
🎬 那我掉的头发算什么 :个人主页
🔥 个人专栏 : 《javaSE》《数据结构》《数据库》《javaEE》
⛺️待到苦尽甘来日

文章目录
Mybatis-plus介绍
MyBatis-Plus (简称 MP) 是一个 MyBatis 的增强工具,在 MyBatis 的基础上只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生。
特性:
润物无声:只做增强不做改变 ,引入它不会对现有工程产生影响,如丝般顺滑。
效率至上:只需简单配置 ,即可快速进行单表 CRUD 操作,从而节省大量时间。
丰富功能:代码生成、自动分页、逻辑删除、自动填充、拦截器等功能一应俱全 。
广泛认可:连续 5 年获得开源中国年度最佳开源项目殊荣,Github 累计 16K Star。
(任何能使用 MyBatis 进行增删改查,并且支持标准 SQL 的数据库应该都在 MyBatis-Plus 的支持范围内)
官网地址:
https://baomidou.com/introduce/

快速上手
准备工作
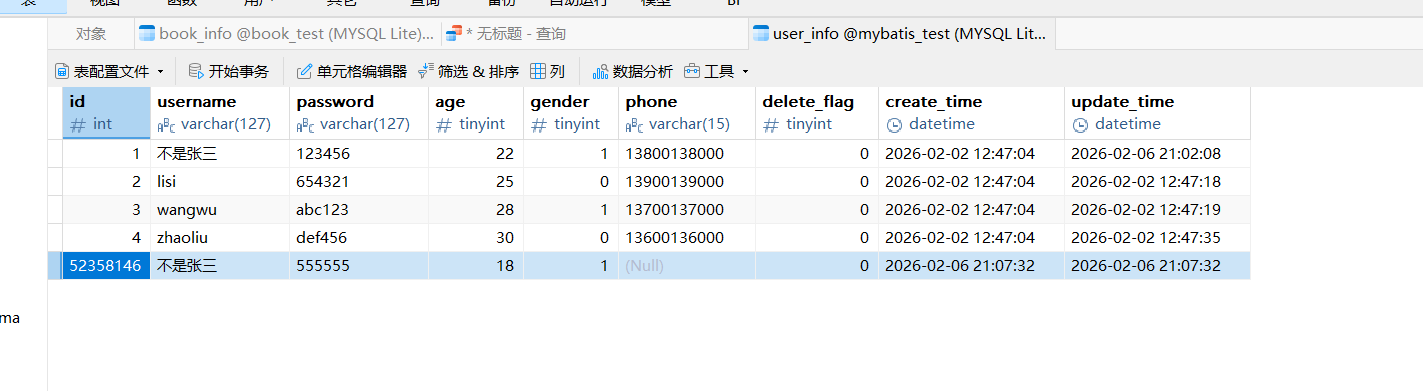
创建数据库
创建一个类似的user_info数据表
项目准备
1.创建springBoot项目
2.添加依赖
java
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-spring-boot4-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.15</version>
</dependency>springBoot版本4.0以后就需要使用这个依赖了。
3.配置yml文件
java
spring:
application:
name: mybatis-plus-demo
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/mybatis_test?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: *****
password: *****
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis-plus:
configuration: # ???? MyBatis??
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
mapper-locations: "classpath*:/mapper/**.xml" # Mapper.xml创建实体类
java
package com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.model;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@TableName("user_info")
public class UserInfo {
@TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
private Integer gender;
private String phone;
