一、图形透视(投影)变换
1、什么是透视变换?
透视变换 是一种将图像从一个视角投影到另一个视角的几何变换,也称为投影变换 或单应性变换 。它模拟了真实世界中近大远小的透视效果。
生活中的例子:
-
拍照时:倾斜拍书本,文字会变形
-
看风景时:远处的山看起来比近处的树小
-
文档扫描:手机倾斜拍摄的发票需要校正
2、代码中的透视变换实现
1) order_points(pts) - 点排序函数
python
def order_points(pts):
rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype="float32")
s = pts.sum(axis=1) # 计算每个点的x+y
rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)] # 左上点:x+y最小
rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)] # 右下点:x+y最大
diff = np.diff(pts, axis=1) # 计算每个点的x-y
rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)] # 右上点:x-y最小
rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)] # 左下点:x-y最大
return rect # 返回排序后的点:[左上, 右上, 右下, 左下]为什么要排序?
-
原始检测到的四个点是乱序的
-
透视变换需要知道点的对应关系
-
必须明确:源图像的左上角对应目标图像的左上角
2)four_point_transform() - 透视变换主函数
这是最核心的部分,我们一步步分解:
步骤1:获取排序后的点
python
rect = order_points(pts) # 排序四个点
(tl, tr, br, bl) = rect # 解包:左上、右上、右下、左下步骤2:计算新图像的宽度
python
# 计算底边宽度(右下到左下)
widthA = np.sqrt(((br[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((br[1] - bl[1]) ** 2))
# 计算顶边宽度(右上到左上)
widthB = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - tl[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2))
# 取最大值作为新宽度
maxWidth = max(int(widthA), int(widthB))为什么取最大值?
-
确保新图像能完整包含原始内容
-
避免裁剪
步骤3:计算新图像的高度
python
# 计算右边高度(右上到右下)
heightA = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - br[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - br[1]) ** 2))
# 计算左边高度(左上到左下)
heightB = np.sqrt(((tl[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((tl[1] - bl[1]) ** 2))
# 取最大值作为新高度
maxHeight = max(int(heightA), int(heightB))步骤4:定义目标点(校正后的矩形)
python
dst = np.array([
[0, 0], # 左上:坐标原点
[maxWidth - 1, 0], # 右上:最右列,最上行
[maxWidth - 1, maxHeight - 1], # 右下:最右列,最下行
[0, maxHeight - 1] # 左下:最左列,最下行
], dtype="float32")步骤5:计算透视变换矩阵(关键!)
python
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect, dst)这个函数做了什么?
