Flutter for OpenHarmony 可视化教学:A* 寻路算法的交互式演示
在人工智能、游戏开发和机器人导航等领域,路径规划(Pathfinding) 是一项基础而关键的技术。其中,A*(A-Star)算法因其高效性与最优性,成为最广为人知的启发式搜索算法之一。然而,其背后的"开启列表"、"关闭列表"、"f = g + h"等概念对初学者而言仍显抽象。
本文将深入解析一段完整的 Flutter 应用代码 ,该应用通过直观的网格界面、动态的颜色反馈和流畅的动画效果,将 A* 算法的执行过程转化为一场沉浸式的可视化学习体验。你将看到:如何用 Dart 实现经典的 A* 逻辑,如何利用 GridView 构建交互式地图,以及如何设计一个既能教学又能娱乐的寻路模拟器。
🌐 加入社区 欢迎加入 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区 ,获取最新资源与技术支持: 👉 开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区
完整效果
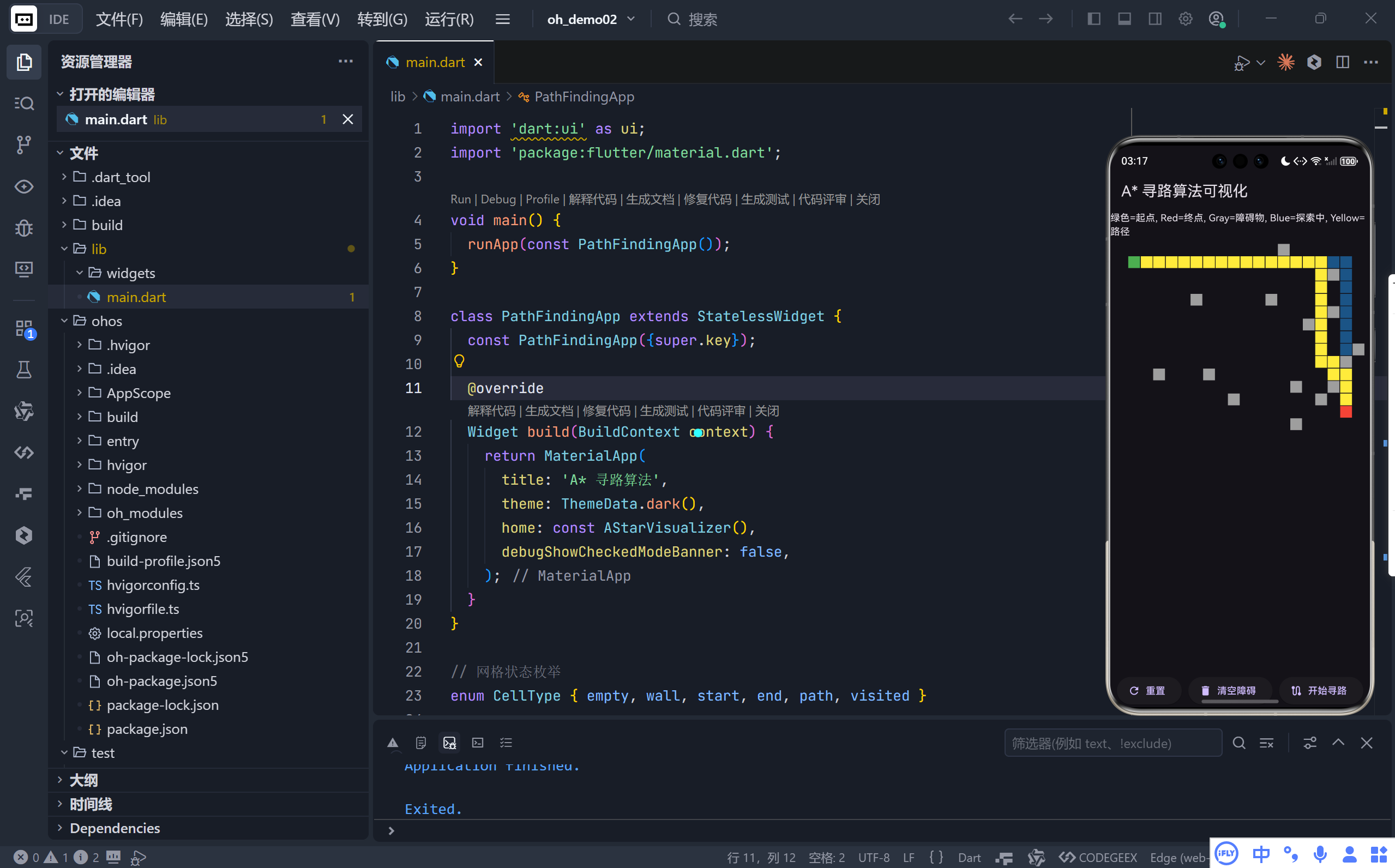
一、应用概览:交互式寻路沙盒
该应用提供了一个 15×20 的网格世界,用户可以:
- 点击任意空白格子:添加或移除灰色障碍物(墙壁);
- 点击"开始寻路":启动 A* 算法,从绿色起点到红色终点寻找最短路径;
- 实时观察:蓝色区域表示算法正在探索的节点,黄色路径即为最终结果;
- 一键重置:恢复初始状态,或仅清除障碍物进行新实验。
💡 核心目标 :让抽象的图搜索算法变得可见、可操作、可理解。
二、A* 算法原理简述
A* 是一种最佳优先搜索 算法,它通过评估函数 f(n) = g(n) + h(n) 来决定下一个要探索的节点:
- g(n) :从起点到当前节点
n的实际代价(本例中为步数); - h(n) :从节点
n到终点的启发式估计代价(本例使用曼哈顿距离); - f(n):总预估代价,值越小,优先级越高。
算法维护两个关键集合:
- 开启列表(Open List):待检查的候选节点;
- 关闭列表(Closed List):已处理完毕的节点。
通过不断从开启列表中选择 f 值最小的节点进行扩展,并更新邻居的代价,最终找到一条从起点到终点的最短路径(若存在)。
三、代码实现详解
1. 数据结构设计
▶ 网格单元类型
dart
enum CellType { empty, wall, start, end, path, visited }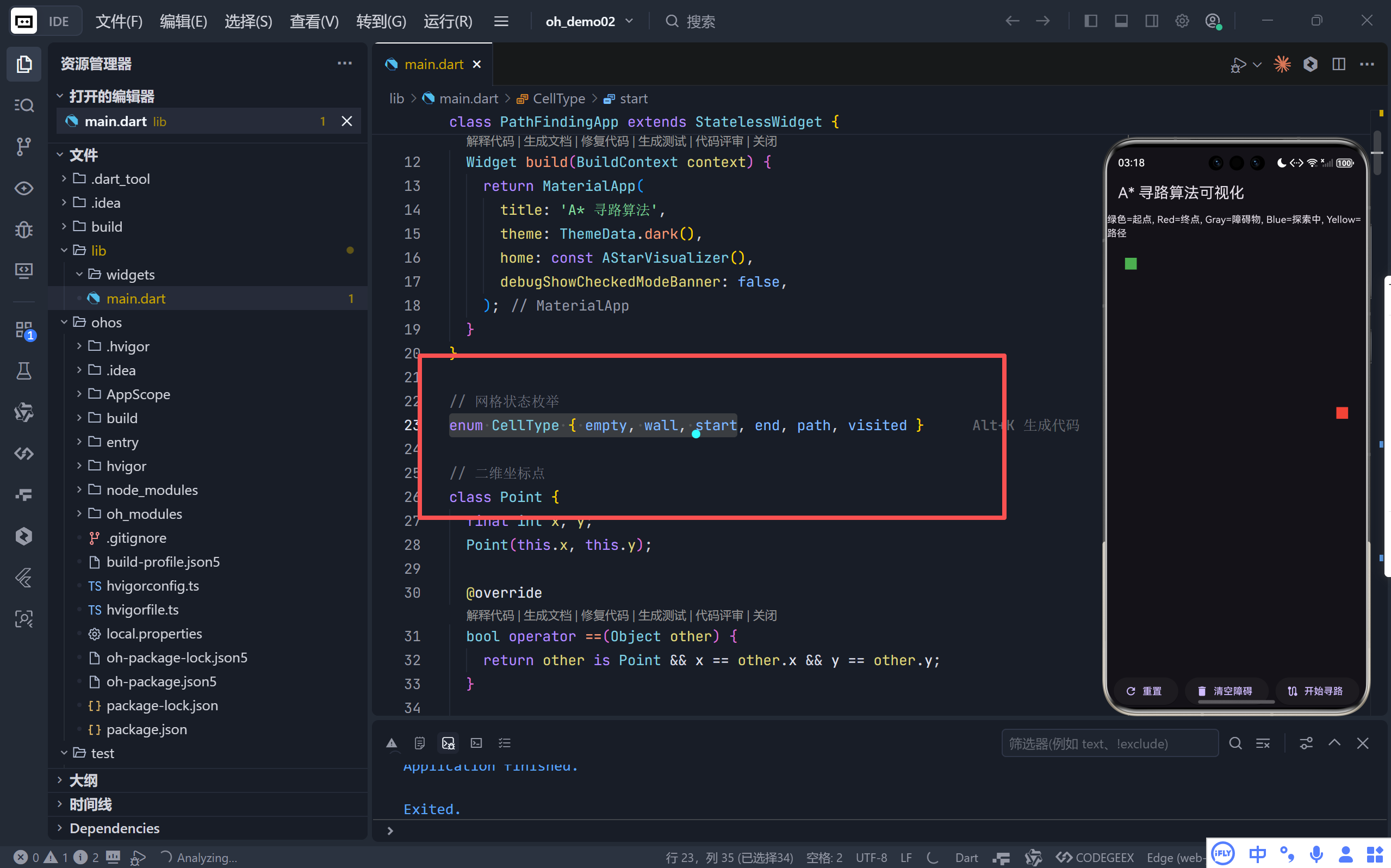
- 清晰定义六种状态,便于 UI 渲染与逻辑判断。
▶ 二维坐标点
dart
class Point {
final int x, y;
// 重写 == 和 hashCode,使其可作为 Map 的 key
}
- 支持集合操作(如
Set<Point>)和映射(如Map<Point, Point>),是实现cameFrom路径回溯的关键。
2. A* 核心逻辑 (_runAStar)
▶ 初始化
dart
List<Point> openList = [start];
Set<Point> closedList = {};
Map<Point, Point> cameFrom = {}; // 记录父节点
Map<Point, double> gScore = {start: 0};
Map<Point, double> fScore = {start: _heuristic(start, end)};▶ 主循环
