- 🍨 本文为🔗365天深度学习训练营 中的学习记录博客
- 🍖 原作者:K同学啊
一、前期工作
1. 设置GPU
python
import tensorflow as tf
gpus = tf.config.list_physical_devices("GPU")
if gpus:
tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpus[0], True) #设置GPU显存用量按需使用
tf.config.set_visible_devices([gpus[0]],"GPU")
print("GPU is available")2. 导入数据
python
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers,models
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os,PIL,pathlib
data_dir = "F:/host/Data/咖啡豆识别数据/"
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
python
image_count = len(list(data_dir.glob('*/*.png')))
print("图片总数为:",image_count)
二、数据预处理
1. 加载数据
使用image_dataset_from_directory方法将磁盘中的数据加载到tf.data.Dataset中
python
batch_size = 8
img_height = 224
img_width = 224
python
train_ds = tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
data_dir,
validation_split=0.2,
subset="training",
seed=123,
image_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=batch_size)
python
val_ds = tf.keras.preprocessing.image_dataset_from_directory(
data_dir,
validation_split=0.1,
subset="validation",
seed=123,
image_size=(img_height, img_width),
batch_size=batch_size)
python
class_names = train_ds.class_names
print(class_names)
2. 可视化数据
python
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4)) # 图形的宽为10高为5
for images, labels in train_ds.take(1):
for i in range(8):
ax = plt.subplot(2, 4, i + 1)
plt.imshow(images[i].numpy().astype("uint8"))
plt.title(class_names[labels[i]])
plt.axis("off")
python
for image_batch, labels_batch in train_ds:
print(image_batch.shape)
print(labels_batch.shape)
break
3. 配置数据集
- shuffle() :打乱数据,关于此函数的详细介绍可以参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/42417456
- prefetch() :预取数据,加速运行,其详细介绍可以参考我前两篇文章,里面都有讲解。
- cache() :将数据集缓存到内存当中,加速运行
python
AUTOTUNE = tf.data.AUTOTUNE
train_ds = train_ds.cache().shuffle(1000).prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)
val_ds = val_ds.cache().prefetch(buffer_size=AUTOTUNE)
python
normalization_layer = layers.experimental.preprocessing.Rescaling(1./255)
train_ds = train_ds.map(lambda x, y: (normalization_layer(x), y))
val_ds = val_ds.map(lambda x, y: (normalization_layer(x), y))
python
image_batch, labels_batch = next(iter(val_ds))
first_image = image_batch[0]
# 查看归一化后的数据
print(np.min(first_image), np.max(first_image))三、构建VGG-16网络
python
from tensorflow.keras import layers, models, Input
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D, Dense, Flatten, Dropout
def VGG16(nb_classes, input_shape):
# 输入层
input_tensor = Input(shape=input_shape)
# 卷积层1
x = Conv2D(64, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block1_conv1')(input_tensor)
x = Conv2D(64, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block1_conv2')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2), name = 'block1_pool')(x)
# 卷积层2
x = Conv2D(128, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block2_conv1')(x)
x = Conv2D(128, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block2_conv2')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2), name = 'block2_pool')(x)
# 卷积层3
x = Conv2D(256, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block3_conv1')(x)
