目录
- 0 专栏介绍
- 1 路径规划插件的意义
- 2 全局规划插件编写模板
-
- 2.1 构造规划插件类
- 2.2 注册并导出插件
- 2.3 编译与使用插件
- 3 全局规划插件开发案例(A*算法)
- 常见问题
0 专栏介绍
本专栏旨在通过对ROS2的系统学习,掌握ROS2底层基本分布式原理,并具有机器人建模和应用ROS2进行实际项目的开发和调试的工程能力。
🚀详情:《ROS2从入门到精通》
1 路径规划插件的意义
在ROS2中,路径规划插件为导航系统提供灵活性和可扩展性。路径规划插件允许用户根据特定的需求和环境条件选择不同的路径规划算法和策略。这些插件可以被动态加载和替换,从而使机器人可以根据实际情况灵活地调整路径规划行为。这种灵活性使得机器人能够适应不同类型的任务,包括室内导航、室外移动和复杂的障碍物避开等。同时也促进了路径规划算法的研究和开发,为导航系统的不断改进提供了可能。
2 全局规划插件编写模板
本节以最简单的直线路径规划插件为例介绍ROS2中插件编码的基本范式
2.1 构造规划插件类
所有全局规划插件的基类是nav2_core::GlobalPlanner,该基类提供了5个纯虚方法来实现规划器插件,一个合法的路径规划插件必须覆盖这5个基本方法:
configure():在规划器服务器进入on_configure状态时会调用此方法,此方法执行ROS2参数声明和规划器成员变量的初始化;activate():在规划器服务器进入on_activate状态时会调用此方法,此方法实现规划器进入活动状态前的必要操作;deactivate():在规划器服务器进入on_deactivate状态时会调用此方法,此方法实现规划器进入非活动状态前的必要操作;cleanup():在规划器服务器进入on_cleanup状态时会调用此方法,此方法清理为规划器创建的各种资源;createPlan():在规划器服务器要求指定开始位姿和目标位姿的全局规划时会调用此方法。此方法输入开始和目标位姿,并会返回携带全局规划路径的nav_msgs::msg::Path
在本例中,直线规划器的createPlan()函数体很简单,就是增量地生成从起点到终点的直线
cpp
nav_msgs::msg::Path StraightLine::createPlan(
const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped & start,
const geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped & goal)
{
nav_msgs::msg::Path global_path;
global_path.poses.clear();
global_path.header.stamp = node_->now();
global_path.header.frame_id = global_frame_;
// calculating the number of loops for current value of interpolation_resolution_
int total_number_of_loop = std::hypot(
goal.pose.position.x - start.pose.position.x,
goal.pose.position.y - start.pose.position.y) /
interpolation_resolution_;
double x_increment = (goal.pose.position.x - start.pose.position.x) / total_number_of_loop;
double y_increment = (goal.pose.position.y - start.pose.position.y) / total_number_of_loop;
for (int i = 0; i < total_number_of_loop; ++i) {
geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped pose;
pose.pose.position.x = start.pose.position.x + x_increment * i;
pose.pose.position.y = start.pose.position.y + y_increment * i;
pose.pose.position.z = 0.0;
pose.pose.orientation.x = 0.0;
pose.pose.orientation.y = 0.0;
pose.pose.orientation.z = 0.0;
pose.pose.orientation.w = 1.0;
pose.header.stamp = node_->now();
pose.header.frame_id = global_frame_;
global_path.poses.push_back(pose);
}
geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped goal_pose = goal;
goal_pose.header.stamp = node_->now();
