1、Cargo.toml文件
toml
复制代码
[dependencies]
docx-rs = "0.4"
serde = { version = "1.0", features = ["derive"] }
serde_json = "1.0"
2、docx模版格式样式
vue
复制代码
我的名字是{name},我的年龄是{age}.....
- 程序会自动替换模版
{xxx}中的内容为数据内容,分别生成docx。
{xxxx}可以根据数据内容自定义名称,以大括号包裹。- 模版内的段落、文字等格式不会改变,运行程序前,请自行设置好模版文档格式。
- 表格内,同样可以使用
{xxxx}模版样式
- 本代码批量生成的新
docx文档位于项目目录下,建议添加新建输出目录
2.1 docx模版样式参考
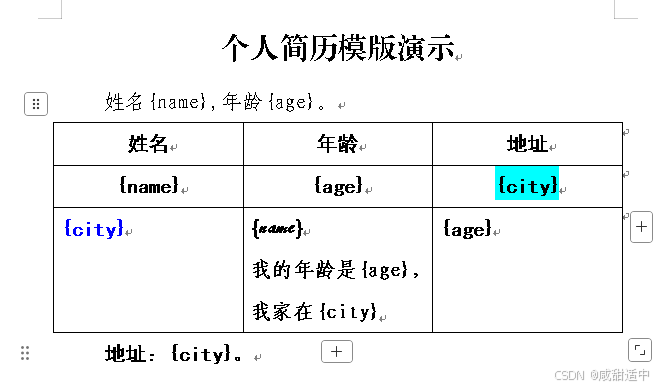
2.2 生成的单个docx文件参考
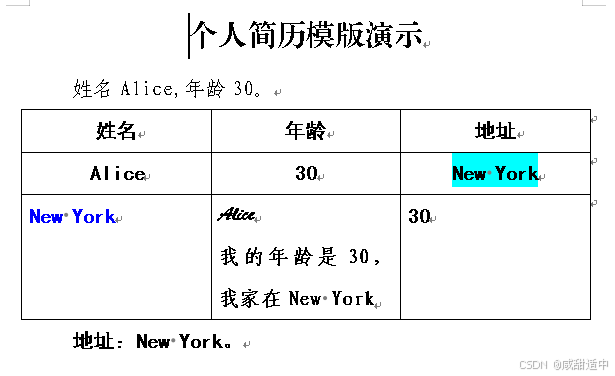
3、遍历模版中的段落和表格生成新docx文档(完整代码)
rust
复制代码
use docx_rs::{Docx, read_docx};
use serde::Deserialize;
use std::collections::HashMap;
use std::fs;
use std::path::Path;
/// 人员数据结构
#[derive(Deserialize, Debug)]
struct PersonData {
name: String,
age: u8,
city: String,
}
/// 将字符串中的占位符替换成实际值
fn replace_placeholders(text: &str, data_map: &HashMap<&str, &str>) -> String {
// 遍历替换数据映射,将占位符替换为实际值
data_map.iter().fold(text.to_string(), |acc, (key, value)| {
// 构建占位符字符串
let placeholder = format!("{{{}}}", key);
// 替换占位符为实际值
acc.replace(&placeholder, value)
})
}
/// 处理单个文档,替换占位符并保存
fn process_document_with_data(
mut doc: Docx,
output_path: &Path,
person: &PersonData,
) -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// 将年龄转换为字符串
let age_str = person.age.to_string();
// 创建替换数据映射
let data_map: HashMap<&str, &str> = [
("name", person.name.as_str()),
("age", age_str.as_str()),
("city", person.city.as_str()),
]
.into_iter()
.collect();
// 遍历文档中的段落、表格,替换占位符
for child in &mut doc.document.children {
// 处理段落
if let docx_rs::DocumentChild::Paragraph(para) = child {
// 遍历段落中的run,替换文本内容并保留格式
for para_child in &mut para.children {
if let docx_rs::ParagraphChild::Run(run) = para_child {
// 保存原始run的所有子元素
let original_children = std::mem::take(&mut run.children);
// 处理每个run子元素
for run_child in original_children {
match run_child {
docx_rs::RunChild::Text(text) => {
// 替换文本内容
let replaced_text = replace_placeholders(&text.text, &data_map);
// 创建新的文本节点并添加到run的children中
run.children
.push(docx_rs::RunChild::Text(docx_rs::Text::new(
replaced_text,
)));
}
other => {
// 保留其他类型的子元素(保留格式)
run.children.push(other);
}
}
}
}
}
}else if let docx_rs::DocumentChild::Table(table) = child { // 处理表格
for table_child in &mut table.rows{
if let docx_rs::TableChild::TableRow(row) =table_child{
for row_child in &mut row.cells{
if let docx_rs::TableRowChild::TableCell(cell) = row_child{
for cell_content in &mut cell.children{
if let docx_rs::TableCellContent::Paragraph(para)=cell_content{
for para_child in &mut para.children{
if let docx_rs::ParagraphChild::Run(run) = para_child {
// 保存原始run的所有子元素
let original_children = std::mem::take(&mut run.children);
// 处理每个run子元素
for run_child in original_children {
match run_child {
