一、什么是文件流(File Stream)
在 C++ 中,文件操作通过 **流(Stream)**完成。
可以把流理解为:
程序 ↔ 数据通道 ↔ 文件
数据像水一样在流中流动。
C++ 文件流库:
#include
提供三个核心类:
类 作用
ifstream 读文件(input file stream)
ofstream 写文件(output file stream)
fstream 读写文件
二、文件流基本使用流程
1. 写文件示例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ofstream fout("data.txt"); // 打开文件
fout << "Hello C++" << endl;
fout << 100 << endl;
fout.close(); // 关闭文件
return 0;
}
2. 读文件示例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ifstream fin("data.txt");
string str;
int num;
fin >> str >> str; // 读 Hello C++
fin >> num;
cout << str << endl;
cout << num << endl;
fin.close();
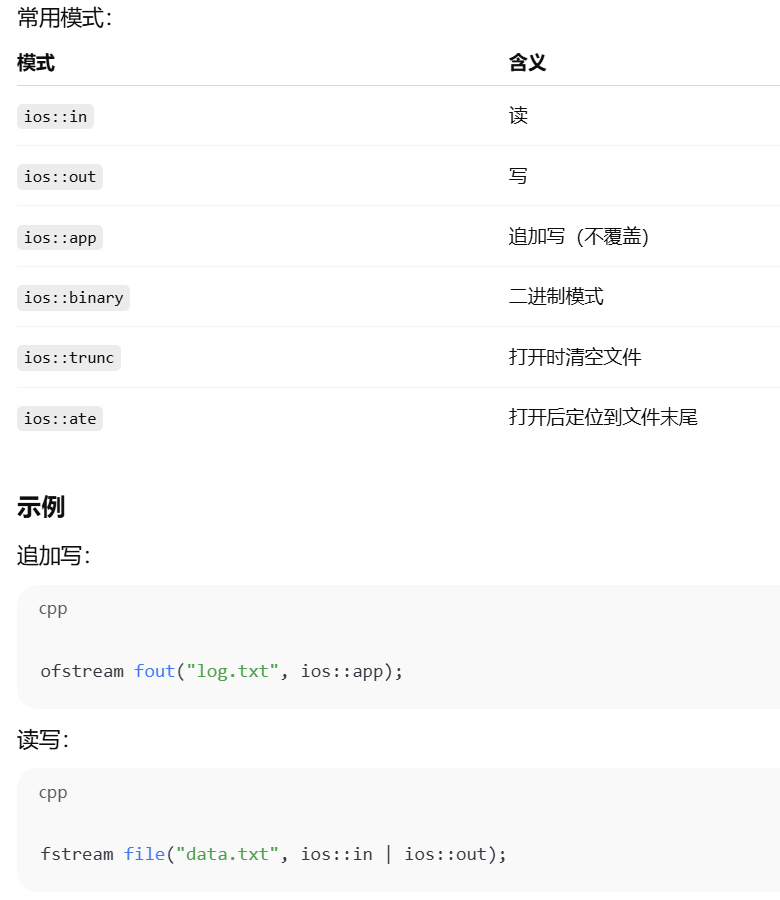
}三、文件打开方式(非常重要)
文件打开有不同模式:
ofstream fout("file.txt", ios::out);
四、文件是否成功打开
必须检查,否则程序可能崩溃。
cpp
ifstream fin("data.txt");
if (!fin) {
cout << "文件打开失败" << endl;
return 1;
}*
或者
*if (fin.is_open()) {
cout << "打开成功";
}五、按行读取(最常用)
cpp
string line;
while (getline(fin, line)) {
cout << line << endl;
}适用于:
文本处理
配置文件
日志分析
六、读到文件结束(EOF)
cpp
while (!fin.eof()) {
string str;
fin >> str;
cout << str << endl;
}七、二进制文件操作(重点)
用于:
图像
音频
结构体保存
网络数据
1. 写二进制
cpp
ofstream fout("data.bin", ios::binary);
int a = 100;
fout.write((char*)&a, sizeof(a));
fout.close();2. 读二进制
cpp
ifstream fin("data.bin", ios::binary);
int a;
fin.read((char*)&a, sizeof(a));
cout << a << endl;3. 保存结构体
cpp
struct Student {
int id;
char name[20];
};
Student s = {1, "Rui"};
ofstream fout("stu.bin", ios::binary);
fout.write((char*)&s, sizeof(s));
fout.close();读取:
cpp
Student s;
ifstream fin("stu.bin", ios::binary);
fin.read((char*)&s, sizeof(s));八、文件指针操作(高级)
文件内部有两个指针:

- 移动读指针
cpp
fin.seekg(10); // 从头移动10字节
fin.seekg(-10, ios::end); //从末尾- 获取当前位置
cpp
cout << fin.tellg() << endl;写指针类似:
cpp
fout.seekp();
fout.tellp();九、文件流状态检查