goal_pose.header.frame_id = global_frame_;
global_path.poses.push_back(goal_pose);
return global_path;
}2.2 注册并导出插件
在创建了自定义规划器的前提下,需要导出该规划器插件以便规划器服务器可以在运行时正确地加载。在ROS2中,插件的导出和加载由pluginlib处理。
-
源文件配置导出宏
cpp#include "pluginlib/class_list_macros.hpp" PLUGINLIB_EXPORT_CLASS(straightline_planner::StraightLinePlanner, nav2_core::GlobalPlanner) -
配置插件描述文件
xxx_planner_plugin.xml,例如本案例为straightline_planner_plugin.xml文件。此XML文件包含以下信息:library path:插件库名称及其位置;class name:规划算法类的名称;class type:规划算法类的类型;base class:规划基类的名称,统一为nav2_core::GlobalPlannerdescription:插件的描述。
实例如下
xml<library path="straightline_planner_plugin"> <class name="straightline_planner/StraightLine" type="straightline_planner::StraightLine" base_class_type="nav2_core::GlobalPlanner"> <description>This is an example of straight path generator.</description> </class> </library> -
配置
CMakeLists.txt文件使用
cmake函数pluginlib_export_plugin_description_file()来导出插件。这个函数会将插件描述文件安装到install/share目录中,并设置ament索引以使其可被发现,实例如下cpluginlib_export_plugin_description_file(nav2_core straightline_planner_plugin.xml) -
配置
package.xml描述文件,实例如下:xml<export> <build_type>ament_cmake</build_type> <nav2_core plugin="${prefix}/straightline_planner_plugin.xml" /> </export>
2.3 编译与使用插件
编译该插件软件包,接着通过配置文件使用插件。
参数的传递链如下:首先在simulation.launch.py中引用配置文件navigation.yaml
python
declare_params_file_cmd = DeclareLaunchArgument(
'params_file',
default_value=os.path.join(simulation_dir, 'config', 'navigation.yaml'),
description='Full path to the ROS2 parameters file to use for all launched nodes')接着在navigation.yaml中修改插件配置,默认如下,是用的是NavfnPlanner插件:
yaml
planner_server:
ros__parameters:
expected_planner_frequency: 20.0
use_sim_time: True
planner_plugins: ["GridBased"]
GridBased:
plugin: "nav2_navfn_planner/NavfnPlanner"
tolerance: 0.5
use_astar: false
allow_unknown: true将上述替换为自己的插件,本案例为:
yaml
planner_server:
ros__parameters:
expected_planner_frequency: 20.0
use_sim_time: True
planner_plugins: ["GridBased"]
GridBased:
plugin: "straightline_planner/StraightLinePlanner"
interpolation_resolution: 0.1接着运行路径规划即可看到规划算法被替换

3 全局规划插件开发案例(A*算法)
接下来正式开始实用型路径规划算法的开发案例,以A*算法为例,核心规划部分如下所示:
cpp
ool AStar::plan(const unsigned char* global_costmap, const Node& start, const Node& goal, std::vector<Node>& path,
std::vector<Node>& expand)
{
// clear vector
path.clear();
expand.clear();
// open list and closed list
