1.NMS
def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh):
"""Pure Python NMS baseline."""
#x1、y1、x2、y2、以及score赋值
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = dets[:, 4]
#每一个检测框的面积
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
#按照score置信度降序排序
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = [] #保留的结果框集合
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i) #保留该类剩余box中得分最高的一个
#得到相交区域,左上及右下
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
#计算相交的面积,不重叠时面积为0
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
#计算IoU:重叠面积 /(面积1+面积2-重叠面积)
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
#保留IoU小于阈值的box
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
order = order[inds + 1] #因为ovr数组的长度比order数组少一个,所以这里要将所有下标后移一位
return keep2.交叉熵损失函数
实际输出(概率)与期望输出(概率)的距离,也就是 交叉熵的值越小,两个概率分布就越接近。
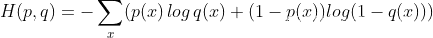
a.Python 实现
def cross_entropy(a, y):
return np.sum(np.nan_to_num(-y*np.log(a)-(1-y)*np.log(1-a)))
b.# tensorflow version
loss = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y), reduction_indices=[1]))
c.# numpy version
loss = np.mean(-np.sum(y_*np.log(y), axis=1))
3.Softmax 函数
将激活值与所有神经元的输出值联系在一起,所有神经元的激活值加起来为1。
第L层(最后一层)的第j个神经元的激活输出为:
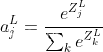
Python 实现:
def softmax(x):
shift_x = x - np.max(x) # 防止输入增大时输出为nan
exp_x = np.exp(shift_x)
return exp_x / np.sum(exp_x)
4.iou
def IoU(box1, box2) -> float:
"""
IOU, Intersection over Union
:param box1: list, 第一个框的两个坐标点位置 box1[x1, y1, x2, y2]
:param box2: list, 第二个框的两个坐标点位置 box2[x1, y1, x2, y2]
:return: float, 交并比
"""
weight = max(min(box1[2], box2[2]) - max(box1[0], box2[0]), 0)
height = max(min(box1[3], box2[3]) - max(box1[1], box2[1]), 0)
s_inter = weight * height
s_box1 = (box1[2] - box1[0]) * (box1[3] - box1[1])
s_box2 = (box2[2] - box2[0]) * (box2[3] - box2[1])
s_union = s_box1 + s_box2 - s_inter
return s_inter / s_union
if name == 'main':
box1 = [0, 0, 50, 50]
box2 = [0, 0, 100, 100]
print('IoU is %f' % IoU(box1, box2))
5. 将一维数组转变成二维数组
python
class Solution:
def construct2DArray(self, original: List[int], m: int, n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
return [original[i: i + n] for i in range(0, len(original), n)] if len(original) == m * n else []6.MAP
AP衡量的是对一个类检测好坏,mAP就是对多个类的检测好坏。就是简单粗暴的把所有类的AP值取平均就好了。比如有两类,类A的AP值是0.5,类B的AP值是0.2,那么mAP=(0.5+0.2)/2=0.35
# AP的计算
def _average_precision(self, rec, prec):
"""
Params:
----------
rec : numpy.array
cumulated recall
prec : numpy.array
cumulated precision
Returns:
----------
ap as float
"""
if rec is None or prec is None:
return np.nan
ap = 0.
for t in np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1): #十一个点的召回率,对应精度最大值
if np.sum(rec >= t) == 0:
p = 0
else:
p = np.max(np.nan_to_num(prec)[rec >= t])
ap += p / 11. #加权平均
return ap7.手写conv2d
python
class Conv2D(Layer):
"""A 2D Convolution Layer.
Parameters:
-----------
n_filters: int
The number of filters that will convolve over the input matrix. The number of channels
of the output shape.
filter_shape: tuple
A tuple (filter_height, filter_width).
input_shape: tuple
The shape of the expected input of the layer. (batch_size, channels, height, width)
Only needs to be specified for first layer in the network.
padding: string
Either 'same' or 'valid'. 'same' results in padding being added so that the output height and width
matches the input height and width. For 'valid' no padding is added.
stride: int
The stride length of the filters during the convolution over the input.