-
输入:4对对应点(源点
rect,目标点dst) -
输出:3×3的变换矩阵M
-
数学上:解一个线性方程组,找到变换参数
步骤6:应用透视变换(关键!)
python
warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image, M, (maxWidth, maxHeight))这个函数做了什么?
-
对图像中每个像素应用变换矩阵M
-
进行插值计算,得到新图像
-
输出尺寸为(maxWidth, maxHeight)
3.实际运用(发票扫描与校正)
这是一个完整的发票/文档扫描与校正程序,实现了从倾斜拍摄的发票到正面校正图像的全流程处理。
1)程序总体流程
读取图像 → 预处理 → 轮廓检测 → 文档定位 → 透视变换 → 后处理2)详细步骤解析
第1部分:图像预处理
1. 定义工具函数
python
def cv_show(name, img): # 显示图像
def resize(image, width=None, height=None): # 保持比例调整大小2. 读取和缩放图像
python
image = cv2.imread('fapiao.jpg') # 读取发票图片
ratio = image.shape[0] / 500.0 # 计算缩放比例(原高/500)
orig = image.copy() # 备份原始图像
image = resize(orig, height=500) # 高度固定为500像素目的 :大图像处理慢,缩小可提高速度,记住ratio用于后续坐标转换。
第2部分:文档轮廓检测
1. 转换为灰度图
python
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)2. 边缘检测与二值化
python
edged = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]OTSU算法:自动计算最佳阈值,适应不同光照条件。
3. 查找所有轮廓
python
cnts = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2]-
RETR_LIST:获取所有轮廓 -
CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE:压缩轮廓点
4. 可视化所有轮廓
python
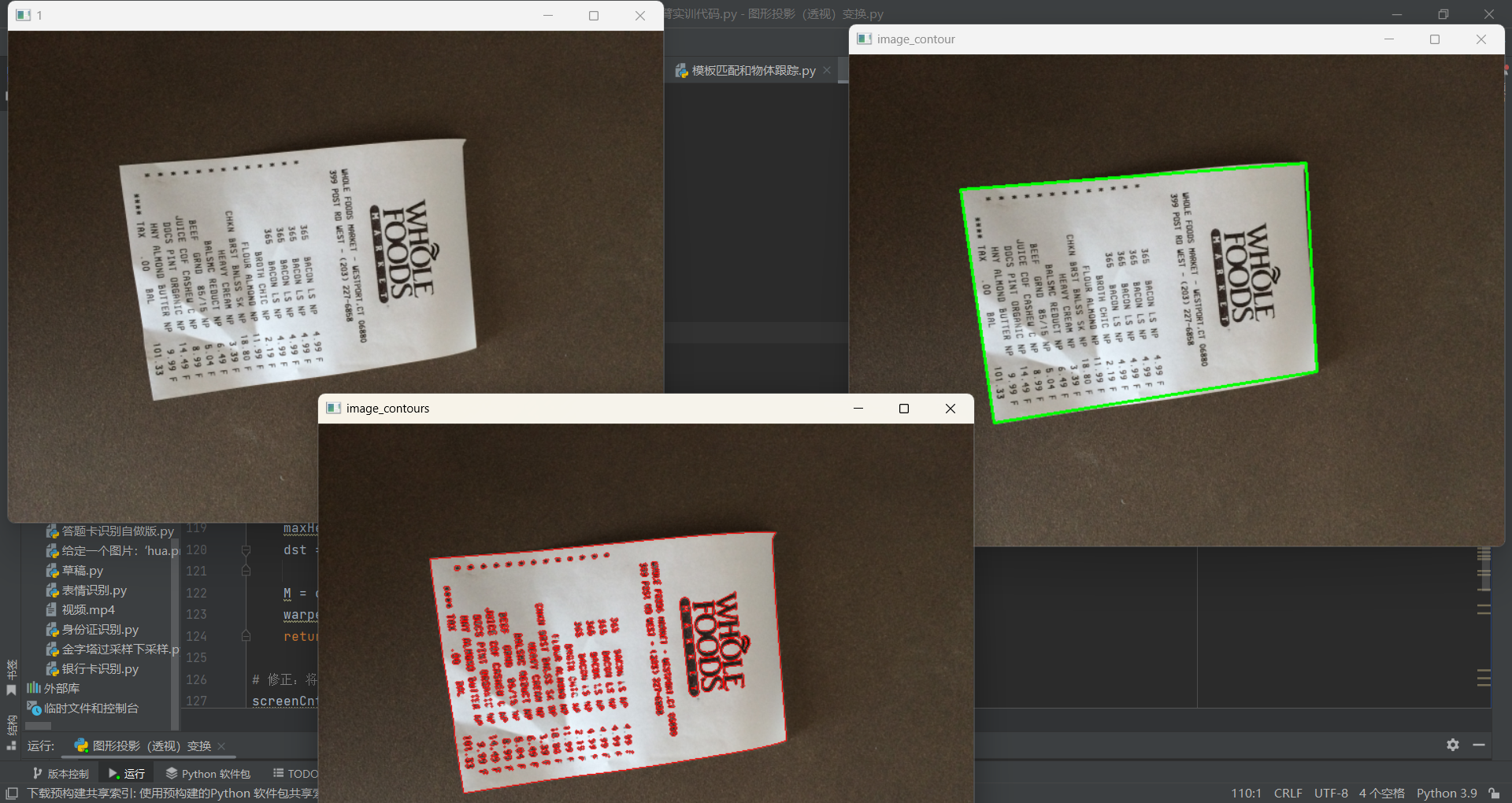
image_contours = cv2.drawContours(image.copy(), cnts, -1, (0, 0, 255), 1)第3部分:文档定位
1. 找到最大轮廓(假设文档最大)
python
screenCnt = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)[0]2. 轮廓多边形近似
python
peri = cv2.arcLength(screenCnt, True) # 计算周长
screenCnt = cv2.approxPolyDP(screenCnt, 0.05 * peri, True) # 近似为多边形approxPolyDP:将曲线轮廓近似为直线多边形,精度=周长的5%。
3. 绘制文档轮廓
python
image_contour = cv2.drawContours(image.copy(), [screenCnt], -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)绿色粗线框出找到的文档边界。
第4部分:透视变换核心函数
1. 点排序函数 order_points()
python
def order_points(pts):
# 将4个无序点排序为:左上、右上、右下、左下
# 方法:计算x+y和x-y,根据大小关系确定位置2. 透视变换主函数 four_point_transform()
python
def four_point_transform(image, pts):
# 1. 排序点
# 2. 计算新图像尺寸(取最大宽度和高度)
# 3. 定义目标矩形
# 4. 计算透视变换矩阵 cv2.getPerspectiveTransform()
# 5. 应用变换 cv2.warpPerspective()第5部分:应用透视变换
1. 坐标映射回原始尺寸
