链表中常用的技巧
- 引入虚拟"头"节点:便于处理边界情况,并且方便对链表操作。
- 不要吝啬空间,大胆定义变量:比如我们在已经存在的链表中插入节点时容易因为插入顺序的原因导致找不到某个节点了,这时只需要定义一个指针变量,指向容易因为插入顺序而找不到的节点,这样通过这个指针就能找到这个节点,以那种顺序插入其他节点就都可以了。
- 使用快慢双指针(适用部分题)。
两数相加
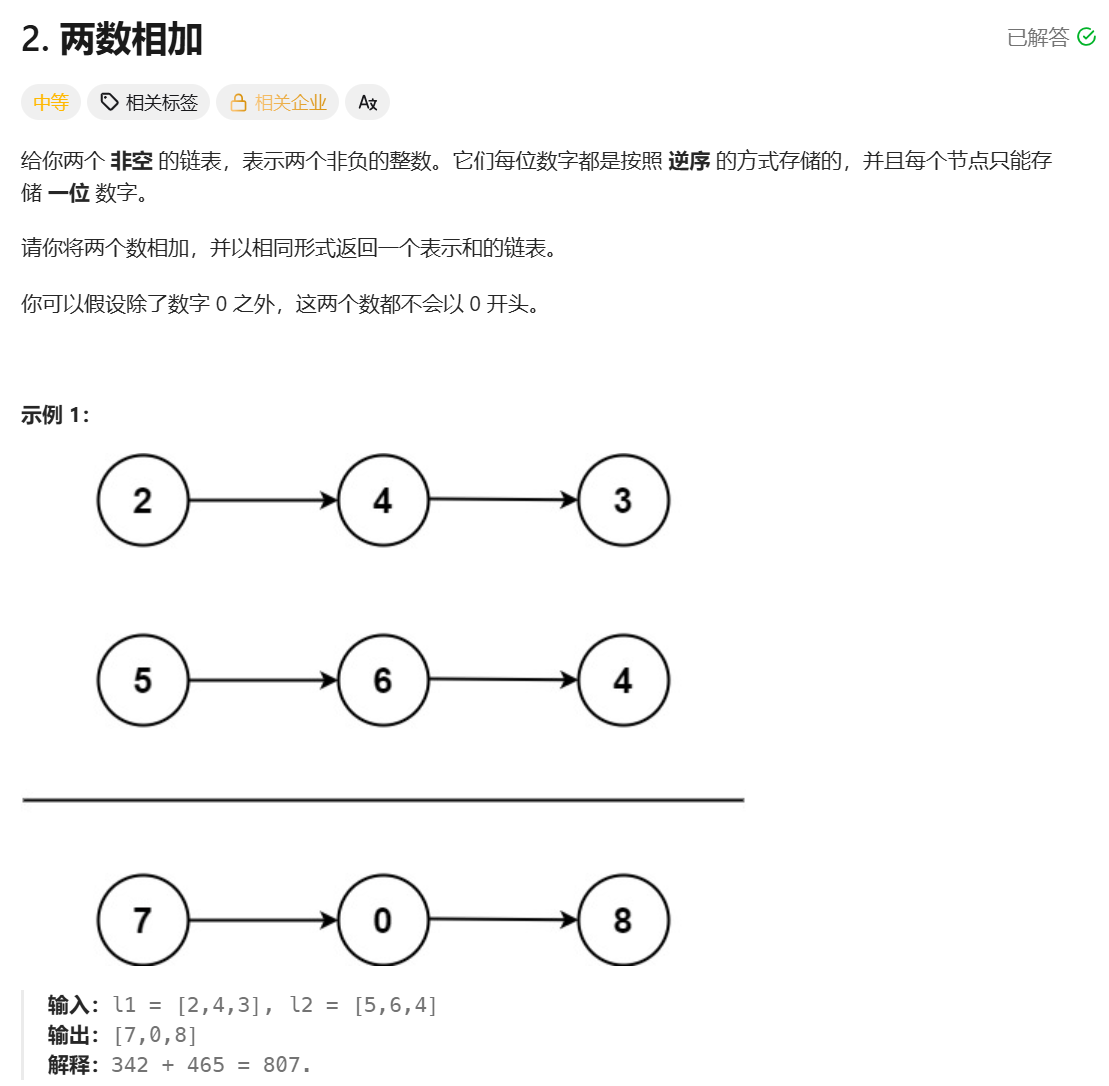
**思路:**定义两个指针分别指向两链表,然后模拟题目说的流程即可,两个节点的值相加时可能会有进位,所以需要定义一个变量存储进位,当两个链表都遍历结束后,还需要单独判断一下进位是否为 0,如果不为 0,还需要在创建一个节点存储最终的进位。
代码:
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* tail = head;
int carry = 0; //存储进位
ListNode* cur1 = l1;
ListNode* cur2 = l2;
while(cur1 != NULL || cur2 != NULL){
if(cur1 != NULL)
carry += cur1->val;
if(cur2 != NULL)
carry += cur2->val;
int num = carry % 10;
carry /= 10;
ListNode* newnode = new ListNode(num);
tail->next = newnode;
tail = newnode;
if(cur1 != NULL)
cur1 = cur1->next;
if(cur2 != NULL)
