欢迎来到 Papicatch的博客

文章目录
🍉引言
人工神经网络(Artificial Neural Networks, ANN)是一种受生物神经系统启发的计算模型,能够学习和执行复杂的非线性映射任务。本文将深入探讨神经元、感知器、损失函数、梯度下降算法、多层感知器(MLP)、激活函数、反向传播算法,并通过实例展示如何手工搭建一个神经网络。
🍉神经元与感知器
🍈神经元(Neuron)
神经元是神经网络的基本单元,模仿生物神经元的结构和功能。它接收来自其他神经元或外部输入的信号,通过加权求和和激活函数转换后输出结果。
一个简单的神经元模型如下:

其中,𝑥𝑖xi 是输入信号,𝑤𝑖wi 是对应的权重,𝑏b 是偏置项,𝜎σ 是激活函数,如 sigmoid、ReLU 等。
🍈感知器
感知器模型结构:

🍈感知器实现and函数
逻辑运算and的真值表
| x1 | x2 | y(and运行结果) |
|---|---|---|
| 0(假) | 0(假) | 0(假) |
| 0(假) | 1(真) | 0(假) |
| 1(真) | 0(假) | 0(假) |
| 1(真) | 1(真) | 1(真) |
🍈代码实现
python
# 定义AND运算的函数
def AND(a, b):
return a & b
# 真值表的输入组合
inputs = [
(0, 0),
(0, 1),
(1, 0),
(1, 1)
]
# 打印真值表
print("A | B | A AND B")
print("---|---|-------")
for a, b in inputs:
result = AND(a, b)
print(f" {a} | {b} | {result}")
感知器(Perceptron)是最简单的神经网络形式,包含一个单层神经元,直接将输入映射到输出,通常用于二分类问题。
🍉损失函数与梯度下降算法
🍈损失函数
损失函数(Loss Function)衡量神经网络预测值与实际标签之间的差异。
常见的损失函数包括:
- 均方误差(Mean Squared Error, MSE):适用于回归问题。
- 交叉熵损失函数(Cross-Entropy Loss):适用于分类问题。
🍈梯度下降算法
梯度下降算法通过最小化损失函数来优化神经网络的参数。核心思想是沿着损失函数梯度的反方向更新权重和偏置,从而逐步改进模型的预测能力。
具体步骤如下:
- 计算损失函数的梯度:使用反向传播算法计算每个参数对损失函数的影响。
- 更新权重和偏置:通过学习率(learning rate)控制更新步长,减小损失函数值。

🍉多层感知器与神经网络
异或(XOR)问题是经典的逻辑运算问题,感知器不能拟合出一条直线将结果分开。要将二者分开,必须采用封闭式的曲线才行。多层感知器可以实现。
异或(XOR)真值表
| A | 𝐵B | 𝐴 XOR 𝐵A XOR B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义激活函数(sigmoid)及其导数
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def sigmoid_derivative(x):
return x * (1 - x)
# 输入数据和目标输出
inputs = np.array([[0, 0],
[0, 1],
[1, 0],
[1, 1]])
expected_output = np.array([[0],
[1],
[1],
[0]])
# 初始化参数
input_layer_neurons = inputs.shape[1]
hidden_layer_neurons = 2
output_neurons = 1
# 初始化权重和偏置
hidden_weights = np.random.uniform(size=(input_layer_neurons, hidden_layer_neurons))
hidden_bias = np.random.uniform(size=(1, hidden_layer_neurons))
output_weights = np.random.uniform(size=(hidden_layer_neurons, output_neurons))
output_bias = np.random.uniform(size=(1, output_neurons))
# 设置学习率和迭代次数
learning_rate = 0.1
epochs = 10000
error_history = []
# 训练神经网络
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 前向传播
hidden_layer_activation = np.dot(inputs, hidden_weights)
hidden_layer_activation += hidden_bias
hidden_layer_output = sigmoid(hidden_layer_activation)
output_layer_activation = np.dot(hidden_layer_output, output_weights)
output_layer_activation += output_bias
predicted_output = sigmoid(output_layer_activation)
# 计算误差
error = expected_output - predicted_output
error_history.append(np.mean(np.abs(error)))
d_predicted_output = error * sigmoid_derivative(predicted_output)
# 反向传播
error_hidden_layer = d_predicted_output.dot(output_weights.T)
d_hidden_layer = error_hidden_layer * sigmoid_derivative(hidden_layer_output)
# 更新权重和偏置
output_weights += hidden_layer_output.T.dot(d_predicted_output) * learning_rate
output_bias += np.sum(d_predicted_output, axis=0, keepdims=True) * learning_rate
hidden_weights += inputs.T.dot(d_hidden_layer) * learning_rate
hidden_bias += np.sum(d_hidden_layer, axis=0, keepdims=True) * learning_rate
# 打印结果
print("Final hidden weights: ", hidden_weights)
print("Final hidden bias: ", hidden_bias)
print("Final output weights: ", output_weights)
print("Final output bias: ", output_bias)
print("Predicted output: ", predicted_output)
# 绘制误差下降图
plt.plot(error_history)
plt.title('Error History')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Error')
plt.show()
# 绘制神经网络预测结果图
def plot_decision_boundary(X, y, model, title):
x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.1),
np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.1))
Z = model(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.8)
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y.flatten(), s=40, edgecolor='k')
plt.title(title)
plt.show()
# 定义预测函数
def predict(X):
hidden_layer_activation = np.dot(X, hidden_weights) + hidden_bias
hidden_layer_output = sigmoid(hidden_layer_activation)
output_layer_activation = np.dot(hidden_layer_output, output_weights) + output_bias
predicted_output = sigmoid(output_layer_activation)
return np.round(predicted_output)
# 绘制决策边界
plot_decision_boundary(inputs, expected_output, predict, 'XOR Decision Boundary')

