欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区:开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:2048游戏算法与优化深度解析
文章目录
- [Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:2048游戏算法与优化深度解析](#Flutter for OpenHarmony 实战:2048游戏算法与优化深度解析)
摘要
2048游戏看似简单,但其背后蕴含了丰富的算法设计与优化技巧。本文深入探讨2048游戏的核心算法实现,包括高效合并算法、启发式AI实现、游戏难度平衡、最优策略分析等高级主题。通过本文学习,读者将掌握如何设计更智能的游戏AI,理解游戏平衡性的设计原理。
一、合并算法优化
1.1 基础合并算法回顾
dart
bool _moveLeft() {
bool moved = false;
for (int r = 0; r < 4; r++) {
final row = _board[r].where((n) => n != 0).toList();
final newRow = <int>[];
for (int i = 0; i < row.length; i++) {
if (i + 1 < row.length && row[i] == row[i + 1]) {
final merged = row[i] * 2;
newRow.add(merged);
_score += merged;
i++; // 跳过下一个
} else {
newRow.add(row[i]);
}
}
while (newRow.length < 4) {
newRow.add(0);
}
for (int c = 0; c < 4; c++) {
if (_board[r][c] != newRow[c]) {
moved = true;
}
_board[r][c] = newRow[c];
}
}
return moved;
}1.2 优化合并算法
使用更高效的合并策略:
dart
class OptimizedMover {
// 向左移动并合并
static (List<List<int>>, bool, int) moveLeft(List<List<int>> board) {
final newBoard = List.generate(4, (r) => List<int>.from(board[r]));
bool moved = false;
int scoreGain = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < 4; r++) {
// 提取非零元素
final row = newBoard[r].where((n) => n != 0).toList();
final merged = <int>[];
int i = 0;
while (i < row.length) {
if (i + 1 < row.length && row[i] == row[i + 1]) {
// 合并相同数字
final value = row[i] * 2;
merged.add(value);
scoreGain += value;
i += 2;
} else {
merged.add(row[i]);
i++;
}
}
// 补齐0
while (merged.length < 4) {
merged.add(0);
}
// 检测变化
for (int c = 0; c < 4; c++) {
if (newBoard[r][c] != merged[c]) {
moved = true;
}
newBoard[r][c] = merged[c];
}
}
return (newBoard, moved, scoreGain);
}
// 向右移动
static (List<List<int>>, bool, int) moveRight(List<List<int>> board) {
final reversed = List.generate(4, (r) => board[r].reversed.toList());
final (newBoard, moved, score) = moveLeft(reversed);
final restored = List.generate(4, (r) => newBoard[r].reversed.toList());
return (restored, moved, score);
}
// 向上移动
static (List<List<int>>, bool, int) moveUp(List<List<int>> board) {
final transposed = _transpose(board);
final (newBoard, moved, score) = moveLeft(transposed);
return (_transpose(newBoard), moved, score);
}
// 向下移动
static (List<List<int>>, bool, int) moveDown(List<List<int>> board) {
final transposed = _transpose(board);
final (newBoard, moved, score) = moveRight(transposed);
return (_transpose(newBoard), moved, score);
}
// 转置矩阵
static List<List<int>> _transpose(List<List<int>> board) {
return List.generate(4, (r) =>
List.generate(4, (c) => board[c][r])
);
}
}二、AI实现

2.1 期望算法
dart
class ExpectimaxAI {
static const int maxDepth = 3;
static String getBestMove(List<List<int>> board) {
double bestScore = -double.infinity;
String bestMove = 'left';
for (final move in ['left', 'right', 'up', 'down']) {
final result = _tryMove(board, move);
if (!result.$2) continue; // 无效移动
final score = _expectimax(result.$1, maxDepth - 1, false);
if (score > bestScore) {
bestScore = score;
bestMove = move;
}
}
return bestMove;
}
static double _expectimax(List<List<int>> board, int depth, bool isMax) {
if (depth == 0) {
return _evaluateBoard(board);
}
if (isMax) {
// 玩家回合:选择最优移动
double maxScore = -double.infinity;
for (final move in ['left', 'right', 'up', 'down']) {
