
❤️@燃于AC之乐 来自重庆 计算机专业的一枚大学生
✨专注 C/C++ Linux 数据结构 算法竞赛 AI
🏞️志同道合的人会看见同一片风景!
👇点击进入作者专栏:
🌟《算法画解》算法相关题目点击即可进入实操🌟
感兴趣的可以先收藏起来,请多多支持,还有大家有相关问题都可以给我留言咨询,希望希望共同交流心得,一起进步,你我陪伴,学习路上不孤单!
文章目录
- 前言(map系列容器概述)
-
- 一、map类介绍
-
- [1.1 map的类模板声明](#1.1 map的类模板声明)
- 二、pair类型介绍
-
- [2.1 pair的结构定义](#2.1 pair的结构定义)
- [2.2 pair的使用要点](#2.2 pair的使用要点)
- 三、map的构造与迭代器
-
- [3.1 构造接口](#3.1 构造接口)
- [3.2 迭代器接口](#3.2 迭代器接口)
- 四、map的增删查操作
-
- [4.1 插入操作](#4.1 插入操作)
- [4.2 查找操作](#4.2 查找操作)
- [4.3 删除操作](#4.3 删除操作)
- [4.4 边界查找操作](#4.4 边界查找操作)
- 五、map的核心特性:数据修改
-
- [5.1 通过迭代器修改value](#5.1 通过迭代器修改value)
- [5.2 operator[]多功能接口](#5.2 operator[]多功能接口)
- 六、map使用详解
-
- [6.1 构造、遍历与插入](#6.1 构造、遍历与插入)
- [6.2 统计水果次数(find+iterator版本)](#6.2 统计水果次数(find+iterator版本))
- [6.3 统计水果次数(operator[]版本)](#6.3 统计水果次数(operator[]版本))
- [6.4 operator[]多功能演示](#6.4 operator[]多功能演示)
- 七、multimap的使用
-
- [7.1 multimap与map的差异](#7.1 multimap与map的差异)
- [7.2 multimap使用样例](#7.2 multimap使用样例)
- 八、map的应用场景
-
- [8.1 场景一:随机链表的复制(力扣138)](#8.1 场景一:随机链表的复制(力扣138))
- [8.2 场景二:前K个高频单词(力扣692)](#8.2 场景二:前K个高频单词(力扣692))
- 九、总结
前言(map系列容器概述)
前文我们学习了set和multiset,它们是key搜索场景 的关联式容器。本章讲解的map和multimap是key/value搜索场景 的关联式容器,底层同样基于红黑树实现。
核心区别:
- set:节点只存储key,用于判断key是否存在
- map:节点存储
pair<key, value>键值对,通过key快速映射到value
一、map类介绍
1.1 map的类模板声明

cpp
template < class Key, // map::key_type
class T, // map::mapped_type
class Compare = less<Key>, // map::key_compare
class Alloc = allocator<pair<const Key,T>> // map::allocator_type
> class map;模板参数说明:
Key:键值的类型,map中key是唯一的T:映射值的类型,通过key映射到valueCompare:比较仿函数,默认less<Key>(按key升序)Alloc:空间配置器,一般使用默认
底层特性:
- 底层结构:红黑树,平衡二叉搜索树
- 增删查改效率:O(logN)
- 迭代器遍历:走中序,按key有序遍历
- 修改限制 :支持修改value,不支持修改key(修改key会破坏二叉搜索树结构)
二、pair类型介绍
2.1 pair的结构定义
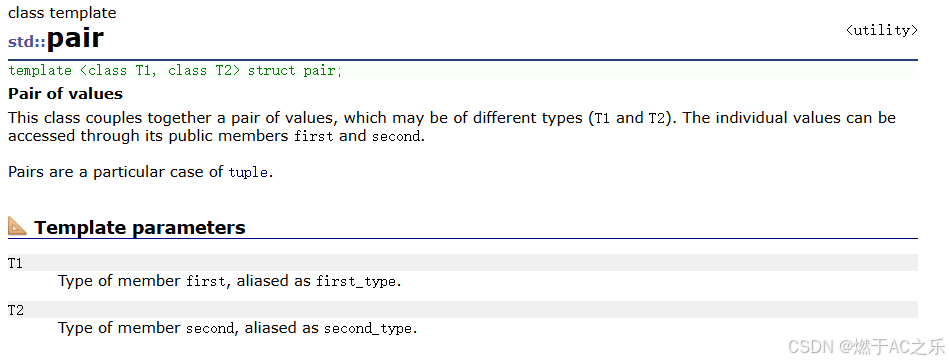
map底层红黑树节点中存储的是pair<const Key, T>键值对。pair是一个模板结构体,将两个数据组合成一个单元:
cpp
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;
template <class T1, class T2>
struct pair
{
typedef T1 first_type;
typedef T2 second_type;
T1 first; // 第一个数据(key)
T2 second; // 第二个数据(value)
// 默认构造
pair(): first(T1()), second(T2())
{}
// 带参构造
pair(const T1& a, const T2& b): first(a), second(b)
{}
// 拷贝构造模板
template<class U, class V>
pair (const pair<U,V>& pr): first(pr.first), second(pr.second)
{}
};
// make_pair函数模板:自动推导类型,简化pair对象创建
template <class T1,class T2>
inline pair<T1,T2> make_pair (T1 x, T2 y)
{
return ( pair<T1,T2>(x,y) );
}2.2 pair的使用要点
接口说明:
first:访问键值key(const属性,不可修改)second:访问映射值value(可修改)make_pair():最推荐的pair创建方式,自动类型推导{key, value}:C++11初始化列表语法,最简洁
三、map的构造与迭代器
3.1 构造接口
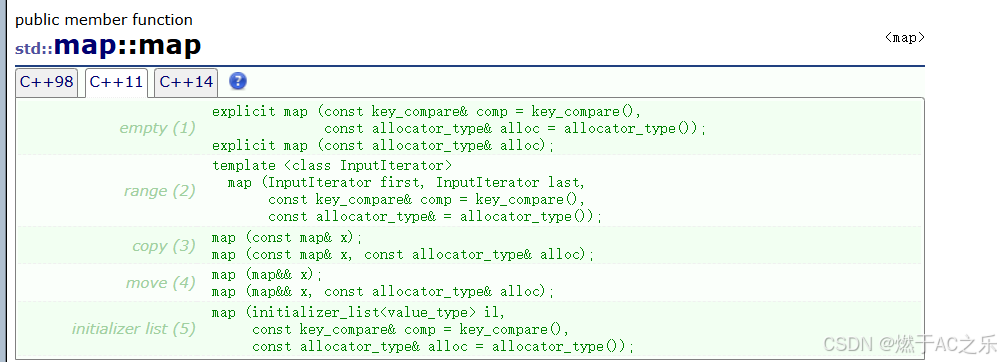
cpp
// 1. 无参默认构造
explicit map (const key_compare& comp = key_compare(),
const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
// 2. 迭代器区间构造
template <class InputIterator>
map (InputIterator first, InputIterator last,
const key_compare& comp = key_compare(),
const allocator_type& = allocator_type());
// 3. 拷贝构造
map (const map& x);
// 4. initializer_list构造(最常用)
map (initializer_list<value_type> il,
const key_compare& comp = key_compare(),
const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());3.2 迭代器接口
cpp
// 正向迭代器(双向迭代器)
iterator begin(); // 返回指向最小key的迭代器
iterator end(); // 返回尾后迭代器
// 反向迭代器
reverse_iterator rbegin(); // 返回指向最大key的迭代器
reverse_iterator rend(); // 返回反向尾后迭代器
// const迭代器
const_iterator cbegin() const;
const_iterator cend() const;
const_reverse_iterator crbegin() const;
const_reverse_iterator crend() const;迭代器特性:
- 双向迭代器,支持
++、--操作 - 遍历走中序,按key升序访问
- 通过迭代器可以修改value ,但不能修改key
- 支持范围for循环
四、map的增删查操作
4.1 插入操作
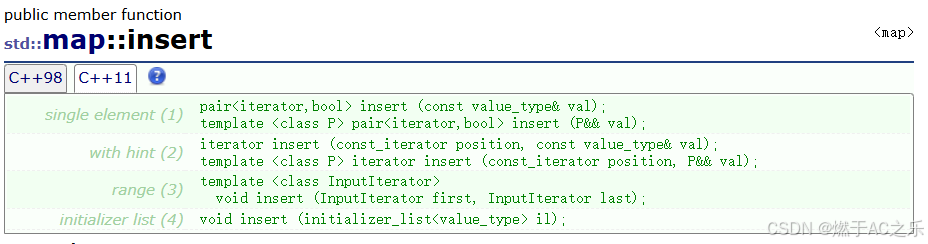
cpp
// 单个数据插入,返回pair<迭代器, 是否成功>
pair<iterator,bool> insert (const value_type& val);
// 列表插入,已存在的key不会插入
void insert (initializer_list<value_type> il);
// 迭代器区间插入
template <class InputIterator>
void insert (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);接口说明:
insert()的参数必须是pair<const Key, T>类型- 插入时按key比较,与value无关
- 如果key已存在,插入失败(即使value不同)
- 返回值
pair<iterator, bool>:first:指向已存在元素或新插入元素的迭代器second:true表示插入成功,false表示key已存在
4.2 查找操作

cpp
// 查找key,返回迭代器,未找到返回end()
iterator find (const key_type& k);
// 查找key的个数(map中只能是0或1)
size_type count (const key_type& k) const;接口说明:
find():O(logN)效率,通过返回的迭代器可以修改valuecount():返回值0或1,常用于存在性判断
4.3 删除操作
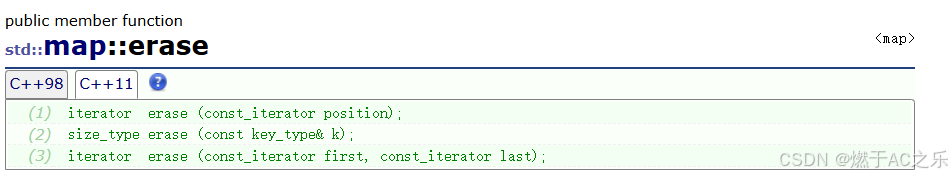
cpp
// 删除迭代器位置的值
iterator erase (const_iterator position);
// 删除key,返回删除个数(0或1)
size_type erase (const key_type& k);
// 删除迭代器区间
iterator erase (const_iterator first, const_iterator last);4.4 边界查找操作

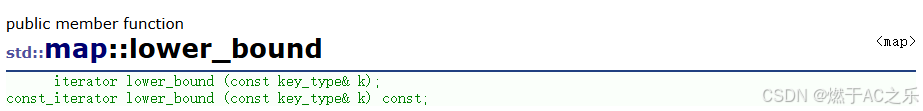
cpp
// 返回 >= k 的第一个元素的迭代器
iterator lower_bound (const key_type& k);
const_iterator lower_bound (const key_type& k) const;
// 返回 > k 的第一个元素的迭代器
iterator upper_bound (const key_type& k);
const_iterator upper_bound (const key_type& k) const;
// 返回pair<lower_bound, upper_bound>
pair<iterator,iterator> equal_range (const key_type& k);
pair<const_iterator,const_iterator> equal_range (const key_type& k) const;五、map的核心特性:数据修改
