RAG通常指的是"Retrieval-Augmented Generation",即"检索增强的生成"。这是一种结合了检索(Retrieval)和生成(Generation)的机器学习模型,通常用于自然语言处理任务,如文本生成、问答系统等。
我们通过一下几个步骤来完成一个基于京东云官网文档的RAG系统
- 数据收集
- 建立知识库
- 向量检索
- 提示词与模型
数据收集
数据的收集再整个RAG实施过程中无疑是最耗人工的,涉及到收集、清洗、格式化、切分等过程。这里我们使用京东云的官方文档作为知识库的基础。文档格式大概这样:
swift
swift复制代码{
"content": "DDoS IP高防结合Web应用防火墙方案说明\n=======================\n\n\nDDoS IP高防+Web应用防火墙提供三层到七层安全防护体系,应用场景包括游戏、金融、电商、互联网、政企等京东云内和云外的各类型用户。\n\n\n部署架构\n====\n\n\n[](\"https://jdcloud-portal.oss.cn-north-1.jcloudcs.com/cn/image/Advanced%20Anti-DDoS/Best-Practice02.png\") \n\nDDoS IP高防+Web应用防火墙的最佳部署架构如下:\n\n\n* 京东云的安全调度中心,通过DNS解析,将用户域名解析到DDoS IP高防CNAME。\n* 用户正常访问流量和DDoS攻击流量经过DDoS IP高防清洗,回源至Web应用防火墙。\n* 攻击者恶意请求被Web应用防火墙过滤后返回用户源站。\n* Web应用防火墙可以保护任何公网的服务器,包括但不限于京东云,其他厂商的云,IDC等\n\n\n方案优势\n====\n\n\n1. 用户源站在DDoS IP高防和Web应用防火墙之后,起到隐藏源站IP的作用。\n2. CNAME接入,配置简单,减少运维人员工作。\n\n\n",
"title": "DDoS IP高防结合Web应用防火墙方案说明",
"product": "DDoS IP高防",
"url": "https://docs.jdcloud.com/cn/anti-ddos-pro/anti-ddos-pro-and-waf"
}每条数据是一个包含四个字段的json,这四个字段分别是"content":文档内容;"title":文档标题;"product":相关产品;"url":文档在线地址
向量数据库的选择与Retriever实现
向量数据库是RAG系统的记忆中心。目前市面上开源的向量数据库很多,那个向量库比较好也是见仁见智。本项目中笔者选择则了clickhouse作为向量数据库。选择ck主要有一下几个方面的考虑:
- ck再langchain社区的集成实现比较好,入库比较平滑
- 向量查询支持sql,学习成本较低,上手容易
- 京东云有相关产品且有专业团队支持,用着放心
文档向量化及入库过程
为了简化文档向量化和检索过程,我们使用了longchain的Retriever工具集
首先将文档向量化,代码如下:
ini
ini复制代码from libs.jd_doc_json_loader import JD_DOC_Loader
from langchain_community.document_loaders import DirectoryLoader
root_dir = "/root/jd_docs"
loader = DirectoryLoader(
'/root/jd_docs', glob="**/*.json", loader_cls=JD_DOC_Loader)
docs = loader.load()langchain 社区里并没有提供针对特定格式的装载器,为此,我们自定义了JD_DOC_Loader来实现加载过程
python
python复制代码import json
import logging
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Iterator, Optional, Union
from langchain_core.documents import Document
from langchain_community.document_loaders.base import BaseLoader
from langchain_community.document_loaders.helpers import detect_file_encodings
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class JD_DOC_Loader(BaseLoader):
"""Load text file.
Args:
file_path: Path to the file to load.
encoding: File encoding to use. If `None`, the file will be loaded
with the default system encoding.
autodetect_encoding: Whether to try to autodetect the file encoding
if the specified encoding fails.
"""
def __init__(
self,
file_path: Union[str, Path],
encoding: Optional[str] = None,
autodetect_encoding: bool = False,
):
"""Initialize with file path."""
self.file_path = file_path
self.encoding = encoding
self.autodetect_encoding = autodetect_encoding
def lazy_load(self) -> Iterator[Document]:
"""Load from file path."""
