一、迭代器设计模式
迭代器设计模式(iterator)是一种行为设计模式, 让你能在不暴露集合底层表现形式 (列表、 栈和树等数据结构) 的情况下遍历集合中所有的元素。
在验证环境中的checker会收集各个monitor上送过来的transactions,如果有一个专用配置寄存器用于开启或关闭ECC计算,那么在其发生更改时,需要遍历checker中的transactions并修改所预测的数据值,以实现正确的预测。任何在对象集合上执行遍历的场景,无论其内部结构如何,都适合使用iterator设计模式进行建模。该解决方案的主要优点是存储数据的内部结构不需要对外可见,因此可以在不影响环境其余部分的情况下进行修改。Iterator设计模式的使用增加了环境的灵活性,且通常没有任何主要缺点,还是比较推荐大家有机会可以试试。
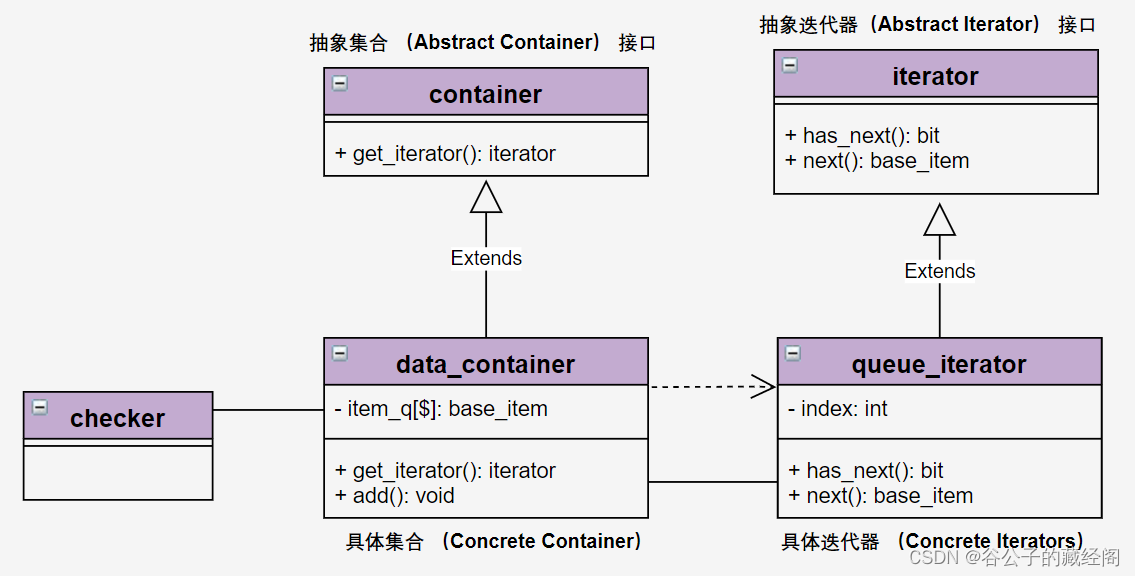
迭代器设计模式主要包含以下几个组件:
- 抽象迭代器(Abstract Iterator ) 接口:声明了遍历集合所需的操作: 获取下一个元素、 获取当前位置和重新开始迭代等。
- 具体迭代器 (Concrete Iterators ) :继承自抽象迭代器,实现遍历集合的一种特定算法。 迭代器对象必须跟踪自身遍历的进度。 这使得多个迭代器可以相互独立地遍历同一集合。
- 抽象集合 (Abstract Container ) 接口:声明一个或多个方法来获取与集合兼容的迭代器。 请注意, 返回方法的类型必须被声明为迭代器接口, 因此具体集合可以返回各种不同种类的迭代器。
- 具体集合 (Concrete Container ):继承自抽象集合, 会在客户端请求迭代器时返回一个特定的具体迭代器类实体。
下图为迭代器设计模式在ECC中应用的UML类图。
二、参考代码
迭代器设计模式的参考代码如下:
cpp
class base_item extends uvm_object;
`uvm_object_utils (base_item)
function new (string name = "base_item");
super.new(name);
endfunction : new
function void re_generate(bit ecc_en);
if ( ecc_en ) $display("%s No ECC", get_name());
else $display("%s Has ECC", get_name());
endfunction : re_generate
endclass : base_item
virtual class iterator extends uvm_object;
function new (string name = "iterator");
super.new(name);
endfunction : new
pure virtual function bit has_next();
pure virtual function base_item next();
endclass : iterator
virtual class container extends uvm_object;
function new (string name = "container");
super.new(name);
endfunction : new
pure virtual function iterator get_iterator();
endclass : container
class data_container extends container;
`uvm_object_utils (data_container)
static base_item item_q[$];
class queue_iterator extends iterator;
`uvm_object_utils (queue_iterator)
int index;
function new (string name = "queue_iterator");
super.new(name);
endfunction : new
virtual function bit has_next();
if ( index < item_q.size() ) begin
return 1;
end
return 0;
endfunction : has_next
virtual function base_item next();
if ( this.has_next() ) begin
return item_q[index++];
end
return null;
endfunction : next
endclass : queue_iterator
function new (string name = "data_container");
super.new(name);
endfunction : new
virtual function iterator get_iterator();
queue_iterator it_q = queue_iterator::type_id::create("iteratora");
return it_q;
endfunction : get_iterator
function void add(base_item _item);
item_q.push_back(_item);
endfunction : add
endclass : data_container模拟测试代码如下:
cpp
data_container data_cont;
base_item item;
base_item item1 = base_item::type_id::create("item1");
base_item item2 = base_item::type_id::create("item2");
base_item item3 = base_item::type_id::create("item3");
data_cont = data_container::type_id::create("data_cont");
data_cont.add(item1);
data_cont.add(item2);
data_cont.add(item3);
for (iterator it = data_cont.get_iterator(); it.has_next(); ) begin
item = it.next();
item.re_generate(1);
end
for (iterator it = data_cont.get_iterator(); it.has_next(); ) begin
item = it.next();
item.re_generate(0);
end输出仿真日志如下:
XML
| item1 No ECC
| item2 No ECC
| item3 No ECC
| item1 Has ECC
| item2 Has ECC
| item3 Has ECC从仿真结果可以看出,添加到container中的三个base_item,在第一次迭代中没有打开ECC,所以都打印出"No ECC"字符串,在第二次迭代中打开了ECC,所以都打印出"Has ECC"字符串。