5.1 通过迭代器修改value
map支持修改value ,不支持修改key 。通过find()返回的迭代器或遍历时的迭代器,可以直接修改second成员:
cpp
auto it = dict.find("left");
if (it != dict.end())
{
it->second = "左边、剩余"; // 修改value
// it->first = "right"; // 错误!不能修改key
}5.2 operator[]多功能接口
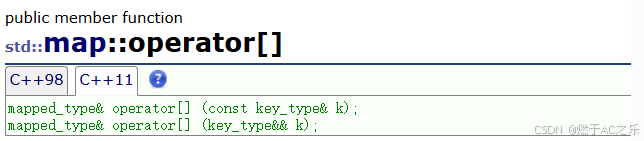
接口说明:
operator[]是map最强大、最常用的接口,集插入、查找、修改于一身:
cpp
mapped_type& operator[] (const key_type& k);内部实现原理:
cpp
mapped_type& operator[] (const key_type& k)
{
// 1. 调用insert:如果k不存在,插入{k, mapped_type()}
// 如果k存在,插入失败,返回已存在节点的迭代器
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert({ k, mapped_type() });
// 2. 无论插入成功还是失败,ret.first都指向k所在的节点
iterator it = ret.first;
// 3. 返回value的引用
return it->second;
}三种场景:
| 场景 | key状态 | operator[]行为 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 插入 | 不存在 | 插入{key, value默认构造} | value的引用 |
| 修改 | 已存在 | 返回已存在value的引用 | value的引用 |
| 查找 | 已存在 | 返回已存在value的引用 | value的引用 |
使用样例:
cpp
map<string, string> dict;
dict["insert"]; // 1. 插入:key不存在,插入{"insert", ""}
dict["left"] = "左边"; // 2. 插入+修改:插入{"left", "左边"}
dict["left"] = "左边、剩余"; // 3. 修改:key已存在,修改value
cout << dict["left"]; // 4. 查找:key已存在,返回value六、map使用详解
6.1 构造、遍历与插入
接口讲解:
本示例演示map的构造、遍历和插入 操作。map的遍历按key升序 进行,插入时需构造pair对象,共四种构造方式,其中初始化列表最简洁。已存在的key插入会失败。
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 1. initializer_list构造(最常用)
map<string, string> dict = {
{"left", "左边"},
{"right", "右边"},
{"insert", "插入"},
{"string", "字符串"}
};
// 2. 迭代器遍历(按key升序)
auto it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
// 方式1:解引用后访问成员
// cout << (*it).first << ":" << (*it).second << endl;
// 方式2:箭头运算符(最常用)
// 第一个->是迭代器重载,返回pair*;第二个->是结构指针访问成员
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
// 3. 插入pair的4种方式(对比学习)
pair<string, string> kv1("first", "第一个"); // 方式1:命名对象
dict.insert(kv1);
dict.insert(pair<string, string>("second", "第二个")); // 方式2:匿名对象
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序")); // 方式3:make_pair(推荐)
dict.insert({ "auto", "自动的" }); // 方式4:初始化列表(最简洁)
// 4. key已存在,插入失败(即使value不同)
dict.insert({ "left", "左边,剩余" });
// 5. 范围for遍历
for (const auto& e : dict)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// 6. 查找演示
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
auto ret = dict.find(str); // O(logN)查找
if (ret != dict.end())
{
cout << "->" << ret->second << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "无此单词,请重新输入" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}输出结果(部分):