🍈多层感知器(MLP)
多层感知器(MLP)是一种前向结构的神经网络,由多个全连接隐藏层和至少一个输出层组成。
每个神经元在每层中执行以下步骤:
- 线性变换:计算加权输入的和。
- 非线性变换(激活函数):通过激活函数如 sigmoid、ReLU 将结果映射到非线性空间。
🍈激活函数
激活函数是神经网络中每个神经元的非线性映射函数,常见的有:
Sigmoid 函数:将输入值压缩到0到1之间。

ReLU 函数:对于正数输入,返回输入值本身;对于负数输入,返回0。

🍈反向传播算法
反向传播算法是训练神经网络的核心技术,通过链式法则计算损失函数相对于每个参数的梯度,并将梯度传播回网络以更新权重和偏置。
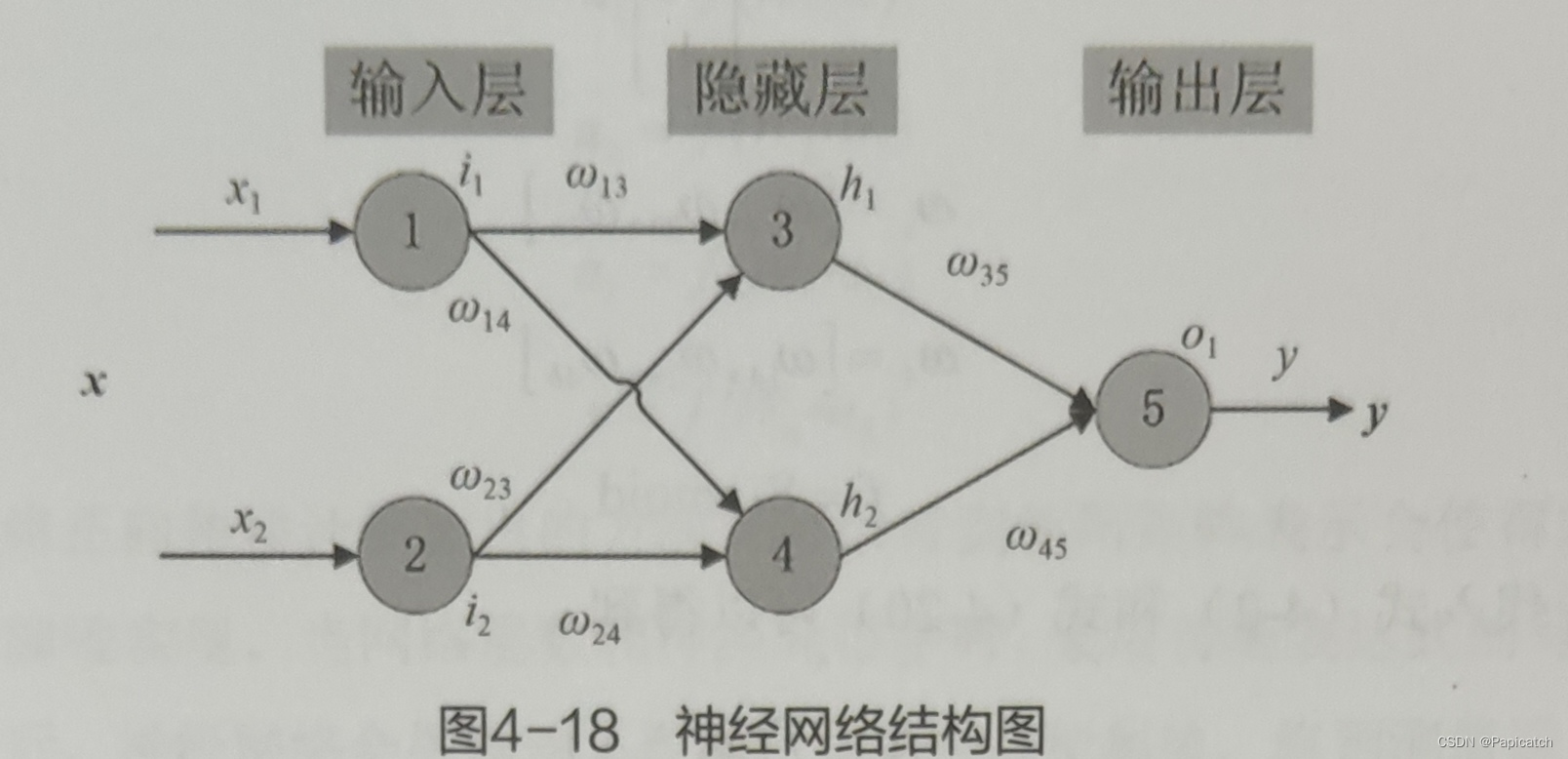
🍉实例