@TableField("delete_flag")
private Integer deleteFlag;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}编写Mapper接口
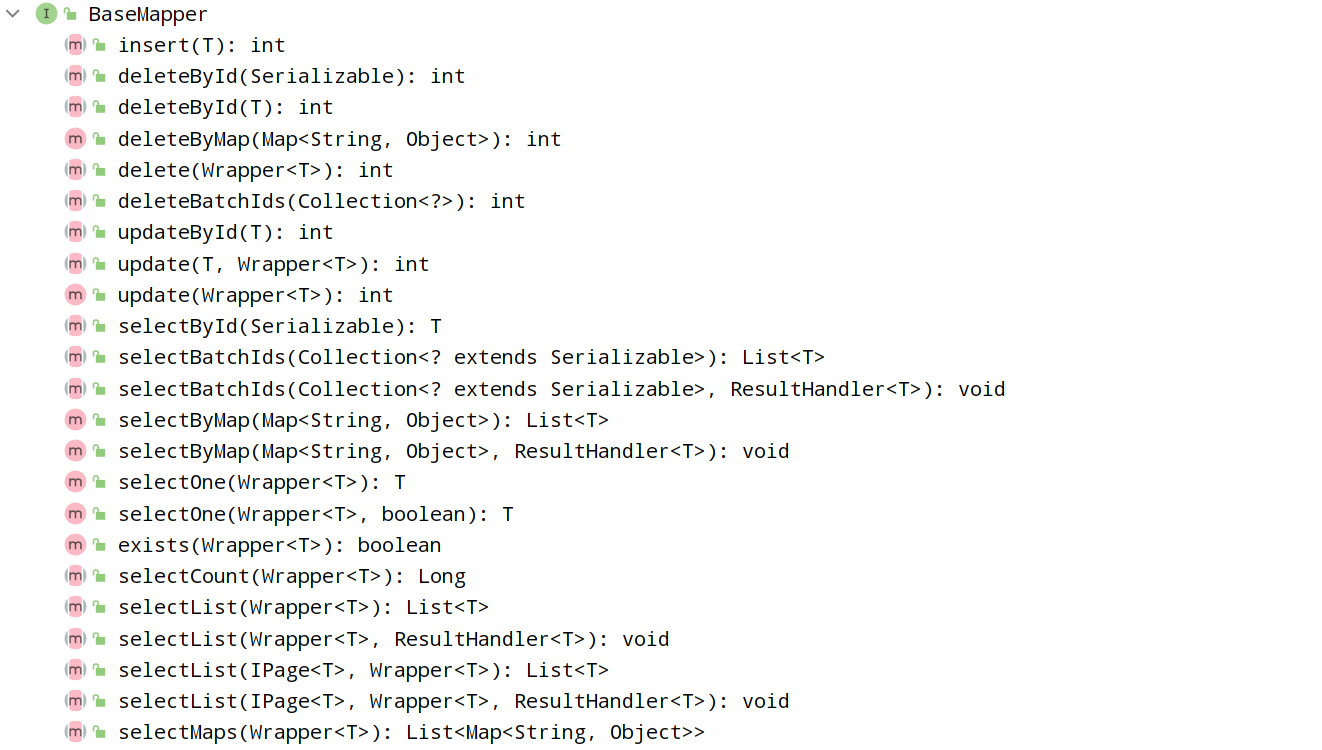
MybatisPlus 提供了一个基础的 BaseMapper 接口,已经实现了单表的 CRUD,我们自定义的 Mapper 只需要继承这个 BaseMapper,就无需自己实现单表 CRUD 了。
java
package com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.model.UserInfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
@Mapper
public interface UserInfoMapper extends BaseMapper<UserInfo> {
}CRUD单元测试
基本的功能都定义好了,直接调用就可以:
java
package com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.mapper;
import com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.model.UserInfo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@SpringBootTest
class UserInfoMapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserInfoMapper userInfoMapper;
@Test
void selectAll(){
userInfoMapper.selectById(1);
}
@Test
void deleteById(){
userInfoMapper.deleteById(20);
}
@Test
void updateById(){
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setId(1);
userInfo.setUsername("不是张三");
userInfoMapper.updateById(userInfo);
}
@Test
void insert(){
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setUsername("不是张三");
userInfo.setAge(18);
userInfo.setGender(1);
userInfo.setPassword("555555");
userInfoMapper.insert(userInfo);
}
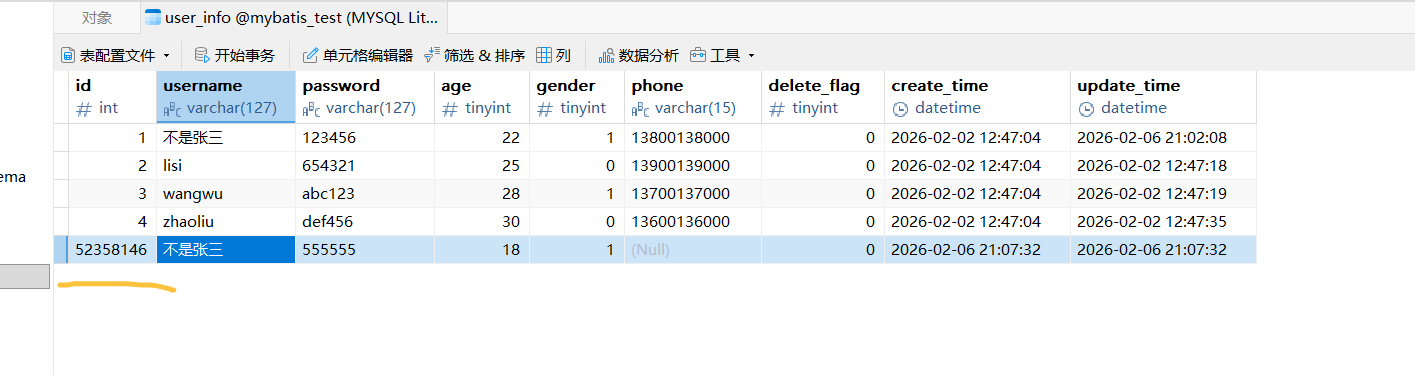
}运行结果没啥问题,观察后端数据库也都成功了。
Mybatis-plus复杂操作
常见注解
在上面的程序中,MyBatis 是如何知道,我们要操作的是哪张表,表里有哪些字段呢?