insert:插入
left:左边
right:右边
string:字符串
auto:自动的
first:第一个
insert:插入
left:左边
right:右边
second:第二个
sort:排序
string:字符串6.2 统计水果次数(find+iterator版本)
接口讲解:
本示例演示传统方式 统计词频:使用find()查找元素是否存在。不存在则插入{单词,1},存在则通过迭代器修改value (ret->second++)。这种方式逻辑清晰,但代码稍显冗长。
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 利用find和iterator修改功能,统计水果出现的次数
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜",
"苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (const auto& str : arr)
{
// 1. 查找水果在不在map中
auto ret = countMap.find(str);
if (ret == countMap.end())
{
// 2. 不存在:第一次出现,插入{水果, 1}
countMap.insert({ str, 1 });
}
else
{
// 3. 存在:通过迭代器修改value(次数+1)
ret->second++;
}
}
// 遍历输出(按key升序:苹果、西瓜、香蕉)
for (const auto& e : countMap)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}输出结果:
苹果:6
西瓜:3
香蕉:26.3 统计水果次数(operator[]版本)
接口讲解:
本示例演示operator[]的优雅用法 。countMap[str]++一句代码完成了插入+查找+修改三个功能:
- 如果str不存在:插入
{str, 0},返回value引用,++后变为1 - 如果str已存在:返回value引用,++后次数+1
这是map最经典的用法,代码极其简洁高效。
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 利用[]插入+修改功能,巧妙实现统计水果出现的次数
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜",
"苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (const auto& str : arr)
{
// []先查找水果在不在map中
// 1、不在:插入{水果, 0},返回次数的引用,++后变成1
// 2、在:返回水果对应次数的引用,++后次数+1
countMap[str]++;
}
for (const auto& e : countMap)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}输出结果:
苹果:6
西瓜:3
香蕉:26.4 operator[]多功能演示
接口讲解:
本示例集中演示operator[]的四种使用场景:插入空值、插入+修改、修改、查找。理解这个例子就掌握了map最核心的操作技巧。
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, string> dict;
// 1. 插入pair对象(传统方式)
dict.insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
// 2. []插入空值
// key不存在 -> 插入 {"insert", string()} (value默认构造为空字符串)
dict["insert"];
// 3. []插入+修改
// key不存在 -> 插入 {"left", "左边"}
dict["left"] = "左边";
// 4. []修改
// key已存在 -> 修改value为"左边、剩余"
dict["left"] = "左边、剩余";
// 5. []查找
// key已存在 -> 返回value的引用
cout << dict["left"] << endl; // 输出:左边、剩余
// 验证insert结果
for (const auto& e : dict)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}输出结果:
左边、剩余
insert:
left:左边、剩余
sort:排序七、multimap的使用
7.1 multimap与map的差异

| 特性 | map | multimap |
|---|---|---|
| 键值冗余 | ❌ 不支持(key唯一) | ✅ 支持(key可重复) |
| insert | key存在时插入失败 | 总是成功 |
| find | 返回任意位置 | 返回中序第一个 |
| count | 返回0或1 | 返回实际个数 |
| erase(val) | 删除0或1个 | 删除所有匹配key的元素 |
| operator[] | ✅ 支持 | ❌ 不支持 |
接口说明:
multimap与map的接口基本一致,主要差异点:
- 不支持
operator[]:因为key可重复,[]无法确定返回哪个value的引用 find()返回中序遍历的第一个匹配元素count()返回实际重复个数erase(key)删除所有匹配key的元素
