605. 种花问题(简单)
假设有一个很长的花坛,一部分地块种植了花,另一部分却没有。可是,花不能种植在相邻的地块上,它们会争夺水源,两者都会死去。
给你一个整数数组
flowerbed表示花坛,由若干0和1组成,其中0表示没种植花,1表示种植了花。另有一个数n,能否在不打破种植规则的情况下种入n朵花?能则返回true,不能则返回false。
解法一、贪心
先种满,数数满了多出来几朵,再讨论n在不在范围内。对边界要求有点高。。
题解里较完美的一个if条件:
if ((i == 0 || f[i - 1] == 0) && f[i] == 0 && (i == m - 1 || f[i + 1] == 0))
java
class Solution {
public boolean canPlaceFlowers(int[] flowerbed, int n) {
int num = flowerbed.length;
int res = 0;
if(num == 1){
return n==0 || flowerbed[0] == 0 && n == 1 ;
}else if(num == 2){
return n==0 || ((flowerbed[0] == 0 && flowerbed[1] == 0) && n == 1);
}
for(int i = 0; i < num;i++){
if(i == 0 && flowerbed[0] == 0 && flowerbed[1] == 0){
flowerbed[0] = 1;
res++;
}else if(i == num-1 && flowerbed[i-1] == 0 && flowerbed[i] == 0){
res++;
}else if(i > 0 && i < num - 1 && flowerbed[i] != 1 && flowerbed[i+1] != 1 && flowerbed[i-1] != 1){
flowerbed[i] = 1;
res++;
}
}
return n <= res;
}
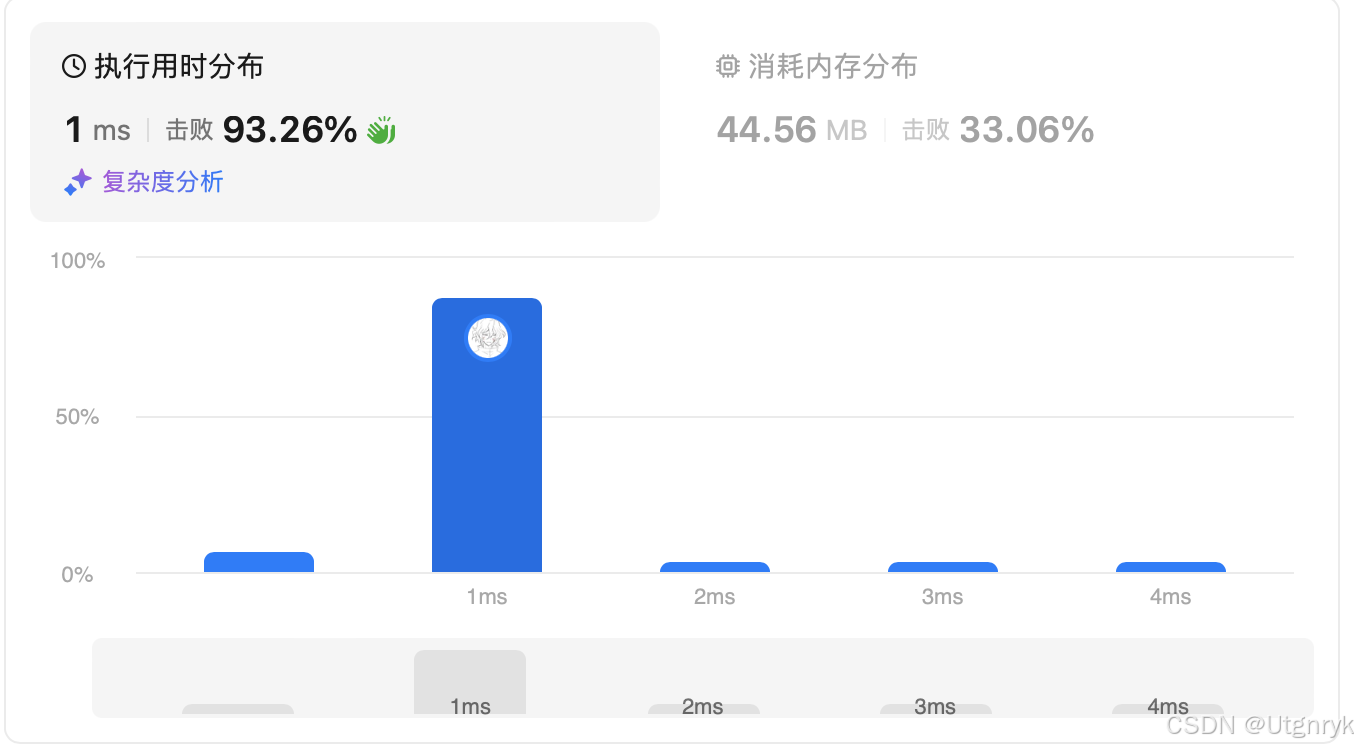
}
121. 买卖股票的最佳时机(简单)
给定一个数组
prices,它的第i个元素prices[i]表示一支给定股票第i天的价格。你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回
0。
解法一、暴力(超时)
一开始确实想不动脑子来着(
java
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int maxprofit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < prices.length; j++) {
int profit = prices[j] - prices[i];
if (profit > maxprofit) {
maxprofit = profit;
}
}
}
return maxprofit;
}
}解法二、类dp
但不需要维护一个dp数组,只需要维护一个从0-k(0<=k<n)的最小买入值就好
java
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int min = prices[0];
int profit = 0;
for(int i = 1;i < prices.length;i++){
profit = Math.max(prices[i] - min,profit);
min = Math.min(min,prices[i]);
}
return profit;
}
}122. 买卖股票的最佳时机 II(中等)
给你一个整数数组
prices,其中prices[i]表示某支股票第i天的价格。在每一天,你可以决定是否购买和/或出售股票。你在任何时候 最多 只能持有 一股 股票。你也可以先购买,然后在 同一天 出售。
返回 你能获得的 最大 利润 。
解法一、贪心
本质思想就是一旦有钱赚马上买入卖出。注意:贪心只能模拟思想过程,不是实际交易过程。如对于[1,3,4],贪心是1买3卖、3买4卖,交易过程是1买4卖。两者利益等价,行为不等价。
本题还有很多其他类型,尤其是dp/递增栈,但果然还是放在dp专题里做比较好吧~这方面就不贪心了!
