一,前言
这是一个关于从电脑安装深度学习环境到实现YOLOv8目标检测在RK3588上部署的全过程。
本人配置:
1,一台笔记本
2,一个香橙派5s
二,深度学习环境配置
2.1 安装anaconda
使用清华镜像源下载https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/archive/根据自己的电脑选择下载安装
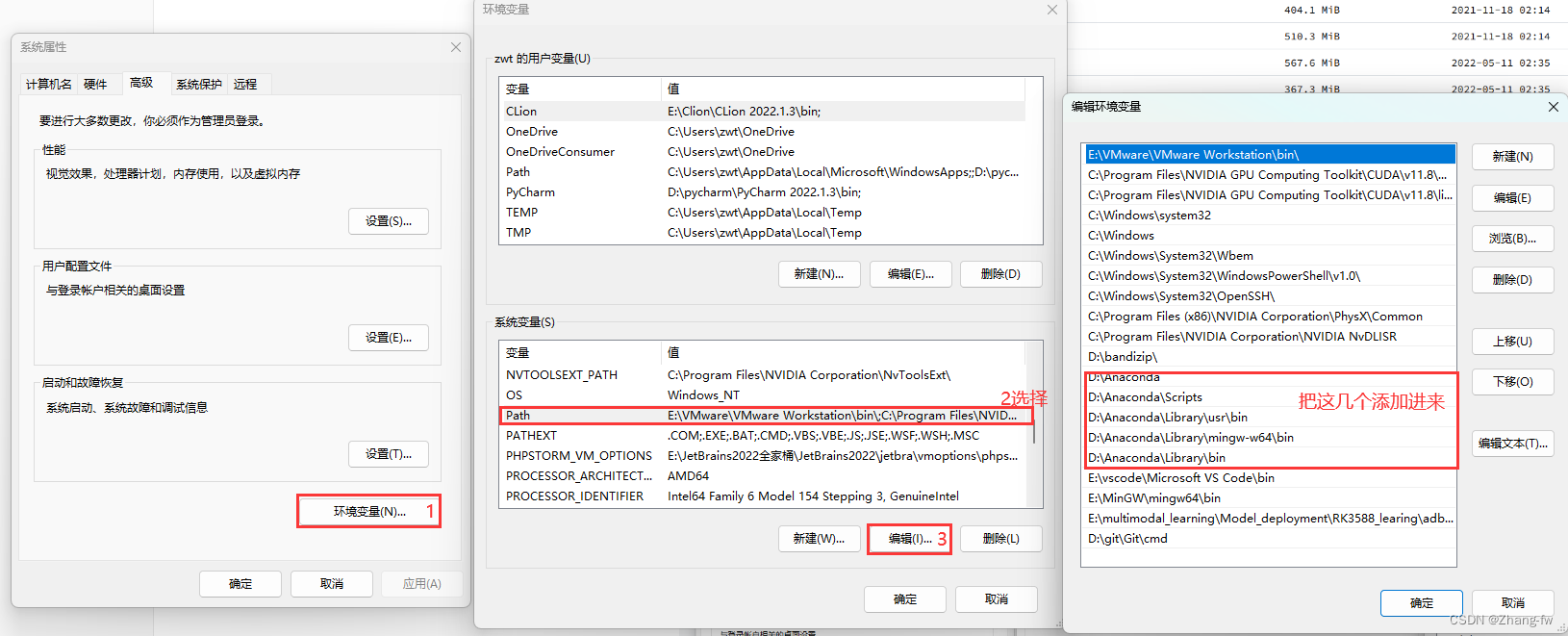
安装之后把下面几个Anaconda的环境变量添加进系统变量中。
2.2 安装Pycharm
去Pycharm官网下载https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/download/,有专业版(收费)和社区版。

2.3 安装CUDA与cuDNN
参考https://blog.csdn.net/zyq880625/article/details/138086225
2.3.1安装CUDA
win+R打开cmd,输入nvidia-smi来查看自己可以安装的CUDA版本(不能超过12.2)。
nvidia-smi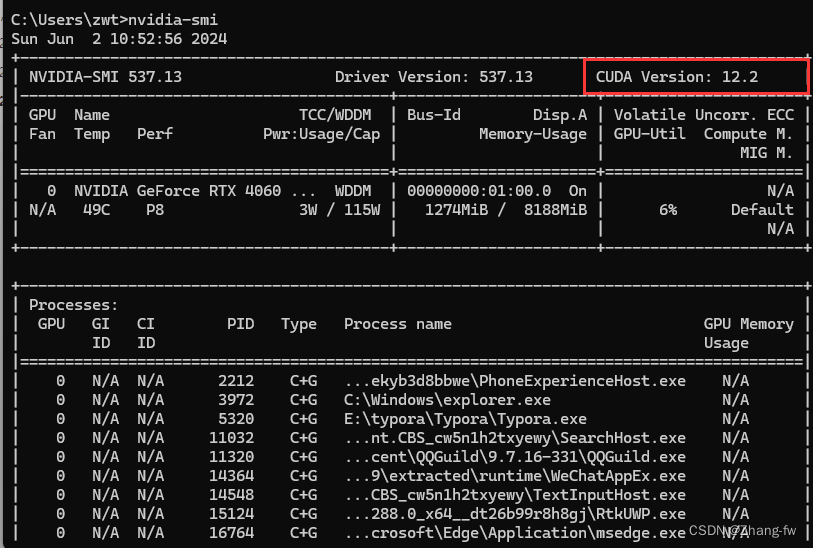
CUDA下载地址CUDA Toolkit Archive | NVIDIA Developer,选择一个不高与自己CUDA的版本,然后进入选择自己电脑的配置最后下载安装。

安装过程
1、双击下载的EXE安装包,开始安装;
2、提取安装文件的(临时)存放位置,保持默认,点击OK,等待文件提取完成;
3、等待检查系统兼容性;
4、许可协议,点击同意并继续;
5、如果是第一次安装,选择精简(精简版本是下载好所有组件,并且会覆盖原有驱动),一直点击下一步即可,安装完成关闭即可;
查看是否安装成功
在cmd中输入nvcc -V
nvcc -V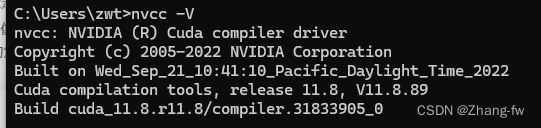
2.3.2 安装cuDNN
去cuDNN Archive | NVIDIA Developer选择与自己CUDA合适的版本下载,下载后将压缩包解压
将解压后的文件夹中的bin、include、lib 三个文件夹,移动到CUDA Development 安装路径下,
与同名文件夹合并。
CUDA Development 默认安装路径:
