https://github.com/Bin-ze/BEVFormer_segmentation_detection
本文记录对一个基于 BEVFormer 的 seg+det 多任务感知模型的源码分析与实现要点,并复现验证 BEV -> feat_cropper -> SegEncode 的数据流与形状兼容性。
模型实现脉络(概览)
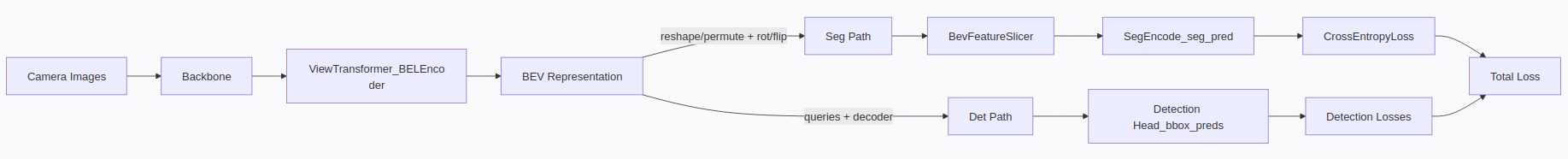
简要说明:
- 输入由多视角图像经
Backbone提取特征并通过View Transformer投影/编码成固定的 BEV 表示(bev_embed)。 bev_embed为中心共享表示:一部分经query+ transformer decoder 用于目标检测(det);另一部分 reshape 后经经验性旋转/翻转并由BevFeatureSlicer重采样到地图像素格,再交给SegEncode输出语义 logits(seg)。- 标签由
RasterizeMapVectors生成semantic_indices(每像素类别索引),seg loss 与 det loss 并列计算并合并用于训练。
关键结论(要点)
- BEV -> seg 的形状链 : Transformer 输出
bev_embed(bev_h*bev_w, B, C) -> reshape & permute -> (B, C, bev_h, bev_w) -> rot90/flip -> feat_cropper(grid_sample) -> resampled (B, C, H_map, W_map) ->SegEncode-> logits (B, outC, H_map, W_map). - 检测(det)要点 : det 分支在
pts_bbox_head中使用num_query构造 decoder queries 进行目标检测,decoder 输出典型形状为(bs, num_query, ...);训练端通过 Hungarian/matching 对预测与 GT 对齐并计算分类与回归损失,最终与 seg_loss 并列计算并合并返回用于反向传播。 - 测试分析摘要 : 单元 shape 测试(
bev_h=30, bev_w=30, bs=2, C=256)复现链路并输出:seg_bev_resampled->torch.Size([2,256,200,400]),seg_pred->torch.Size([2,4,200,400])。结论:空间尺寸与通道/类别维度对齐,可直接用于 CrossEntropyLoss;但需关注 rot90/flip 与 rasterize 的坐标系一致性,以及BevFeatureSlicer的 grid 计算。 - 工程与调试建议 : 在 pipeline/CI 中添加形状断言(batch 与空间维度),可视化
seg_pred.argmax(1)与semantic_indices进行对齐验证,若多任务训练不稳定优先调整损失权重或先单独训练 seg 分支以验证坐标对齐。
配置(关键片段,来自 projects/configs/bevformer/bevformer_small_seg_det_300x300.py)
python
pts_bbox_head = dict(
type='BEVFormerHead',
bev_h=bev_h_,
bev_w=bev_w_,
num_query=900,
num_classes=10,
in_channels=_dim_,
...
task=dict(seg=True, det=True),
det_grid_conf=det_grid_conf,
map_grid_conf=map_grid_conf,
seg_encoder=dict(
type='SegEncode',
inC=256,
outC=4),
loss_seg=dict(
type='CrossEntropyLoss',
use_sigmoid=False,
loss_weight=3.0,
class_weight=[0.3, 2.0, 2.0, 2.0]),
...