python
screenCnt_points = screenCnt.reshape(4, 2) * ratio关键 :screenCnt是在小图(高500px)上找到的点,需要乘ratio得到原图坐标。
2. 执行透视变换
python
warped = four_point_transform(orig, screenCnt_points)输入原始大图和四个角点,输出校正后的矩形文档。
3. 调整大小便于显示
python
warped_resized = resize(warped, height=500)第6部分:图像后处理
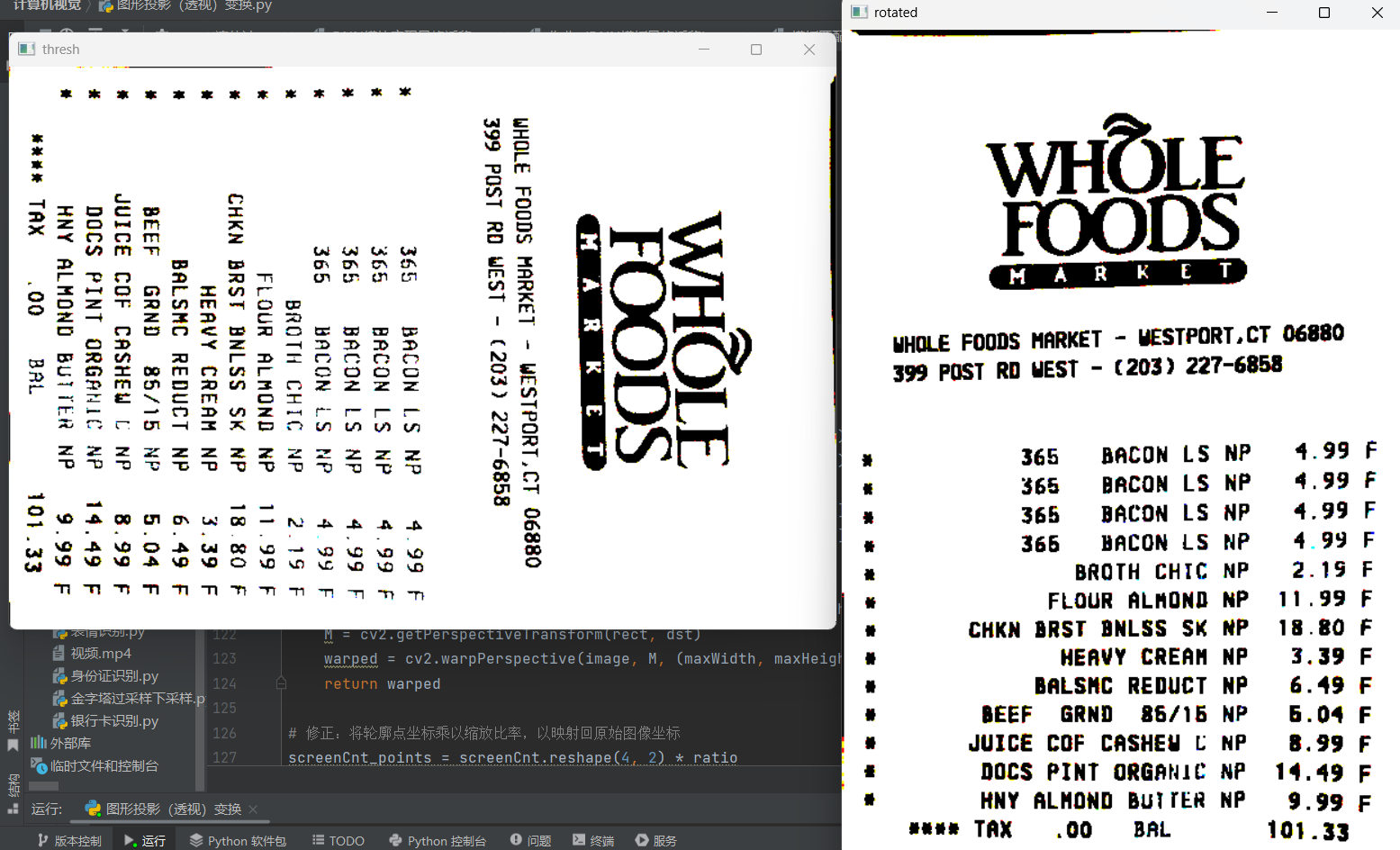
1. 二值化(黑白化)
python
thresh = cv2.threshold(warped_resized, 120, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]阈值120:>120变白,≤120变黑,增强对比度。
2. 腐蚀去噪
python
kernel = np.ones((2, 2), np.uint8)
erode_1 = cv2.erode(thresh, kernel, iterations=1)消除细小噪声,让文字更清晰。
3. 旋转校正
python
rotated = cv2.rotate(erode_1, cv2.ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE)逆时针旋转90度,可能是因为原始发票是横向拍摄的。
完整代码部分
python
import numpy as np
import cv2
def cv_show(name, img):
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
def resize(image,width=None,height=None,inter=cv2.INTER_AREA):
dim=None
(h,w)=image.shape[:2]
if width is None and height is None:
return image
if width is None:
r=height/float(h)
dim=(int(w*r),height)
else:
r=width/float(w)
dim=(width,int(h*r))
resized=cv2.resize(image,dim,interpolation=inter) #默认为cv2.INTER_AREA,即面积插值,适用于缩放图像。
return resized
# 读取输入
image = cv2.imread('fapiao.jpg')
cv_show('image', image)
# 图片过大,进行缩小处理
ratio = image.shape[0] / 500.0 # 计算缩小比率
orig = image.copy()
image = resize(orig, height=500)
cv_show('1', image)
# 轮廓检测
print("STEP 1:轮廓检测")
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 读取灰度图
edged = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1] # 自动寻找阈值二值化
cnts = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2]
image_contours = cv2.drawContours(image.copy(), cnts, -1, (0, 0, 255), 1)
cv_show('image_contours', image_contours)
print("STEP 2:获取最大轮廓")
screenCnt = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)[0] # 获取面积最大的轮廓
