%%capture
%pip install imagecodecs
%pip install rasterio
# Installed libraries
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import imagecodecs
import pywt
import pywt.data
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
from skimage import img_as_float
from pywt import swt2, iswt2
from scipy.ndimage.morphology import grey_opening
from typing import Optional
import rasterio
from rasterio.plot import show
from skimage.util import view_as_windowsGeneral functions
def read_tiff_img(input_path: str) -> np.ndarray:
with rasterio.open(input_path) as src:
return src.read(1), src.meta
def save_tiff_img(output_path: str, img: np.ndarray, meta=None):
if not meta:
meta = {
"driver": "GTiff",
"height": img.shape[0],
"width": img.shape[1],
"count": 3,
"dtype": img.dtype,
"crs":"+proj=latlong",
}
import rasterio
with rasterio.open(
output_path,
'w',
**meta
) as dst:
dst.write(img[:, :, 0], 1)
dst.write(img[:, :, 1], 2)
dst.write(img[:, :, 2], 3)
def create_rgb_image(red_band_path: str,
green_band_path: str,
blue_band_path: str,
output_path: str):
# Read the bands using rasterio
with rasterio.open(red_band_path) as src_red:
R = src_red.read(1)
meta = src_red.meta
with rasterio.open(green_band_path) as src_green:
G = src_green.read(1)
with rasterio.open(blue_band_path) as src_blue:
B = src_blue.read(1)
RGB = np.stack((R, G, B), axis=-1)
meta.update({
'count': 3,
})
save_tiff_img(output_path, RGB, meta=meta)
return RGB, meta
def save_tiff_img_single_band(output_path: str, img: np.ndarray, meta=None):
if not meta:
meta = {
"driver": "GTiff",
"height": img.shape[0],
"width": img.shape[1],
"count": 1,
"dtype": img.dtype,
"crs":"+proj=latlong",
}
import rasterio
with rasterio.open(
output_path,
'w',
**meta
) as dst:
dst.write(img, 1)Use Fourier transform to filter noise from Landsat8 image
Input: pandchromatic image
ex1_band8_url = "images/LC08_L1TP_127045_20200730_20200908_02_T1_B8.TIF"
ex1_band8, ex1_band8_metadata = read_tiff_img(ex1_band8_url)
show(ex1_band8)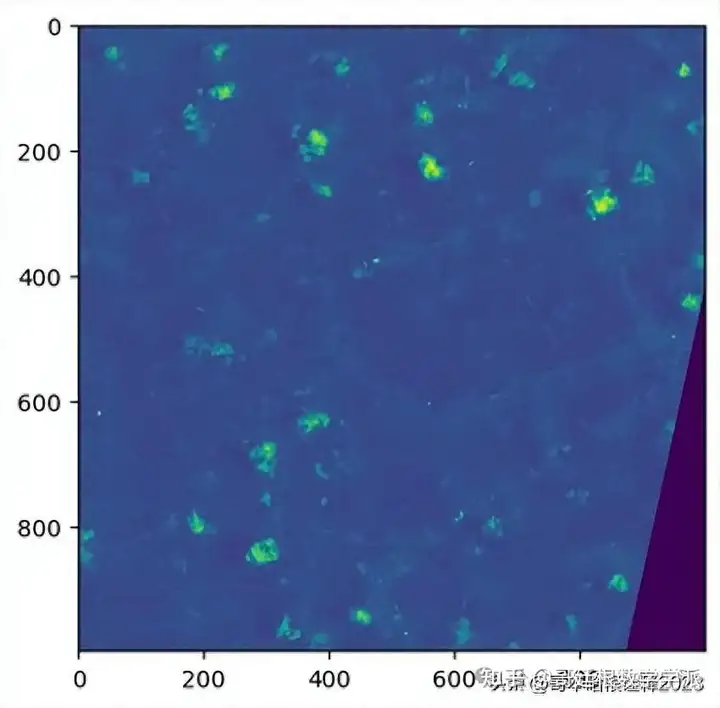
Use fourier transform to filter noise
Steps:
-
Convert the image to the frequency domain.
-
Shift the image in the frequency domain so that the zero frequency and low frequencies are centered in the image; otherwise, these frequencies will start at the top left of the image.
-
Create a mask filter in the frequency domain.
-
Apply the mask filter in the frequency domain.
-
Shift the image back to the top left position.
-
Use the inverse Fourier transform to convert the image back to the spatial domain.
def denoise_img_fourier_transform(img: np.ndarray, mask_radius: int) -> np.ndarray:
"""Reduce noise from image
Args:
img (np.ndarray): Input image
mask_radius (int): Radius used for filtering image in frequent domain
Returns:
np.ndarray: Ouput image (after reduce noise)
"""
# 1.
dft = cv2.dft(np.float64(img), flags=cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
