文章目录
- [一、 相交链表](#一、 相交链表)
- [二、 反转链表](#二、 反转链表)
- [三、 回文链表](#三、 回文链表)
- [四、 环形链表](#四、 环形链表)
- [五、 环形链表 II](#五、 环形链表 II)
- [六、 合并两个有序链表](#六、 合并两个有序链表)
- [七、 两数相加](#七、 两数相加)
- [八、 删除链表的倒数第N个节点](#八、 删除链表的倒数第N个节点)
- [九、 随机链表的复制](#九、 随机链表的复制)
一、 相交链表
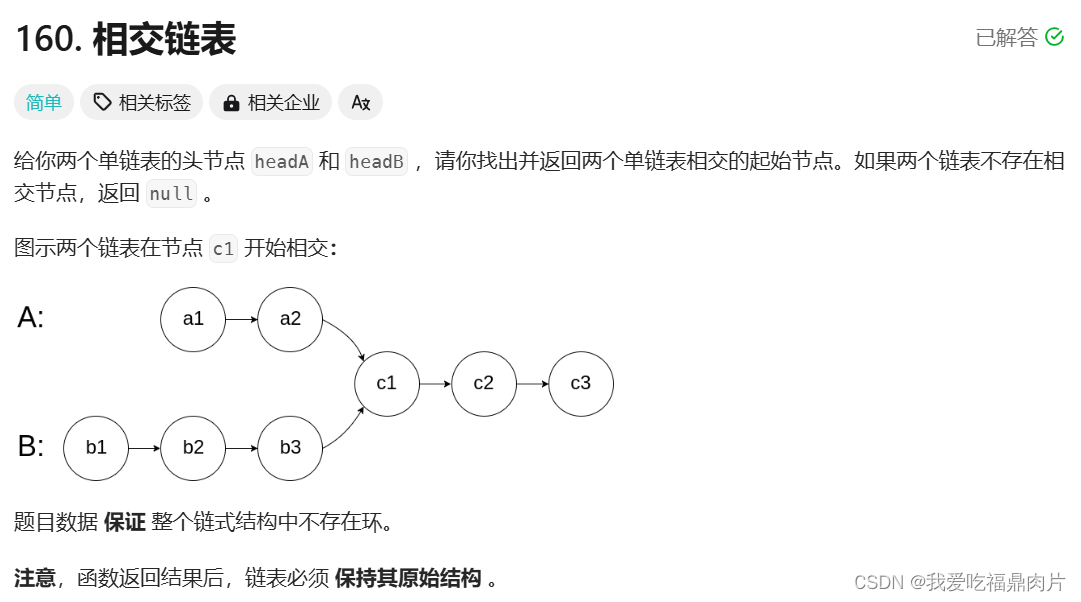
双指针法
c
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
struct ListNode* curA = headA;
struct ListNode* curB = headB;
int lenA = 1,lenB = 1;
while(curA->next)
{
curA = curA->next;
lenA++;
}
while(curB->next)
{
curB = curB->next;
lenB++;
}
//终点相同才能进行下一步
if(curB != curA)
{
return NULL;
}
//假设法
//长的先走
int gap = abs(lenA - lenB);
struct ListNode* longlist = headA;
struct ListNode* shortlist = headB;
if(lenB>lenA)
{
longlist = headB;
shortlist = headA;
}