- 选点 :从
openList中选出fScore最小的节点current;- 终止条件 :若
current == end,调用_reconstructPath回溯路径;- 标记访问 :将
current加入closedList,并在 UI 上标记为蓝色(CellType.visited);- 探索邻居 :遍历上下左右四个方向;
- 跳过越界、墙壁或已在
closedList中的点;- 计算临时
gScore,若更优则更新gScore、fScore和cameFrom,并将邻居加入openList。
▶ 启发式函数(曼哈顿距离)
dart
double _heuristic(Point a, Point b) {
return (a.x - b.x).abs() + (a.y - b.y).abs();
}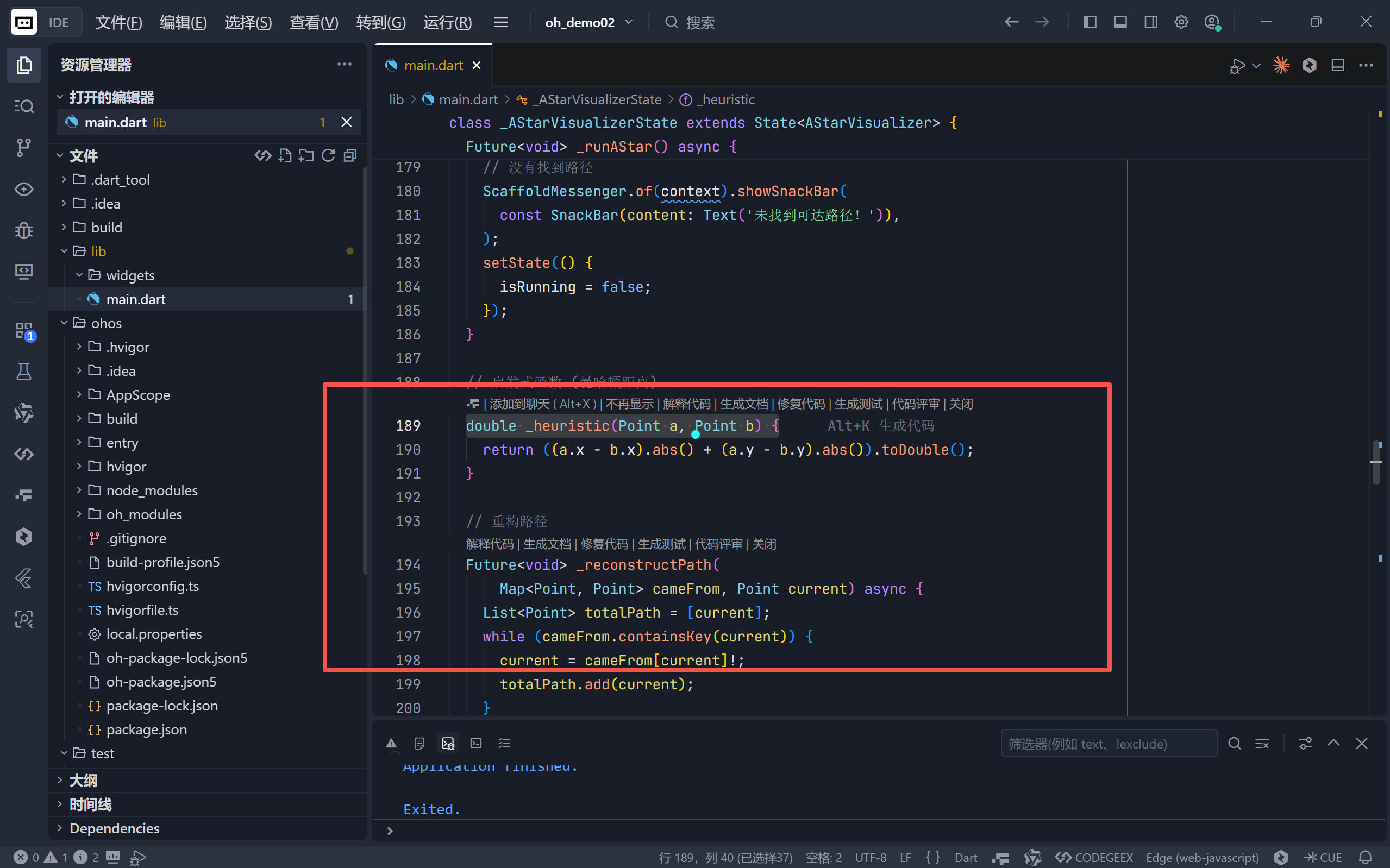
- 适用于只能上下左右移动的网格地图,保证可采纳性(Admissible),即不会高估实际代价,从而确保找到最优解。
▶ 路径重构
dart
Future<void> _reconstructPath(Map<Point, Point> cameFrom, Point current) async {
List<Point> totalPath = [];
while (cameFrom.containsKey(current)) {
current = cameFrom[current]!;
totalPath.add(current);
}
// 从起点到终点反向遍历,再反转
totalPath = totalPath.reversed.toList();
// 逐个高亮为黄色
}3. 异步与动画
await Future.delayed(...):在每次更新网格状态后暂停片刻,形成"探索"和"绘制路径"的动画效果;setState(() {}):触发 UI 重绘,实时反映算法进展;isRunning标志:防止用户在运行时误操作,保证状态一致性。
四、UI/UX 设计亮点
1. 直观的色彩编码
| 颜色 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 🟢 绿色 | 起点 (start) |
| 🔴 红色 | 终点 (end) |
| ⚪ 透明/白色 | 空地 (empty) |
| ⚫ 灰色 | 障碍物 (wall) |
| 🔵 蓝色(半透) | 已探索节点 (visited) |
| 🟡 黄色 | 最终路径 (path) |
这种设计让用户一眼就能分辨算法的当前状态。
2. 交互式网格 (GridView.builder)
- 每个格子都是一个
GestureDetector,点击即可切换空地/墙壁; - 使用
SliverGridDelegateWithFixedCrossAxisCount精确控制列数,确保网格比例协调; mainAxisSpacing和crossAxisSpacing添加 1px 间隙,提升视觉清晰度。
3. 控制面板
三个功能按钮布局合理:
- 重置:恢复初始布局(含默认起点终点);
- 清空障碍:保留起点终点,仅移除墙壁,方便快速测试不同障碍配置;
- 开始寻路:核心操作,运行时显示"运行中..."并禁用其他按钮。
五、教育价值与应用场景
教学场景
- 算法课演示:动态展示 A* 如何"聪明地"避开障碍,优先向终点方向搜索;
- 启发式函数对比 :可轻松扩展为支持欧几里得距离、对角线移动等,观察不同