7.2 multimap使用样例
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// multimap:支持key重复
multimap<string, string> authors = {
{"鲁迅", "狂人日记"},
{"余华", "活着"},
{"鲁迅", "朝花夕拾"},
{"余华", "许三观卖血记"},
{"村上春树", "挪威的森林"}
};
// 遍历(按key有序,相同key连续存放)
for (const auto& e : authors)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// find返回中序第一个
auto pos = authors.find("鲁迅");
if (pos != authors.end())
{
cout << "鲁迅的第一部作品:" << pos->second << endl;
}
// count返回实际个数
cout << "鲁迅作品数:" << authors.count("鲁迅") << endl;
// erase(key)删除所有匹配项
authors.erase("余华");
for (const auto& e : authors)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
return 0;
}输出结果:
村上春树:挪威的森林
鲁迅:狂人日记
鲁迅:朝花夕拾
余华:活着
余华:许三观卖血记
鲁迅的第一部作品:狂人日记
鲁迅作品数:2
村上春树:挪威的森林
鲁迅:狂人日记
鲁迅:朝花夕拾八、map的应用场景
8.1 场景一:随机链表的复制(力扣138)
接口讲解:
本示例展示map在复杂链表拷贝 中的妙用。传统方法需要将拷贝节点链接在原节点后,非常繁琐。使用map建立原节点→拷贝节点 的映射关系,处理random指针时直接通过nodeMap[cur->random]O(logN)获取对应拷贝节点,降维打击。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
// 1. 建立原节点 -> 拷贝节点的映射
map<Node*, Node*> nodeMap;
Node* copyhead = nullptr;
Node* copytail = nullptr;
Node* cur = head;
// 2. 第一次遍历:拷贝next指针链,同时建立映射
while(cur)
{
if(copytail == nullptr)
{
copyhead = copytail = new Node(cur->val);
}
else
{
copytail->next = new Node(cur->val);
copytail = copytail->next;
}
// 存储映射关系
nodeMap[cur] = copytail;
cur = cur->next;
}
// 3. 第二次遍历:处理random指针
cur = head;
Node* copy = copyhead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->random == nullptr)
{
copy->random = nullptr;
}
else
{
// O(logN)查找原节点random对应的拷贝节点
copy->random = nodeMap[cur->random];
}
cur = cur->next;
copy = copy->next;
}
return copyhead;
}
};算法复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(NlogN)(N次map查找)
- 空间复杂度:O(N)(存储映射关系)
8.2 场景二:前K个高频单词(力扣692)
解法1:stable_sort
接口讲解:
本示例要求按频率降序 返回前K个单词,频率相同则按字典序升序 。map已按key(单词)字典序排序,因此相同频率的单词在遍历时已经是字典序升序。使用稳定的排序算法 stable_sort可以保持这一相对顺序。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
struct Compare
{
// 按频率降序
bool operator()(const pair<string, int>& x, const pair<string, int>& y) const
{
return x.second > y.second;
}
};
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
// 1. map统计词频(自动按单词字典序排序)
map<string, int> countMap;
for(auto& e : words)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
// 2. 将map数据拷贝到vector中
vector<pair<string, int>> v(countMap.begin(), countMap.end());
// 3. 稳定排序:频率降序,相同频率保持字典序(因为map已排序)
stable_sort(v.begin(), v.end(), Compare());
// 4. 取前k个