final result = _tryMove(board, move);
if (!result.$2) continue;
final score = _expectimax(result.$1, depth - 1, false);
if (score > maxScore) {
maxScore = score;
}
}
return maxScore == -double.infinity ? _evaluateBoard(board) : maxScore;
} else {
// 随机回合:计算期望值
final emptyCells = _getEmptyCells(board);
if (emptyCells.isEmpty) {
return _expectimax(board, depth - 1, true);
}
double totalScore = 0;
int count = 0;
// 尝试在空位放置2或4
for (final cell in emptyCells) {
for (final value in [2, 4]) {
final newBoard = _placeTile(board, cell.x, cell.y, value);
final probability = value == 2 ? 0.9 : 0.1;
final score = _expectimax(newBoard, depth - 1, true);
totalScore += score * probability;
count++;
}
}
return totalScore / count;
}
}
// 评估棋盘
static double _evaluateBoard(List<List<int>> board) {
double score = 0;
// 1. 空格数量(越多越好)
final emptyCells = _getEmptyCells(board);
score += emptyCells.length * 100;
// 2. 单调性(数字沿边缘递增)
score += _getMonotonicity(board) * 10;
// 3. 平滑度(相邻数字相近)
score += _getSmoothness(board) * 3;
// 4. 最大值位置(角落最好)
score += _getCornerBonus(board) * 50;
return score;
}
static int _getMonotonicity(List<List<int>> board) {
int totals[] = [0, 0, 0, 0]; // 上、下、左、右
// 左右方向
for (int r = 0; r < 4; r++) {
int current = 0;
for (int c = 1; c < 4; c++) {
if (board[r][c] > board[r][c - 1]) {
current++;
} else if (board[r][c] < board[r][c - 1]) {
current--;
}
}
totals[2] += current;
totals[3] -= current;
}
// 上下方向
for (int c = 0; c < 4; c++) {
int current = 0;
for (int r = 1; r < 4; r++) {
if (board[r][c] > board[r - 1][c]) {
current++;
} else if (board[r][c] < board[r - 1][c]) {
current--;
}
}
totals[0] += current;
totals[1] -= current;
}
return totals.reduce(max);
}
static double _getSmoothness(List<List<int>> board) {
double smoothness = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < 4; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < 4; c++) {
if (board[r][c] != 0) {
// 检查右边
if (c + 1 < 4 && board[r][c + 1] != 0) {
smoothness -= (board[r][c] - board[r][c + 1]).abs();
}
// 检查下边
if (r + 1 < 4 && board[r + 1][c] != 0) {
smoothness -= (board[r][c] - board[r + 1][c]).abs();
}
}
}
}
return smoothness;
}
static int _getCornerBonus(List<List<int>> board) {
// 检查最大值是否在角落
int maxValue = 0;
for (int r = 0; r < 4; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < 4; c++) {
if (board[r][c] > maxValue) {
maxValue = board[r][c];
}
}
}
if (board[0][0] == maxValue ||
board[0][3] == maxValue ||
board[3][0] == maxValue ||
board[3][3] == maxValue) {
return maxValue;
}
return 0;
}
static List<Point> _getEmptyCells(List<List<int>> board) {
final cells = <Point>[];
for (int r = 0; r < 4; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < 4; c++) {
if (board[r][c] == 0) {
cells.add(Point(r, c));
}
}
}
return cells;
}
static (List<List<int>>, bool) _tryMove(List<List<int>> board, String move) {
switch (move) {
case 'left':
return OptimizedMover.moveLeft(board);
case 'right':
return OptimizedMover.moveRight(board);
case 'up':
return OptimizedMover.moveUp(board);
case 'down':
return OptimizedMover.moveDown(board);
default:
return (board, false);
}
}
static List<List<int>> _placeTile(
List<List<int>> board, int x, int y, int value
) {
final newBoard = List.generate(4, (r) => List<int>.from(board[r]));
newBoard[x][y] = value;