x = Conv2D(256, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block3_conv2')(x)
x = Conv2D(256, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block3_conv3')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2), name = 'block3_pool')(x)
# 卷积层4
x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block4_conv1')(x)
x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block4_conv2')(x)
x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block4_conv3')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2), name = 'block4_pool')(x)
# 卷积层5
x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block5_conv1')(x)
x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block5_conv2')(x)
x = Conv2D(512, (3,3), activation='relu', padding='same',name='block5_conv3')(x)
x = MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2), name = 'block5_pool')(x)
# 展平层
x = Flatten()(x)
# 全连接层1
x = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='fc1')(x)
# 全连接层2
x = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='fc2')(x)
# 输出层
output_tensor = Dense(nb_classes, activation='softmax',name='predictions')(x)
# 创建模型
model = Model(input_tensor, output_tensor)
return model
# 创建模型
model=VGG16(len(class_names), (img_width, img_height, 3))
# 打印模型结构
model.summary()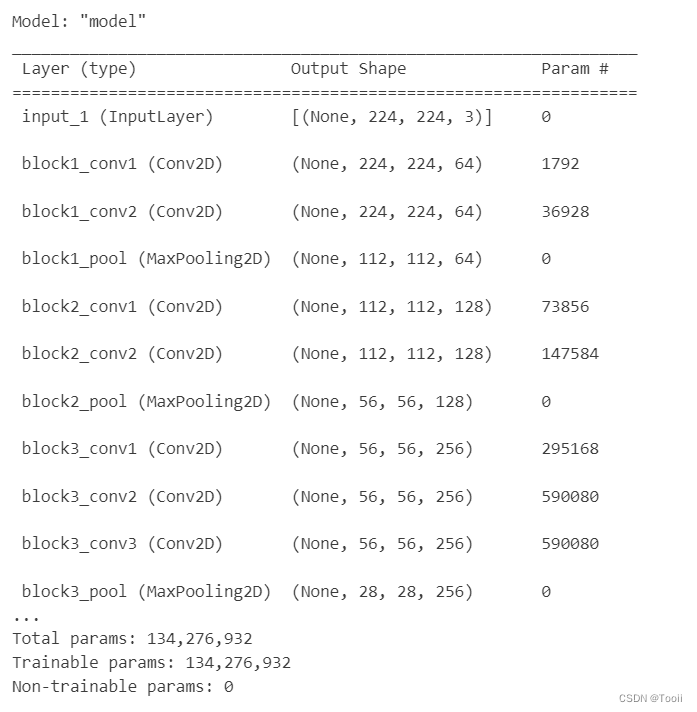
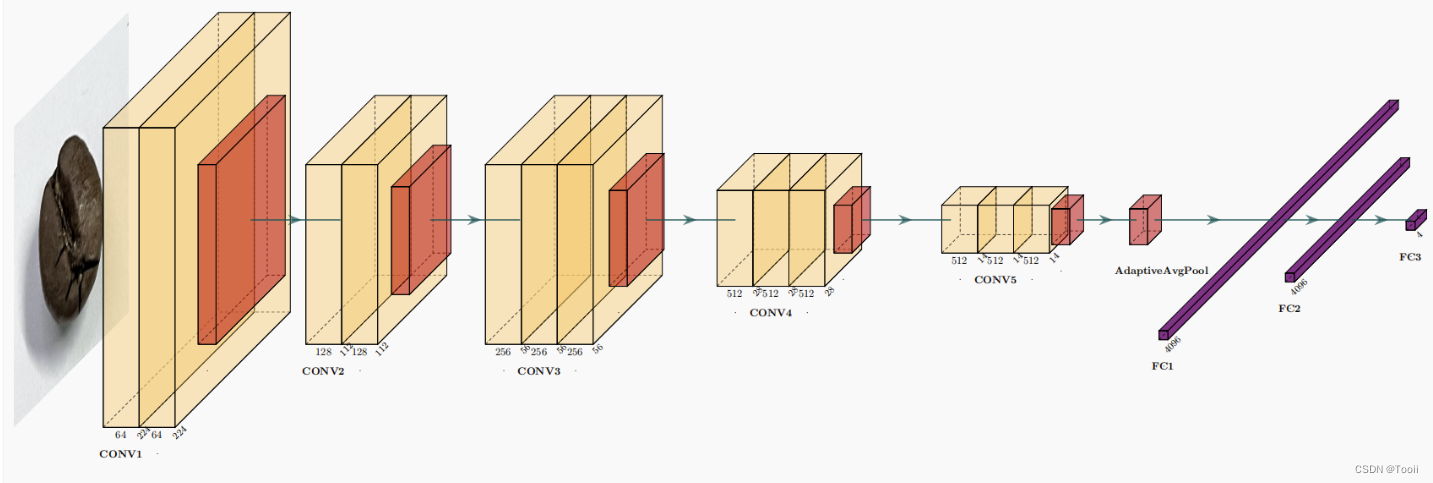
3. 网络结构图
关于卷积的相关知识可以参考文章:https://mtyjkh.blog.csdn.net/article/details/114278995
结构说明:
- 13个卷积层(Convolutional Layer),分别用blockX_convX表示
- 3个全连接层(Fully connected Layer),分别用fcX与predictions表示
- 5个池化层(Pool layer),分别用blockX_pool表示
VGG-16包含了16个隐藏层(13个卷积层和3个全连接层),故称为VGG-16
四、编译
在准备对模型进行训练之前,还需要再对其进行一些设置。以下内容是在模型的编译步骤中添加的:
- 损失函数(loss):用于衡量模型在训练期间的准确率。
- 优化器(optimizer):决定模型如何根据其看到的数据和自身的损失函数进行更新。
- 指标(metrics):用于监控训练和测试步骤。以下示例使用了准确率,即被正确分类的图像的比率。
python
# 设置初始学习率
initial_learning_rate = 1e-4
lr_schedule = tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay(
initial_learning_rate,
decay_steps=30, # 敲黑板!!!这里是指 steps,不是指epochs
decay_rate=0.92, # lr经过一次衰减就会变成 decay_rate*lr
staircase=True)
# 设置优化器
opt = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=initial_learning_rate)
model.compile(optimizer=opt,
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])五、训练模型
python
epochs = 20
history = model.fit(
train_ds,
validation_data=val_ds,
epochs=epochs
)
六、可视化结果
python
acc = history.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs_range = range(epochs)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(epochs_range, acc, label='Training Accuracy')
plt.plot(epochs_range, val_acc, label='Validation Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Accuracy')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(epochs_range, loss, label='Training Loss')
plt.plot(epochs_range, val_loss, label='Validation Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training and Validation Loss')
plt.show()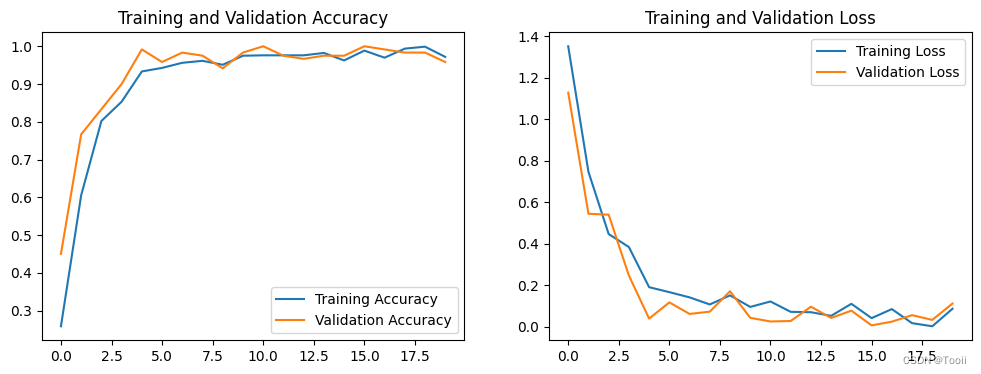
七、个人小结
在本次咖啡豆识别项目中,我们通过设置GPU、导入并预处理数据、构建深度学习模型,以及对模型进行训练和评估,实现了对咖啡豆图像的自动识别。整个过程涵盖了数据加载与可视化、数据集配置、模型构建与优化等关键步骤,最终显著提升了图像分类的准确性,同时也加深了我们对深度学习技术的实践理解。