UserInfoMapper 在继承 BaseMapper 时,指定了一个泛型,这个 UserInfo 就是与数据库表相对应的实体类。MyBatis-Plus 会根据这个实体类来推断表的信息。
默认情况下:
表名:实体类的驼峰表示法转换成蛇形表示法(下划线分割),作为表名。比如 UserInfo -> user_info
字段:根据实体类的属性名 转换为蛇形表示法作为字段名。比如 deleteFlag -> delete_flag
主键:默认为ID
那如果实体类和数据库不是按照上面的原则定义的呢??这时候就需要一些注解来帮忙了:
@TableName、@TableField、@Table
java
package com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.model;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@TableName("user_info")
public class Userinfo {
@Table("id")
private Integer userId;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
private Integer gender;
private String phone;
@TableField("delete_flag")
private Integer deleteflag;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}如果咱们在定义类和类的属性时命名不规范,我们可以使用注解显示表明我们某一个属性或者类对应的是数据库中的哪张表或者哪个属性。
@TableId
我们上面插入一个新数据时,新数据的ID是随机的。但是我们定义数据库时明明设置了自增,要想恢复这个功能可以加上这个注解:
java
package com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.model;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@TableName("user_info")
public class UserInfo {
@TableId(value = "id",type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age;
private Integer gender;
private String phone;
@TableField("delete_flag")
private Integer deleteFlag;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}然后再在设计表中把下一个id改成6就可以了。
条件构造器
