基本概念
在SpringBoot中实现多数据源的核心原理是通过配置多个DataSource实例,并集和动态数据源切换机制来实现对不同数据库的访问
DataSource:Spring中用于管理数据库连接的核心接口,每个数据源对应一个独立的数据库
多数据源:在一个应用中配置多个DataSource实例分别指向不同的数据库
Yaml配置文件
mysql-datasoure1、mysql-datasource2是自定义数据源
spring:
# 数据源配置
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #声明数据源类型
mysql-datasource1: ##声明第一个数据源所需数据
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/lym?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: root
password: 123456
mysql-datasource2: ##声明第二个数据源所需数据
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/lym_slave?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useSSL=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
username: root
password: 123456
druid: ##druid数据库连接池的基本初始化属性 ##连接池初始化大小 ##最小空闲线程数 ##最大活动png线程数
initial-size: 5
min-idle: 1
max-active: 20
#Mp配置
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
logging:
level:
dao: debug
# 全局配置文件位置(可选)
# config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
# Mapper XML文件位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
# 配置实体类所在的包名,MyBatis-Plus会自动扫描并注册为别名
type-aliases-package: com.lym.**.entity
# 全局配置
global-config:
# 配置表前缀
db-config:
table-prefix: lym_
# 开启驼峰命名规则转换
capital-mode: true
# 配置逻辑删除相关属性
logic-delete-value: 1
logic-not-delete-value: 0
# 分页插件配置
pagination:
enabled: true
page-size: 10
reasonable: true创建多个DataSource Bean
使用 @Primary 注解标记默认数据源。
@ConfigurationProperties注解用于将YAML中指定的数据创建成指定对象,
但是YMAL中的数据必须要与对象中的属性名同名,不然Spring Boot无法完成赋值
java
/**
* 定义多个数据源
*/
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Bean(name="mysqlDatasource1")
@Primary
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.mysql-datasource1")
public DataSource dataSource1(){
DruidDataSource build = DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
return build;
}
@Bean(name="mysqlDatasource2")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.mysql-datasource2")
public DataSource dataSource2(){
DruidDataSource build = DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
return build;
}
}禁用SpringBoot数据源自动配置
由于我们要定义多个数据源,所以在Spring Boot数据源自动配置类中就无法确定导入哪个数据源来完成初始化配置,所以我们需要禁用掉Spring Boot的数据源自动配置类,然后使用我们自定义的数据源配置类来完成数据源的初始化与管理
禁用方法:在启动类上添加配置:exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class}
java
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class LymApplication {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SpringApplication.run(LymApplication.class, args);
}方案一 实现DataSource接口
现DataSource接口,本质上是使用了一个方法,就是getConnection()这个无参方法,但是在实现Datasource接口的时候,里面的所有方法都要实现,只是不用写方法体而已,也就存在很多"废方法"
@Primary注解 == @Order(1) 用于设置此类的注入顺序
java
import com.lym.common.utils.string.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* 实现DataSource接口
*/
@Component
@Primary //@Primary == @Order(1) 用于设置此类的注入顺序
public class DynamicDataSource implements DataSource {
//使用ThreadLocal而不是String,可以在多线程的时候保证数据的可靠性
public static ThreadLocal<String> flag = new ThreadLocal<>();
@Resource
private DataSource mysqlDatasource1; //注入第一个数据源
@Resource
private DataSource mysqlDatasource2; //注入第二个数据源
public DynamicDataSource(){ //使用构造方法初始化ThreadLocal的值
flag.set("");
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
//通过修改ThreadLocal来修改数据源
//为什么通过修改状态就能改变已经注入的数据源?这是源码里面决定的
if("db2".equals(flag.get())){
return mysqlDatasource2.getConnection();
}
return mysqlDatasource1.getConnection();
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
}缺点:会产生大量代码冗余,在代码中存在硬编程
测试使用