# # 2.
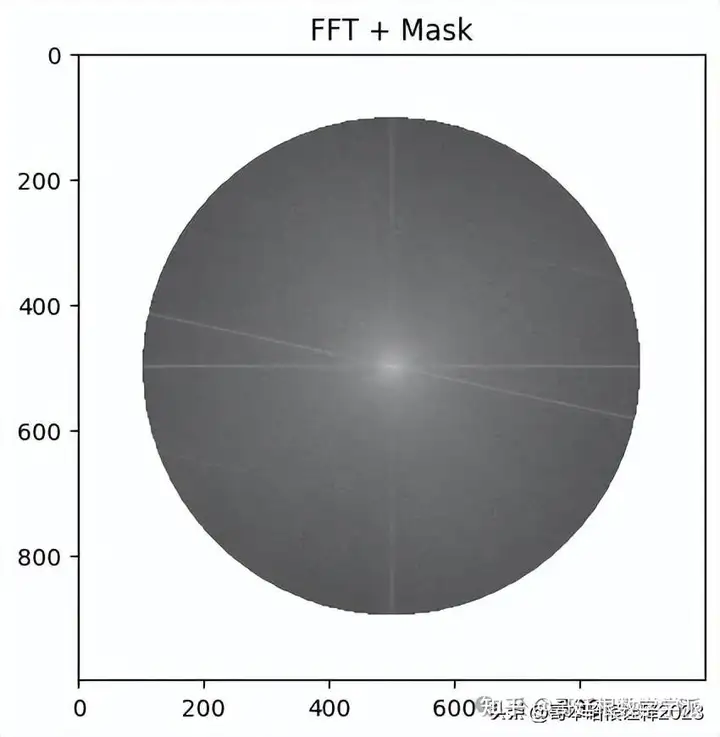
dft_shift = np.fft.fftshift(dft)# only for plot purpose magnitude_spectrum = 20 * np.log(cv2.magnitude(dft_shift[:, :, 0], dft_shift[:, :, 1])) # 3. # Get center of image rows, cols = img.shape crow, ccol = int(rows / 2), int(cols / 2) center = [crow, ccol] # Mask filter with size is the same with original image, value = 0 if pixel # is out of radius (from origin) and 1 otherwise mask = np.ones((rows, cols, 2), np.uint16) x, y = np.ogrid[:rows, :cols] mask_area = (x - center[0]) ** 2 + (y - center[1]) ** 2 > mask_radius * mask_radius mask[mask_area] = 0 # 4. fshift = dft_shift * mask # Tính toán biểu đồ biên độ (cho mục đích vẽ) fshift_mask_magnitude = 20 * np.log(cv2.magnitude(fshift[:, :, 0], fshift[:, :, 1])) # 5. f_ishift = np.fft.ifftshift(fshift) # 6. # Result is 2D complex array img_back = cv2.idft(f_ishift) # Get magnitude of every point to get real value img_back = cv2.magnitude(img_back[:, :, 0], img_back[:, :, 1]) # Plot result # fig, ax = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10)) # ax.imshow(img, cmap='gray') # ax.title.set_text('Input Image') # fig, ax = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10)) # plt.imshow(magnitude_spectrum, cmap="gray") # plt.title('FFT of image') plt.imshow(fshift_mask_magnitude, cmap="gray") plt.title("FFT + Mask") # ax3 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,3) # ax3.imshow(fshift_mask_magnitude, cmap='gray') # ax3.title.set_text('FFT + Mask') # ax4 = fig.add_subplot(2,2,4) # ax4.imshow(img_back, cmap='gray') # ax4.title.set_text('After inverse FFT') # plt.show() return img_backcleaned_img = denoise_img_fourier_transform(img=ex1_band8, mask_radius=400)
normalized_cleaned_img = ((cleaned_img - np.min(cleaned_img))
/ (np.max(cleaned_img) - np.min(cleaned_img)))
cleaned_img = (normalized_cleaned_img * (2**16 - 1)).astype(np.uint16)save_tiff_img_single_band("images/clean_img.TIF", cleaned_img, ex1_band8_metadata)
Assessment
def mad(image: np.ndarray) -> float:
# Calculate the median of the image
median = np.median(image)
# Calculate the absolute deviation from the median
absolute_deviation = np.abs(image - median)
# Calculate the MAD
mad = np.median(absolute_deviation)
return mad
def lv(image: np.ndarray, window_size: int) -> float:
# Extract sliding windows from the image
windows = view_as_windows(image, (window_size, window_size))
# Calculate the variance of each window
local_variances = np.var(windows, axis=(2, 3))
# Estimate the noise variance as the median of local variances
noise_variance = np.median(local_variances)
return noise_variance
print("Before using Fourier Transform to reduce noise:")
print("{:<5}:{:.4f}".format("MAD", mad(ex1_band8)))
print("{:<5}:{:.4f}".format("LV", lv(ex1_band8, 8)))
print("-" * 100)