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
if(carry != 0){
ListNode* newnode = new ListNode(carry);
tail->next = newnode;
tail = newnode;
}
ListNode* newhead = head->next;
delete head;
return newhead;
}
};两两交换链表中的节点
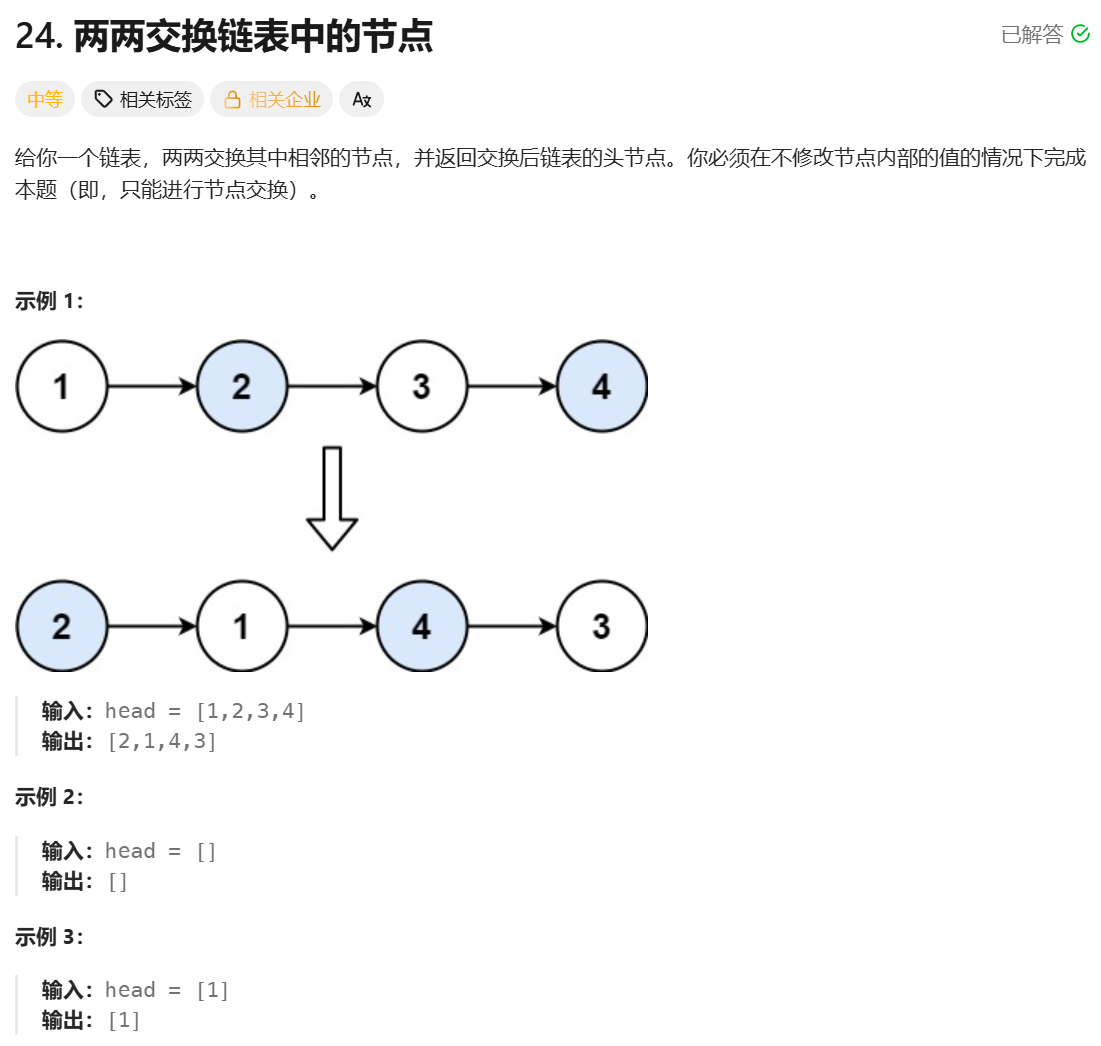
**思路:**定义一个虚拟头节点,然后定义四个指针,分别指向要交换的两个节点的前一个节点,要交换的两个节点,要交换的两个节点的后一个节点,通过这四个指针就能完成这两个节点位置的交换,然后再移动这四个指针指向下一对交换的节点,继续这个过程直到所有节点完成交换。
循环结束条件是 cur 指针为空(对应节点为偶数个)或者 next 指针为空(对应节点为奇数个)
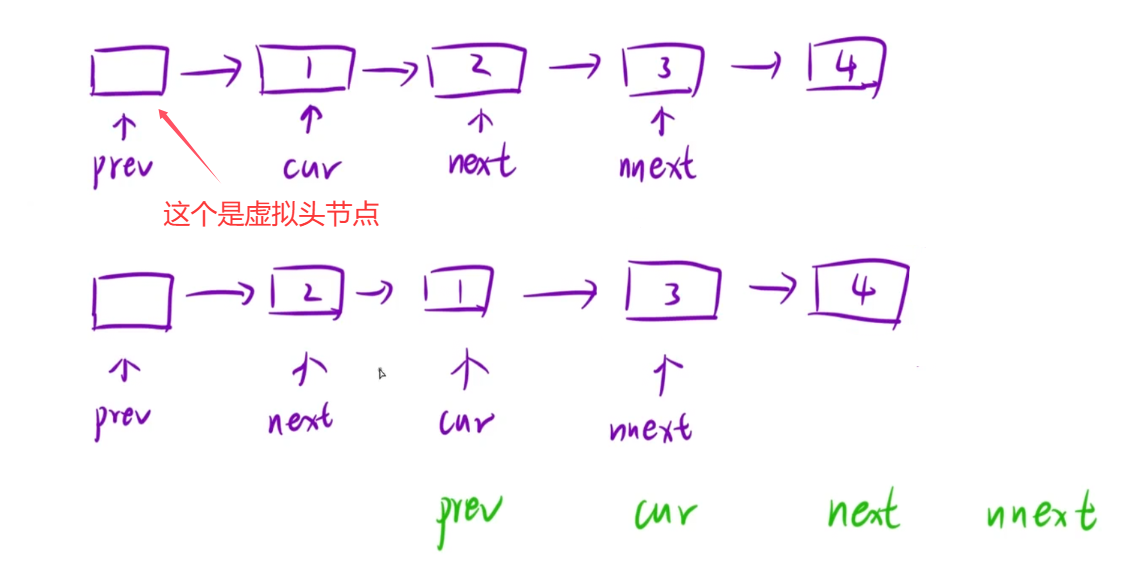
代码:
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
ListNode* newnode = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* prev = newnode;
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* next = head->next;
ListNode* nnext = next->next;
while(cur != NULL && next != NULL){
prev->next = next;