h(n)对搜索效率的影响; - 失败案例分析:当终点被完全包围时,应用会弹出提示"未找到可达路径!",帮助学生理解算法的局限性。
开发参考
- 游戏 AI:可作为 NPC 自动寻路的基础模块;
- 地图应用:室内导航、仓库机器人路径规划的简化模型;
- 性能基准:通过调整网格大小,测试算法在不同规模问题下的表现。
六、总结
这段 Flutter 代码不仅是一个功能完整的 A* 寻路演示器,更是一个优秀的计算思维教学工具。它将复杂的图搜索过程分解为可视化的步骤,通过颜色、动画和即时反馈,极大地降低了学习门槛。
完整代码
bash
import 'dart:ui' as ui;
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(const PathFindingApp());
}
class PathFindingApp extends StatelessWidget {
const PathFindingApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'A* 寻路算法',
theme: ThemeData.dark(),
home: const AStarVisualizer(),
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
);
}
}
// 网格状态枚举
enum CellType { empty, wall, start, end, path, visited }
// 二维坐标点
class Point {
final int x, y;
Point(this.x, this.y);
@override
bool operator ==(Object other) {
return other is Point && x == other.x && y == other.y;
}
@override
int get hashCode => Object.hash(x, y);
}
class AStarVisualizer extends StatefulWidget {
const AStarVisualizer({super.key});
@override
State<AStarVisualizer> createState() => _AStarVisualizerState();
}
class _AStarVisualizerState extends State<AStarVisualizer> {
static const int rows = 15;
static const int cols = 20;
late List<List<CellType>> grid;
Point? start;
Point? end;
bool isRunning = false;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_resetGrid();
}
void _resetGrid() {
grid = List.generate(rows, (i) {
return List.generate(cols, (j) {
return CellType.empty;
});
});
start = Point(1, 1);
end = Point(rows - 2, cols - 2);