cleaned_img = cleaned_img.astype(np.uint8)
print("After:")
print("{:<5}:{:.4f}".format("MAD", mad(cleaned_img)))
print("{:<5}:{:.4f}".format("LV", lv(cleaned_img, 8)))
Before using Fourier Transform to reduce noise:
MAD :608.0000
LV :398552.4841
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
After:
MAD :64.0000
LV :5344.7888Use wavelet transform for Landsat8 image
ex3_band2_url = "images/LC08_L2SP_127045_20141002_20200910_02_T1_SR_B2.TIF"
ex3_band3_url = "images/LC08_L2SP_127045_20141002_20200910_02_T1_SR_B3.TIF"
ex3_band4_url = "images/LC08_L2SP_127045_20141002_20200910_02_T1_SR_B4.TIF"
ex3_rgb_url = "images/LC08_L2SP_127045_20141002_20200910_02_T1_SR_RGB.TIF"
ex3_band2= rasterio.open(ex3_band2_url)
ex3_band3 = rasterio.open(ex3_band3_url)
ex3_band4 = rasterio.open(ex3_band4_url)
fig, (axr, axg, axb) = plt.subplots(1,3, figsize=(21,7))
show(ex3_band4.read(1), ax=axr, cmap='Reds', title='red channel')
show(ex3_band3.read(1), ax=axg, cmap='Greens', title='green channel')
show(ex3_band2.read(1), ax=axb, cmap='Blues', title='blue channel')
plt.show()
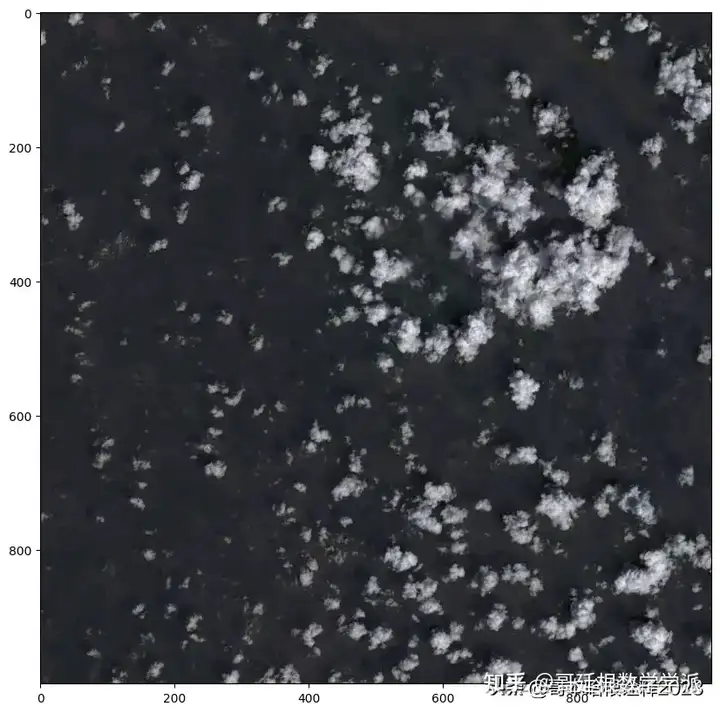
ex3_rgb, ex3_rgb_meta = create_rgb_image(ex3_band4_url, ex3_band3_url, ex3_band2_url, ex3_rgb_url)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
show(ex3_rgb.transpose((2, 0, 1)), adjust=True)
ex3_rgb.dtype
ex3_rgb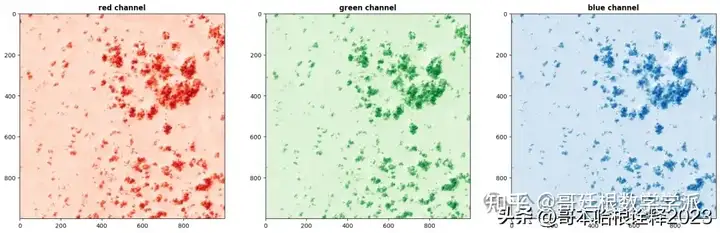
Use wavelet tranform
# Wavelet transform of image, and plot approximation and details
titles = ["approx", "horz_det",
"verz_det", "diag_det"]
coeffs2 = pywt.dwt2(ex3_rgb.transpose((2, 0, 1)), "bior1.3")
LL, (LH, HL, HH) = coeffs2
for idx, img in enumerate([LL, LH, HL, HH]):
save_tiff_img("images/{}.tif".format(titles[idx]), img, ex3_rgb_meta)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
show(img, ax=ax, adjust=True)
plt.savefig("images/{}.png".format(titles[idx]))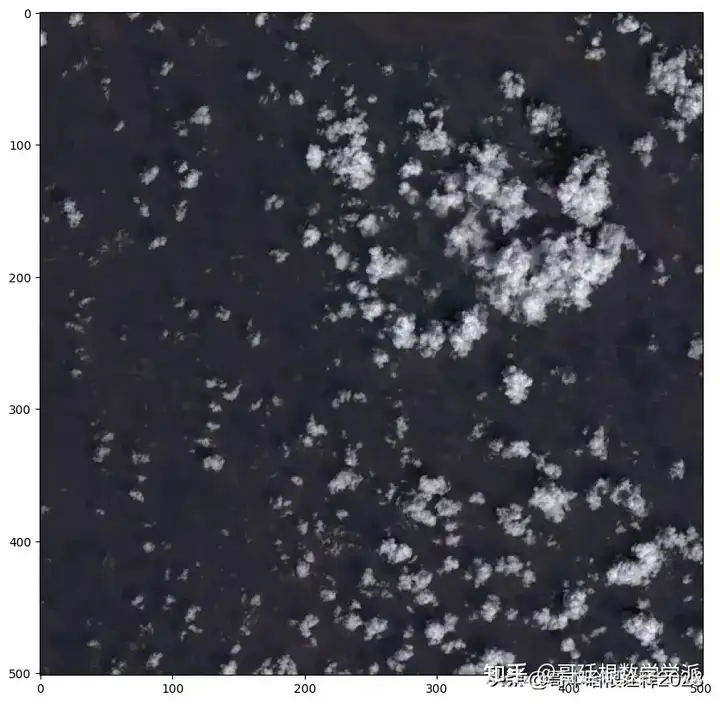
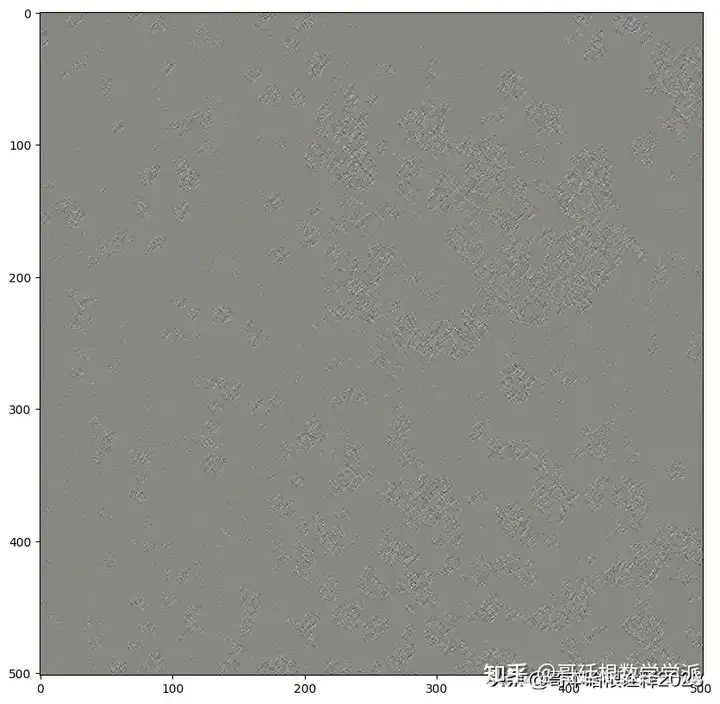
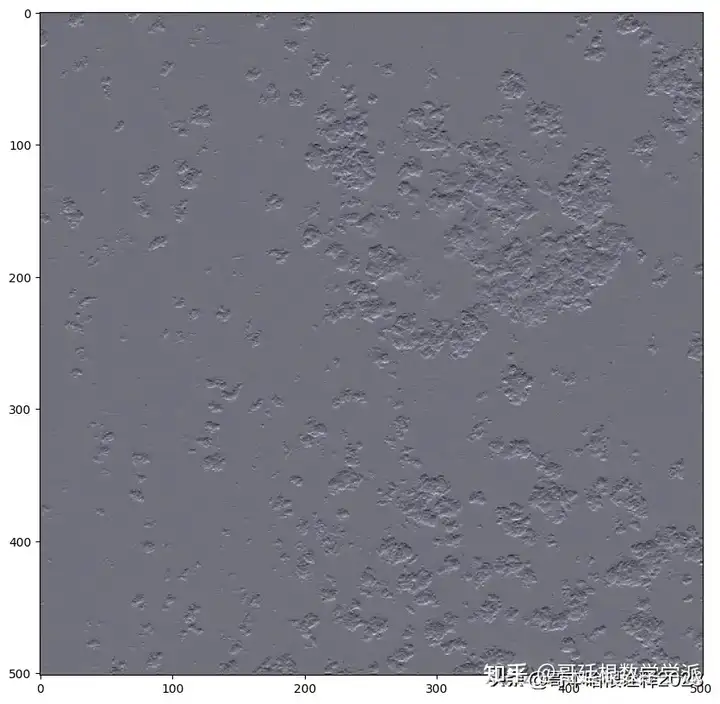
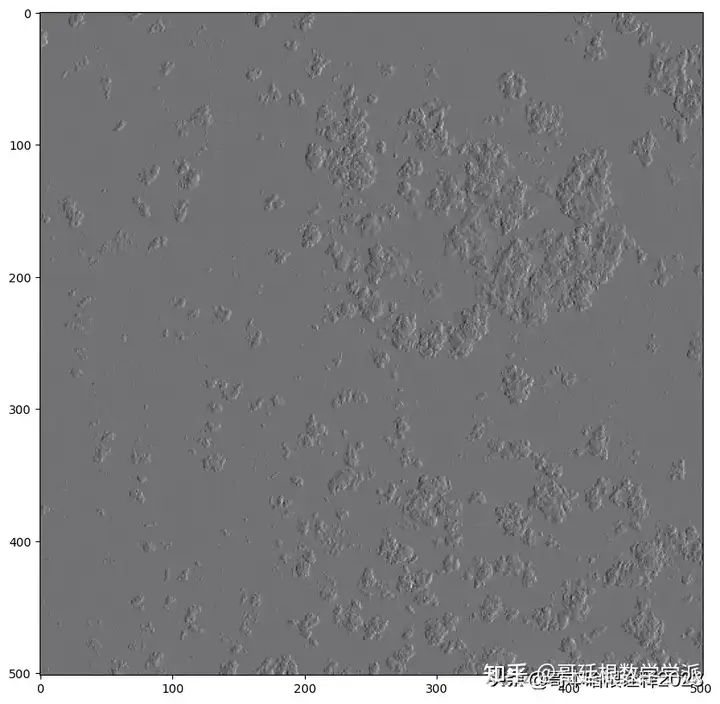

Apply wavelet transform for defogging
ex4_band2_url = "images/LC08_L1TP_127045_20220618_20220630_02_T1_B2.TIF"
ex4_band3_url = "images/LC08_L1TP_127045_20220618_20220630_02_T1_B3.TIF"
ex4_band4_url = "images/LC08_L1TP_127045_20220618_20220630_02_T1_B4.TIF"
ex4_rgb_url = "images/LC08_L1TP_127045_20220618_20220630_02_T1_RGB.TIF"
ex4_rgb, ex4_rgb_metadata = create_rgb_image(
ex4_band4_url,
ex4_band3_url,
ex4_band2_url,
ex4_rgb_url
)
show(ex4_rgb.transpose((2, 0, 1)), adjust=True)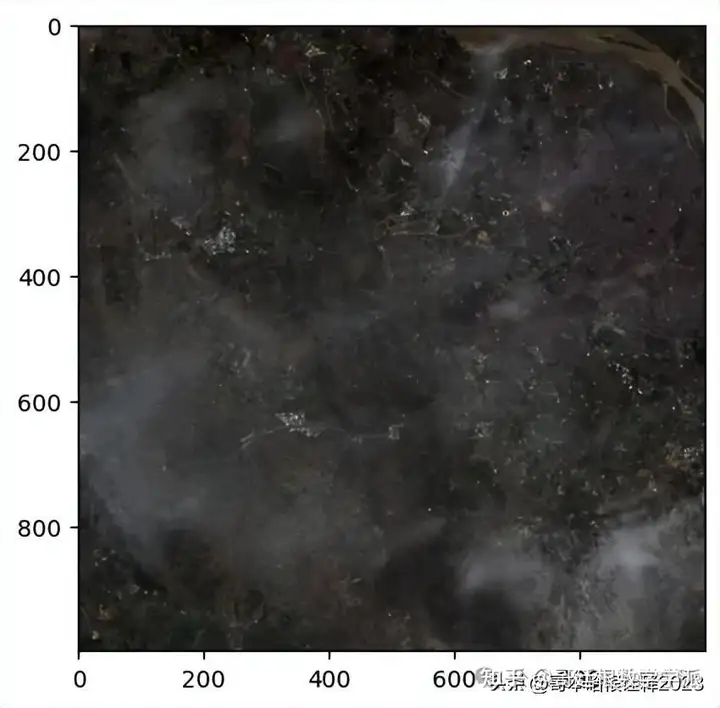
Use Wavelet transform for defogging
def RF(img: np.ndarray, sigma_s: float, sigma_r: int, num_iterations: int=3, joint_image: Optional[np.ndarray]=None):
"""Domain transform recursive edge-preserving filter
Args:
img (np.ndarray): Input image to be filtered.