入门程序里的使用,都是简单的 CRUD,在实际的应用场景中,我们还需要使用更复杂的操作,MyBatis-Plus 也给我们提供了相应的支持。
MyBatis-Plus 提供了一套强大的条件构造器 (Wrapper),用于构建复杂的数据库查询条件。Wrapper 类允许开发者以链式调用的方式构造查询条件,无需编写繁琐的 SQL 语句,从而提高开发效率并减少 SQL 注入的风险。
以下是主要的 Wrapper 类及其功能:
・AbstractWrapper:这是一个抽象基类,提供了所有 Wrapper 类共有的方法和属性。
・QueryWrapper:用于构造查询条件,在 AbstractWrapper 的基础上拓展了一个 select 方法,允许指定查询字段。
・UpdateWrapper: 用于构造更新条件,可以在更新数据时指定条件。
・LambdaQueryWrapper:基于 Lambda 表达式的查询条件构造器,它通过 Lambda 表达式来引用实体类的属性,从而避免了硬编码字段名。
・LambdaUpdateWrapper: 基于 Lambda 表达式的更新条件构造器,它允许你使用 Lambda 表达式来指定更新字段和条件,同样避免了硬编码字段名的问题。
1.QueryMapper
QueryWrapper并不只用于查询语句, 无论是修改, 删除, 查询, 都可以使用QueryWrapper来构建查询条件.
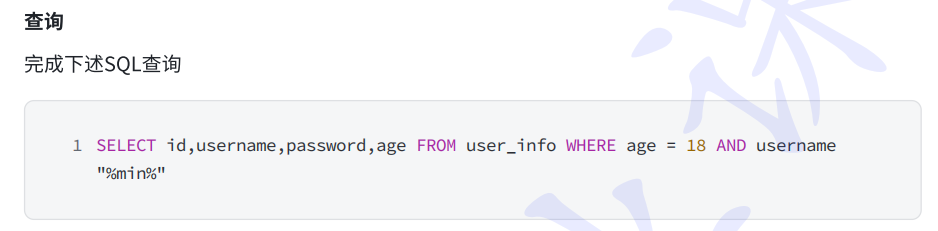
java
@Test
void selectByCondition() {
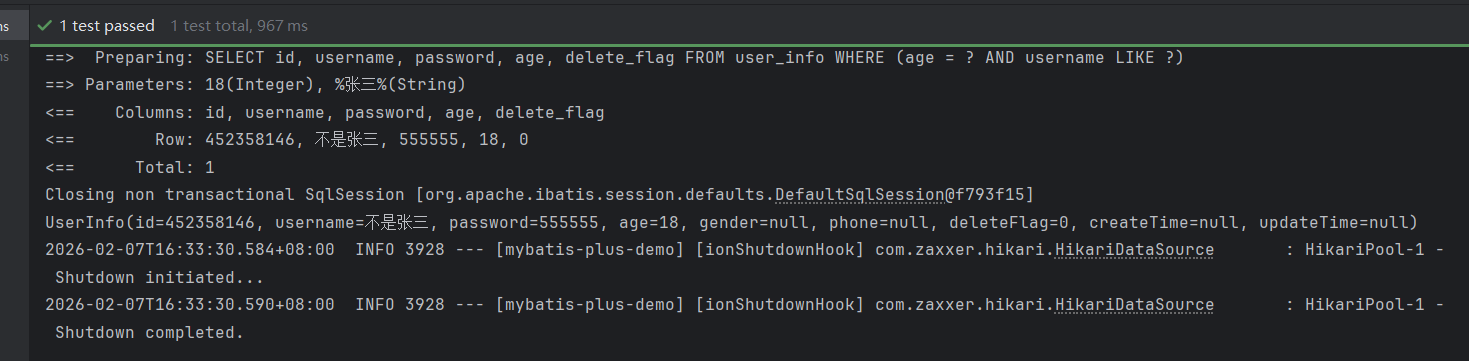
QueryWrapper<UserInfo> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.select("id, username, password, age, delete_flag")
.eq("age", 18)
.like("username", "张三");
List<UserInfo> userInfos = userInfoMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
userInfos.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
}
注意:默认情况下 Mybatis-Plus 会根据 @TableField 生成别名,当指定了 QueryWrapper 的 select 属性后就仅仅是属性值而没有了别名,查询出来的结果会对应不上。
解决办法:
1.自己写自定义 SQL
2.实体类名和字段名保持一致
3.不指定 QueryWrapper 的 select 字段
4.使用 LambdaQueryWrapper 实现
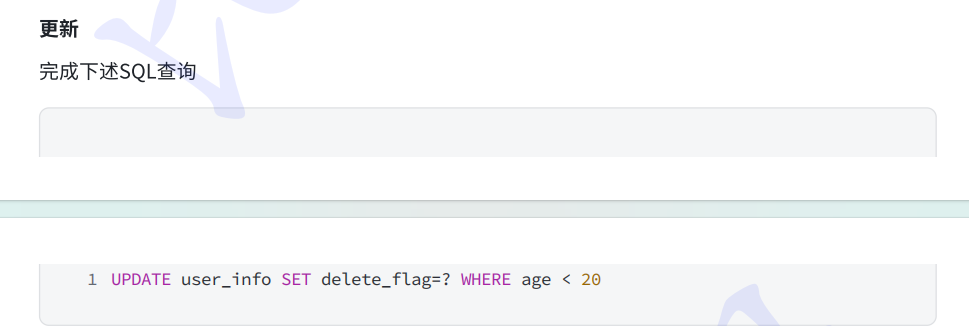