grid[start!.x][start!.y] = CellType.start;
grid[end!.x][end!.y] = CellType.end;
}
void _clearWalls() {
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == CellType.wall) {
grid[i][j] = CellType.empty;
}
}
}
}
// A* 算法核心
Future<void> _runAStar() async {
if (start == null || end == null) return;
setState(() {
isRunning = true;
});
// 开启列表:待检查的节点
List<Point> openList = [Point(start!.x, start!.y)];
// 关闭列表:已检查的节点
Set<Point> closedList = {};
// 记录路径 (父节点映射)
Map<Point, Point> cameFrom = {};
// gScore: 从起点到该节点的实际代价
Map<Point, double> gScore = {};
gScore[start!] = 0;
// fScore: 从起点经由该节点到终点的预估总代价
Map<Point, double> fScore = {};
fScore[start!] = _heuristic(start!, end!);
while (openList.isNotEmpty) {
// 1. 找到fScore最小的节点
Point current = openList.reduce((a, b) {
return (fScore[a] ?? double.infinity) < (fScore[b] ?? double.infinity)
? a
: b;
});
// 2. 如果到达终点,重构路径
if (current == end) {
await _reconstructPath(cameFrom, current);
setState(() {
isRunning = false;
});
return;
}
// 3. 将当前节点移出开启列表,加入关闭列表
openList.remove(current);
closedList.add(current);
// 可视化:标记为已访问
if (grid[current.x][current.y] != CellType.start &&
grid[current.x][current.y] != CellType.end) {
grid[current.x][current.y] = CellType.visited;
setState(() {});
await Future.delayed(const Duration(milliseconds: 50));
}
// 4. 检查邻居 (上下左右)
List<Point> neighbors = [
Point(current.x - 1, current.y),
Point(current.x + 1, current.y),
Point(current.x, current.y - 1),
Point(current.x, current.y + 1),
];
for (Point neighbor in neighbors) {
int x = neighbor.x;
int y = neighbor.y;