sigma_s (float): Filter spatial standard deviation.
sigma_r (int): Filter range standard deviation.
num_iterations (int): Number of iterations to perform (default: 3).
joint_image (Optional[np.ndarray]): Optional image for joint filtering.
"""
I = img.astype(np.float64)
if joint_image is not None:
J = joint_image.astype(np.float64)
if I.shape[:2] != J.shape[:2]:
raise ValueError('Input and joint images must have equal width and height.')
else:
J = I
# Temporary change
J = np.stack((J,) * 1, axis=-1)
I = np.stack((I,) * 1, axis=-1)
h, w, num_joint_channels = J.shape
# Compute the domain transform (Equation 11 of the paper).
dIcdx = np.diff(J, axis=1)
dIcdy = np.diff(J, axis=0)
dIdx = np.zeros((h, w))
dIdy = np.zeros((h, w))
# Compute the l1-norm distance of neighbor pixels.
for c in range(num_joint_channels):
dIdx[:, 1:] += np.abs(dIcdx[:, :, c])
dIdy[1:, :] += np.abs(dIcdy[:, :, c])
# Compute the derivatives of the horizontal and vertical domain transforms.
dHdx = 1 + sigma_s / sigma_r * dIdx
dVdy = 1 + sigma_s / sigma_r * dIdy
# The vertical pass is performed using a transposed image.
dVdy = dVdy.T
# Perform the filtering.
N = num_iterations
F = I.copy()
sigma_H = sigma_s
for i in range(num_iterations):
# Compute the sigma value for this iteration (Equation 14 of the paper).
sigma_H_i = sigma_H * np.sqrt(3) * 2**(N - (i + 1)) / np.sqrt(4**N - 1)
F = TransformedDomainRecursiveFilter_Horizontal(F, dHdx, sigma_H_i)
F = image_transpose(F)
F = TransformedDomainRecursiveFilter_Horizontal(F, dVdy, sigma_H_i)
F = image_transpose(F)
return F.astype(img.dtype)
def TransformedDomainRecursiveFilter_Horizontal(I, D, sigma):
# Feedback coefficient (Appendix of the paper).
a = np.exp(-np.sqrt(2) / sigma)
F = I.copy()
V = a**D
h, w, num_channels = I.shape
# Left -> Right filter.
for i in range(1, w):
for c in range(num_channels):
F[:, i, c] += V[:, i] * (F[:, i - 1, c] - F[:, i, c])
# Right -> Left filter.
for i in range(w - 2, -1, -1):
for c in range(num_channels):
F[:, i, c] += V[:, i + 1] * (F[:, i + 1, c] - F[:, i, c])
return F
def image_transpose(I):
h, w, num_channels = I.shape
T = np.zeros((w, h, num_channels), dtype=I.dtype)
for c in range(num_channels):
T[:, :, c] = I[:, :, c].T
return T
# Use open dark channel to obtain the darkest channel, then use the gray_opening
# technique to remove small noise andenhance the details and important features
# of the obtained grayscale image
def opendarkchannel(I, N=7):
"""
This is the reference implementation of the open dark channel
described in the paper:
Scene-adaptive Single Image Dehazing via Opening Dark Channel Model
IET image processing, vol. 10, no. 11, pp, 877-884, 2016
Efficient single image dehazing and denoising: An efficient multi-scale correlated wavelet approach
Computer Vision and Image Understanding. Volume 162 (2017), Pages 23-33.