"""
def __init__(self, n_filters, filter_shape, input_shape=None, padding='same', stride=1):
self.n_filters = n_filters
self.filter_shape = filter_shape
self.padding = padding
self.stride = stride
self.input_shape = input_shape
self.trainable = True
def initialize(self, optimizer):
# Initialize the weights
filter_height, filter_width = self.filter_shape
channels = self.input_shape[0]
limit = 1 / math.sqrt(np.prod(self.filter_shape))
self.W = np.random.uniform(-limit, limit, size=(self.n_filters, channels, filter_height, filter_width))
self.w0 = np.zeros((self.n_filters, 1))
# Weight optimizers
self.W_opt = copy.copy(optimizer)
self.w0_opt = copy.copy(optimizer)
def parameters(self):
return np.prod(self.W.shape) + np.prod(self.w0.shape)
def forward_pass(self, X, training=True):
batch_size, channels, height, width = X.shape
self.layer_input = X
# Turn image shape into column shape
# (enables dot product between input and weights)
self.X_col = image_to_column(X, self.filter_shape, stride=self.stride, output_shape=self.padding)
# Turn weights into column shape
self.W_col = self.W.reshape((self.n_filters, -1))
# Calculate output
output = self.W_col.dot(self.X_col) + self.w0
# Reshape into (n_filters, out_height, out_width, batch_size)
output = output.reshape(self.output_shape() + (batch_size, ))
# Redistribute axises so that batch size comes first
return output.transpose(3,0,1,2)
def backward_pass(self, accum_grad):
# Reshape accumulated gradient into column shape
accum_grad = accum_grad.transpose(1, 2, 3, 0).reshape(self.n_filters, -1)
if self.trainable:
# Take dot product between column shaped accum. gradient and column shape
# layer input to determine the gradient at the layer with respect to layer weights
grad_w = accum_grad.dot(self.X_col.T).reshape(self.W.shape)
# The gradient with respect to bias terms is the sum similarly to in Dense layer
grad_w0 = np.sum(accum_grad, axis=1, keepdims=True)
# Update the layers weights
self.W = self.W_opt.update(self.W, grad_w)
self.w0 = self.w0_opt.update(self.w0, grad_w0)
# Recalculate the gradient which will be propogated back to prev. layer
accum_grad = self.W_col.T.dot(accum_grad)
# Reshape from column shape to image shape
accum_grad = column_to_image(accum_grad,
self.layer_input.shape,
self.filter_shape,
stride=self.stride,
output_shape=self.padding)
return accum_grad
def output_shape(self):
channels, height, width = self.input_shape
pad_h, pad_w = determine_padding(self.filter_shape, output_shape=self.padding)
output_height = (height + np.sum(pad_h) - self.filter_shape[0]) / self.stride + 1
output_width = (width + np.sum(pad_w) - self.filter_shape[1]) / self.stride + 1
return self.n_filters, int(output_height), int(output_width)8.手写PyTorch加载和保存模型
仅保存和加载模型参数(推荐)
a.保存模型参数
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128, 16), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(16, 1))
保存整个模型
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'sample_model.pt')
加载模型参数
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
下载模型参数 并放到模型中
loaded_model = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128, 16), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(16, 1))
loaded_model.load_state_dict(torch.load('sample_model.pt'))
print(loaded_model)
显示如下:
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=16, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=1, bias=True)
)
state_dict:PyTorch中的state_dict是一个python字典对象,将每个层映射到其参数Tensor。state_dict对象存储模型的可学习参数,即权重和偏差,并且可以非常容易地序列化和保存。
b. 保存和加载整个模型
保存整个模型
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(128, 16), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(16, 1))
保存整个模型,包含模型结构和参数
torch.save(net, 'sample_model.pt')
#加载整个模型
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
加载整个模型,包含模型结构和参数
loaded_model = torch.load('sample_model.pt')
print(loaded_model)
显示如下:
Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=128, out_features=16, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=1, bias=True)
)