print(screenCnt.shape)
peri = cv2.arcLength(screenCnt, True) # 计算轮廓周长
screenCnt = cv2.approxPolyDP(screenCnt, 0.05 * peri, True) # 轮廓近似
print(screenCnt.shape)
image_contour = cv2.drawContours(image.copy(), [screenCnt], -1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.imshow("image_contour", image_contour)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def order_points(pts):
rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype="float32")
s = pts.sum(axis=1)
rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)]
rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)]
diff = np.diff(pts, axis=1)
rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)]
rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)]
return rect
def four_point_transform(image, pts):
rect = order_points(pts)
(tl, tr, br, bl) = rect
widthA = np.sqrt(((br[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((br[1] - bl[1]) ** 2))
widthB = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - tl[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2))
maxWidth = max(int(widthA), int(widthB))
heightA = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - br[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - br[1]) ** 2))
heightB = np.sqrt(((tl[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((tl[1] - bl[1]) ** 2))
maxHeight = max(int(heightA), int(heightB))
dst = np.array([[0, 0], [maxWidth - 1, 0],
[maxWidth - 1, maxHeight - 1], [0, maxHeight - 1]], dtype="float32")
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect, dst)
warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image, M, (maxWidth, maxHeight))
return warped
# 修正:将轮廓点坐标乘以缩放比率,以映射回原始图像坐标
screenCnt_points = screenCnt.reshape(4, 2) * ratio
warped = four_point_transform(orig, screenCnt_points)
warped_resized = resize(warped, height=500)