Copyright @ He Zhang and Xin Liu, 2017.
"""
if not N:
N = 7
# Compute the dark channel
dc = np.min(I, axis=0)
se = np.ones((N, N))
# Apply morphological opening to the dark channel
dark = grey_opening(dc, structure=se)
return dark
# Predict the color of the atmosphere in the image
# Find the brightest pixels in the dark channel and take their average value
def atmlight(im, JDark):
# the color of the atmospheric light is very close to the color of the sky
# so just pick the first few pixels that are closest to 1 in JDark
# and take the average
# pick top 0.1% brightest pixels in the dark channel
# get the image size
_, height, width = im.shape
imsize = width * height
numpx = max(imsize // 1000, 1) # accommodate for small images
JDarkVec = JDark.reshape(imsize, 1) # a vector of pixels in JDark
ImVec = im.reshape(3, imsize) # a vector of pixels in my image
indices = np.argsort(JDarkVec)
indices = indices[imsize-numpx:] # need the last few pixels because those are closest to 1
atmSum = np.zeros((3, 1))
for ind in range(numpx):
atmSum += ImVec[:, indices[ind]]
A = atmSum / numpx
return A.flatten()
def transmissionEstimate(im, A, N=15):
omega = 0.95 # the amount of haze we're keeping
im3 = np.zeros_like(im)
for ind in range(3):
im3[ind, :, :] = im[ind, :, :] / A[ind]
transmission = 1 - omega * opendarkchannel(im3, N)
return transmission
def boxfilter(imSrc, r):
"""
BOXFILTER O(1) time box filtering using cumulative sum
- Definition imDst(x, y)=sum(sum(imSrc(x-r:x+r,y-r:y+r)));
- Running time independent of r;
- Equivalent to the function: colfilt(imSrc, [2*r+1, 2*r+1], 'sliding', @sum);
- But much faster.
"""
hei, wid = imSrc.shape
imDst = np.zeros_like(imSrc)
# cumulative sum over Y axis
imCum = np.cumsum(imSrc, axis=0)
# difference over Y axis
imDst[0:r+1, :] = imCum[r:2*r+1, :]
imDst[r+1:hei-r, :] = imCum[2*r+1:hei, :] - imCum[0:hei-2*r-1, :]
imDst[hei-r:hei, :] = np.tile(imCum[hei-1, :], (r, 1)) - imCum[hei-2*r-1:hei-r-1, :]
# cumulative sum over X axis
imCum = np.cumsum(imDst, axis=1)
# difference over X axis
imDst[:, :r+1] = imCum[:, r:2*r+1]
imDst[:, r+1:wid-r] = imCum[:, 2*r+1:wid] - imCum[:, :wid-2*r-1]
imDst[:, wid-r:wid] = np.tile(imCum[:, wid-1], (r, 1)).T - imCum[:, wid-2*r-1:wid-r-1]
return imDst
def guidedfilter(I, p, r, eps):
"""
O(1) time implementation of guided filter.
- guidance image: I (should be a gray-scale/single channel image)
- filtering input image: p (should be a gray-scale/single channel image)
- local window radius: r
- regularization parameter: eps
"""
h, w = I.shape
N = boxfilter(np.ones((h, w)), r) # the size of each local patch; N=(2r+1)^2 except for boundary pixels.
mean_I = boxfilter(I, r) / N
mean_p = boxfilter(p, r) / N
mean_Ip = boxfilter(I * p, r) / N
cov_Ip = mean_Ip - mean_I * mean_p # this is the covariance of (I, p) in each local patch.
mean_II = boxfilter(I * I, r) / N
var_I = mean_II - mean_I * mean_I
a = cov_Ip / (var_I + eps) # Eqn. (5) in the paper
b = mean_p - a * mean_I # Eqn. (6) in the paper
mean_a = boxfilter(a, r) / N
mean_b = boxfilter(b, r) / N
q = mean_a * I + mean_b # Eqn. (8) in the paper
return q
def recover(I, tran, A, tx=0.1):
h, w, c = I.shape
res = np.zeros((h, w, c))
tran = np.where(tran < tx, tx, tran)
res[:,:,0] = (I[:,:,0] - A[0]) / tran + A[0]
res[:,:,1] = (I[:,:,1] - A[1]) / tran + A[1]
res[:,:,2] = (I[:,:,2] - A[2]) / tran + A[2]
return res
def dehaze(I, level, N=8, t0=0.3):
d = 2 ** level
# Get open dark channel
dark = opendarkchannel(I, N)
# Extract transmission map
A = atmlight(I, dark)