// 检查是否越界或为墙壁
if (x < 0 ||
x >= rows ||
y < 0 ||
y >= cols ||
grid[x][y] == CellType.wall) {
continue;
}
// 如果已经在关闭列表,跳过
if (closedList.contains(neighbor)) {
continue;
}
// 计算临时的gScore (从起点到邻居的代价)
double tentativeGScore = (gScore[current] ?? double.infinity) + 1;
// 如果该邻居不在开启列表中,或者找到了更短的路径
if (!openList.contains(neighbor) ||
tentativeGScore < (gScore[neighbor] ?? double.infinity)) {
// 记录路径
cameFrom[neighbor] = current;
gScore[neighbor] = tentativeGScore;
fScore[neighbor] = tentativeGScore + _heuristic(neighbor, end!);
if (!openList.contains(neighbor)) {
openList.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
// 没有找到路径
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(content: Text('未找到可达路径!')),
);
setState(() {
isRunning = false;
});
}
// 启发式函数 (曼哈顿距离)
double _heuristic(Point a, Point b) {
return ((a.x - b.x).abs() + (a.y - b.y).abs()).toDouble();
}
// 重构路径
Future<void> _reconstructPath(
Map<Point, Point> cameFrom, Point current) async {
List<Point> totalPath = [current];
while (cameFrom.containsKey(current)) {
current = cameFrom[current]!;
totalPath.add(current);
}
totalPath = totalPath.reversed.toList();
// 高亮显示路径
for (Point p in totalPath) {
if (p != start && p != end) {
grid[p.x][p.y] = CellType.path;
setState(() {});
await Future.delayed(const Duration(milliseconds: 100));
}
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('A* 寻路算法可视化'),
),
body: Column(
children: [
const Text('绿色=起点, Red=终点, Gray=障碍物, Blue=探索中, Yellow=路径'),
Expanded(
child: GridView.builder(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8),