docx_rs::RunChild::Text(text) => {
// 替换文本内容
let replaced_text = replace_placeholders(&text.text, &data_map);
// 创建新的文本节点并添加到run的children中
run.children
.push(docx_rs::RunChild::Text(docx_rs::Text::new(
replaced_text,
)));
}
other => {
// 保留其他类型的子元素(保留格式)
run.children.push(other);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
println!("这是表格!");
}
}
// 保存修改后的文档
let file = fs::File::create(output_path)?;
let xml_docx = doc.build();
xml_docx.pack(file)?;
Ok(())
}
/// 读取模板文档
fn read_template(template_path: &Path) -> Result<Docx, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let template_content = fs::read(template_path)?;
let doc = read_docx(&template_content)?;
Ok(doc)
}
fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// 示例人员数据集
let persons = vec![
PersonData {
name: "Alice".to_string(),
age: 30,
city: "New York".to_string(),
},
PersonData {
name: "Bob".to_string(),
age: 25,
city: "San Francisco".to_string(),
},
PersonData {
name: "Charlie".to_string(),
age: 35,
city: "Chicago".to_string(),
},
];
// 模板文件路径
let template_path = Path::new("template.docx");
// 验证模板文件存在
if !template_path.exists() {
return Err(format!("模板文件不存在: {:?}", template_path).into());
}
// 读取模板文档(只读取一次,提高性能)
let template_doc = read_template(template_path)?;
// 循环处理每个人员的数据
for (i, person) in persons.iter().enumerate() {
// 为每个人员生成唯一的输出文件名
let output_filename = format!("output_{}.docx", i + 1);
// 输出文件路径
let output_path = Path::new(&output_filename);
// 克隆模板文档,避免重复读取文件
let doc = template_doc.clone();
match process_document_with_data(doc, output_path, person) {
Ok(_) => println!("✅ 已成功生成 {}", output_filename),
Err(e) => {
eprintln!("❌ 处理失败 {}: {:?}", output_filename, e);
// 继续处理下一个文档,不中断整个流程
}
};
}
println!("🎉 全部文档均已生成完毕!");
Ok(())
}
4、提取段落相同代码为函数后(完整代码)
rust
复制代码
use docx_rs::{Docx, read_docx, Paragraph};
use serde::Deserialize;
use std::collections::HashMap;
use std::fs;
use std::path::Path;
/// 人员数据结构
#[derive(Deserialize, Debug)]
struct PersonData {
name: String,
age: u8,
city: String,
}
/// 将字符串中的占位符替换成实际值
fn replace_placeholders(text: &str, data_map: &HashMap<&str, &str>) -> String {
// 遍历替换数据映射,将占位符替换为实际值
data_map.iter().fold(text.to_string(), |acc, (key, value)| {
// 构建占位符字符串
let placeholder = format!("{{{}}}", key);
// 替换占位符为实际值
acc.replace(&placeholder, value)
})
}
/// 处理单个文档,替换占位符并保存
fn process_document_with_data(
mut doc: Docx,
output_path: &Path,
person: &PersonData,
) -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// 将年龄转换为字符串
let age_str = person.age.to_string();
// 创建替换数据映射
let data_map: HashMap<&str, &str> = [
("name", person.name.as_str()),
("age", age_str.as_str()),
("city", person.city.as_str()),
]
.into_iter()
.collect();