transmission = transmissionEstimate(I, A)
I = I.transpose((1, 2, 0))
jointImg = rgb2gray(I)
transmission = guidedfilter(jointImg, transmission, int(np.ceil(30 / d)), 0.0001)
jointImg = np.stack((jointImg,) * 1, axis=-1)
t = RF(I, 10, 0.1, 3, jointImg)
t = np.mean(t, axis=2)
out = recover(I, t, A, t0)
return out, t
def waveletdehaze(f: np.ndarray, level: int=2, wname: str='sym4'):
"""
Args:
f (ndarray): Input image (foggy image)
level (int): Wavelet decomposition level
wname (string): The name of the wavelet used for the decomposition
"""
coef = 2 ** level
A = pywt.wavedec2(f, wname, level=level)[0]
D = pywt.wavedec2(f, wname, level=level)[1:]
# estimate the noise standard deviation from the detail coefficients at level 1
if level == 0:
tau = 0
else:
det1 = np.abs(D[0])
tau = np.median(det1) / 0.6745
# A_dehaized: Haze-free low frequency
# t: transmission map
A_dehaized, t = dehaze(A / coef, level)
print("A_dehaized shape:", A_dehaized.shape)
print("tranmission_map shape:", t.shape)
NA = (A_dehaized * coef).transpose((2, 0, 1))
new_D = []
for n in range(level, 0, -1):
CHD, CVD, CDD = pywt.wavedec2(f, wname, level=level)[n]
t = cv2.resize(t, (CHD.shape[1], CHD.shape[2]), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
tD = np.stack([t, t, t], axis=0)
# Soft thresholding
CHD = pywt.threshold(CHD, value=tau, mode='soft')
CVD = pywt.threshold(CVD, value=tau, mode='soft')
CDD = pywt.threshold(CDD, value=tau, mode='soft')
# Enhanced details
NCHD = CHD / tD
NCVD = CVD / tD
NCDD = CDD / tD
new_D.append((NCHD, NCVD, NCDD))
print(NA.shape)
for x in D:
for i in range(3):
print(x[i].shape)
d = pywt.waverec2([NA, *new_D[::-1]], wname)
d = np.clip(d, 0, 1)
return d
def find_dark_channel(image, patch_size=15):
number_of_rows = image.shape[0]
number_of_columns = image.shape[1]
r = image[:,:,0]
g = image[:,:,1]
b = image[:,:,2]
dark_channel = np.zeros([number_of_rows, number_of_columns])
# ----- find min of channels:
min_of_channels = np.zeros([number_of_rows, number_of_columns])
for row in range(number_of_rows):
for column in range(number_of_columns):
min_of_channels[row,column] = min(r[row,column], g[row,column], b[row,column])
# ----- find min in patches:
t = int((patch_size-1)/2)
for row in range(0, number_of_rows):
for column in range(0, number_of_columns):
minimum = float('inf') # infinite number
# iteration on neighbors of pixel in patch:
for i in range(row-t, row+t+1):
for j in range(column-t, column+t+1):
if (i >= 0) and (i < number_of_rows) and (j >= 0) and (j < number_of_columns): # if the pixel is in the range of image
if min_of_channels[i,j] < minimum:
minimum = min_of_channels[i,j]
dark_channel[row,column] = minimum
return dark_channel
def find_atmospheric_light(image, dark_channel, threshold=0.1/100):
number_of_rows = image.shape[0]
number_of_columns = image.shape[1]
# ------ find brightest in dark channel:
dark_channel_reshaped = dark_channel.ravel()
dark_channel_reshaped.sort() # sort from smallest to largest
dark_channel_reshaped = dark_channel_reshaped[::-1] # sort from largest to smallest
brightest_in_dark_channel = dark_channel_reshaped[0]
# ------ pick the 'threshold' number of brightes pixels:
n = int(threshold * (number_of_rows * number_of_columns))
indices_of_top_brightest_pixels_in_dark_channel = (-dark_channel_reshaped).argsort()[:n] # https://stackoverflow.com/questions/16486252/is-it-possible-to-use-argsort-in-descending-order
counter = 0
bright_pixels_in_dark_channel = np.zeros([indices_of_top_brightest_pixels_in_dark_channel.shape[0],2])