next->next = cur;
cur->next = nnext;
prev = cur;
cur = nnext;
if(cur)
next = cur->next;
if(cur && next)
nnext = next->next;
}
head = newnode->next;
delete newnode;
return head;
}
};重排链表
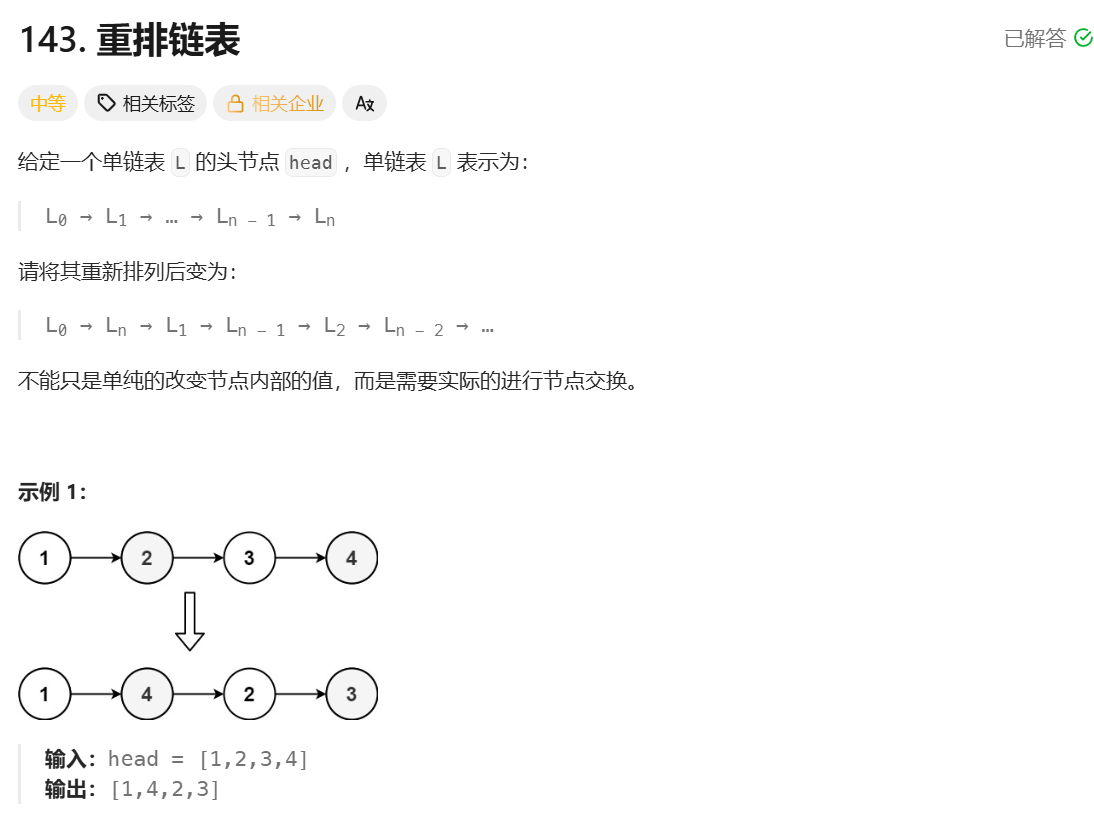
**思路:**找到链表的中间节点,把链表分成两部分,把后面部分逆序,然后合并两个链表。将链表逆序可以先创建一个虚拟头节点,然后将要逆序的部分头插到这个虚拟头节点的链表中即可。合并两个链表先创建一个虚拟头节点,然后使用尾插就行。
代码:
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL || head->next == NULL || head->next->next == NULL)
return;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
while(cur){
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = newhead->next;
newhead->next = cur;
cur = next;
}
ListNode* newhead2 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* tail = newhead2;
ListNode* cur1 = head;
ListNode* cur2 = newhead->next;
while(cur1){