)SegEncode(主要实现,摘自 projects/mmdet3d_plugin/bevformer/modules/seg_subnet.py)
python
@SEG_ENCODER.register_module()
class SegEncode(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inC, outC):
super(SegEncode, self).__init__()
trunk = resnet18(pretrained=False, zero_init_residual=True)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inC, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = trunk.bn1
self.relu = trunk.relu
self.layer1 = trunk.layer1
self.layer2 = trunk.layer2
self.layer3 = trunk.layer3
self.up1 = Up(64 + 256, 256, scale_factor=4)
self.up2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, outC, kernel_size=1, padding=0),
)
def forward(self, x): # x: [B, 256, H, W]
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x1 = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x1)
x2 = self.layer3(x)
x = self.up1(x2, x1)
x = self.up2(x)
return x # [B, outC, H_map, W_map]Up 模块(核心片段)
python
class Up(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, scale_factor=2):
self.up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=scale_factor, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x1, x2):
x1 = self.up(x1)
x1 = torch.cat([x2, x1], dim=1)
return self.conv(x1)BEV -> seg 的调用链(head 中要点)
- 在构造时,head 根据配置创建
self.feat_cropper = BevFeatureSlicer(self.det_grid_conf, self.map_grid_conf)和self.seg_decoder = build_seg_encoder(seg_encoder),并构造self.loss_seg。 - forward 中,关键变换:
python
# bev_embed: (bev_h*bev_w, bs, C)
seg_bev = bev_embed.reshape(self.bev_h, self.bev_w, bs, -1).permute(2, 3, 0, 1) # -> (bs, C, bev_h, bev_w)
seg_bev = torch.rot90(seg_bev, k=-1, dims=[2, 3])
seg_bev = torch.flip(seg_bev, dims=[3])
seg_bev = self.feat_cropper(seg_bev) # grid_sample -> (bs, C, H_map, W_map)
seg_pred = self.seg_decoder(seg_bev) # -> (bs, outC, H_map, W_map)检测(det)解析
检测分支在 pts_bbox_head(BEVFormerHead)内部沿着另一条路径使用同样的 BEV 表示完成:
-
输入与查询:head 使用配置中的
num_query(例如 900)构造一组 decoder queries,这些 queries 与 transformer decoder 一起生成针对每个 query 的类别 logits 和边界框回归(或 BEV 相关回归参数)。 -
输出形状:decoder 的输出在实现上通常为每层与最终层两种表示,最终可得到每个样本的预测集合,典型形状为
(bs, num_query, ...)(类别 logits、bbox 回归值等)。如果实现返回多层输出,则可能为(num_layers, bs, num_query, ...)。 -
匹配与损失:训练时 head 会对 decoder 输出使用 Hungarian 匹配(或指定的 assigner),将预测与 ground-truth 对齐后计算分类损失与回归损失(如 L1、GIoU 等)。这些损失与 seg 分支的损失是并列计算的------在
bevformer.py中,如果同时存在 seg_preds 和检测输出,代码会分别计算det_losses和seg_losses并合并返回:det_losses:由 detection head 提供(分类 + 回归 + 其它子损失)。seg_losses:由 seg head 提供(CrossEntropyLoss 等)。- 最终:
det_losses.update(seg_losses)将二者合并用于反向传播。
-
实践要点与断言建议:
-
确认
num_query与训练期预期一致(过多/过少会影响匹配质量与计算量)。 -
在调试阶段输出并断言 detection 最终预测的形状,例如:
assert final_cls_preds.shape[0] == bsassert final_cls_preds.shape[1] == num_query
-
若发现检测结果与 seg 的空间语义存在冲突(例如大量 false positives 在语义地图上对应特定类别区域),优先检查两者的坐标系与时间同步(BEV 时间帧是否一致)、以及损失权重的配比
loss_seg.loss_weight与检测各项损失的相对权重。
-
综上:det 分支直接消费 BEV 表示的 query-化输出进行目标检测,seg 分支通过 grid_sample 将 BEV 重采样到地图 canvas 进行语义分割。二者在训练中并列计算并合并损失,正确的坐标/分辨率对齐与适当的损失权重是保证多任务训练稳定的关键。
生成标签(Rasterize)
RasterizeMapVectors 会调用 preprocess_map 产出 semantic_masks(one-hot per-class masks),随后计算 semantic_indices(每像素的类索引)并打包到样本结果中:
python
results.update({
'semantic_map': torch.from_numpy(semantic_masks),
'instance_map': torch.from_numpy(instance_masks),
'semantic_indices': torch.from_numpy(semantic_indices).long(),
...