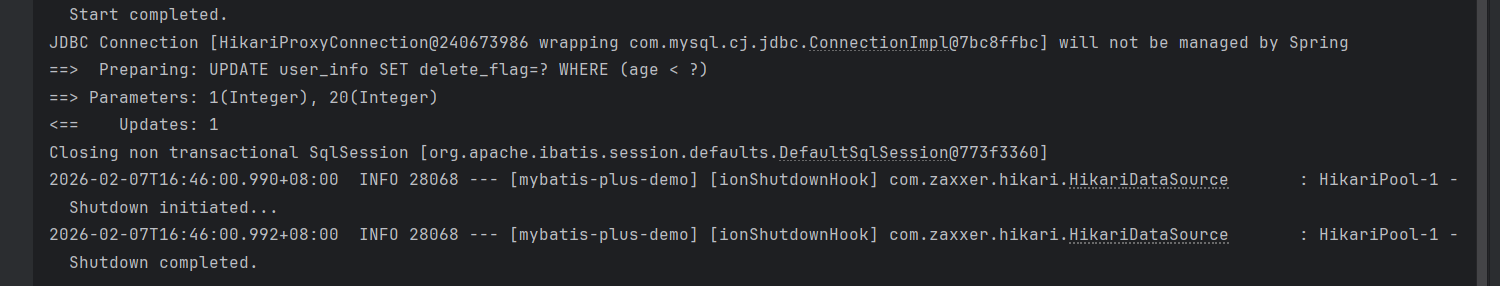
java
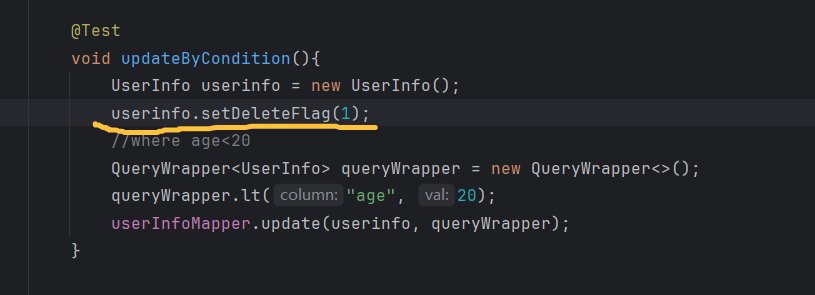
@Test
void updateByCondition(){
UserInfo userinfo = new UserInfo();
userinfo.setDeleteFlag(1);
//where age<20
QueryWrapper<UserInfo> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.lt("age", 20);
userInfoMapper.update(userinfo, queryWrapper);
}
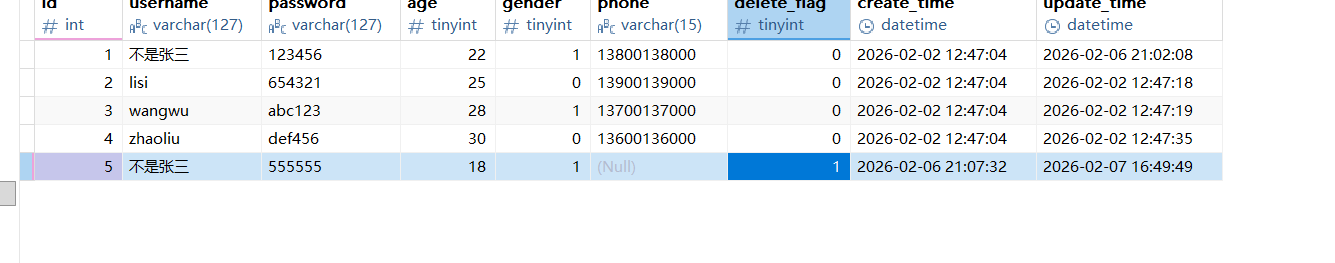

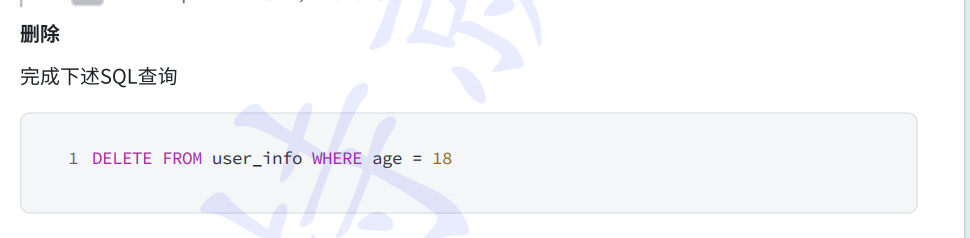
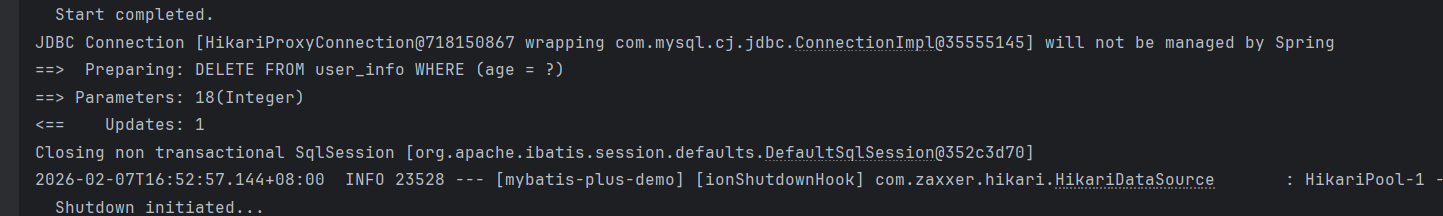
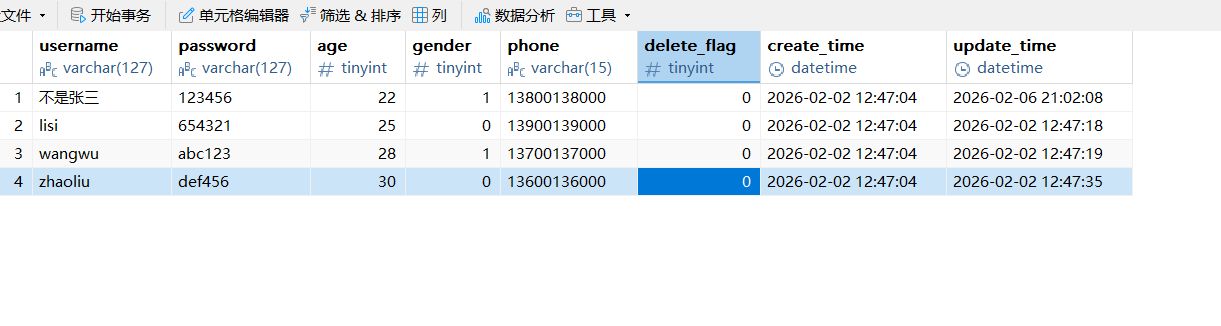
java
@Test
void deleteByCondition(){
QueryWrapper<UserInfo> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("age",18);
userInfoMapper.delete(queryWrapper);
}
2.UpdateWrapper
咱们前面的更新操作,对于set属性设置的值,需要建立一个新的对象来表示:
在不创建实体类的情况下,我们可以使用UpdateWrapper来直接设置更新字段和条件。
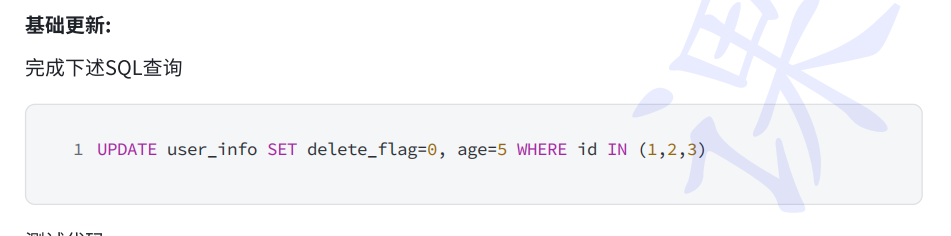
java
@Test
void updateByCondition2(){
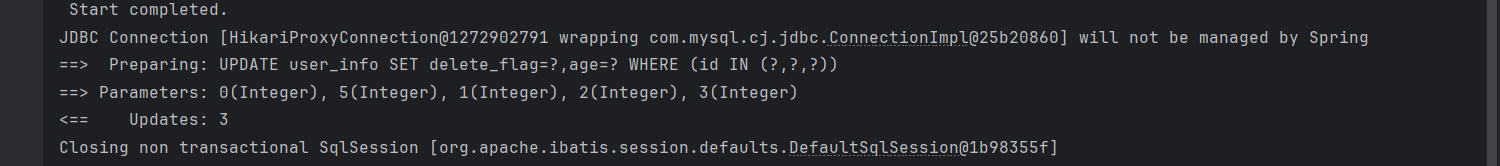
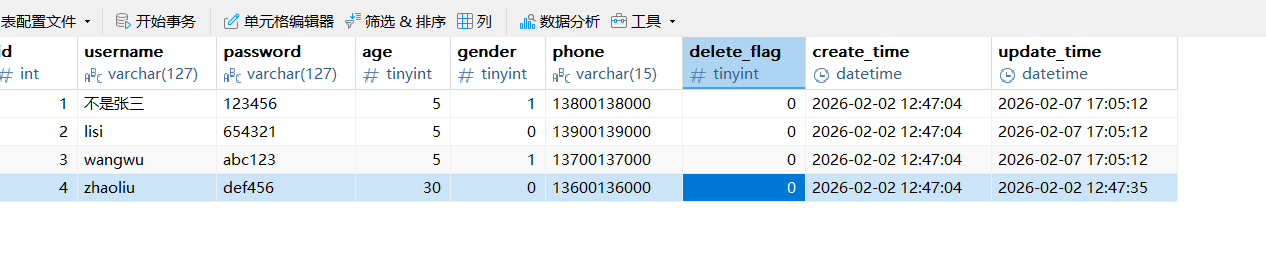
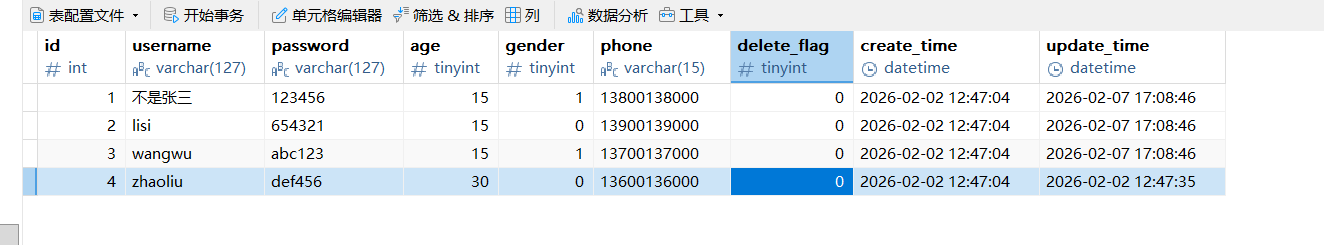
UpdateWrapper<UserInfo> updateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
updateWrapper.set("delete_flag",0)
.set("age",5)
.in("id",List.of(1,2,3));
userInfoMapper.update(updateWrapper);
}
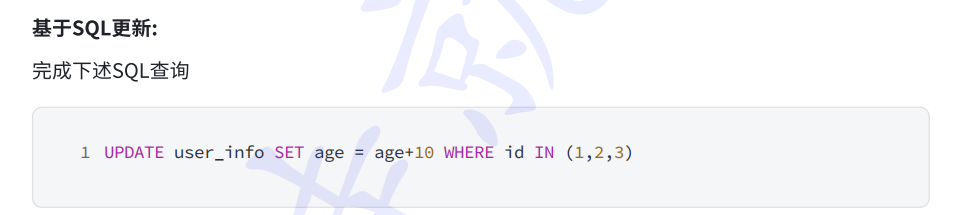
java
@Test
void updateByCondition3(){
UpdateWrapper<UserInfo> updateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