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.0添加至系统变量:
往系统环境变量中的 path 添加如下路径(根据自己的路径进行修改)
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.0\bin
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.0\include
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.0\lib
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.0\libnvvp2.4 安装GPU版本的Pytorch
打开 Anaconda prompt
使用 conda create -n 虚拟环境名字 虚拟环境的python版本 来创建虚拟环境
conda create -n pytorch python=3.9创建完虚拟环境后,再激活虚拟环境,,左边括号表示现在所处的环境
conda activate pytorch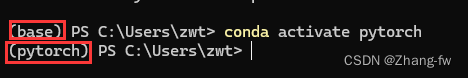
pytorch 的下载链接:download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html,torch,torchvision的对应关系如下
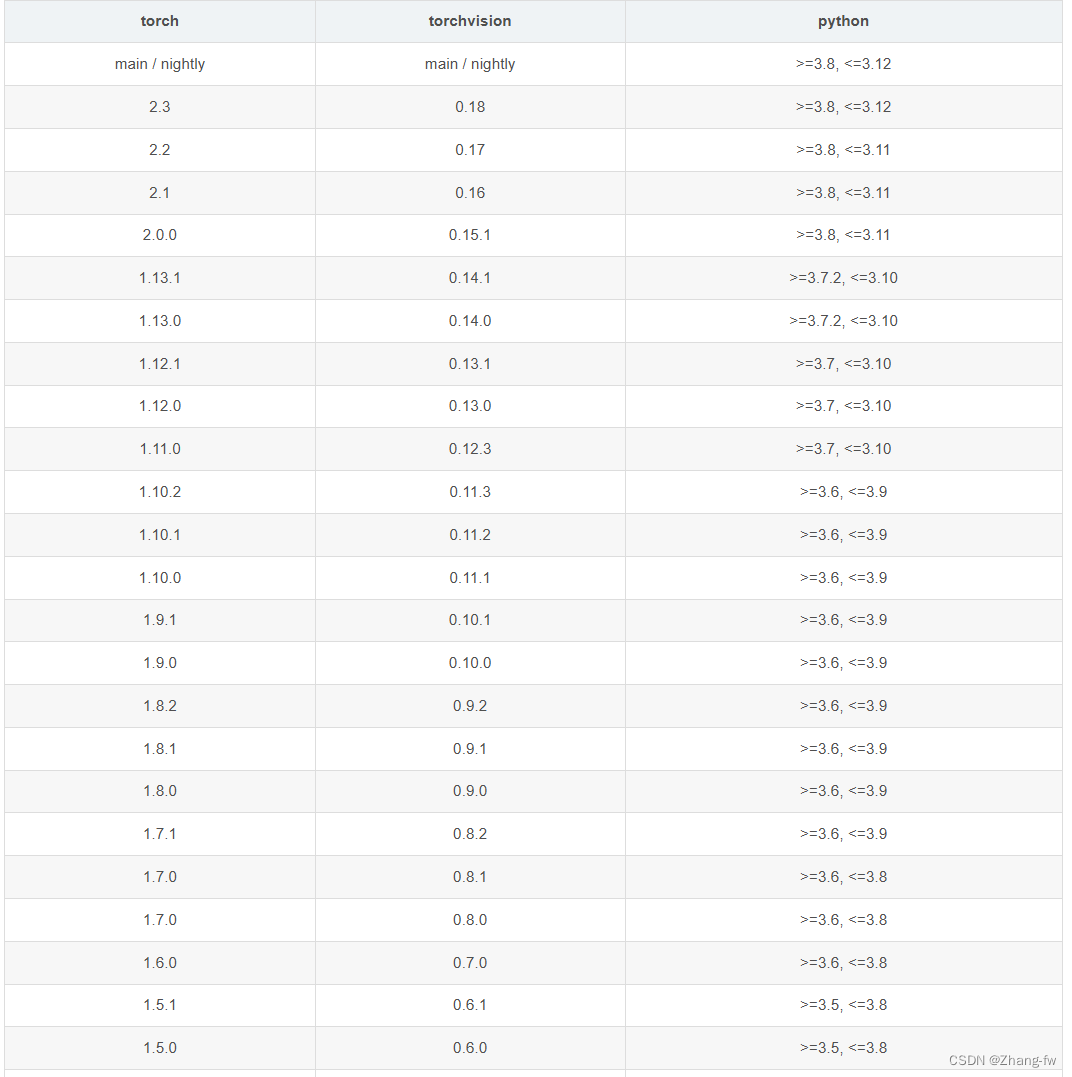
因为我创建的pytorch环境的python是3.9所以我选择的是torch=2.0.0,torchvision=0.15.1
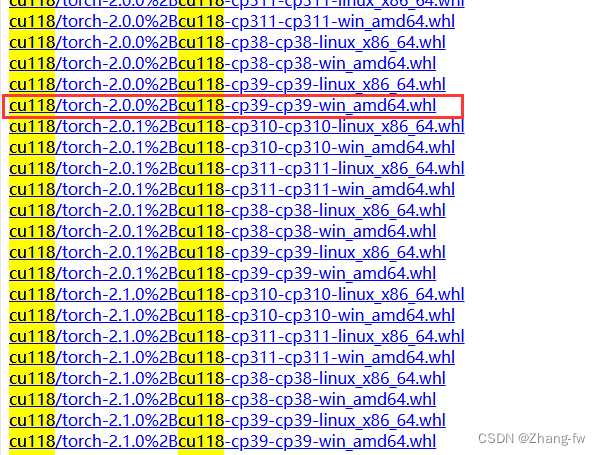

下载完成后在Anaconda prompt使用下面命令安装
pip install torch-2.0.0+cu118-cp39-cp39-win_amd64.whl
pip install torchvision-0.15.1+cu118-cp39-cp39-win_amd64.whl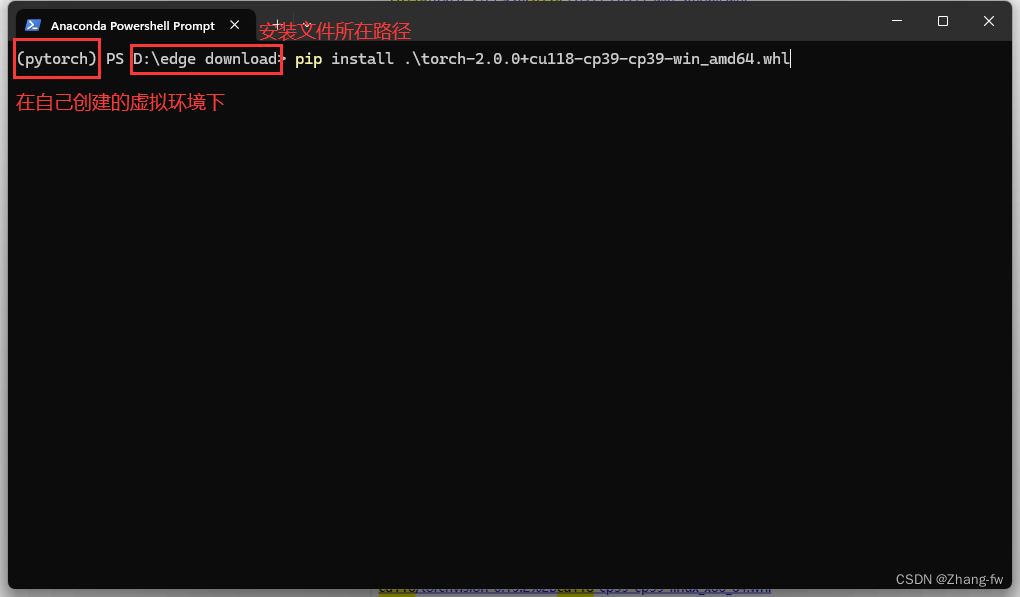
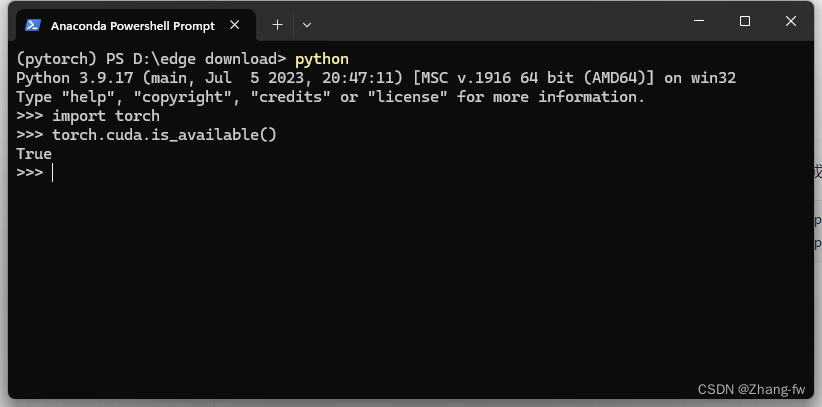
安装完成后在Anaconda prompt中打开python,使用下面命令查看是否可以使用GPU。
python