thresh=cv2.threshold(warped_resized,120,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
#腐蚀操作
kernel = np.ones((2, 2), np.uint8) # 创建一个2x2的矩形结构元素
erode_1 = cv2.erode(thresh, kernel, iterations=1)
# 逆时针旋转90度
rotated = cv2.rotate(erode_1, cv2.ROTATE_90_COUNTERCLOCKWISE)
# 或者顺时针旋转90度
# rotated = cv2.rotate(image, cv2.ROTATE_90_CLOCKWISE)
# 旋转180度
# rotated = cv2.rotate(image, cv2.ROTATE_180)
# cv2.imwrite('invoice_new.jpg', warped_resized)
# cv_show('warped', warped_resized)
# cv_show('warped_resized', warped_resized)
cv_show('thresh',thresh)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv_show('rotated',rotated)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()运行结果
3)核心算法总结
| 步骤 | 关键函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| 预处理 | cv2.resize() |
调整尺寸 |
| 边缘检测 | cv2.threshold(OTSU) |
自动二值化 |
| 轮廓查找 | cv2.findContours() |
提取轮廓 |
| 轮廓近似 | cv2.approxPolyDP() |
多边形近似 |
| 透视变换 | cv2.getPerspectiveTransform() |
计算变换矩阵 |
| 图像变换 | cv2.warpPerspective() |
应用透视变换 |
| 后处理 | cv2.erode(), cv2.rotate() |
去噪和旋转 |
这是一个完整的、可实际使用的文档扫描系统,涵盖了计算机视觉中的多个关键技术:边缘检测、轮廓分析、几何变换、图像增强等。
二、图片拼接
1、cv2.findHomography()
这是图像拼接和计算机视觉中最核心的函数之一 ,用于计算两个平面之间的单应性变换矩阵(Homography Matrix)。
计算透视变换矩阵
findHomography(srcPoints, dstPoints, method=None, ransacReprojThreshold=None, mask=None, maxIters=None, confidence=None)
参数说明:
srcPoints: 原图像匹配点坐标(这里是图片B的特征点)
dstPoints: 目标图像匹配点坐标(这里是图片A的特征点)
method: 计算变换矩阵的方法:
0 - 使用所有的点,最小二乘
RANSAC - 基于随机样本一致性
LMEDS - 最小中值
RHO - 基于渐近样本一致性
ransacReprojThreshold: 最大允许重投影错误阈值(默认为3)
返回值:H为变换矩阵,mask为掩模标志,指示哪些点是内点/外点2、参数详细说明
python
(H, mask) = cv2.findHomography(srcPoints, dstPoints, method=cv2.RANSAC,
ransacReprojThreshold=3.0, maxIters=2000,
confidence=0.995)1) srcPoints - 源点
-
类型:
np.array,形状为 (N, 1, 2) 或 (N, 2) -
说明:第一幅图像中的特征点坐标
-
在你的代码中:
ptsB(右图的特征点)
2.)dstPoints - 目标点
-
类型:
np.array,形状为 (N, 1, 2) 或 (N, 2) -
说明:第二幅图像中的对应特征点坐标
-
在你的代码中:
ptsA(左图的特征点)
3)method - 计算方法(最重要!)
