵节点出现的第n个节点处right
同时移动,直到righ为尾节点
此时 left->next 就是待删除的节点
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *removeNthFromEnd(ListNode *head, int n)
{
// n == head.size() 的情况 带头链表可以处理
ListNode *ret = new ListNode(-1);
ret->next = head;
ListNode *left = ret, *right = ret;
while (n--)
right = right->next;
while (right && right->next)
{
left = left->next;
right = right->next;
}
ListNode *tmp = left->next;
left->next = left->next->next;
delete tmp;
ListNode *ans = ret->next;
delete ret;
return ans;
}
};删除排序链表中的重复元素

cpp
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *deleteDuplicates(ListNode *head)
{
ListNode *ret = new ListNode(-101);
ret->next = head;
ListNode *prev = ret, *cur = ret;
while (cur && cur->next)
{
// 删除重复元素
if (cur->val == cur->next->val)
{
ListNode *begin = cur, *end = cur;
while (end->next && end->val == end->next->val)
end = end->next;
// 此时 begin 和 end 是待删除链表的头和尾
prev->next = end->next;
while (true)
{
ListNode *next = begin->next;
delete begin;
begin = next;
if (begin == end)
{
// 删除最后一个节点之前,先更新当前节点的位置
cur = end->next;
delete begin;
break;
}
}
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
ListNode *ans = ret->next;
delete ret;
return ans;
}
};旋转链表
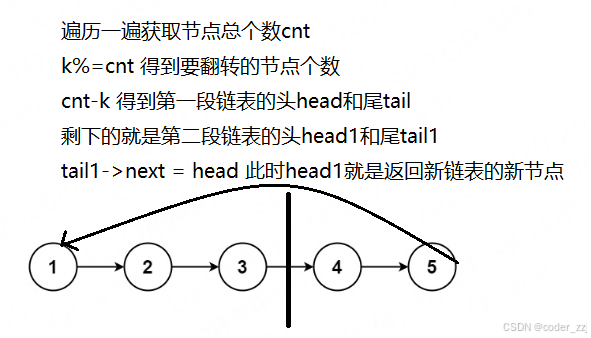
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *rotateRight(ListNode *head, int k)
{
if (head == nullptr || k == 0)
return head;
int cnt = 0;
ListNode *tail = head;
while (tail)
{
cnt++;
tail = tail->next;
}
k %= cnt;
if (k == 0)
return head;
int tmp = cnt - k;
tail = head;
while (--tmp)
tail = tail->next;
// 第二段链表的头和尾
ListNode *head1 = tail->next;
// 尾节点的下一个置空
tail->next = nullptr;
ListNode *tail1 = head1;
while (tail1->next)
tail1 = tail1->next;
tail1->next = head;
return head1;
}
};分割链表
解法:模拟
创建比x小的链表small和big
遍历收集节点到指定的链表中
最后两个链表合并之后进行返回
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode *partition(ListNode *head, int x)
{
ListNode *small = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *big = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *smallTail = small, *bigTail = big;
while (head)
{
if (head->val < x)
{
smallTail->next = head;
smallTail = head;
}
else
{
bigTail->next = head;
bigTail = head;
}
head = head->next;
}
smallTail->next = big->next;
bigTail->next = nullptr;
delete big;
ListNode *ret = small->next;
delete small;
return ret;
}
};LRU缓存
解法:链表
使用哈希表和双链表储存信息key和value,哈希表<key,ListNode*>
主要处理put方法:
当储存中有key值时:通过哈希表找到指定节点,并修改当中的val,最后把该节点进行头插
当节点个数为0时:把尾节点拿出来销毁,同时哈希表储存的键值对也删除,cnt++
创建新节点,哈希表和双链表储存信息(头插新链表),cnt++
cpp
// LRU 缓存
class LRUCache
{
public:
struct ListNode
{
struct ListNode *next;
struct ListNode *prev;
int key;
int val;
ListNode(int Key, int Val)
: key(Key), val(Val)
{}
};
unordered_map<int, ListNode *> hash;
ListNode *head = new ListNode(-1, -1);
int cnt = 0;
LRUCache(int capacity)
{
head->next = head;
head->prev = head;
cnt = capacity;
}
// 取节点
void DatchNode(ListNode *node)
{
node->prev->next = node->next;
node->next->prev = node->prev;
}
// 头插
void PushFromHead(ListNode *node)
{
ListNode *next = head->next;
head->next = node;
node->prev = head;
node->next = next;
next->prev = node;
}
int get(int key)
{
if (hash.contains(key))
{
ListNode *tmp = hash[key];
DatchNode(tmp);
PushFromHead(tmp);
return tmp->val;
}
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value)
{
if (hash.contains(key))
{
ListNode *tmp = hash[key];
tmp->val = value;
hash[key] = tmp;
DatchNode(tmp);
PushFromHead(tmp);
return;
}
else if (cnt == 0)
{
ListNode *tmp = head->prev;
DatchNode(tmp);
hash.erase(tmp->key);
delete tmp;
cnt++;
}
ListNode *newHead = new ListNode(key, value);
hash[key] = newHead;
PushFromHead(newHead);
cnt--;
}
};