import torch
torch.cuda.is_available()返回True则表示安装成功。
三,训练自己的模型
3.1 YOLO环境配置
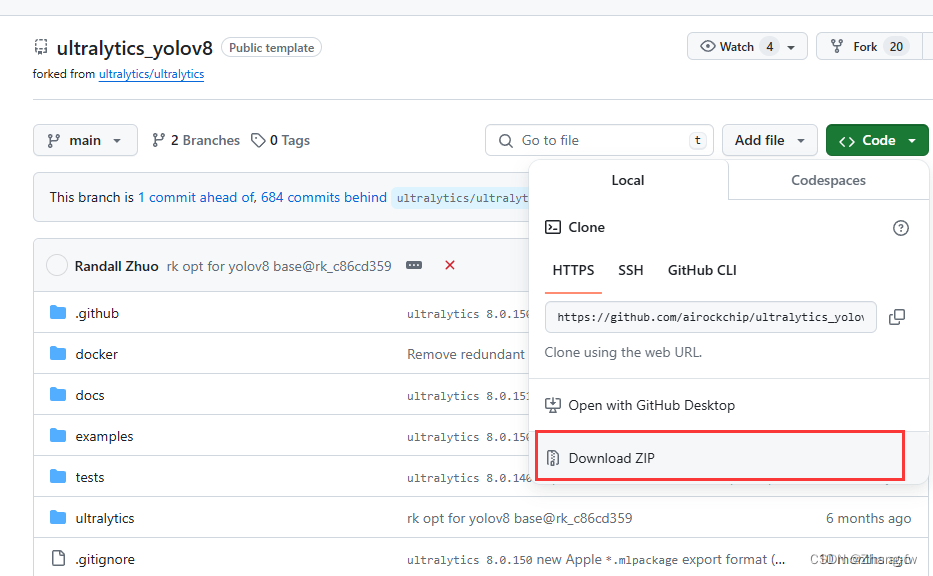
下载瑞星微 提供的工程https://github.com/airockchip/ultralytics_yolov8.git,**不要使用YOLO官方提供的**,下载完成后解压
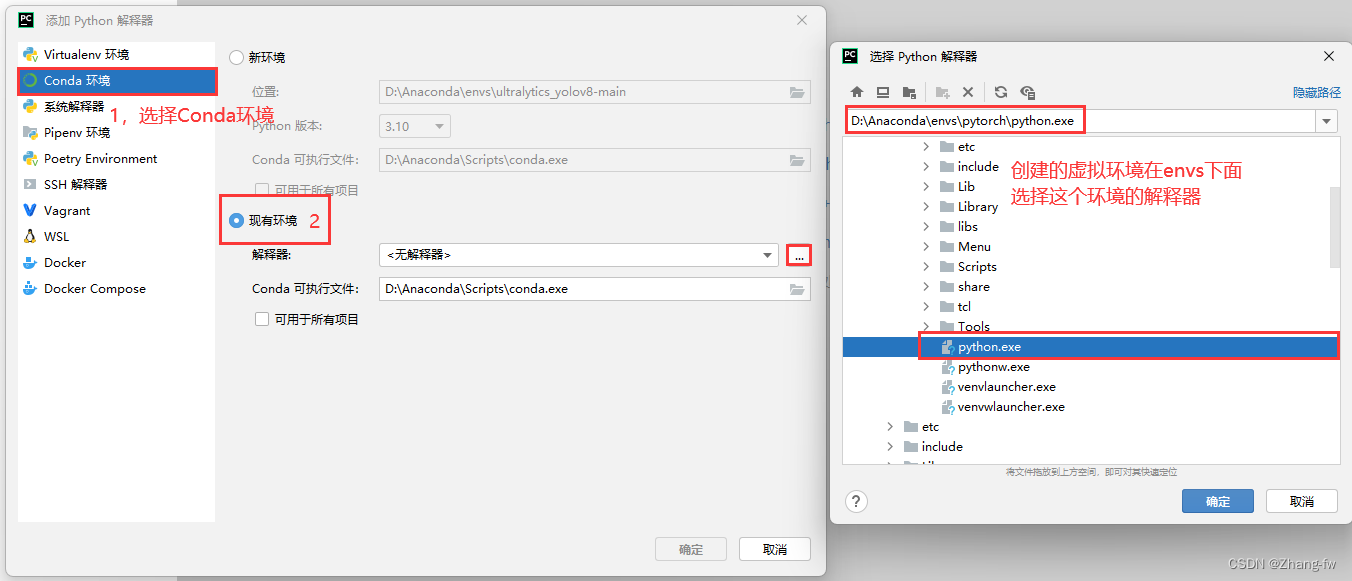
使用Pycharm打开刚才解压的工程文件如下所示,然后点击右下角选择添加解释器
找到自己Anaconda的位置,然后选择自己创建的环境的解释器。
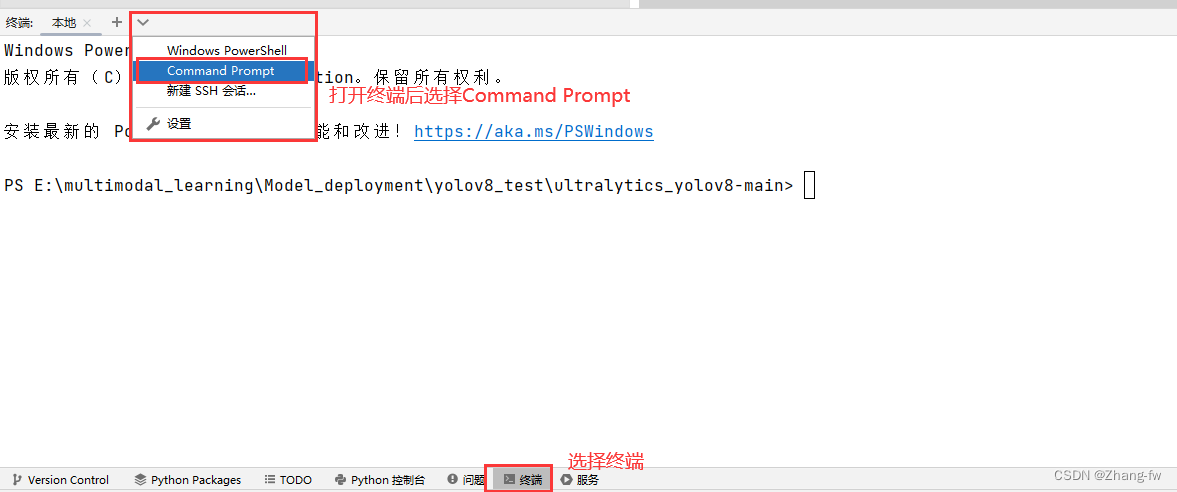
在下方点开终端选择Command Prompt就可以执行Anaconda prompt下的操作
使用下面的命令安装YOLOv8需要的依赖
pip install ultralytics 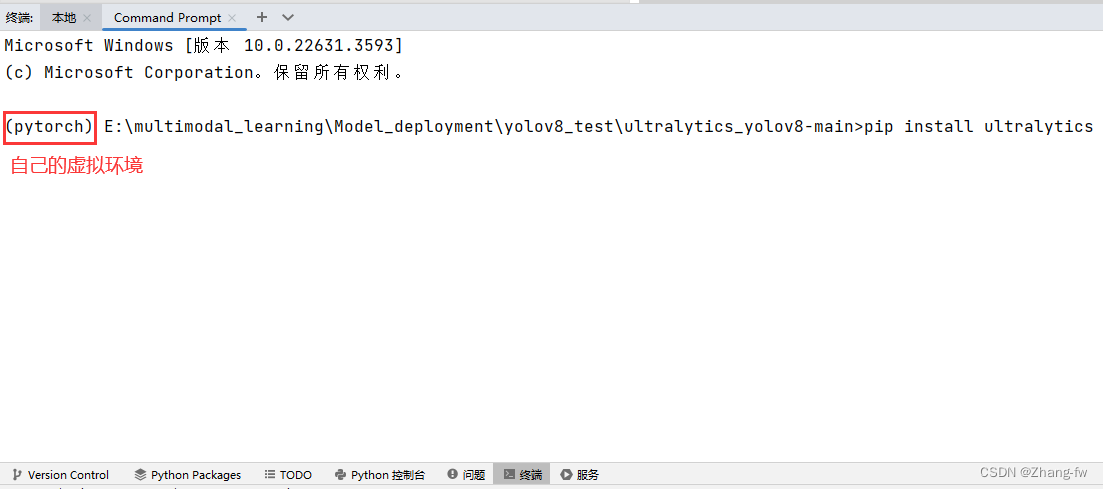
3.2 训练自己的数据集
3.2.1 数据集制作
在工程下面新建一个my_dataset文件夹用来存放数据集的图片images和标签labels。train和va和test的比例通常为8:1:1
my_dataset
│
└───images
│ train
│ val
│ test
│
└───labels
│ train
│ val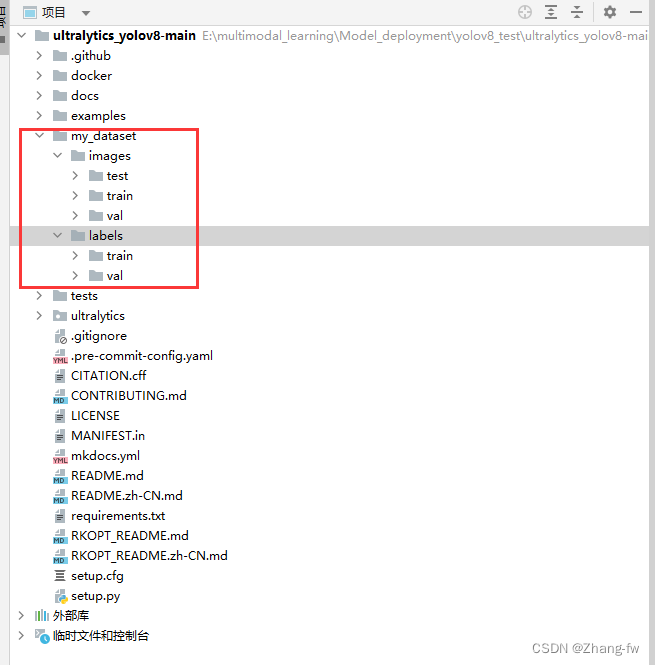
若有其他格式的标签可以网上找代码转换成YOLO格式的,也可以使用labelimg进行数据集进行标注
安装labelimg
pip install labelimg在终端输入下面命令直接打开
labelimg


标记完成后可以打开标签文件查看
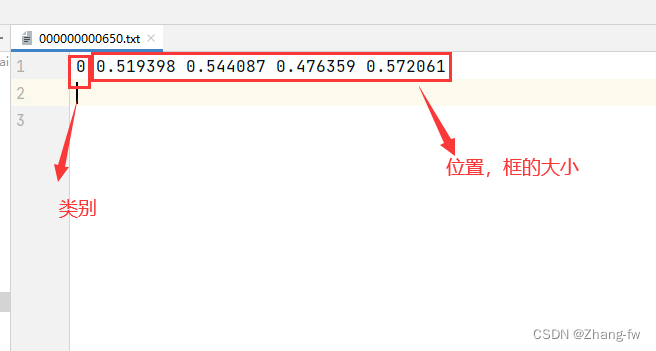
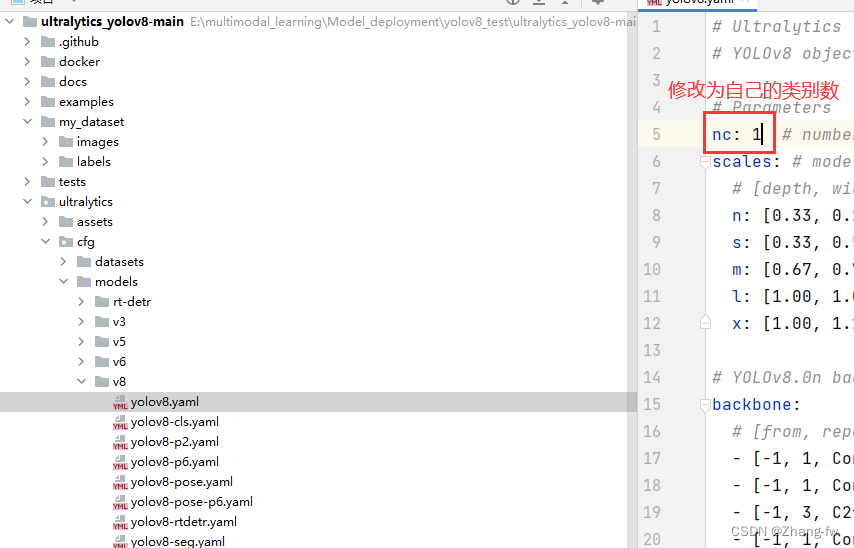
3.2.2 修改配置文件
修改ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/yolov8.yaml文件中的nc为自己的类别数
ultralytics_yolov8-main/ultralytics/cfg/datasets下新建my_dataset.yaml,与文件夹下其他yaml内容文件类似指明训练,验证的路径和自己类别的标签