std::priority_queue<Node, std::vector<Node>, Node::compare_cost> open_list;
std::unordered_map<int, Node> closed_list;
open_list.push(start);
// get all possible motions
const std::vector<Node> motions = Node::getMotion();
// main process
while (!open_list.empty())
{
// pop current node from open list
Node current = open_list.top();
open_list.pop();
// current node does not exist in closed list
if (closed_list.find(current.id_) != closed_list.end())
continue;
closed_list.insert(std::make_pair(current.id_, current));
expand.push_back(current);
// goal found
if (current == goal)
{
path = _convertClosedListToPath(closed_list, start, goal);
return true;
}
// explore neighbor of current node
for (const auto& motion : motions)
{
// explore a new node
Node node_new = current + motion;
node_new.id_ = grid2Index(node_new.x_, node_new.y_);
// node_new in closed list
if (closed_list.find(node_new.id_) != closed_list.end())
continue;
node_new.pid_ = current.id_;
// next node hit the boundary or obstacle
// prevent planning failed when the current within inflation
if ((node_new.id_ < 0) || (node_new.id_ >= ns_) ||
(global_costmap[node_new.id_] >= lethal_cost_ * 0.8 &&
global_costmap[node_new.id_] >= global_costmap[current.id_]))
continue;
// if using dijkstra implementation, do not consider heuristics cost
if (!is_dijkstra_)
node_new.h_ = helper::dist(node_new, goal);
// if using GBFS implementation, only consider heuristics cost
if (is_gbfs_)
node_new.g_ = 0.0;
// else, g will be calculate through node_new = current + m
open_list.push(node_new);
}
}
return false;
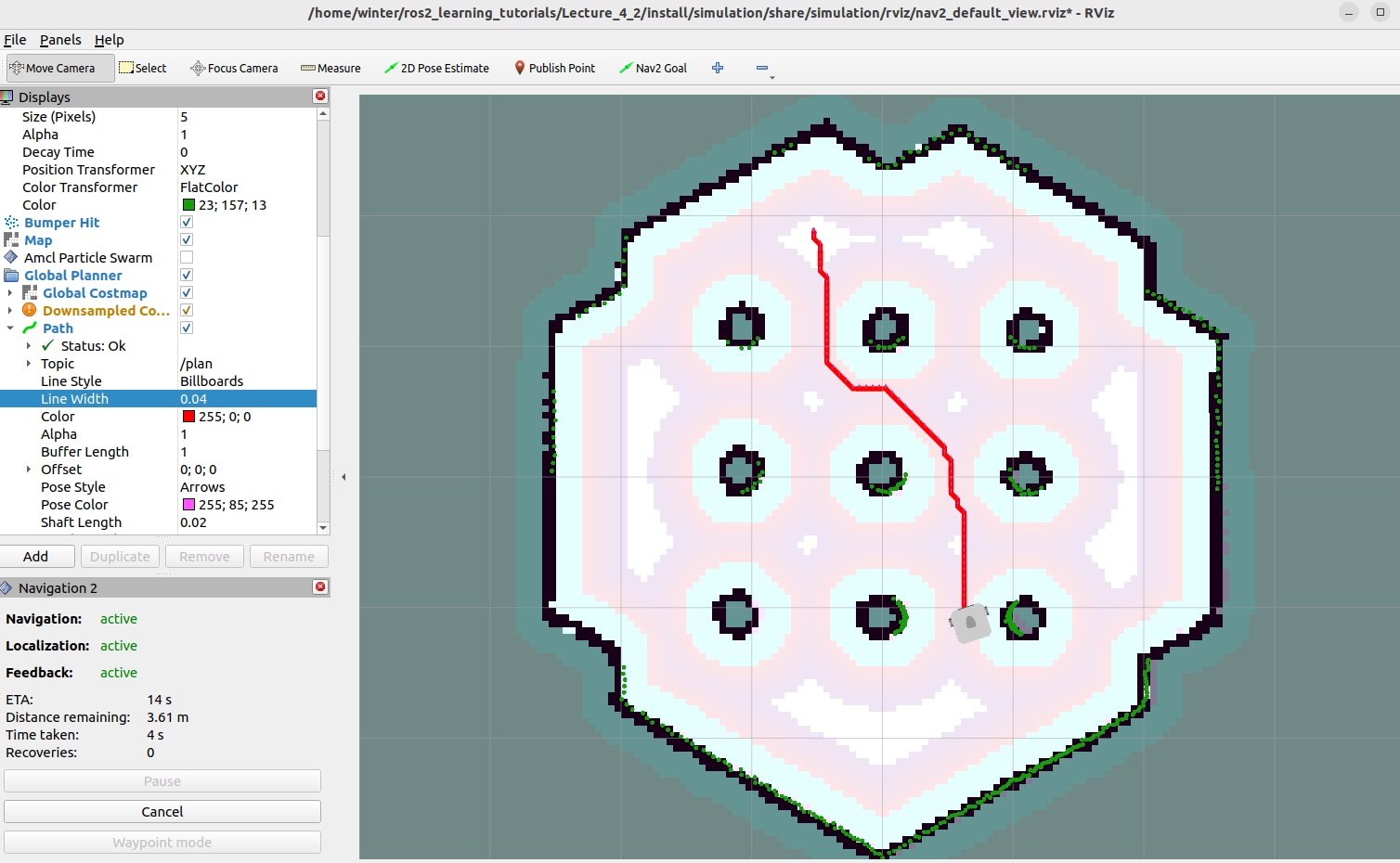
}按照第二节的步骤导出并启动规划即可,效果如下
常见问题
-
/opt/ros/noetic/lib/move_base/move_base: symbol lookup error: /home/winter/ROS/ros_learning_tutorials/Lecture19/devel/lib//libmy_planner.so: undefined symbol: _ZN18base_local_planner12CostmapModelC1ERKN10costmap_2d9Costmap2DE解决方案:未定义符号错误
undefined symbol一般是依赖配置错误导致,采用c++filt工具解析符号shellc++filt _ZN18base_local_planner12CostmapModelC1ERKN10costmap_2d9Costmap2DE base_local_planner::CostmapModel::CostmapModel(costmap_2d::Costmap2D const&)可以看出是
base_local_planner的问题,需要在功能包CMakeLists.txt中配置base_local_planner的相关依赖。c++filt是什么?g++编译器有名字修饰机制,其目的是给同名的重载函数不同的、唯一的签名识别,所有函数在编译后的文件中都会生成唯一的符号,c++filt可以逆向解析符号,还原函数,定位代码。
完整工程代码请联系下方博主名片获取
🔥 更多精彩专栏:
👇源码获取 · 技术交流 · 抱团学习 · 咨询分享 请联系👇