vector<string> strV;
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
strV.push_back(v[i].first);
}
return strV;
}
};解法2:sort统一排序
接口讲解:
本解法将频率降序 和字典序升序 两个规则合并到一个仿函数中,直接用sort排序。仿函数逻辑:频率高的排前面;频率相同时,字典序小的排前面。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
struct Compare
{
bool operator()(const pair<string, int>& x, const pair<string, int>& y) const
{
// 频率降序,或频率相等时字典序升序
return x.second > y.second ||
(x.second == y.second && x.first < y.first);
}
};
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
map<string, int> countMap;
for(auto& e : words)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
vector<pair<string, int>> v(countMap.begin(), countMap.end());
// 仿函数控制排序规则
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), Compare());
vector<string> strV;
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
strV.push_back(v[i].first);
}
return strV;
}
};解法3:priority_queue
接口讲解:
本解法使用优先级队列 (堆)来选出前K个高频单词。需要注意的是,priority_queue的仿函数与sort相反 :sort的Compare返回true表示前者应在前;priority_queue的Compare返回true表示前者优先级低 (即大堆需要<比较)。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
struct Compare
{
bool operator()(const pair<string, int>& x, const pair<string, int>& y) const
{
// 优先级队列:大堆要实现小于比较
// 频率低优先级低,字典序大优先级低
return x.second < y.second ||
(x.second == y.second && x.first > y.first);
}
};
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
map<string, int> countMap;
for(auto& e : words)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
// 将map中的<单词,次数>放到priority_queue中
// 仿函数控制大堆:频率高的在堆顶,频率相同时字典序小的在堆顶
priority_queue<pair<string, int>,
vector<pair<string, int>>,
Compare> p(countMap.begin(), countMap.end());
vector<string> strV;
for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
strV.push_back(p.top().first);
p.pop();
}
return strV;
}
};九、总结
| 容器 | 底层结构 | key唯一性 | key有序性 | 修改value | 修改key | operator[] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| map | 红黑树 | ✅ 唯一 | ✅ 升序 | ✅ 支持 | ❌ 禁止 | ✅ 支持 |
| multimap | 红黑树 | ❌ 可重复 | ✅ 升序 | ✅ 支持 | ❌ 禁止 | ❌ 不支持 |
核心要点:
-
map是key/value搜索结构 ,节点存储
pair<const Key, T> -
插入:参数必须是pair对象,key已存在时插入失败(与value无关)
-
查找 :
find()返回迭代器,可通过迭代器修改value -
operator[] :map的灵魂接口,集插入、查找、修改于一身
- key不存在:插入{key, value默认构造},返回value引用
- key已存在:返回value引用
-
multimap :支持key重复,不支持operator[] ,
find()返回中序第一个,erase(key)删除所有匹配项 -
应用价值 :map在处理键值映射 、词频统计 、复杂链表拷贝 、前K个问题 等场景中具有不可替代的优势,代码简洁高效,是降维打击的利器。

加油!志同道合的人会看到同一片风景。
看到这里请点个赞 ,关注 ,如果觉得有用就收藏一下吧。后续还会持续更新的。 创作不易,还请多多支持!