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("datasource1")
public class DataSourceOneDemo {
@Autowired
private IUserService userService;
@GetMapping("/testone1")
public ResultUtils getData(){
//默认使用dataSource1
List<LymUser> list = userService.list();
return ResultUtils.success(list);
}
@GetMapping("/testone2")
public ResultUtils getData1(){
//使用第二数据库dataSource2
DynamicDataSource.flag.set("db2");
List<LymUser> list = userService.list();
return ResultUtils.success(list);
}
}方案二 继承AbstrictRoutingDataSource类
减少代码的冗余,但是还是会存在硬编码
AbstrictRoutingDataSource的本质就是利用一个Map将数据源存储起来,然后通过Key来得到Value来修改数据源
配置文件和定义数据源同上
java
@Component
@Primary
public class DynamicDataSource1 extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
public static ThreadLocal<String> flag = new ThreadLocal<>();
@Resource
private DataSource mysqlDatasource1;
@Resource
private DataSource mysqlDatasource2;
public DynamicDataSource1(){
flag.set("dbSession");
}
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return flag.get();
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet(){
Map<Object, Object> objectObjectConcurrentHashMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
objectObjectConcurrentHashMap.put("dbSession",mysqlDatasource1);
//将第一个数据源设置为默认的数据源
super.setDefaultTargetDataSource(mysqlDatasource1);
objectObjectConcurrentHashMap.put("dbSession2",mysqlDatasource2);
//将Map对象赋值给AbstrictRoutingDataSource内部的Map对象中
super.setTargetDataSources(objectObjectConcurrentHashMap);
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}测试使用
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("datasource1")
public class DataSourceOneDemo1 {
@Autowired
private IUserService userService;
@GetMapping("/testone1")
public ResultUtils getData(){
//默认使用dataSource1
List<LymUser> list = userService.list();
return ResultUtils.success(list);
}
@GetMapping("/testone2")
public ResultUtils getData1(){
//使用第二数据库dataSource2
DynamicDataSource1.flag.set("dbSession2");
List<LymUser> list = userService.list();
return ResultUtils.success(list);
}
}方案三 Spring AOP+自定义注解
Spring AOP+自定义注解的形式是一种推荐的写法,减少代码的冗余且不存在硬编码
此方法适合对制定功能操作指定数据库的模式
配置文件和定义数据源同上
首先确定你的项目是否导入AOP
导入依赖
开启AOP支持
java
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "com.lym.*.*",exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})//配置SpringBoot扫描路径、配置禁用数据源自动装配
@MapperScan("com.lym.**.mapper")//扫描指定的Mapper文件
@EnableScheduling // 启用定时任务
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy//开启Spring Boot对AOP的支持
public class LymApplication {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// System.setProperty("spring.devtools.restart.enabled", "false");
SpringApplication.run(LymApplication.class, args);
System.out.println("\"\n" +
" \uD83C\uDF89(♥◠‿◠)ノ゙✨ Lym-System ✨启动成功!\uD83C\uDF8A\uD83C\uDF8A \n" +
" ٩(。•́‿•̀。)۶ \uD83C\uDF38 欢迎使用!一起升华吧~ \uD83C\uDF08\n" +
" \n" +
" ___ .__ __. _______ __ ______ ______ \n" +
" / \\\\ | \\\\ | | | ____|| | / __ \\\\ / __ \\\\ \n" +
" / ^ \\\\ | \\\\| | | |__ | | | | | | | | | |\n" +
" / /_\\\\ \\\\ | . ` | | __| | | | | | | | | | |\n" +
" / _____ \\\\ | |\\\\ | | | | | | `--' | | `--' |\n" +
" /__/ \\\\__\\\\ |__| \\\\__| |__| |__| \\\\______/ \\\\______/\n" +
" \n" +
" \"");
}
}定义枚举来表示数据源标识
java
/**
* 多数据源注解-枚举类型
*/
public enum DataSourceType {
MYSQL_DATASOURCE1,
MYSQL_DATASOURCE2
}继承AbstractRoutingDataSource类
java
/**
* 继承AbstractRoutingDataSource类
*/
@Primary
@Component