text = ""
from_url = ""
try:
with open(self.file_path, encoding=self.encoding) as f:
doc_data = json.load(f)
text = doc_data["content"]
title = doc_data["title"]
product = doc_data["product"]
from_url = doc_data["url"]
# text = f.read()
except UnicodeDecodeError as e:
if self.autodetect_encoding:
detected_encodings = detect_file_encodings(self.file_path)
for encoding in detected_encodings:
logger.debug(f"Trying encoding: {encoding.encoding}")
try:
with open(self.file_path, encoding=encoding.encoding) as f:
text = f.read()
break
except UnicodeDecodeError:
continue
else:
raise RuntimeError(f"Error loading {self.file_path}") from e
except Exception as e:
raise RuntimeError(f"Error loading {self.file_path}") from e
# metadata = {"source": str(self.file_path)}
metadata = {"source": from_url, "title": title, "product": product}
yield Document(page_content=text, metadata=metadata)以上代码功能主要是解析json文件,填充Document的page_content字段和metadata字段。
接下来使用langchain 的 clickhouse 向量工具集进行文档入库
ini
ini复制代码import langchain_community.vectorstores.clickhouse as clickhouse
from langchain.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
model_kwargs = {"device": "cuda"}
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(
model_name="/root/models/moka-ai-m3e-large", model_kwargs=model_kwargs)
settings = clickhouse.ClickhouseSettings(
table="jd_docs_m3e_with_url", username="default", password="xxxxxx", host="10.0.1.94")
docsearch = clickhouse.Clickhouse.from_documents(
docs, embeddings, config=settings)入库成功后,进行一下检验
ini
ini复制代码import langchain_community.vectorstores.clickhouse as clickhouse
from langchain.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
model_kwargs = {"device": "cuda"}~~~~
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(
model_name="/root/models/moka-ai-m3e-large", model_kwargs=model_kwargs)
settings = clickhouse.ClickhouseSettings(
table="jd_docs_m3e_with_url_splited", username="default", password="xxxx", host="10.0.1.94")
ck_db = clickhouse.Clickhouse(embeddings, config=settings)
ck_retriever = ck_db.as_retriever(
search_type="similarity_score_threshold", search_kwargs={'score_threshold': 0.9})
ck_retriever.get_relevant_documents("如何创建mysql rds")有了知识库以后,可以构建一个简单的restful 服务,我们这里使用fastapi做这个事儿
ini
ini复制代码from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
from singleton_decorator import singleton
from langchain_community.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
import langchain_community.vectorstores.clickhouse as clickhouse
import uvicorn
import json
app = FastAPI()
app = FastAPI(docs_url=None)
app.host = "0.0.0.0"
model_kwargs = {"device": "cuda"}
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(
model_name="/root/models/moka-ai-m3e-large", model_kwargs=model_kwargs)
settings = clickhouse.ClickhouseSettings(
table="jd_docs_m3e_with_url_splited", username="default", password="xxxx", host="10.0.1.94")
ck_db = clickhouse.Clickhouse(embeddings, config=settings)
ck_retriever = ck_db.as_retriever(
search_type="similarity", search_kwargs={"k": 3})
class question(BaseModel):
content: str
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"ok"}
@app.post("/retriever")
async def retriver(question: question):
global ck_retriever
result = ck_retriever.invoke(question.content)
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='retriever_api:app', host="0.0.0.0",
port=8000, reload=True)返回结构大概这样:
swift
swift复制代码[
{
"page_content": "云缓存 Redis--Redis迁移解决方案\n###RedisSyncer 操作步骤\n####数据校验\n```\nwget https://github.com/TraceNature/rediscompare/releases/download/v1.0.0/rediscompare-1.0.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz\nrediscompare compare single2single --saddr \"10.0.1.101:6479\" --spassword \"redistest0102\" --taddr \"10.0.1.102:6479\" --tpassword \"redistest0102\" --comparetimes 3\n\n```\n**Github 地址:** [https://github.com/TraceNature/redissyncer-server](\"https://github.com/TraceNature/redissyncer-server\")",
"metadata": {
"product": "云缓存 Redis",
"source": "https://docs.jdcloud.com/cn/jcs-for-redis/doc-2",
"title": "Redis迁移解决方案"
},
"type": "Document"
},
{