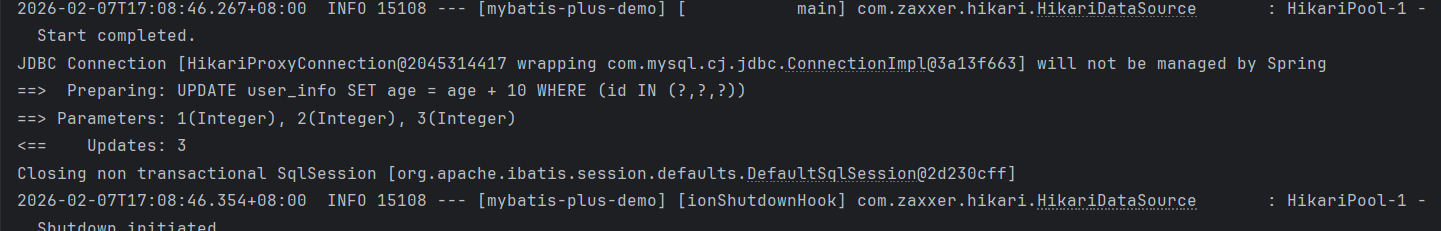
updateWrapper.setSql("age = age + 10")
.in("id",List.of(1,2,3));
userInfoMapper.update(updateWrapper);
}
3.LambdaQueryWrapper
QueryWrapper 和 UpdateWrapper 存在一个问题,就是需要写死字段名,如果字段名发生变更,可能会因为测试不到位酿成事故。
MyBatis-Plus 给我们提供了一种基于 Lambda 表达式的条件构造器,它通过 Lambda 表达式来引用实体类的属性,从而避免了硬编码字段名,也提高了代码的可读性和可维护性。
・LambdaQueryWrapper
・LambdaUpdateWrapper
分别对应上述的 QueryWrapper 和 UpdateWrapper
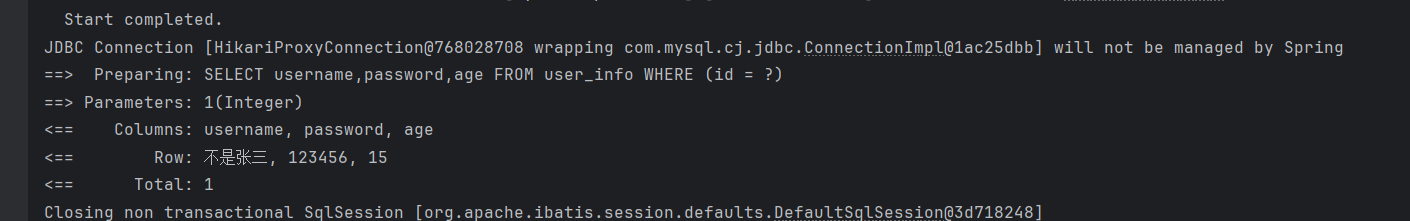
java
@Test
void lambdaQueryWrapper(){
QueryWrapper<UserInfo> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.lambda()
.select(UserInfo::getUsername,UserInfo::getPassword,UserInfo::getAge)
.eq(UserInfo::getId,1);
userInfoMapper.selectList(queryWrapper).forEach(System.out::println);
}4.LambdaUpdateWrapper
用法与LambdaQueryWrapper相似
java
@Test
void lambdaUpdateWrapper(){
UpdateWrapper<UserInfo> updateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
updateWrapper.lambda()
.set(UserInfo::getDeleteFlag,0)
.set(UserInfo::getAge,5)
.in(UserInfo::getId,List.of(1,2,3));
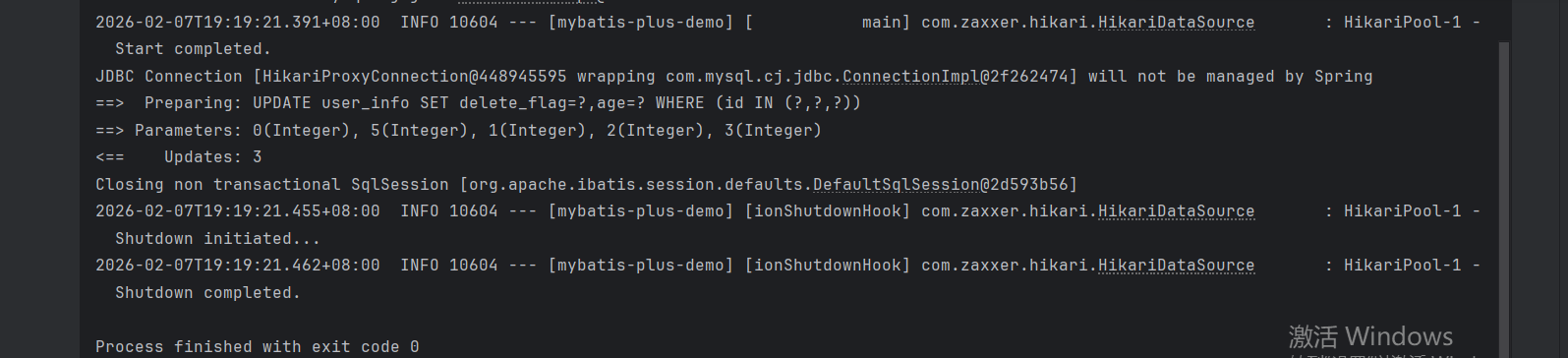
userInfoMapper.update(updateWrapper);
}
自定义SQL
在实际的开发中,MyBatis-Plus 提供的操作不能满足我们的实际需求,MyBatis-Plus 也提供了自定义 SQL 的功能,我们可以利用 Wrapper 构造查询条件,再结合 Mapper 编写 SQL。
java