三层神经网络结构
🍈手工搭建神经网络
以下是一个简单的 Python 示例代码,演示如何手工实现一个包含单隐藏层的多层感知器,并训练它解决 XOR 问题。
python
import numpy as np
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):
self.weights1 = np.random.randn(input_size, hidden_size)
self.bias1 = np.zeros((1, hidden_size))
self.weights2 = np.random.randn(hidden_size, output_size)
self.bias2 = np.zeros((1, output_size))
def sigmoid(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def sigmoid_derivative(self, x):
return x * (1 - x)
def forward_pass(self, X):
self.hidden_layer_input = np.dot(X, self.weights1) + self.bias1
self.hidden_layer_output = self.sigmoid(self.hidden_layer_input)
self.output_layer_input = np.dot(self.hidden_layer_output, self.weights2) + self.bias2
self.output = self.sigmoid(self.output_layer_input)
return self.output
def backward_pass(self, X, y, output):
self.output_error = y - output
self.output_delta = self.output_error * self.sigmoid_derivative(output)
self.hidden_layer_error = np.dot(self.output_delta, self.weights2.T)
self.hidden_layer_delta = self.hidden_layer_error * self.sigmoid_derivative(self.hidden_layer_output)
self.weights2 += np.dot(self.hidden_layer_output.T, self.output_delta)
self.bias2 += np.sum(self.output_delta, axis=0, keepdims=True)
self.weights1 += np.dot(X.T, self.hidden_layer_delta)
self.bias1 += np.sum(self.hidden_layer_delta, axis=0, keepdims=True)
def train(self, X, y, epochs):
for epoch in range(epochs):
output = self.forward_pass(X)
self.backward_pass(X, y, output)
if epoch % 1000 == 0:
print(f'Epoch {epoch}, Loss: {np.mean(np.square(y - output))}')
if __name__ == "__main__":
input_size = 2
hidden_size = 3
output_size = 1
nn = NeuralNetwork(input_size, hidden_size, output_size)
X = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]])
y = np.array([[0], [1], [1], [0]])
nn.train(X, y, epochs=10000)
print('Final predictions:')
print(nn.forward_pass(X))
🍉总结
本文详细讲解了人工神经网络的核心组成部分和关键技术。从神经元、感知器到多层感知器的演进,再到损失函数、梯度下降算法和反向传播算法的实际应用,读者可以全面理解神经网络的工作原理及其在实际问题中的应用。通过手工搭建神经网络的示例,读者不仅能够加深对神经网络内部运作的理解,还能够通过修改和扩展代码来探索更复杂的神经网络结构和任务。神经网络作为深度学习的基础,对于理解和实践现代机器学习技术具有重要意义。

希望能给大家提供一些帮助!!!