public class DataSourceManagement extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
public static ThreadLocal<String> flag = new ThreadLocal<>();
@Resource
private DataSource mysqlDatasource1;
@Resource
private DataSource mysqlDatasource2;
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return flag.get();
}
public void afterPropertiesSet(){
ConcurrentHashMap<Object, Object> targetDataSource = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
targetDataSource.put(DataSourceType.MYSQL_DATASOURCE1.name(),mysqlDatasource1);
targetDataSource.put(DataSourceType.MYSQL_DATASOURCE2.name(),mysqlDatasource2);
super.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSource);
super.setDefaultTargetDataSource(mysqlDatasource1);
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}自定义多数据源注解
java
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 定义多数据源注解
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface TargetDataSource {
DataSourceType value() default DataSourceType.MYSQL_DATASOURCE1;
}实现自定义注解
java
/**
* 实现自定义注解
*/
@Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class TargetDataSourceAspect {
@Before("@within(TargetDataSource) || @annotation(TargetDataSource)")
public void beforeNoticeUpdateDataSource(JoinPoint joinPoint){
TargetDataSource targetDataSource = null;
Class<?> aClass = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass();
if(aClass.isAnnotationPresent(TargetDataSource.class)){
//判断类上是否标注注解
targetDataSource = aClass.getAnnotation(TargetDataSource.class);
log.info("类上标注了注解");
}else{
Method method = ((MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod();
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(TargetDataSource.class)){
//判断方法上是否标注了注解,如果类上和方法上都没有标注则报错
targetDataSource = method.getAnnotation(TargetDataSource.class);
log.info("方法上标注了注解");
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("@TargetDataSource注解只能用于类或方法上,错误出现在:["+aClass.toString()+" "+method.toString()+"]");
}
}
//切换数据源
DataSourceManagement.flag.set(targetDataSource.value().name());
}
}测试使用
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("datasource1")
@TargetDataSource(value = DataSourceType.MYSQL_DATASOURCE1)
public class DataSourceOneDemo2 {
@Autowired
private IUserService userService;
@GetMapping("/testone1")
public ResultUtils getData(){
//默认使用dataSource1
List<LymUser> list = userService.list();
return ResultUtils.success(list);
}
}
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("datasource2")
@TargetDataSource(value = DataSourceType.MYSQL_DATASOURCE2)
public class DataSourceOneDemo3 {
@Autowired
private IUserService userService;
@GetMapping("/testone2")
public ResultUtils getData(){
List<LymUser> list = userService.list();
return ResultUtils.success(list);
}
}方案四 通过SqlSessionFactory指定的数据源来操作指定目录的xml文件
使用此方法则不会与上面所述的类有任何关系,本方法会重新定义类
本方法也是一种推荐的方法,适用于对指定数据库的操作,也就是适合读写返利。不会存在代码冗余和存在硬编码
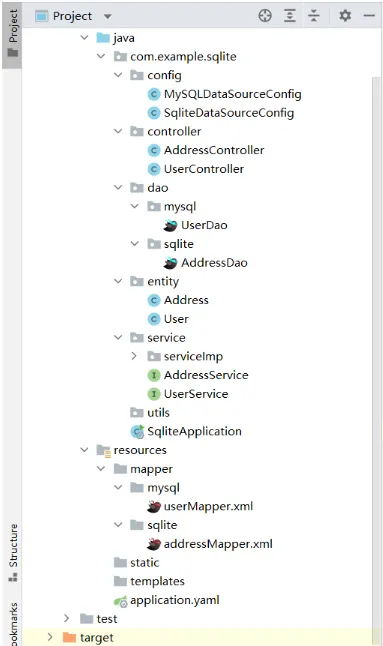
项目结构调整
对所需要操作的数据库的Mapper层和dao层分别建立一个文件夹。
配置YAML文件
java
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
mysql-datasource:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
sqlite-datasource:
jdbc-url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bookstore?useSSL=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
druid:
initial-size: 5
min-idle: 1
max-active: 20
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath:/mapper/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.example.sqlite.entity针对Mapper层通过SqlSessionFactory指定数据源来操作