while(gap--)
{
longlist = longlist->next;
}
while(shortlist != longlist)
{
shortlist = shortlist->next;
longlist = longlist->next;
}
return shortlist;
}二、 反转链表
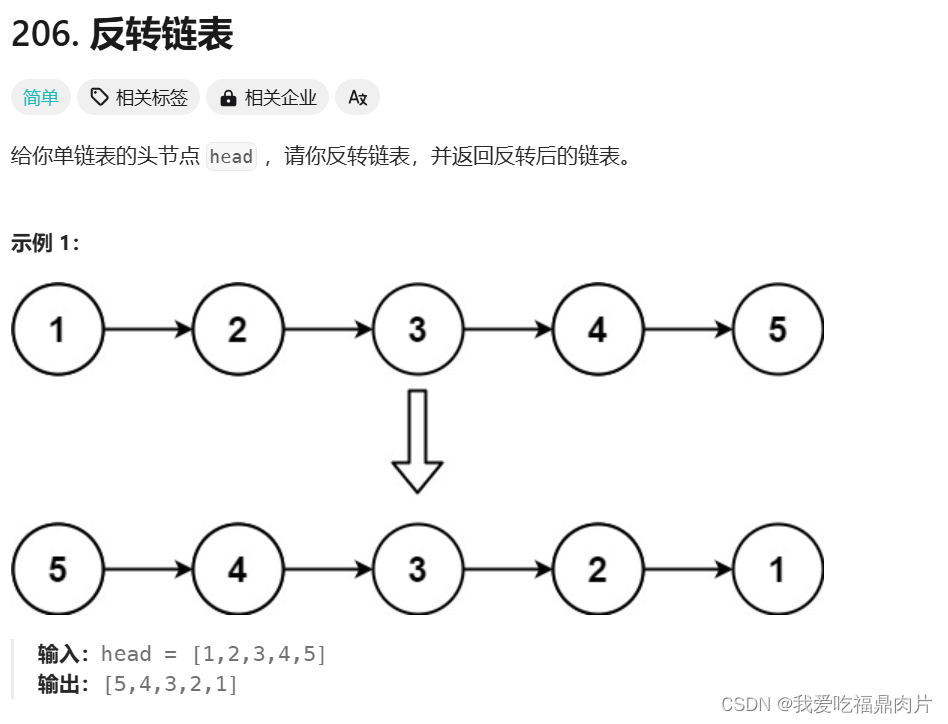
注意第一个节点的next要为空
c
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL)
{
return head;
}
ListNode* n1,* n2, *n3;
n1 = NULL;
n2 = head;
n3 = n2->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}三、 回文链表
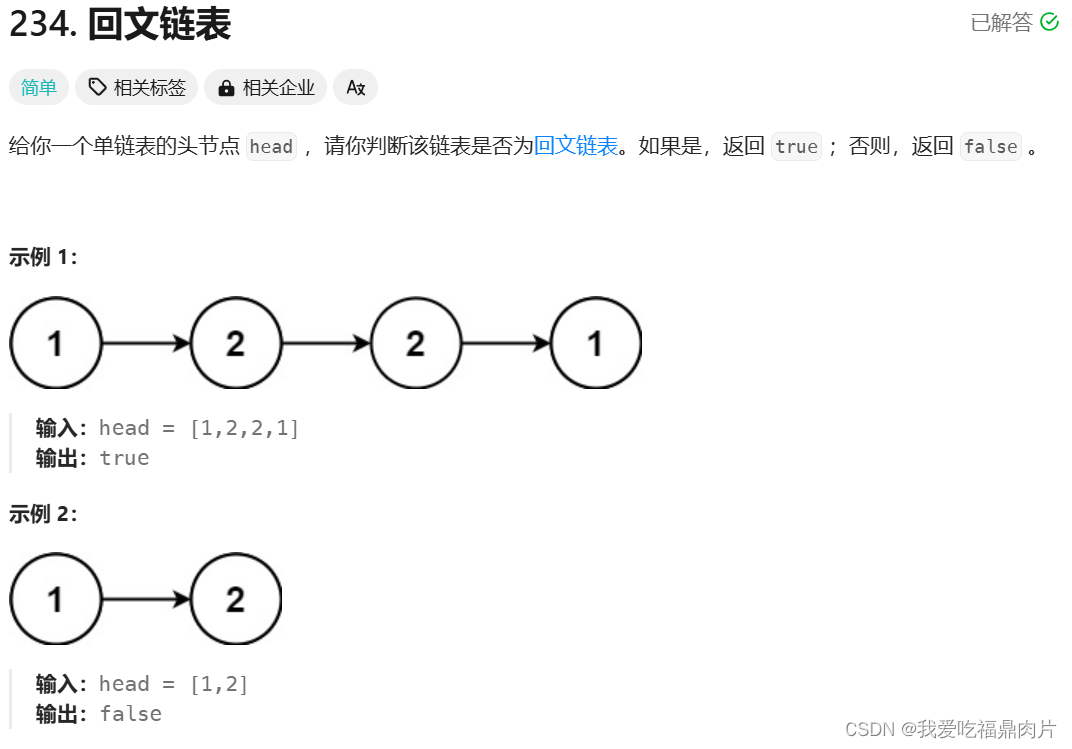
这题两个选择,反转前半部分再对比,或者反转后半部分再对比
如果反转前半部分,那么找中间值的条件就为fast->next && fast->next->next不为空,我选择反转后半部分,相对更容易理解
反转的部分参考反转链表
c
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head)
{
if(head == NULL)
{
return head;
}
ListNode* n1,* n2, *n3;
n1 = NULL;
n2 = head;
n3 = n2->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}