python
path: E:/multimodal_learning/Model_deployment/yolov8_test/ultralytics_yolov8-main/my_dataset # dataset root dir
train: ./images/train
val: ./images/val
test: ./images/test
# Classes 修改为自己的标签
names:
0: cat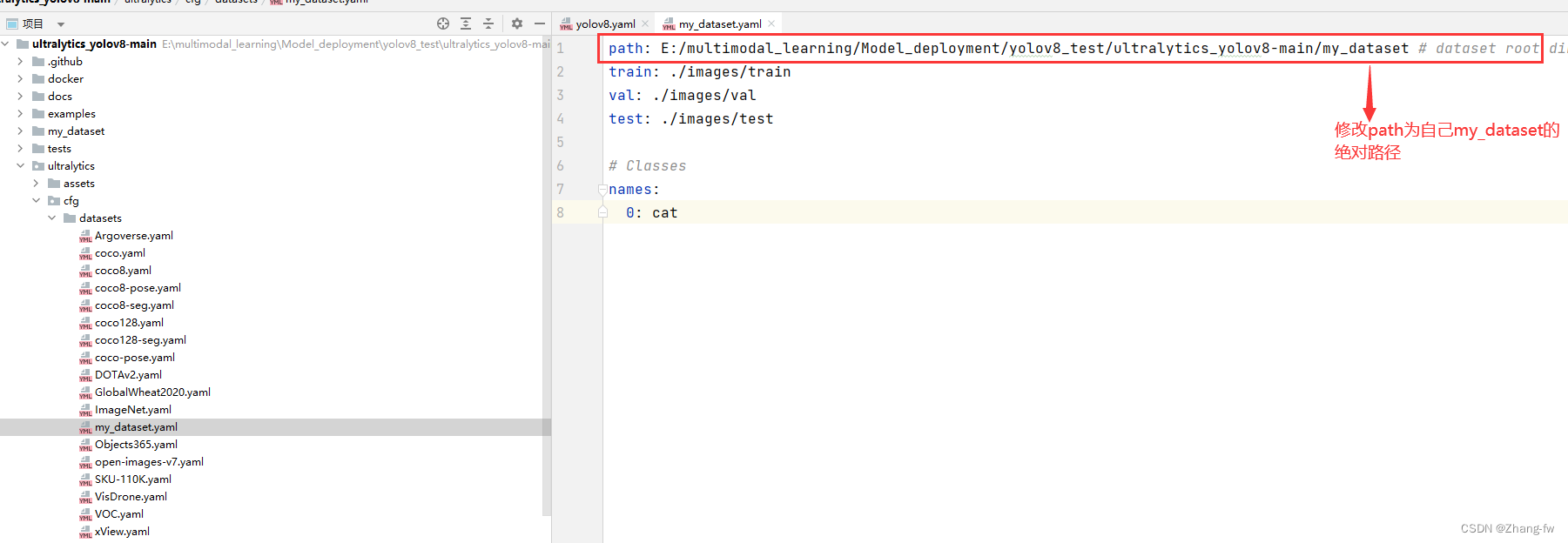
3.2.3 开始训练
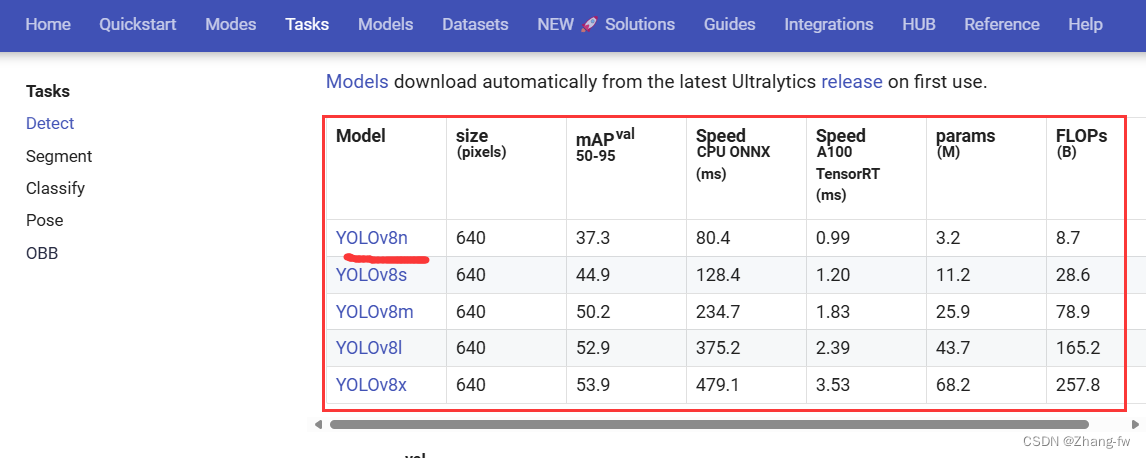
如果想要使用YOLO官网的预训练权重的可以在Detect - Ultralytics YOLO Docs 下载预训练权重,此处下载的是YOLOv8n的权重文件
在根目录下新建一个train.py使用下面的程序,并把下载的预训练权重文件移动过来,鼠标右键后点击训练
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = YOLO('./ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/yolov8.yaml').load("./yolov8n.pt")#创建模型并加载预训练权重
# Train the model
model.train(epochs=100, batch=8 ,data='./ultralytics/cfg/datasets/my_dataset.yaml')
#epochs表示训练的轮数,batch表示每次加载图片的数量,data是数据集的路径这里使用的是之前创建的yaml文件训练结束R结果保存在 runs\detect\train下面,可以点开验证图片进行查看,weights保存着best.pt是我们训练出来的最好的权重文件
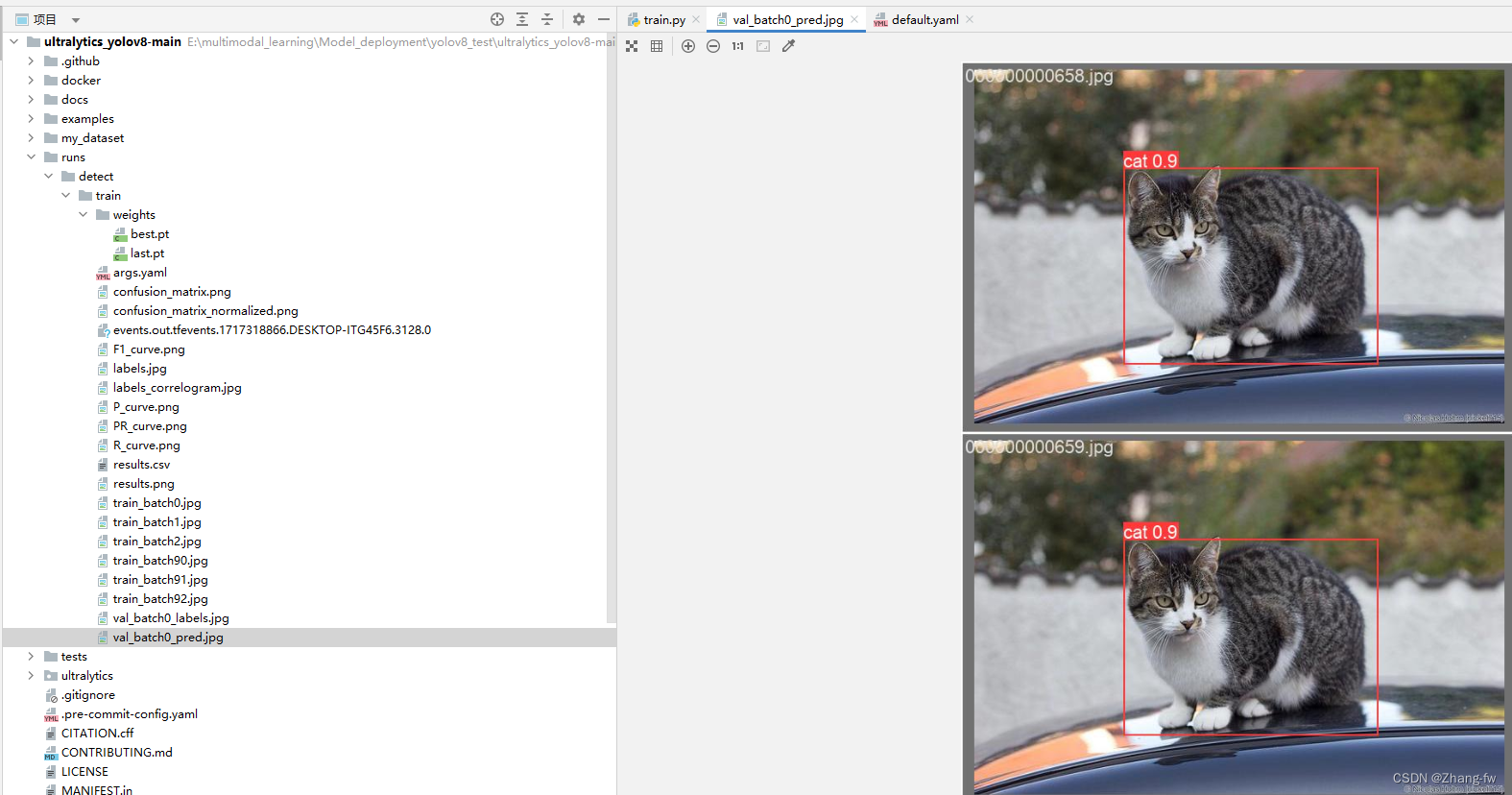
可以新建一个predict.py来测试,加载自己训练的权重文件对测试图片进行预测,保存路径会打印出来
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
model = YOLO("./runs/detect/train/weights/best.pt") # load a custom model