for i in indices_of_top_brightest_pixels_in_dark_channel:
row_of_pixel = int(i / number_of_columns)
column_of_pixel = int(i % number_of_columns)
bright_pixels_in_dark_channel[counter,0] = row_of_pixel
bright_pixels_in_dark_channel[counter,1] = column_of_pixel
counter += 1
# ------ find the highest intensities of bright_pixels_in_dark_channel in the input image:
atmospheric_light = np.zeros(3) # has 3 channels
max_in_channel_red = 0; max_in_channel_green = 0; max_in_channel_blue = 0
for pixel in range(0, bright_pixels_in_dark_channel.shape[0]):
row_of_pixel = int(bright_pixels_in_dark_channel[pixel,0])
column_of_pixel = int(bright_pixels_in_dark_channel[pixel,1])
# channel red:
if image[row_of_pixel, column_of_pixel, 0] > max_in_channel_red:
max_in_channel_red = image[row_of_pixel, column_of_pixel, 0]
atmospheric_light[0] = max_in_channel_red
# channel green:
if image[row_of_pixel, column_of_pixel, 1] > max_in_channel_green:
max_in_channel_green = image[row_of_pixel, column_of_pixel, 1]
atmospheric_light[1] = max_in_channel_green
# channel blue:
if image[row_of_pixel, column_of_pixel, 2] > max_in_channel_blue:
max_in_channel_blue = image[row_of_pixel, column_of_pixel, 2]
atmospheric_light[2] = max_in_channel_blue
return atmospheric_light
def find_transmission(image, atmospheric_light, weight=0.95, patch_size=15):
# --- normalizing input image with atmospheric_light in each channel (r, g, and b):
image_array_normalized = np.zeros(image.shape)
image_array_normalized[:,:,0] = image[:,:,0] / atmospheric_light[0]
image_array_normalized[:,:,1] = image[:,:,1] / atmospheric_light[1]
image_array_normalized[:,:,2] = image[:,:,2] / atmospheric_light[2]
dark_channel_of_normalized_hazy_image = find_dark_channel(image=image_array_normalized, patch_size=patch_size)
# --- find the transmission map:
transmission_map = 1 - (weight * dark_channel_of_normalized_hazy_image)
return transmission_map
def remove_haze(image, atmospheric_light, transmission_map, t_0=0.1):
number_of_rows = image.shape[0]
number_of_columns = image.shape[1]
recovered_image = np.zeros(image.shape)
for channel in range(3):
for row in range(0, number_of_rows):
for column in range(0, number_of_columns):
recovered_image[row, column, channel] = ((image[row,column,channel] - atmospheric_light[channel]) / max(transmission_map[row,column],t_0)) + atmospheric_light[channel]
return recovered_image
print(ex4_rgb.shape)
dark_channel = find_dark_channel(ex4_rgb, patch_size=15)
print("Calculate dark channel done")
print(dark_channel)
print("-" * 100)
atmospheric_light = find_atmospheric_light(image=ex4_rgb, dark_channel=dark_channel, threshold=0.1/100)
print("Calculate atmospheric light done")
print(atmospheric_light)
print("-" * 100)
transmission_map = find_transmission(image=ex4_rgb, atmospheric_light=atmospheric_light, weight=0.95, patch_size=15)
print("Calculate transmission map done")
print(transmission_map)
print("-" * 100)
recover_image = remove_haze(image=ex4_rgb, atmospheric_light=atmospheric_light, transmission_map=transmission_map, t_0=0.1)
print("Calculate recover image done")
print(recover_image)
print("-" * 100)
print(recover_image.shape)
recover_image.dtype
recover_image = (recover_image - np.min(recover_image)) / (np.max(recover_image) - np.min(recover_image))
recover_image = (recover_image * (2**16 - 1)).astype(np.uint16)
print(recover_image)
print(np.max(recover_image))
print(np.min(recover_image))
print(np.mean(recover_image))
print(recover_image.shape)
show(recover_image.transpose((2, 0, 1)), adjust=True)