bool isPalindrome(struct ListNode* head) {
//先找到中间节点
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
//反转后一半节点
ListNode* p = reverse(slow);
ListNode* q = head;
//对比
while(q != slow)
{
if(q->val != p->val)
return false;
q = q->next;
p = p->next;
}
return true;
}四、 环形链表
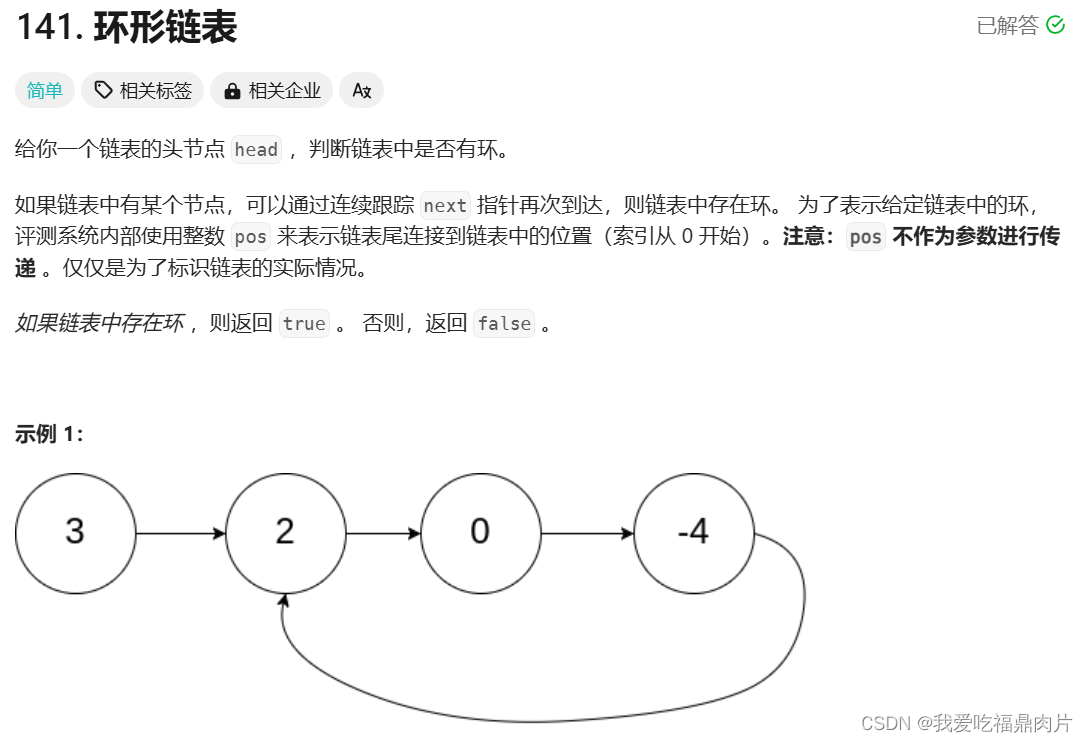
快慢指针:用fast先走,等fast进圈后再去追slow
c
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(fast == slow)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}五、 环形链表 II
先看代码,这题的代码很简单,但是要明白所以然
c
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(slow == fast)
{
ListNode* meet = slow;
while(head != meet)
{
head = head->next;
meet = meet->next;
}
return head;
}
}
return NULL;
}
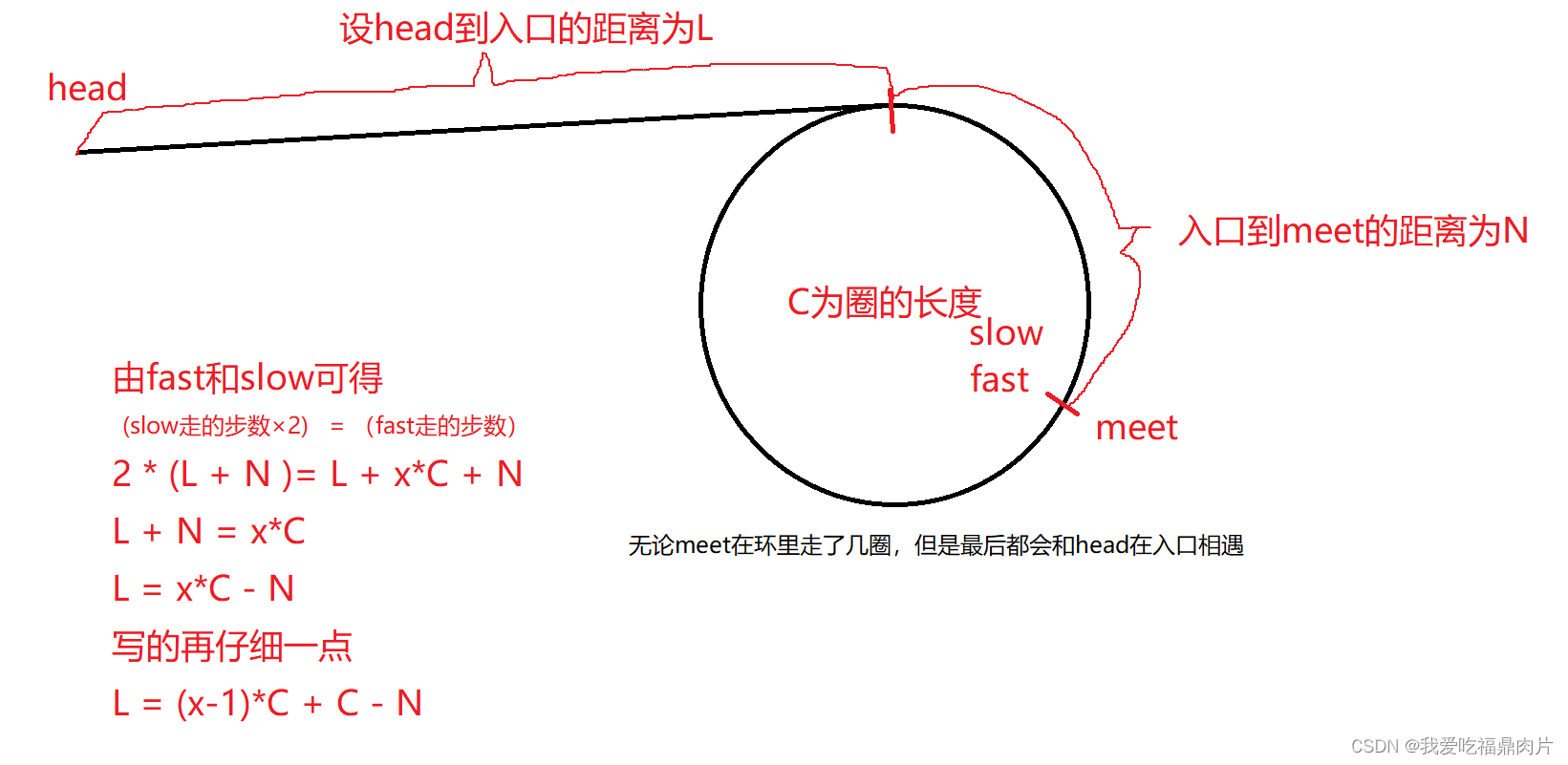