# Predict with the model
results = model("./my_dataset/images/test/000000000650.jpg",save=True)3.3 导出onnx模型
新建一个py文件运行后会在 runs\detect\train\weights下生成best.onnx文件,
python
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
model = YOLO('./runs/detect/train/weights/best.pt')
# Export the model
model.export(format='rknn',opset=12)可以使用Netron来查看自己的模型,这里查看下导出的onnx文件。
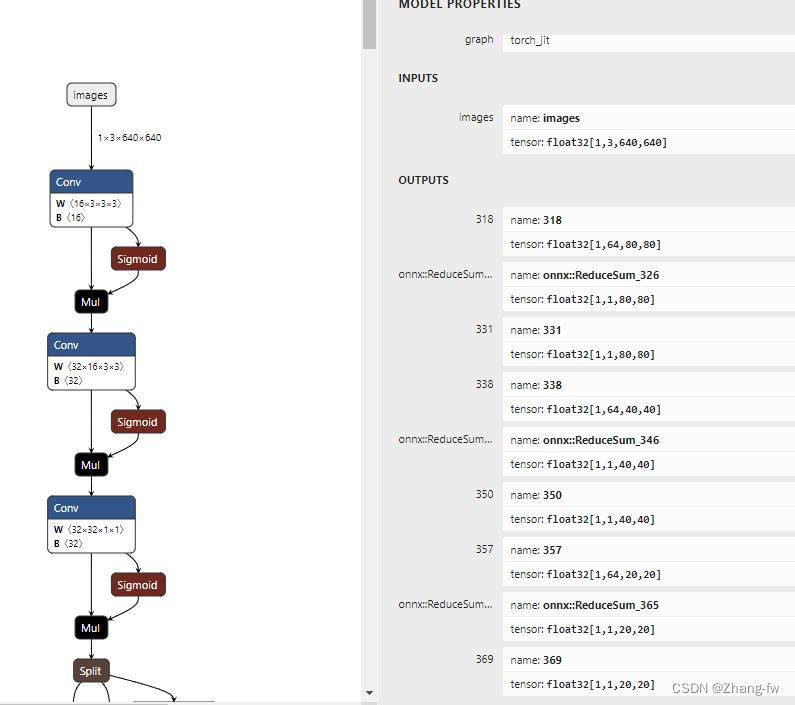
四,模型转换
4.1 转换环境安装
把onnx模型转换成rknn模型需要一个linux环境的电脑,如果没有可以在电脑上安装虚拟机,这里使用一台Ubuntu环境的服务器。
在服务器中也需要安装Anaconda和Pycharm与前面2.1节和2.2节类似,这里不再赘述。
先创建一个rk3588的虚拟环境
conda create -n rk3588 python=3.9进入rk3588环境
conda activate rk3588下载rknn-toolkit2https://github.com/airockchip/rknn-toolkit2.git我选择的1.6.0的版本
解压后进入rknn-toolkit2-1.6.0/rknn-toolkit2/packages/中

安装依赖
pip install -r requirements_cp39-1.6.0.txt -i https://mirror.baidu.com/pypi/simple安装rknn_toolkit2
pip install rknn_toolkit2-1.6.0+81f21f4d-cp39-cp39-linux_x86_64.whl安装完成后进入python,使用下面命令没有报错,则安装成功。
python
from rknn.api import RKNN
4.2 转换成rknn模型
新建一个yolov8_test的文件夹来存放我们的文件
best.onnx是我们3.3导出的onnx模型,dataset下面放一张测试图片000000000650.jpg和dataset.txt,txt中写的是测试图片的名字。
dataset-1下面放的是我们要测试的图片,测试的结果会保存在dataset-2下。
.
├── best.onnx
├── dataset
│ ├── 000000000650.jpg
│ └── dataset.txt
├── dataset-1
│ └── 000000000650.jpg
├── dataset-2
└── inference_test-2.pyinference_test-2.py内容如下,包含模型转换和python部署的后处理
python
import os
import cv2
from rknn.api import RKNN
import numpy as np
IMG_FOLDER = "dataset-1"
RESULT_PATH = './dataset-2'
#修改为自己的类别
CLASSES = ['cat']
OBJ_THRESH = 0.45
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
MODEL_SIZE = (640, 640)
color_palette = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(CLASSES), 3))
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def letter_box(im, new_shape, pad_color=(0, 0, 0), info_need=False):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
ratio = r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=pad_color) # add border
if info_need is True:
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
else:
return im
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
"""Filter boxes with object threshold.