"page_content": "云缓存 Redis--Redis迁移解决方案\n###RedisSyncer 操作步骤\n####数据校验\n```\nwget https://github.com/TraceNature/rediscompare/releases/download/v1.0.0/rediscompare-1.0.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz\nrediscompare compare single2single --saddr \"10.0.1.101:6479\" --spassword \"redistest0102\" --taddr \"10.0.1.102:6479\" --tpassword \"redistest0102\" --comparetimes 3\n\n```\n**Github 地址:** [https://github.com/TraceNature/redissyncer-server](\"https://github.com/TraceNature/redissyncer-server\")",
"metadata": {
"product": "云缓存 Redis",
"source": "https://docs.jdcloud.com/cn/jcs-for-redis/doc-2",
"title": "Redis迁移解决方案"
},
"type": "Document"
},
{
"page_content": "云缓存 Redis--Redis迁移解决方案\n###RedisSyncer 操作步骤\n####数据校验\n```\nwget https://github.com/TraceNature/rediscompare/releases/download/v1.0.0/rediscompare-1.0.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz\nrediscompare compare single2single --saddr \"10.0.1.101:6479\" --spassword \"redistest0102\" --taddr \"10.0.1.102:6479\" --tpassword \"redistest0102\" --comparetimes 3\n\n```\n**Github 地址:** [https://github.com/TraceNature/redissyncer-server](\"https://github.com/TraceNature/redissyncer-server\")",
"metadata": {
"product": "云缓存 Redis",
"source": "https://docs.jdcloud.com/cn/jcs-for-redis/doc-2",
"title": "Redis迁移解决方案"
},
"type": "Document"
}
]返回一个向量距离最小的list
结合模型和prompt,回答问题
为了节约算力资源,我们选择qwen 1.8B模型,一张v100卡刚好可以容纳一个qwen模型和一个m3e-large embedding 模型
- answer 服务
ini
ini复制代码from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
from langchain_community.llms import VLLM
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
import requests
import uvicorn
import json
import logging
app = FastAPI()
app = FastAPI(docs_url=None)
app.host = "0.0.0.0"
logger = logging.getLogger()
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
to_console = logging.StreamHandler()
logger.addHandler(to_console)
# load model
# model_name = "/root/models/Llama3-Chinese-8B-Instruct"
model_name = "/root/models/Qwen1.5-1.8B-Chat"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
llm_llama3 = VLLM(
model=model_name,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
task="text-generation",
temperature=0.2,
do_sample=True,
repetition_penalty=1.1,
return_full_text=False,
max_new_tokens=900,
)
# prompt
prompt_template = """
你是一个云技术专家
使用以下检索到的Context回答问题。
如果不知道答案,就说不知道。
用中文回答问题。
Question: {question}
Context: {context}
Answer:
"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["context", "question"],
template=prompt_template,
)
def get_context_list(q: str):
url = "http://10.0.0.7:8000/retriever"
payload = {"content": q}
res = requests.post(url, json=payload)
return res.text
class question(BaseModel):
content: str
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"ok"}
@app.post("/answer")
async def answer(q: question):
logger.info("invoke!!!")
global prompt
global llm_llama3
context_list_str = get_context_list(q.content)
context_list = json.loads(context_list_str)
context = ""
source_list = []
for context_json in context_list:
context = context+context_json["page_content"]
source_list.append(context_json["metadata"]["source"])
p = prompt.format(context=context, question=q.content)
answer = llm_llama3(p)
result = {
"answer": answer,
"sources": source_list
}
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
uvicorn.run(app='retriever_api:app', host="0.0.0.0",
port=8888, reload=True)代码通过使用Retriever接口查找与问题相似的文档,作为context组合prompt推送给模型生成答案。
主要服务就绪后可以开始画一张脸了,使用gradio做个简易对话界面
- gradio 服务
ini
ini复制代码import json
import gradio as gr
import requests
def greet(name, intensity):
return "Hello, " + name + "!" * int(intensity)
def answer(question):
url = "http://127.0.0.1:8888/answer"
payload = {"content": question}
res = requests.post(url, json=payload)
res_json = json.loads(res.text)
return [res_json["answer"], res_json["sources"]]
demo = gr.Interface(
fn=answer,
# inputs=["text", "slider"],
inputs=[gr.Textbox(label="question", lines=5)],
# outputs=[gr.TextArea(label="answer", lines=5),
# gr.JSON(label="urls", value=list)]
outputs=[gr.Markdown(label="answer"),
gr.JSON(label="urls", value=list)]
)
demo.launch(server_name="0.0.0.0")如何学习大模型 AI ?