package com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.Wrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.Constants;
import com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.model.UserInfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface UserInfoMapper extends BaseMapper<UserInfo> {
@Select("select id,username,password,age from user_info ${ew.customSqlSegment}")
List<UserInfo> queryUserByCustom(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<UserInfo> wrapper);
}
java
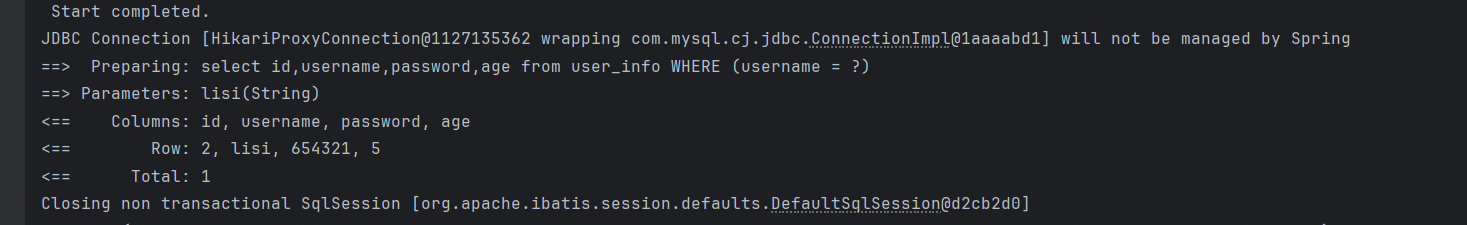
@Test
void queryUserByCustom() {
QueryWrapper<UserInfo> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("username","lisi");
userInfoMapper.queryUserByCustom(queryWrapper).forEach(System.out::println);
}
注意事项:
・参数命名:在自定义 SQL 时,传递 Wrapper 对象作为参数时,参数名必须为 ew,或者使用注解 @Param (Constants.WRAPPER) 明确指定参数为 Wrapper 对象。
・使用 {ew.customSqlSegment}:在 SQL 语句中,使用 {ew.customSqlSegment} 来引用 Wrapper 对象生成的 SQL 片段。
・不支持基于 entity 的 where 语句:自定义 SQL 时,Wrapper 对象不会基于实体类自动生成 where 子句,你需要手动编写完整的 SQL 语句。
MyBatis-Plus 在 MyBatis 的基础上只做增强不做改变, 所以也支持XML的实现方式
java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.mapper.UserInfoMapper">
<select id="queryUserByCustom2" resultType="com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.model.UserInfo">
select id,username,password,age from user_info ${ew.customSqlSegment}
</select>
</mapper>
java
package com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.Wrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.Constants;
import com.hbu.mybatisplusdemo.model.UserInfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface UserInfoMapper extends BaseMapper<UserInfo> {
@Select("select id,username,password,age from user_info ${ew.customSqlSegment}")
List<UserInfo> queryUserByCustom(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<UserInfo> wrapper);
List<UserInfo> queryUserByCustom2(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<UserInfo> wrapper);
}
java
@Test
void queryUserByCustom2() {
QueryWrapper<UserInfo> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq("username","lisi");
userInfoMapper.queryUserByCustom2(queryWrapper).forEach(System.out::println);
}当然传递其他参数也是原来一样不变:
java
@Update("update user_info set age = age + @{addAge} ${ew.customSqlSegment}" )
Integer updateUserByCustom(Integer addAge,@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<UserInfo> wrapper);
java
@Test
void updateUserByCustom() {
QueryWrapper<UserInfo> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<UserInfo>()
.in("id",List.of(1,2,3));
userInfoMapper.updateUserByCustom(10, queryWrapper);
}以上就是本篇博客全部内容!