"""
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
candidate, class_num = box_class_probs.shape
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score * box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
scores = (class_max_score * box_confidences)[_class_pos]
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
"""Suppress non-maximal boxes.
# Returns
keep: ndarray, index of effective boxes.
"""
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def softmax(x, axis=None):
x = x - x.max(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
y = np.exp(x)
return y / y.sum(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
def dfl(position):
# Distribution Focal Loss (DFL)
n, c, h, w = position.shape
p_num = 4
mc = c // p_num
y = position.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
y = softmax(y, 2)
acc_metrix = np.array(range(mc), dtype=float).reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
y = (y * acc_metrix).sum(2)
return y
def box_process(position):
grid_h, grid_w = position.shape[2:4]
col, row = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, grid_w), np.arange(0, grid_h))
col = col.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
row = row.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=1)
stride = np.array([MODEL_SIZE[1] // grid_h, MODEL_SIZE[0] // grid_w]).reshape(1, 2, 1, 1)
position = dfl(position)
box_xy = grid + 0.5 - position[:, 0:2, :, :]
box_xy2 = grid + 0.5 + position[:, 2:4, :, :]
xyxy = np.concatenate((box_xy * stride, box_xy2 * stride), axis=1)
return xyxy
def post_process(input_data):
boxes, scores, classes_conf = [], [], []
defualt_branch = 3
pair_per_branch = len(input_data) // defualt_branch
# Python 忽略 score_sum 输出
for i in range(defualt_branch):
boxes.append(box_process(input_data[pair_per_branch * i]))
classes_conf.append(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1])
scores.append(np.ones_like(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1][:, :1, :, :], dtype=np.float32))
def sp_flatten(_in):
ch = _in.shape[1]
_in = _in.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
return _in.reshape(-1, ch)
boxes = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in boxes]
classes_conf = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in classes_conf]
scores = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in scores]
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
classes_conf = np.concatenate(classes_conf)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
# filter according to threshold
boxes, classes, scores = filter_boxes(boxes, scores, classes_conf)
# nms
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
if len(keep) != 0:
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw_detections(img, left, top, right, bottom, score, class_id):
"""
Draws bounding boxes and labels on the input image based on the detected objects.
Args:
img: The input image to draw detections on.
box: Detected bounding box.
score: Corresponding detection score.
class_id: Class ID for the detected object.
Returns:
None
"""
# Retrieve the color for the class ID
color = color_palette[class_id]
# Draw the bounding box on the image
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), color, 2)
# Create the label text with class name and score
label = f"{CLASSES[class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
# Calculate the dimensions of the label text
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
# Calculate the position of the label text
label_x = left
label_y = top - 10 if top - 10 > label_height else top + 10
# Draw a filled rectangle as the background for the label text
cv2.rectangle(img, (label_x, label_y - label_height), (label_x + label_width, label_y + label_height), color,
cv2.FILLED)
# Draw the label text on the image
cv2.putText(img, label, (label_x, label_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
img_h, img_w = image.shape[:2]
# Calculate scaling factors for bounding box coordinates
x_factor = img_w / MODEL_SIZE[0]
y_factor = img_h / MODEL_SIZE[1]
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = [int(_b) for _b in box]
left = int(x1 * x_factor)
top = int(y1 * y_factor) - 10
right = int(x2 * x_factor)
bottom = int(y2 * y_factor) + 10
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(left, top, right, bottom))
# Retrieve the color for the class ID
draw_detections(image, left, top, right, bottom, score, cl)
# cv2.rectangle(image, (left, top), (right, bottom), color, 2)
# cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
# (left, top - 6),
# cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
# 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 确定目标设备
target = 'RK3588'
# 创建RKNN对象
rknn = RKNN()
# 配置RKNN模型
print('--> config model')
rknn.config(
mean_values=[[0, 0, 0]],
std_values=[[255, 255, 255]],
target_platform=target,
)
print('done')
# 加载 .onnx模型
print('--> loading model')
ret = rknn.load_onnx(model="./best.onnx")
if ret != 0:
print("load model failed!")
rknn.release()
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 构建RKNN模型
print('--> building model')
ret = rknn.build(do_quantization=True, dataset="./dataset/dataset.txt")
if ret != 0:
print("build model failed!")
rknn.release()
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 导出RKNN模型
print('-->export RKNN model')
ret = rknn.export_rknn('./yolov8.rknn')
if ret != 0:
print('export RKNN model failed')
rknn.release()
exit(ret)
# 初始化 runtime 环境
print('--> Init runtime environment')
# run on RK356x/RK3588 with Debian OS, do not need specify target.
#ret = rknn.init_runtime(target='rk3588', device_id='48c122b87375ccbc')
# 如果使用电脑进行模拟测试
ret = rknn.init_runtime()
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 数据处理
img_list = os.listdir(IMG_FOLDER)
for i in range(len(img_list)):
img_name = img_list[i]
img_path = os.path.join(IMG_FOLDER, img_name)
if not os.path.exists(img_path):
print("{} is not found", img_name)
continue
img_src = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img_src is None:
print("文件不存在\n")
# Due to rga init with (0,0,0), we using pad_color (0,0,0) instead of (114, 114, 114)
pad_color = (0, 0, 0)
img = letter_box(im=img_src.copy(), new_shape=(MODEL_SIZE[1], MODEL_SIZE[0]), pad_color=(0, 0, 0))
# img = cv2.resize(img_src, (640, 512), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) # direct resize
input = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
outputs = rknn.inference([input])
boxes, classes, scores = post_process(outputs)
img_p = img_src.copy()
if boxes is not None:
draw(img_p, boxes, scores, classes)
# 保存结果
if not os.path.exists(RESULT_PATH):
os.mkdir(RESULT_PATH)
result_path = os.path.join(RESULT_PATH, img_name)
cv2.imwrite(result_path, img_p)
print('Detection result save to {}'.format(result_path))
pass
rknn.release()运行inference_test-2.py 文件,会在yolov8_test文件夹下生成yolov8.rknn,测试结果的图片保存在dataset-2文件夹下。
python inference_test-2.py 五,模型部署
5.1 香橙派(RK3588)环境安装
首先参考Orange Pi - Orangepi官网安装Ubuntu系统
然后打开时ssh服务,我这里使用的MobaXterm进行连接的
sudo apt-get install openssh-server首先安装Miniconda --- Anaconda documentation
下载后使用命令来安装Miniconda3
./Miniconda3-latest-Linux-aarch64.sh更新环境变量
source /home/topeet/.bashrc创建环境
conda create -n rknn python=3.9激活环境
conda activate rknn安装rknn_toolkit_lite2
在4.1下载的rknn-toolkit2-1.6.0/rknn_toolkit_lite2/packages中有rknn_toolkit_lite2-1.6.0-cp39-cp39-linux_aarch64.whl,把它移动到开发板上然后使用下面的命令安装
pip install rknn_toolkit_lite2-1.6.0-cp39-cp39-linux_aarch64.whl -i https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple/安装opencv
pip install opencv-python -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple5.2 python部署
在开发板上新建一个yolov8_test来存放文件,dataset-1是存放的测试图片,dataset-2是保存测试结果的位置,yolov8.rknn是我们的rknn模型,rk3588_test-2.py是我们的测试脚本
.