a) method=0 或 cv2.LMEDS
最小二乘法(使用所有点)
python
(H, _) = cv2.findHomography(ptsB, ptsA, 0)-
原理:最小化所有点的重投影误差平方和
-
优点:数学上最优(无异常点时)
-
缺点:对异常点(错误匹配)非常敏感
-
适用:所有匹配点都准确的情况(罕见)
b) method=cv2.RANSAC ★ 最常用
随机采样一致性算法
python
(H, mask) = cv2.findHomography(ptsB, ptsA, cv2.RANSAC, ransacReprojThreshold=3.0)-
原理:
-
随机选择4对点(最小样本集)
-
计算临时单应性矩阵
-
统计有多少点符合该矩阵(内点)
-
重复多次(如2000次),选择内点最多的模型
-
用所有内点重新计算精确矩阵
-
-
优点:对异常点(错误匹配)鲁棒
-
缺点:计算量稍大,结果具有随机性
-
你的代码中:使用了这个方法,阈值设为10(较宽松)
c) method=cv2.LMEDS
最小中值法
-
原理:最小化误差的中值
-
对异常点有一定鲁棒性,但不如RANSAC
d) method=cv2.RHO
渐进一致采样算法
-
原理:基于PROSAC改进,更高效
-
适用:当有很多匹配点时效率高
4) ransacReprojThreshold - RANSAC重投影阈值
-
默认值:3.0(像素)
-
你的代码:10.0(更宽松)
-
含义:一个点被认为是"内点"的最大允许误差
5)maxIters - 最大迭代次数
-
默认:2000
-
RANSAC算法最多尝试的次数
-
更多迭代 → 更可能找到好模型,但更慢
6)confidence - 置信度
-
默认:0.995(99.5%)
-
表示算法至少找到一个只包含内点的样本的概率
-
更高置信度 → 更多迭代次数
3、总结
cv2.findHomography() 是计算机视觉中的基石函数:
-
功能:计算两个视图之间的透视变换关系
-
核心算法:RANSAC(处理错误匹配的关键)
-
关键参数 :
ransacReprojThreshold(平衡严格与宽松) -
输出:变换矩阵H + 内点掩码mask
-
应用:图像拼接、增强现实、相机标定、三维重建等
4、实际运用
右边图片进行透视变换,把左边图片拼接上去