cv2.imwrite("images/{}.TIF".format("dehaze6"), recover_image)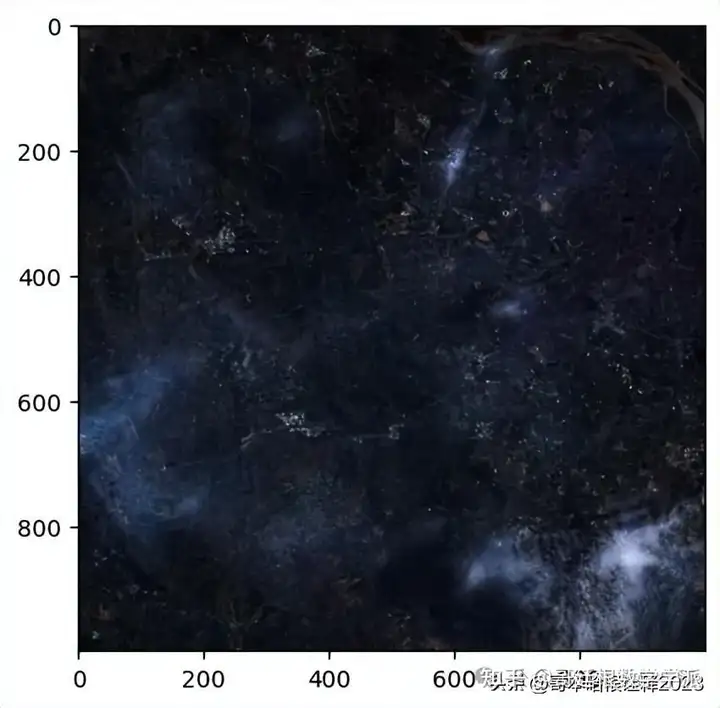
Apply wavelet transform for pan-sharpening
ex5_band2_url = "images/LC08_L1TP_127045_20200730_20200908_02_T1_B2.TIF"
ex5_band3_url = "images/LC08_L1TP_127045_20200730_20200908_02_T1_B3.TIF"
ex5_band4_url = "images/LC08_L1TP_127045_20200730_20200908_02_T1_B4.TIF"
ex5_band8_url = "images/LC08_L1TP_127045_20200730_20200908_02_T1_B8.TIF"
ex5_rgb_url = "images/LC08_L1TP_127045_20200730_20200908_02_T1_RGB.TIF"
ex5_pan_sharpened_url = "images/pan_sharpened.TIF"
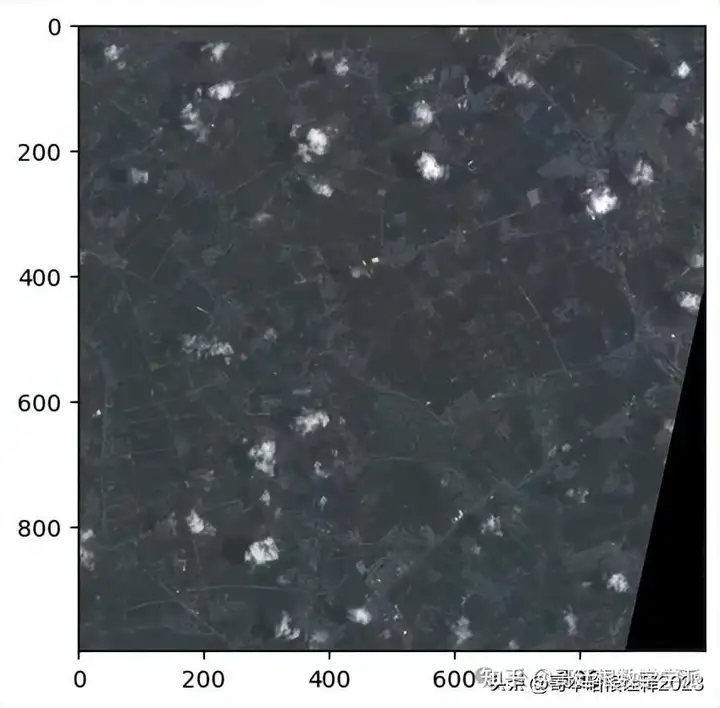
ex5_rgb, ex5_rgb_metadata = create_rgb_image(ex5_band4_url, ex5_band3_url, ex5_band2_url, ex5_rgb_url)
show(ex5_rgb.transpose((2, 0, 1)), adjust=True)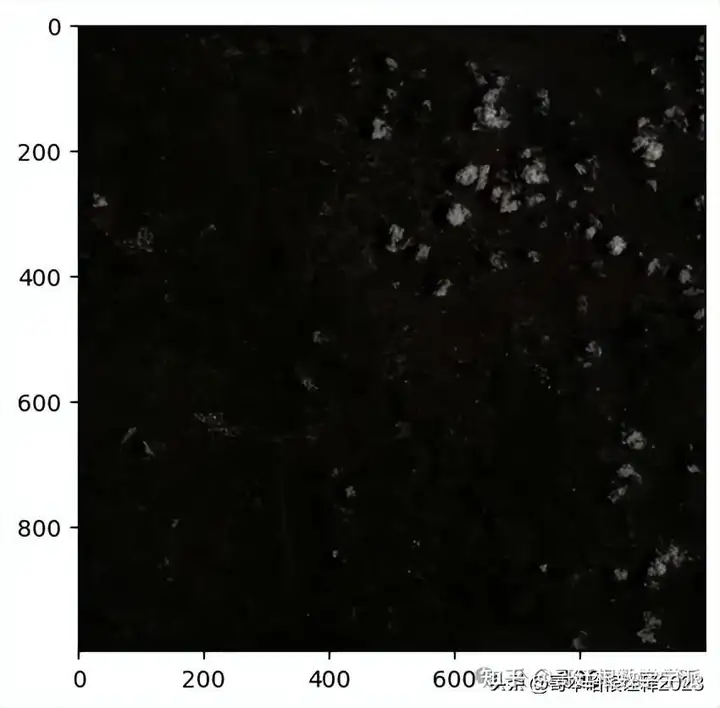
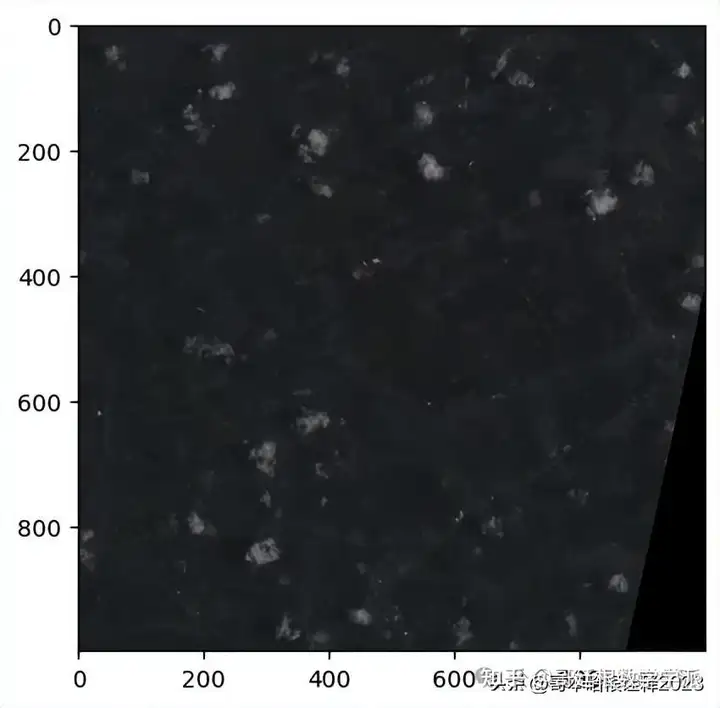
ex5_band8, ex5_band8_metadata = read_tiff_img(ex5_band8_url)
show(ex5_band8, adjust=True, cmap="gray")
print(ex5_band8_metadata)Using pandromatic image with greater resolution and multispectral image but poor resolution to make a synthetic RGB image with better resolution
ex5_band8_metadata.update({"count": 3})
def pan_sharpening(img_pandchromatic, rgb_img):
# Convert image value to float
Ia1 = img_as_float(img_pandchromatic)
Ia2 = img_as_float(rgb_img)
# DWT for pandchromatic image
coeffs1 = swt2(Ia1, 'sym4', level=1)
ca1, (chd1, cvd1, cdd1) = coeffs1[0]
dec1 = np.block([[ca1, chd1], [cvd1, cdd1]])
enc1 = iswt2([(ca1, (chd1, cvd1, cdd1))], 'sym4')
show(dec1, cmap="gray")
# DWT for multispectral image
coeffs2 = swt2(Ia2, 'sym4', level=1, axes=(0, 1))
ca2, (chd2, cvd2, cdd2) = coeffs2[0]
dec2_1 = np.block([[ca2[:, :, 0], chd2[:, :, 0]], [cvd2[:, :, 0], cdd2[:, :, 0]]])
dec2_2 = np.block([[ca2[:, :, 1], chd2[:, :, 1]], [cvd2[:, :, 1], cdd2[:, :, 1]]])
dec2_3 = np.block([[ca2[:, :, 2], chd2[:, :, 2]], [cvd2[:, :, 2], cdd2[:, :, 2]]])
dec2 = np.stack([dec2_1, dec2_2, dec2_3], axis=2)
show(dec2.transpose((2, 0, 1)))
# Injection model
gk = []
for ik in range(3):
s = ca2[:, :, ik]
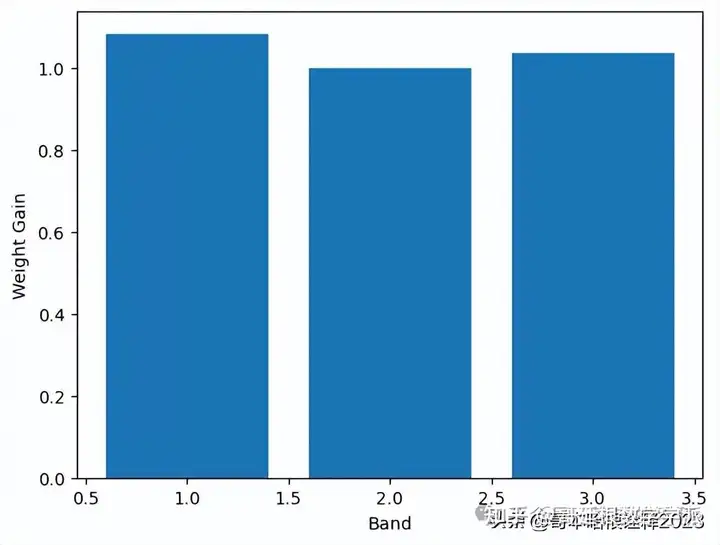
gk.append(np.cov(np.hstack((s.flatten(), ca1.flatten()))) / np.var(ca1.flatten()))
# Show gain
plt.figure()
plt.bar(range(1, 4), gk)
plt.xlabel('Band')
plt.ylabel('Weight Gain')
plt.show()
# Fusion into approximate image
# LL
y = 0.33 * ca2[:, :, 0] + 0.34 * ca2[:, :, 1] + 0.33 * ca2[:, :, 2]
Ims2LL = ca2.copy()
for i in range(3):
Ims2LL[:, :, i] = ca2[:, :, i] + gk[i] * (ca1 - y)
show(Ims2LL.transpose((2, 0, 1)))
Ims2LH = chd2.copy()
for i in range(3):
Ims2LH[:, :, i] = (chd1 + chd2[:, :, i]) / 2
Ims2HL = cvd2.copy()
for i in range(3):
Ims2HL[:, :, i] = (cvd1 + cvd2[:, :, i]) / 2
Ims2HH = cdd2.copy()
for i in range(3):
Ims2HH[:, :, i] = (cdd1 + cdd2[:, :, i]) / 2
# Inverse conversion
X = []
for i in range(3):
X.append(iswt2([(Ims2LL[:, :, i], (Ims2LH[:, :, i], Ims2HL[:, :, i], Ims2HH[:, :, i]))], 'sym4'))
X = np.stack(X, axis=2)
show(X.transpose((2, 0, 1)))
return X
ex5_pan_sharpened = pan_sharpening(ex5_band8, ex5_rgb)
print(ex5_pan_sharpened.shape)
print(ex5_pan_sharpened.dtype)
normalized = (ex5_pan_sharpened - np.min(ex5_pan_sharpened)) / (np.max(ex5_pan_sharpened) - np.min(ex5_pan_sharpened))
ex5_pan_sharpened = (normalized * (2**16 - 1)).astype(np.uint16)
print(ex5_pan_sharpened)
cv2.imwrite(ex5_pan_sharpened_url, ex5_pan_sharpened)
# save_tiff_img(ex5_pan_sharpened_url, ex5_pan_sharpened, ex5_band8_metadata)
知乎学术咨询:
https://www.zhihu.com/consult/people/792359672131756032?isMe=1擅长领域:现代信号处理,机器学习,深度学习,数字孪生,时间序列分析,设备缺陷检测、设备异常检测、设备智能故障诊断与健康管理PHM等。