})因此训练时 semantic_indices 的尺寸 (H_map, W_map) 必须与 seg_pred 的 H_map/W_map 一致。
shape验证测试
下面展示一个轻量化的单元测试脚本(构造随机 bev_embed -> 复现 head 中的 reshape/permute/rot/flip -> 使用简化的 BevFeatureSlicer 做 grid_sample -> 调用 SegEncode),输出如下:
Loaded SegEncode variants: True True True
bev_embed: torch.Size([900, 2, 256])
after reshape+permute: torch.Size([2, 256, 30, 30])
after rot/flip: torch.Size([2, 256, 30, 30])
after feat_cropper (resampled): torch.Size([2, 256, 200, 400])
seg_pred: torch.Size([2, 4, 200, 400])测试与结果分析
测试脚本:
bash
PYTHONPATH=/home/nuvo/BEVFormer_segmentation_detection python3 - <<'PY'
import sys, torch, traceback
seg_file = '/home/nuvo/BEVFormer_segmentation_detection/projects/mmdet3d_plugin/bevformer/modules/seg_subnet.py'
# read and remove relative import
with open(seg_file,'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
new_lines = [ln for ln in lines if 'from ..modules.builder import SEG_ENCODER' not in ln]
seg_src = ''.join(new_lines)
# dummy registry
class _DummyRegistry:
@staticmethod
def register_module():
def _decorator(cls):
return cls
return _decorator
SEG_ENCODER = _DummyRegistry()
# prepare globals for exec
_glob = {
'__name__': '__main__',
'torch': torch,
'nn': torch.nn,
'resnet18': __import__('torchvision.models.resnet', fromlist=['resnet18']).resnet18,
'SEG_ENCODER': SEG_ENCODER,
}
try:
exec(seg_src, _glob)
SegEncode = _glob.get('SegEncode')
SegEncode_v1 = _glob.get('SegEncode_v1')
DeconvEncode = _glob.get('DeconvEncode')
print('Loaded SegEncode variants:', bool(SegEncode), bool(SegEncode_v1), bool(DeconvEncode))
# BevFeatureSlicer copied
import torch.nn.functional as F
def calculate_birds_eye_view_parameters(x_bounds, y_bounds, z_bounds):
bev_resolution = torch.tensor([row[2] for row in [x_bounds, y_bounds, z_bounds]])
bev_start_position = torch.tensor([row[0] + row[2] / 2.0 for row in [x_bounds, y_bounds, z_bounds]])
bev_dimension = torch.tensor([(row[1] - row[0]) / row[2] for row in [x_bounds, y_bounds, z_bounds]], dtype=torch.long)
return bev_resolution, bev_start_position, bev_dimension
class BevFeatureSlicer(object):
def __init__(self, grid_conf, map_grid_conf):
if grid_conf == map_grid_conf:
self.identity_mapping = True
else:
self.identity_mapping = False
bev_resolution, bev_start_position, bev_dimension = calculate_birds_eye_view_parameters(
grid_conf['xbound'], grid_conf['ybound'], grid_conf['zbound'],)
map_bev_resolution, map_bev_start_position, map_bev_dimension = calculate_birds_eye_view_parameters(
map_grid_conf['xbound'], map_grid_conf['ybound'], map_grid_conf['zbound'],)
self.map_x = torch.arange(map_bev_start_position[0], map_grid_conf['xbound'][1], map_bev_resolution[0])
self.map_y = torch.arange(map_bev_start_position[1], map_grid_conf['ybound'][1], map_bev_resolution[1])
self.norm_map_x = self.map_x / (- bev_start_position[0])
self.norm_map_y = self.map_y / (- bev_start_position[1])
self.map_grid = torch.stack(torch.meshgrid(self.norm_map_x, self.norm_map_y), dim=2).permute(1, 0, 2)
def __call__(self, x):
if self.identity_mapping:
return x
else:
grid = self.map_grid.unsqueeze(0).type_as(x).repeat(x.shape[0], 1, 1, 1)