当fast和slow相遇后,我们将meet点设为新的起点,然后head点和meet点往后走,终究会相遇,相遇的点就是环的入口。
六、 合并两个有序链表
这题需要注意返回新链表的头节点,所以新链表创建两个节点来记录头和尾节点最方便
c
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
ListNode* l1 = list1;
ListNode* l2 = list2;
//判断链表为空
if(l1 == NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2 == NULL)
{
return l1;
}
//创建新的链表
ListNode* newhead,* newtail;
newhead = newtail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
while(l1 && l2)
{
if(l1->val < l2->val)
{ //l1尾插
newtail->next = l1 ;
newtail = newtail->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{ //l2尾插
newtail->next = l2;
newtail = newtail->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}//跳出循环后还有两种情况,不是l1走到空,就是l2先走到空
if(l1)
{
newtail->next = l1;
}
if(l2)
{
newtail->next = l2;
}
//手动释放动态内存空间
ListNode* ret = newhead->next;
free(newhead);
newhead = NULL;
return ret;
}七、 两数相加
这题使用递归的方法最好理解
c
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* _addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1,ListNode* l2,int cur)
{
int sums = cur;
if(l1 == NULL && l2 == NULL && cur == 0)
{
return NULL;
}
else{
if(l1 != NULL)
{
sums += l1->val;
l1 = l1->next;
}
if(l2 != NULL)
{
sums += l2->val;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
ListNode* a = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
a->val = sums%10;
a->next = _addTwoNumbers(l1,l2,sums/10);
return a;
}
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
return _addTwoNumbers(l1,l2,0);
}cur为进位值,所以和就为l1->val+l2->val+cur
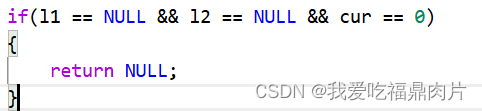