return newBoard;
}
}三、难度平衡设计
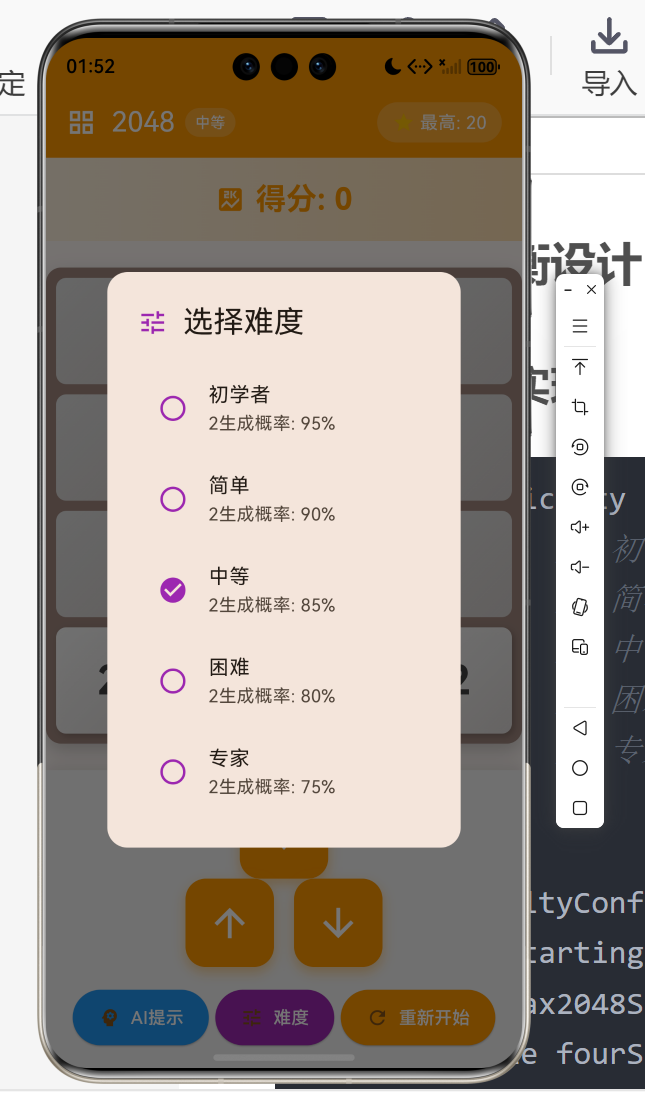
3.1 难度级别实现
dart
enum GameDifficulty {
beginner, // 初学者
easy, // 简单
medium, // 中等
hard, // 困难
expert, // 专家
}
class DifficultyConfig {
final int startingTiles;
final int max2048Spawn;
final double fourSpawnRate;
const DifficultyConfig({
required this.startingTiles,
required this.max2048Spawn,
required this.fourSpawnRate,
});
factory DifficultyConfig.fromDifficulty(GameDifficulty difficulty) {
switch (difficulty) {
case GameDifficulty.beginner:
return const DifficultyConfig(
startingTiles: 3,
max2048Spawn: 256,
fourSpawnRate: 0.05,
);
case GameDifficulty.easy:
return const DifficultyConfig(
startingTiles: 2,
max2048Spawn: 512,
fourSpawnRate: 0.1,
);
case GameDifficulty.medium:
return const DifficultyConfig(
startingTiles: 2,
max2048Spawn: 1024,
fourSpawnRate: 0.1,
);
case GameDifficulty.hard:
return const DifficultyConfig(
startingTiles: 2,
max2048Spawn: 2048,
fourSpawnRate: 0.15,
);
case GameDifficulty.expert:
return const DifficultyConfig(
startingTiles: 2,
max2048Spawn: 4096,
fourSpawnRate: 0.2,
);
}
}
}3.2 动态难度调整
dart
class DynamicDifficulty {
int consecutiveWins = 0;
int consecutiveLosses = 0;
GameDifficulty currentDifficulty = GameDifficulty.medium;
void onGameWin(int moves, int maxTile) {
consecutiveWins++;
consecutiveLosses = 0;
// 如果快速获胜且达到高数字,提升难度
if (consecutiveWins >= 2 && maxTile >= 2048 && moves < 500) {
_increaseDifficulty();
}
}
void onGameLoss(int moves, int maxTile) {
consecutiveLosses++;
consecutiveWins = 0;
// 如果快速失败,降低难度
if (consecutiveLosses >= 2 && maxTile < 512 && moves < 200) {
_decreaseDifficulty();
}
}
void _increaseDifficulty() {
final difficulties = GameDifficulty.values;
final currentIndex = difficulties.indexOf(currentDifficulty);
if (currentIndex < difficulties.length - 1) {
currentDifficulty = difficulties[currentIndex + 1];
}
}
void _decreaseDifficulty() {
final difficulties = GameDifficulty.values;
final currentIndex = difficulties.indexOf(currentDifficulty);
if (currentIndex > 0) {
currentDifficulty = difficulties[currentIndex - 1];
}
}
}四、性能优化
4.1 状态缓存
dart
class GameStateCache {
final Map<String, double> _cache = {};
static const int maxCacheSize = 10000;
String _boardToString(List<List<int>> board) {
return board.map((row) => row.join(',')).join('|');
}
double? get(List<List<int>> board) {
final key = _boardToString(board);
return _cache[key];
}
void set(List<List<int>> board, double value) {
if (_cache.length >= maxCacheSize) {
_cache.clear();
}
final key = _boardToString(board);
_cache[key] = value;
}
}4.2 位运算优化
使用位运算表示棋盘状态:
dart
class BitBoard {
// 使用64位整数表示4x4棋盘
// 每个格子用4位表示(0-15对应数字0-15的2^n)
final int board;
const BitBoard(this.board);
int getTile(int row, int col) {
final shift = (row * 4 + col) * 4;
return (board >> shift) & 0xF;
}
BitBoard setTile(int row, int col, int value) {
final shift = (row * 4 + col) * 4;
final mask = 0xF << shift;
return BitBoard((board & ~mask) | ((value & 0xF) << shift));
}
// 快速比较
bool operator ==(Object other) =>
other is BitBoard && board == other.board;
@override
int get hashCode => board.hashCode;
}五、总结
本文深入探讨了2048游戏的算法优化:
- 合并算法优化:高效的行处理、转置操作
- AI实现:期望算法、启发式评估
- 难度平衡:多级难度、动态调整
- 性能优化:状态缓存、位运算
这些技术不仅适用于2048游戏,也可以应用到其他滑动类游戏中。
欢迎加入开源鸿蒙跨平台社区 : 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区