tail->next = cur1;
tail = cur1;
cur1 = cur1->next;
if(cur2){
tail->next = cur2;
tail = cur2;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
}
delete newhead;
delete newhead2;
}
};合并 K 个升序链表

**思路:**这道题可以使用优先级队列来解决,创建一个小根堆,然后将所有链表头节点放入小根堆中,每次取出堆顶元素尾插到结果链表中,然后判断一下,如果取出的这个节点后面还有其他节点,将它后面的节点也扔入小根堆中(每次只扔一个)。另外,这个结果链表要有一个虚拟头节点,方便插入数据和返回结果时找到头节点。
代码:
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
struct cmp{
bool operator()(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2){
return l1->val > l2->val;
}
};
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
priority_queue<ListNode*, vector<ListNode*>, cmp> heap;
for(auto l : lists){
if(l)
heap.push(l);
}
ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* tail = newhead;
while(!heap.empty()){
ListNode* node = heap.top();
heap.pop();
tail->next = node;
tail = node;
if(node->next)
heap.push(node->next);
}
tail = newhead->next;
delete newhead;
return tail;
}
};K 个一组翻转链表
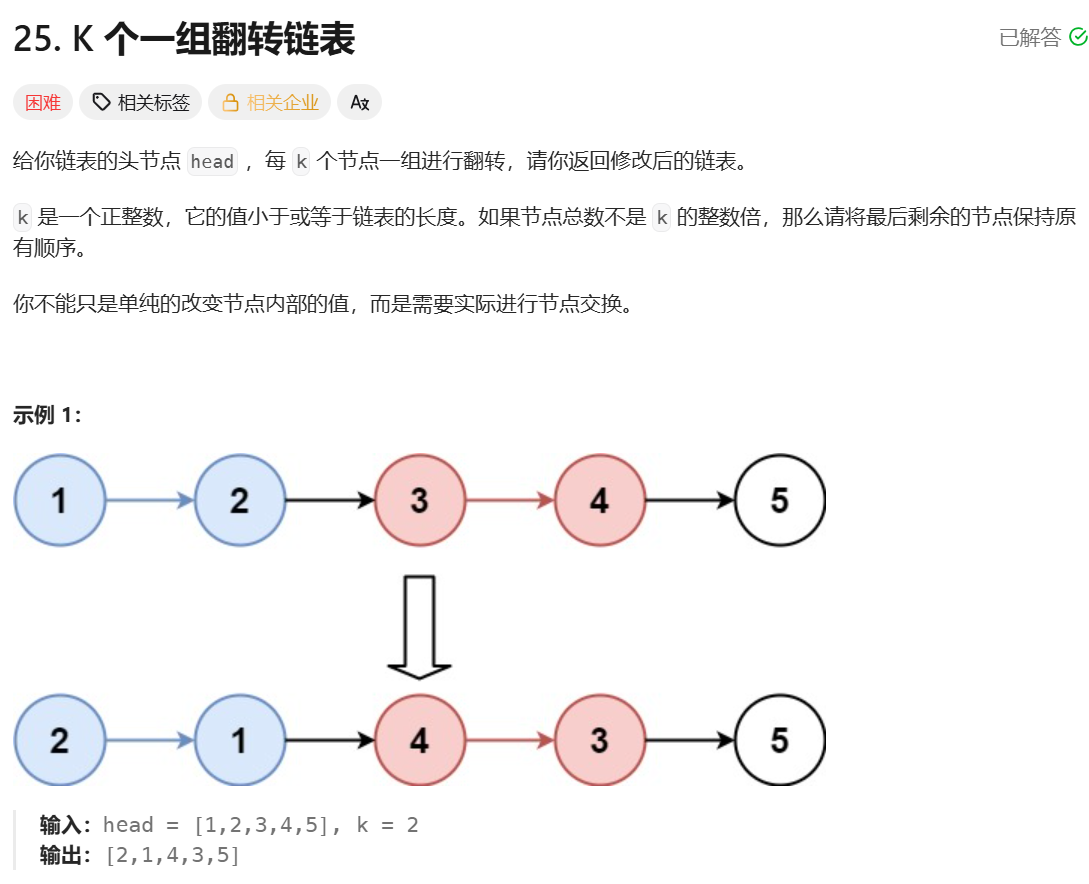
**思路:**先求出需要逆序多少组,然后重复 n 次长度为 k 的链表逆序即可。逆序还是使用创建虚拟头节点然后头插的方法就可以。
代码:
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k)
{
int n = 0;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
n++;
cur = cur->next;
}
n /= k;
ListNode* newhead = new ListNode();
ListNode* prev = newhead;
cur = head;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ListNode* tmp = cur;
for(int j = 0; j < k; j++)
{
ListNode* next = cur->next;
cur->next = prev->next;
prev->next = cur;
cur = next;
}
prev = tmp;
}
prev->next = cur;
cur = newhead->next;
delete newhead;
return cur;
}
};