判断cur是防止极端情况的发生,例如:

八、 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
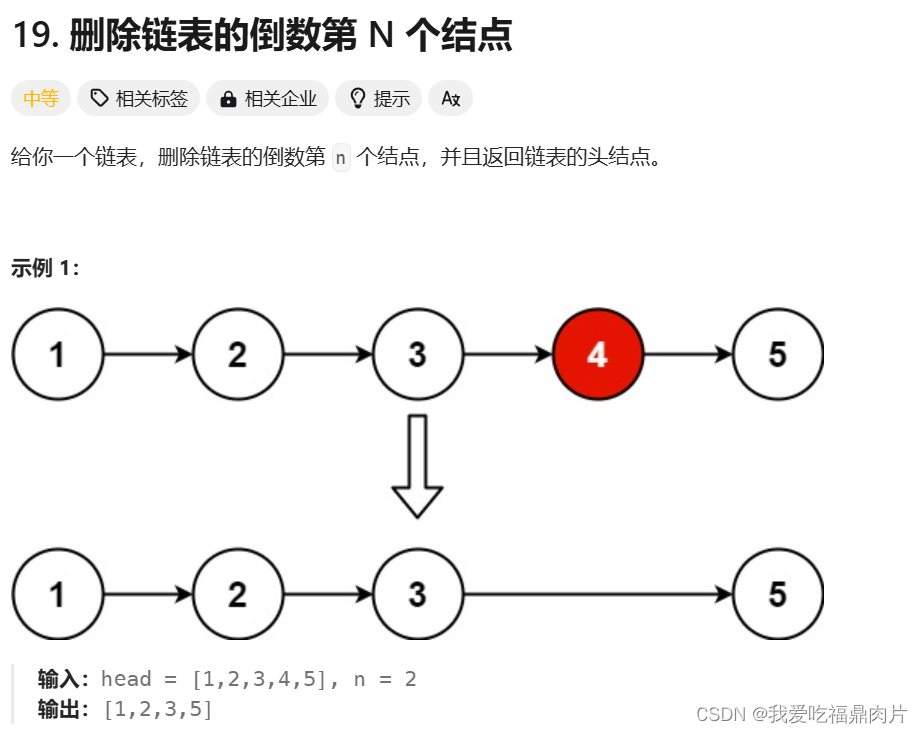
先记录链表长度,再找到要删除节点的上一个节点
c
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n) {
int length = 1;
struct ListNode* p = head;
struct ListNode* q = head;
//记录链表长度
while(p->next)
{
p = p->next;
length++;
}
int del = length - n + 1;
int j = 1;
//找到要删除节点的上一个节点
while(j + 1 < del)
{
q = q->next;
j++;
}
if(del != 1)
{
q->next = q->next->next;
return head;
}
else
{
return head = q->next;
}
}九、 随机链表的复制
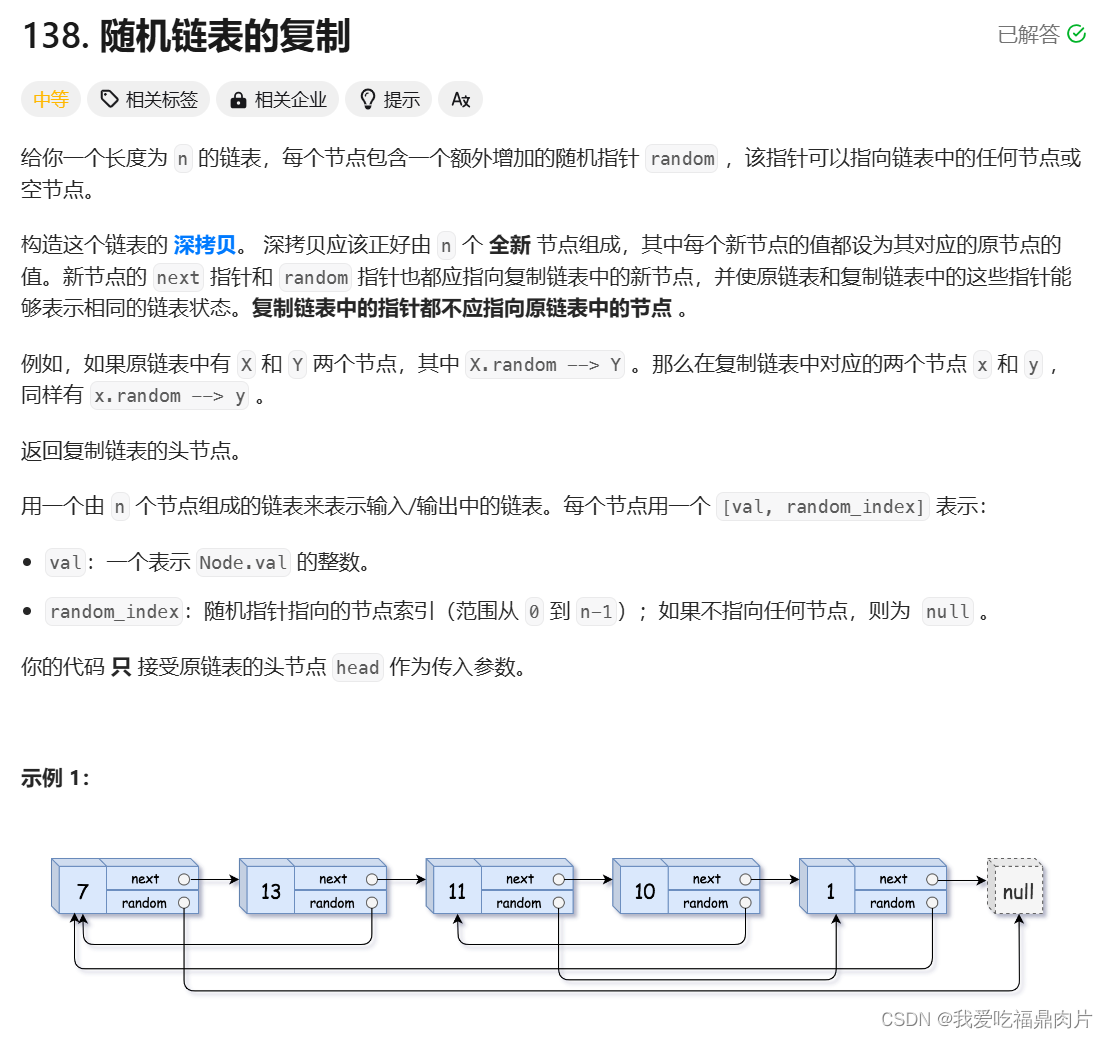
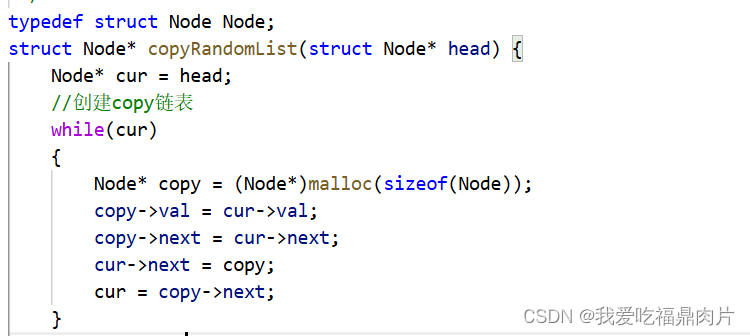
创建一个copy链表
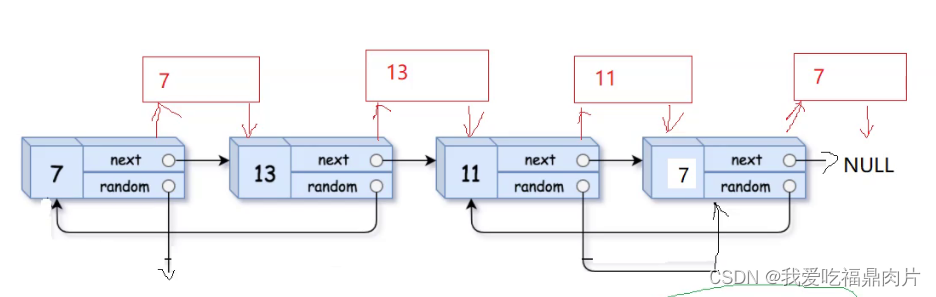
再控制random
把copy取出尾插为新的链表(恢复原链表)

源代码:
c
typedef struct Node Node;