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import sys
def cv_show(name, img):
"""显示图像"""
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
def detectAndDescribe(image):
"""检测图像特征点并计算描述符"""
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转为灰度图
sift = cv2.SIFT_create() # 创建SIFT检测器
(kps, des) = sift.detectAndCompute(gray, None) # 检测关键点并计算描述符
kps_float = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kps]) # 提取关键点坐标(浮点型)
return (kps, kps_float, des)
# 读取图像
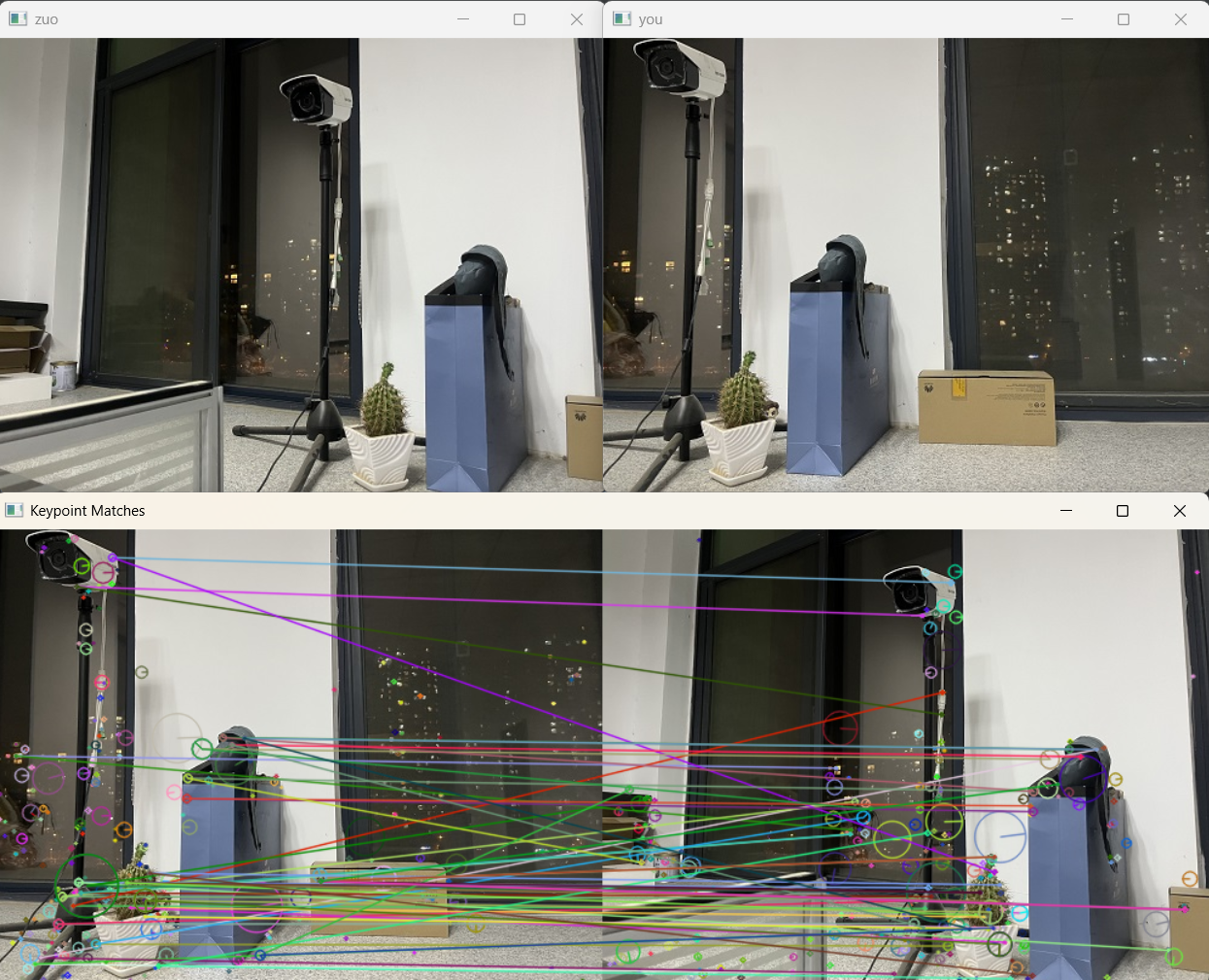
imageA = cv2.imread("zuo.jpg")
cv_show('zuo', imageA)
imageB = cv2.imread("you.jpg")
cv_show('you', imageB)
# 提取特征
(kpsA, kps_floatA, desA) = detectAndDescribe(imageA)
(kpsB, kps_floatB, desB) = detectAndDescribe(imageB)
# 使用暴力匹配器进行特征匹配
matcher = cv2.BFMatcher()
rawMatches = matcher.knnMatch(desB, desA, k=2)
# 筛选匹配对
good = []
matches = []
for m in rawMatches:
if len(m) == 2 and m[0].distance < 0.65 * m[1].distance:
good.append(m)
matches.append((m[0].queryIdx, m[0].trainIdx))