├── dataset-1
│ └── 000000000650.jpg
├── dataset-2
├── rk3588_test-2.py
└── yolov8.rknnrk3588_test-2.py文件如下所示
python
import os
import cv2
from rknnlite.api import RKNNLite
import numpy as np
RKNN_MODEL = "./yolov8.rknn"
IMG_FOLDER = "dataset-1"
RESULT_PATH = './dataset-2'
CLASSES = ['car']
OBJ_THRESH = 0.45
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
MODEL_SIZE = (640, 640)
color_palette = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(CLASSES), 3))
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def letter_box(im, new_shape, pad_color=(0, 0, 0), info_need=False):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
ratio = r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=pad_color) # add border
if info_need is True:
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
else:
return im
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
"""Filter boxes with object threshold.
"""
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
candidate, class_num = box_class_probs.shape
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score * box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
scores = (class_max_score * box_confidences)[_class_pos]
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
"""Suppress non-maximal boxes.
# Returns
keep: ndarray, index of effective boxes.
"""
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def softmax(x, axis=None):
x = x - x.max(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
y = np.exp(x)
return y / y.sum(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
def dfl(position):
# Distribution Focal Loss (DFL)
n, c, h, w = position.shape
p_num = 4
mc = c // p_num
y = position.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
y = softmax(y, 2)
acc_metrix = np.array(range(mc), dtype=float).reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
y = (y * acc_metrix).sum(2)
return y
def box_process(position):
grid_h, grid_w = position.shape[2:4]
col, row = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, grid_w), np.arange(0, grid_h))
col = col.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
row = row.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=1)
stride = np.array([MODEL_SIZE[1] // grid_h, MODEL_SIZE[0] // grid_w]).reshape(1, 2, 1, 1)
position = dfl(position)
box_xy = grid + 0.5 - position[:, 0:2, :, :]
box_xy2 = grid + 0.5 + position[:, 2:4, :, :]
xyxy = np.concatenate((box_xy * stride, box_xy2 * stride), axis=1)
return xyxy
def post_process(input_data):
boxes, scores, classes_conf = [], [], []
defualt_branch = 3
pair_per_branch = len(input_data) // defualt_branch
# Python 忽略 score_sum 输出
for i in range(defualt_branch):
boxes.append(box_process(input_data[pair_per_branch * i]))
classes_conf.append(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1])
scores.append(np.ones_like(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1][:, :1, :, :], dtype=np.float32))
def sp_flatten(_in):
ch = _in.shape[1]
_in = _in.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
return _in.reshape(-1, ch)
boxes = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in boxes]
classes_conf = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in classes_conf]
scores = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in scores]
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
classes_conf = np.concatenate(classes_conf)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
# filter according to threshold
boxes, classes, scores = filter_boxes(boxes, scores, classes_conf)
# nms
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
if len(keep) != 0:
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw_detections(img, left, top, right, bottom, score, class_id):
"""
Draws bounding boxes and labels on the input image based on the detected objects.
Args:
img: The input image to draw detections on.
box: Detected bounding box.
score: Corresponding detection score.
class_id: Class ID for the detected object.
Returns:
None
"""
# Retrieve the color for the class ID
color = color_palette[class_id]
# Draw the bounding box on the image
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), color, 2)
# Create the label text with class name and score
label = f"{CLASSES[class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
# Calculate the dimensions of the label text
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
# Calculate the position of the label text
label_x = left
label_y = top - 10 if top - 10 > label_height else top + 10
# Draw a filled rectangle as the background for the label text
cv2.rectangle(img, (label_x, label_y - label_height), (label_x + label_width, label_y + label_height), color,
cv2.FILLED)
# Draw the label text on the image
cv2.putText(img, label, (label_x, label_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
img_h, img_w = image.shape[:2]
# Calculate scaling factors for bounding box coordinates
x_factor = img_w / MODEL_SIZE[0]
y_factor = img_h / MODEL_SIZE[1]
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = [int(_b) for _b in box]
left = int(x1 * x_factor)
top = int(y1 * y_factor)
right = int(x2 * x_factor)
bottom = int(y2 * y_factor)
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(left, top, right, bottom))
# Retrieve the color for the class ID
draw_detections(image, left, top, right, bottom, score, cl)
# cv2.rectangle(image, (left, top), (right, bottom), color, 2)
# cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
# (left, top - 6),
# cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
# 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建RKNN对象
rknn_lite = RKNNLite()
# 加载RKNN模型
print('--> Load RKNN model')
ret = rknn_lite.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model failed')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 初始化 runtime 环境
print('--> Init runtime environment')
# run on RK356x/RK3588 with Debian OS, do not need specify target.
ret = rknn_lite.init_runtime()
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 数据处理
img_list = os.listdir(IMG_FOLDER)
for i in range(len(img_list)):
img_name = img_list[i]
img_path = os.path.join(IMG_FOLDER, img_name)
if not os.path.exists(img_path):
print("{} is not found", img_name)
continue
img_src = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img_src is None:
print("文件不存在\n")
# Due to rga init with (0,0,0), we using pad_color (0,0,0) instead of (114, 114, 114)
pad_color = (0, 0, 0)
img = letter_box(im=img_src.copy(), new_shape=(MODEL_SIZE[1], MODEL_SIZE[0]), pad_color=(0, 0, 0))
# img = cv2.resize(img_src, (640, 512), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) # direct resize
input = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
outputs = rknn_lite.inference([input])
boxes, classes, scores = post_process(outputs)
img_p = img_src.copy()
if boxes is not None:
draw(img_p, boxes, scores, classes)
# 保存结果
if not os.path.exists(RESULT_PATH):
os.mkdir(RESULT_PATH)
result_path = os.path.join(RESULT_PATH, img_name)
cv2.imwrite(result_path, img_p)
print('Detection result save to {}'.format(result_path))
pass
# cv2.imshow("full post process result", img_p)
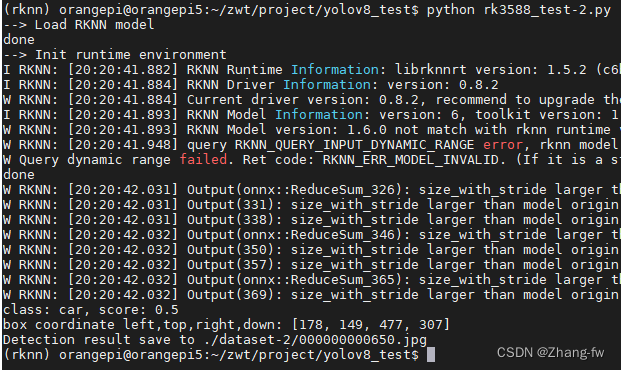
rknn_lite.release()使用下面命令来执行
python rk3588_test-2.py会输出检测的结果如下图所示
!