// 遍历文档中的段落,替换占位符
for child in &mut doc.document.children {
if let docx_rs::DocumentChild::Paragraph(para) = child {
// 遍历段落中的run,替换文本内容并保留格式
paragraph_replace(para,data_map.clone());
}else if let docx_rs::DocumentChild::Table(table) = child {
for table_child in &mut table.rows{
if let docx_rs::TableChild::TableRow(row) =table_child{
for row_child in &mut row.cells{
if let docx_rs::TableRowChild::TableCell(cell) = row_child{
for cell_content in &mut cell.children{
if let docx_rs::TableCellContent::Paragraph(para)=cell_content{
// 遍历段落中的run,替换文本内容并保留格式
paragraph_replace(para,data_map.clone());
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 保存修改后的文档
let file = fs::File::create(output_path)?;
let xml_docx = doc.build();
xml_docx.pack(file)?;
Ok(())
}
/// 替换段落内的模版内容,因段落、表格单独遍历,所以提取内容重复使用
fn paragraph_replace(para: &mut Paragraph,data_map: HashMap<&str, &str>) {
// 遍历段落中的run,替换文本内容并保留格式
for para_child in &mut para.children {
if let docx_rs::ParagraphChild::Run(run) = para_child {
// 保存原始run的所有子元素
let original_children = std::mem::take(&mut run.children);
// 处理每个run子元素
for run_child in original_children {
match run_child {
docx_rs::RunChild::Text(text) => {
// 替换文本内容
let replaced_text = replace_placeholders(&text.text, &data_map);
// 创建新的文本节点并添加到run的children中
run.children
.push(docx_rs::RunChild::Text(docx_rs::Text::new(
replaced_text,
)));
}
other => {
// 保留其他类型的子元素(保留格式)
run.children.push(other);
}
}
}
}
}
}
/// 读取模板文档
fn read_template(template_path: &Path) -> Result<Docx, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let doc = read_docx(&fs::read(template_path)?)?;
Ok(doc)
}
fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// 示例人员数据集
let persons = vec![
PersonData {
name: "Alice".to_string(),
age: 30,
city: "New York".to_string(),
},
PersonData {
name: "Bob".to_string(),
age: 25,
city: "San Francisco".to_string(),
},
PersonData {
name: "Charlie".to_string(),
age: 35,
city: "Chicago".to_string(),
},
];
// 模板文件路径
let template_path = Path::new("template.docx");
// 验证模板文件存在
if !template_path.exists() {
return Err(format!("模板文件不存在: {:?}", template_path).into());
}
// 读取模板文档(只读取一次,提高性能)
let template_doc = read_template(template_path)?;
// 循环处理每个人员的数据
for (i, person) in persons.iter().enumerate() {
// 为每个人员生成唯一的输出文件名
let output_filename = format!("output_{}.docx", i + 1);
// 输出文件路径
let output_path = Path::new(&output_filename);
// 克隆模板文档,避免重复读取文件
let doc = template_doc.clone();
match process_document_with_data(doc, output_path, person) {
Ok(_) => println!("✅ 已成功生成 {}", output_filename),
Err(e) => {
eprintln!("❌ 处理失败 {}: {:?}", output_filename, e);
// 继续处理下一个文档,不中断整个流程
}
};
}
println!("🎉 全部文档均已生成完毕!");
Ok(())
}