return F.grid_sample(x, grid=grid, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
det_grid_conf = {'xbound': [-51.2, 51.2, 0.34], 'ybound': [-51.2, 51.2, 0.34], 'zbound': [-10.0,10.0,20.0], 'dbound': [1.0,60.0,1.0]}
map_grid_conf = {'xbound': [-30.0, 30.0, 0.15], 'ybound': [-15.0, 15.0, 0.15], 'zbound': [-10.0,10.0,20.0], 'dbound': [1.0,60.0,1.0]}
bev_h, bev_w = 30, 30
bs, C = 2, 256
bev_embed = torch.randn(bev_h * bev_w, bs, C)
print('bev_embed:', bev_embed.shape)
seg_bev = bev_embed.reshape(bev_h, bev_w, bs, -1).permute(2, 3, 0, 1)
print('after reshape+permute:', seg_bev.shape)
seg_bev = torch.rot90(seg_bev, k=-1, dims=[2, 3])
seg_bev = torch.flip(seg_bev, dims=[3])
print('after rot/flip:', seg_bev.shape)
feat_cropper = BevFeatureSlicer(det_grid_conf, map_grid_conf)
seg_bev_resampled = feat_cropper(seg_bev)
print('after feat_cropper (resampled):', seg_bev_resampled.shape)
seg_decoder = SegEncode(inC=C, outC=4)
seg_pred = seg_decoder(seg_bev_resampled)
print('seg_pred:', seg_pred.shape)
except Exception:
traceback.print_exc()
sys.exit(1)
PY关键输出摘录:
Loaded SegEncode variants: True True True
bev_embed: torch.Size([900, 2, 256])
after reshape+permute: torch.Size([2, 256, 30, 30])
after rot/flip: torch.Size([2, 256, 30, 30])
after feat_cropper (resampled): torch.Size([2, 256, 200, 400])
seg_pred: torch.Size([2, 4, 200, 400])解析要点:
-
流程复现:测试里选择的
bev_h=30, bev_w=30, bs=2, C=256,从随机bev_embed开始,按 head 中逻辑 reshape/permute 后得到 (2,256,30,30),经经验性旋转/翻转保持同尺寸。 -
重采样行为:
BevFeatureSlicer将 BEV 特征从 (30,30) 重采样到地图 canvas (200,400)。这说明 det/map grid 配置(det_grid_conf与map_grid_conf)决定了最终语义图的 H×W。 -
通道与类别对齐:
SegEncode输出为[B, outC, H_map, W_map],本次测试outC=4,直接对应配置中的loss_seg.class_weight长度(4),可直接用于 CrossEntropyLoss。 -
断言建议(CI/单测):在 pipeline 中加入断言:
assert seg_bev_resampled.shape[0] == semantic_indices.shape[0](batch 对齐)assert seg_pred.shape[2:] == semantic_indices.shape[-2:](空间尺寸一致)
-
诊断项:若训练中语义结果与
semantic_indices不匹配,应依次检查:rot90/flip 的顺序与方向、BevFeatureSlicer的 grid 生成(起始坐标与分辨率)、以及RasterizeMapVectors的坐标系与像素下标约定。
注意:测试运行时触发了关于 torch.meshgrid 的警告(未来需要传入 indexing 参数),以及 torch.arange 的隐式整数转换警告;这些不影响当前验证,但建议在长期维护中补齐以避免未来报错。
说明:测试表明 SegEncode 输出空间尺寸与重采样后特征一致,故在形状层面可以直接与 semantic_indices 计算交叉熵损失。
注意与建议
- 若在实际训练中发现语义错位,请先可视化
seg_pred.argmax(1)与semantic_indices,对比旋转/翻转是否正确;常见修复是调整 rot90/flip 的顺序或 axis。 - 若 seg loss 显著干扰检测训练,可先单独训练
SegEncode(或使用轻量SegEncode_v1)验证坐标对齐与类权重配置,然后再多任务联合训练并调节loss_seg.loss_weight。 - 如果使用上游 MapTR 的原生 CUDA 内核(
modules/ops/geometric_kernel_attn),请保证本地编译的.so与源同步;二者不一致会导致运行时差异。
快速复现场景(伪码)
python
import torch
bev_h, bev_w, bs, C = 300, 300, 2, 256
bev_embed = torch.randn(bev_h*bev_w, bs, C)
seg_bev = bev_embed.reshape(bev_h, bev_w, bs, C).permute(2, 3, 0, 1)
seg_bev = torch.rot90(seg_bev, k=-1, dims=[2,3])
seg_bev = torch.flip(seg_bev, dims=[3])
seg_bev_resampled = feat_cropper(seg_bev)
seg_pred = seg_decoder(seg_bev_resampled)
assert seg_pred.shape[2:] == semantic_indices.shape[-2:]下一步
- 我可以把上述形状测试封装成项目内的单元脚本(例如
tools/tests/test_seg_shape.py)并打开一个 PR;你想我现在创建该脚本吗?
文件位置: <docs/bevformer_seg_det_maptr_blog.md>
如果你需要我把该 Markdown 转成仓库的 blog post(加入资产图、可视化示例或 CI 单元测试),我可以继续完善。