print(f"匹配对数: {len(good)}")
print("匹配索引列表:", matches)
# 绘制匹配结果
vis = cv2.drawMatchesKnn(imageB, kpsB, imageA, kpsA, good,
outImg=None,
flags=cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DRAW_RICH_KEYPOINTS)
cv_show("Keypoint Matches", vis)
# 透视变换
if len(matches) > 4: # 当筛选后的匹配对大于4时,计算视角变换矩阵
# 获取匹配对的点坐标
# matches是通过阈值筛选之后的特征点对象
# kps_floatA/kps_floatB是图片A/B中的全部特征点坐标
ptsB = np.float32([kps_floatB[i] for (i, _) in matches])
ptsA = np.float32([kps_floatA[i] for (_, i) in matches])
# 计算透视变换矩阵
(H, mask) = cv2.findHomography(ptsB, ptsA, cv2.RANSAC, ransacReprojThreshold=10)
else:
print('图片未找到4个以上的匹配点')
sys.exit()
# 对图片B进行透视变换
# dsize参数指定输出图像大小:宽度为两图宽度之和,高度为图片B的高度
result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageB, H,
dsize=(imageB.shape[1] + imageA.shape[1], imageB.shape[0]))
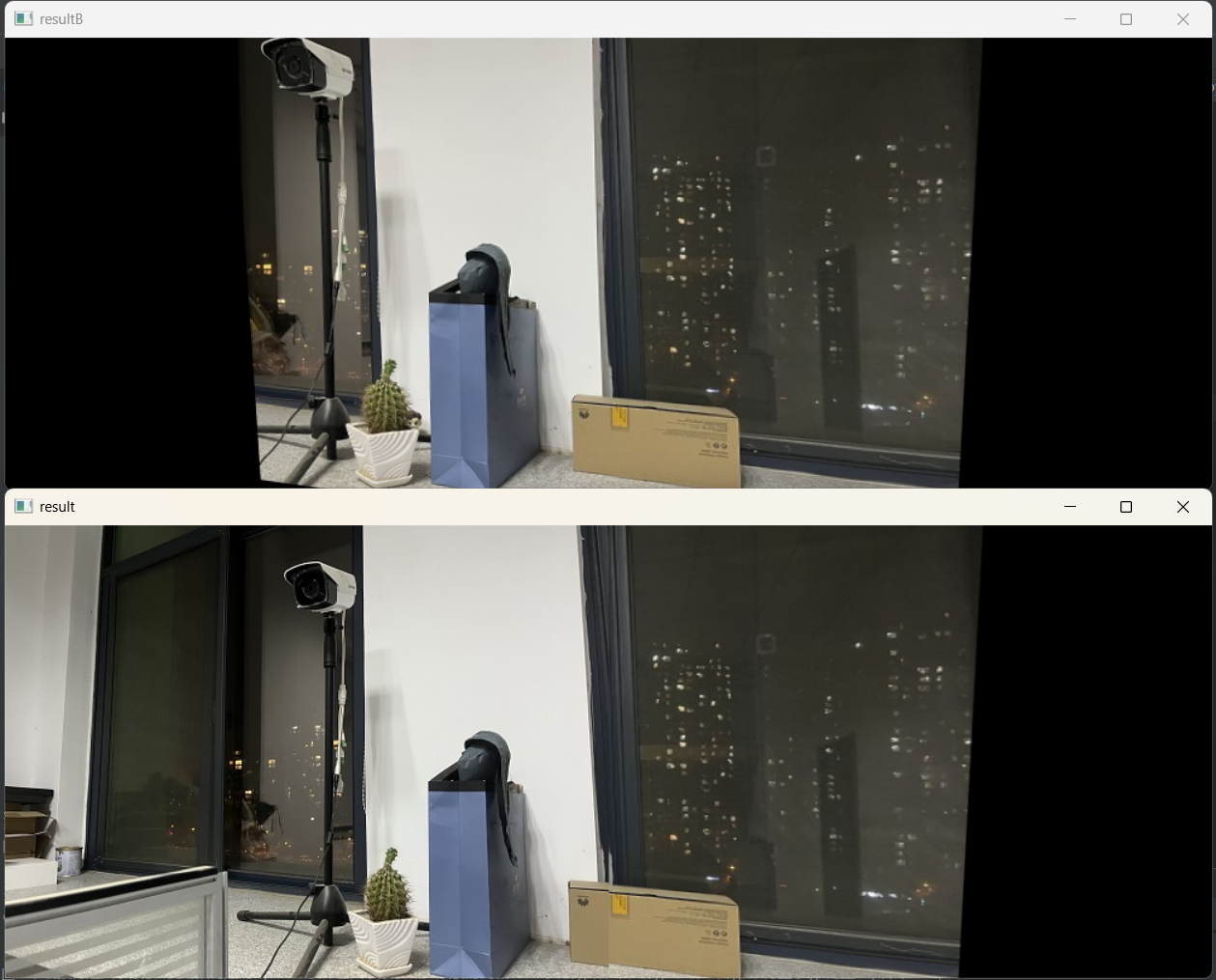
cv_show('resultB', result)
# 将图片A拼接到结果图片的最左端
result[0:imageA.shape[0], 0:imageA.shape[1]] = imageA
cv_show('result', result)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()运行结果