由于新岗位的生产效率,要优于被取代岗位的生产效率,所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。
但是具体到个人,只能说是:
"最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势"。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在人工智能学习中的很多困惑,所以在工作繁忙的情况下还是坚持各种整理和分享。但苦于知识传播途径有限,很多互联网行业朋友无法获得正确的资料得到学习提升,故此将并将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。
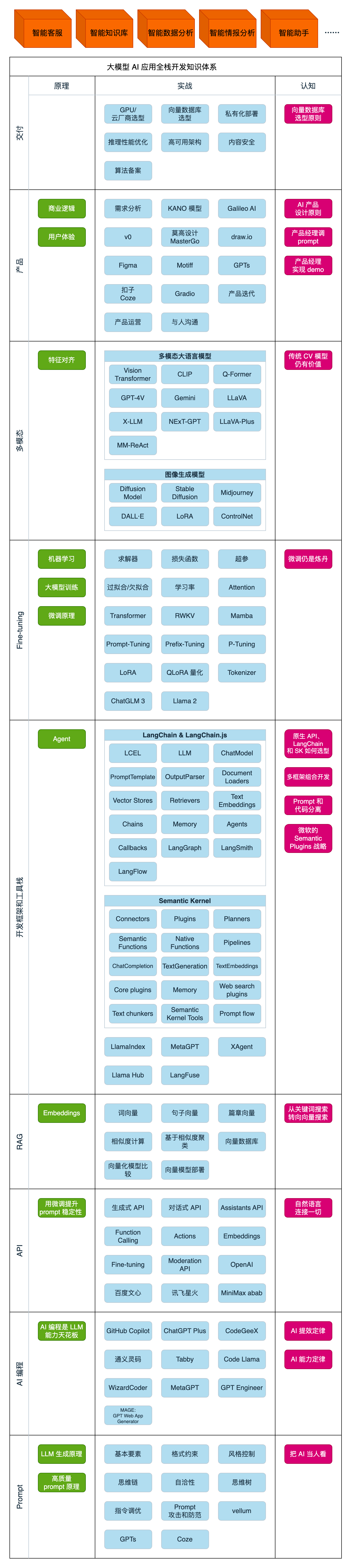
第一阶段(10天):初阶应用
该阶段让大家对大模型 AI有一个最前沿的认识,对大模型 AI 的理解超过 95% 的人,可以在相关讨论时发表高级、不跟风、又接地气的见解,别人只会和 AI 聊天,而你能调教 AI,并能用代码将大模型和业务衔接。
- 大模型 AI 能干什么?
- 大模型是怎样获得「智能」的?
- 用好 AI 的核心心法
- 大模型应用业务架构
- 大模型应用技术架构
- 代码示例:向 GPT-3.5 灌入新知识
- 提示工程的意义和核心思想
- Prompt 典型构成
- 指令调优方法论
- 思维链和思维树
- Prompt 攻击和防范
- ...
第二阶段(30天):高阶应用
该阶段我们正式进入大模型 AI 进阶实战学习,学会构造私有知识库,扩展 AI 的能力。快速开发一个完整的基于 agent 对话机器人。掌握功能最强的大模型开发框架,抓住最新的技术进展,适合 Python 和 JavaScript 程序员。
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 搭建一个简单的 ChatPDF
- 检索的基础概念
- 什么是向量表示(Embeddings)
- 向量数据库与向量检索
- 基于向量检索的 RAG
- 搭建 RAG 系统的扩展知识
- 混合检索与 RAG-Fusion 简介
- 向量模型本地部署
- ...
第三阶段(30天):模型训练
恭喜你,如果学到这里,你基本可以找到一份大模型 AI相关的工作,自己也能训练 GPT 了!通过微调,训练自己的垂直大模型,能独立训练开源多模态大模型,掌握更多技术方案。
到此为止,大概2个月的时间。你已经成为了一名"AI小子"。那么你还想往下探索吗?
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 什么是模型
- 什么是模型训练
- 求解器 & 损失函数简介
- 小实验2:手写一个简单的神经网络并训练它
- 什么是训练/预训练/微调/轻量化微调
- Transformer结构简介
- 轻量化微调
- 实验数据集的构建
- ...
第四阶段(20天):商业闭环
对全球大模型从性能、吞吐量、成本等方面有一定的认知,可以在云端和本地等多种环境下部署大模型,找到适合自己的项目/创业方向,做一名被 AI 武装的产品经理。
- 硬件选型
- 带你了解全球大模型
- 使用国产大模型服务
- 搭建 OpenAI 代理
- 热身:基于阿里云 PAI 部署 Stable Diffusion
- 在本地计算机运行大模型
- 大模型的私有化部署
- 基于 vLLM 部署大模型
- 案例:如何优雅地在阿里云私有部署开源大模型
- 部署一套开源 LLM 项目
- 内容安全
- 互联网信息服务算法备案
- ...
学习是一个过程,只要学习就会有挑战。天道酬勤,你越努力,就会成为越优秀的自己。
如果你能在15天内完成所有的任务,那你堪称天才。然而,如果你能完成 60-70% 的内容,你就已经开始具备成为一名大模型 AI 的正确特征了。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传CSDN,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方CSDN官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】