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
Node* cur = head;
//创建copy链表
while(cur)
{
Node* copy = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
copy->next = cur->next;
cur->next = copy;
cur = copy->next;
}
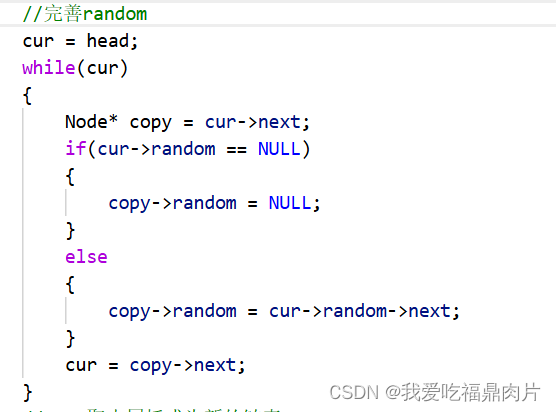
//完善random
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
Node* copy = cur->next;
if(cur->random == NULL)
{
copy->random = NULL;
}
else
{
copy->random = cur->random->next;
}
cur = copy->next;
}
//copy取出尾插成为新的链表
cur = head;
Node* copyhead = NULL;
Node* copytail = NULL;
while(cur)
{
Node* copy = cur->next;
Node* next = copy->next;
if(copyhead == NULL)
{
copyhead = copytail = copy;
}
else
{
copytail->next = copy;
copytail = copy;
}
//cur->next = next;
cur = next;
next = copy->next;
}
return copyhead;
}