@MapperScan注解中的basePackages指向的是指定的Dao层。
@MapperScan注解中sqlSessionFactoryRef 用来指定使用某个SqlSessionFactory来操作数据源。
bean.setMapperLocations(
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver()
.getResources("classpath*:mapper/sqlite/*.xml")); 指向的是操作执行数据库的Mapper层。
如果使用SQLite数据库,那么就必须在项目中内嵌SQLite数据库,这个一个轻量级的数据库,不同于Mysql,SQLite不需要服务器,SQLite适合使用于移动APP开发。
像微信,用户的聊天记录就是使用这个数据库进行存储。SQLite也可以使用在Web端,只是不太方便。
创建Mysql数据源
java
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.example.sqlite.dao.mysql", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "MySQLSqlSessionFactory")
public class MySQLDataSourceConfig {
@Bean(name = "MySQLDataSource")
@Primary
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.mysql-datasource")
public DataSource getDateSource1() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "MySQLSqlSessionFactory")
@Primary
public SqlSessionFactory test1SqlSessionFactory(
@Qualifier("MySQLDataSource") DataSource datasource) throws Exception {
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean ();
bean.setDataSource(datasource);
bean.setMapperLocations(// 设置mybatis的xml所在位置
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapper/mysql/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean("MySQLSqlSessionTemplate")
@Primary
public SqlSessionTemplate test1SqlSessionTemplate(
@Qualifier("MySQLSqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionFactory);
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("MySQLDataSource")DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}创建Sqlite数据源
java
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.example.sqlite.dao.sqlite", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "SqliteSqlSessionFactory")
public class SqliteDataSourceConfig {
@Bean(name = "SqliteDateSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.sqlite-datasource")
public DataSource getDateSource1() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "SqliteSqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory test1SqlSessionFactory(
@Qualifier("SqliteDateSource") DataSource datasource) throws Exception {
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(datasource);
bean.setMapperLocations(
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapper/sqlite/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean("SqliteSqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate test1SqlSessionTemplate(
@Qualifier("SqliteSqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionFactory);
}
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("SqliteDateSource")DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}测试使用
java
// 访问第一个数据库
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping(value = "/user_list")
public List<User> showUserList(){
List<User> list = userService.list();
return list;
}
}
java
// 访问第二个数据库
@RestController
public class AddressController {
@Resource
private AddressService addressService;
@GetMapping(value = "/address_list")
public List<Address> getAddressList(){
List<Address> list = addressService.list();
return list;
}
}使用此种方法不会存在任何代码的冗余以及硬编码的存在,但是需要分层明确。
唯一的不足就是添加一个数据源就需要重新写一个类,而这个类中的代码大部分又是相同的。
总结
- 实现DataSource接口这种写法是不推荐的。
- 推荐使用Spring Boot + 自定义注解的方式与SqlSessionFactory方式。
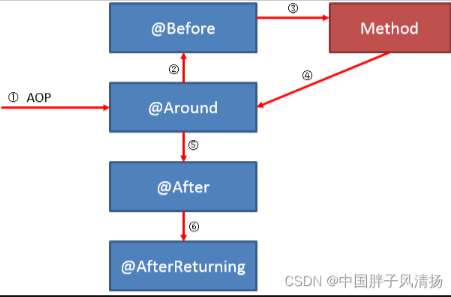
另外,Spring AOP中各种通知的执行顺序如下图所示:
注意事项
1、跨数据源联查的时候需要注意事务管理
2、分布式事务需要考虑支持,保证数据一致性