gridDelegate: SliverGridDelegateWithFixedCrossAxisCount(
crossAxisCount: cols,
mainAxisSpacing: 1,
crossAxisSpacing: 1,
),
itemCount: rows * cols,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
int row = index ~/ cols;
int col = index % cols;
bool isStart = Point(row, col) == start;
bool isEnd = Point(row, col) == end;
Color color = Colors.transparent;
if (grid[row][col] == CellType.wall) {
color = Colors.grey;
} else if (grid[row][col] == CellType.visited) {
color = Colors.blue.withOpacity(0.5);
} else if (grid[row][col] == CellType.path) {
color = Colors.yellow;
} else if (isStart) {
color = Colors.green;
} else if (isEnd) {
color = Colors.red;
}
return GestureDetector(
onTap: () {
if (isRunning) return;
setState(() {
if (grid[row][col] == CellType.empty) {
grid[row][col] = CellType.wall;
} else if (grid[row][col] == CellType.wall) {
grid[row][col] = CellType.empty;
}
});
},
child: Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(color: color),
child: const SizedBox(),
),
);
},
),
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
ElevatedButton.icon(
onPressed: () {
if (!isRunning) {
_resetGrid();
setState(() {});
}
},
icon: const Icon(Icons.refresh),
label: const Text('重置'),
),
ElevatedButton.icon(
onPressed: () {
if (!isRunning) {
_clearWalls();
setState(() {});
}
},
icon: const Icon(Icons.delete),
label: const Text('清空障碍'),
),
ElevatedButton.icon(
onPressed: _runAStar,
icon: const Icon(Icons.route),
label: Text(isRunning ? '运行中...' : '开始寻路'),
),
],
),
],
),
);
}
}