java
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int profit = 0;
if(prices.length < 2)return 0;
for(int i = 1;i < prices.length;i++){
if(prices[i] > prices[i-1])profit += prices[i] - prices[i-1];
}
return profit;
}
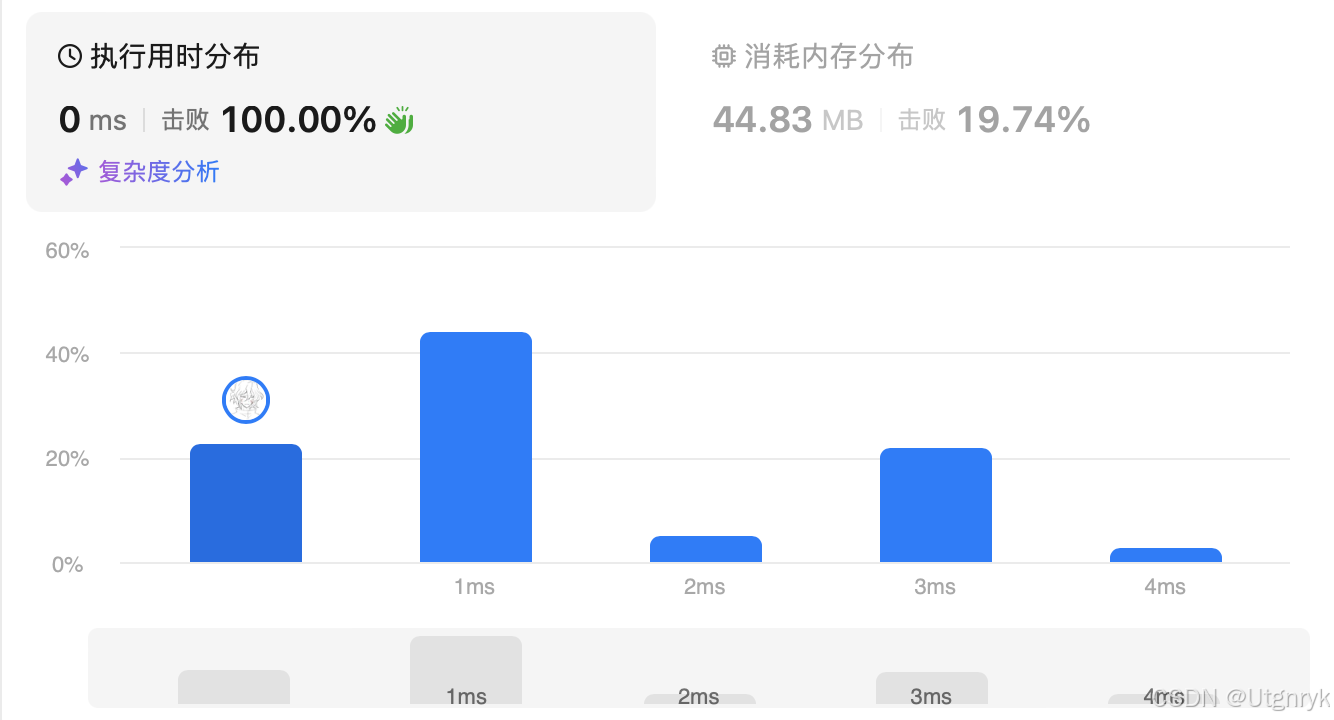
}
561. 数组拆分(简单)
给定长度为
2n的整数数组nums,你的任务是将这些数分成n对, 例如(a1, b1), (a2, b2), ..., (an, bn),使得从1到n的min(ai, bi)总和最大。返回该 最大总和 。
解法一、排序
要取最大,也就是尽量把小的和小的堆一起,大的和大的堆一起。所以先排序,排序后数组偶数位置的和就是所求。
java
class Solution {
public int arrayPairSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int n = nums.length,sum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i +=2){
sum+=nums[i];
}
return sum;
}
}解法二、数组排序
从代码示例那边看到的。这个和之前看到的那个取maxSum、minSum然后/2的技法其实有点像,桶排序虽然麻烦但是耗时真的很低。这里直接取gpt的解释吧。
index用来追踪当前已经遍历的数值的累计个数。
res是用于存储最终的结果。每当
arr[i] > 0,意味着索引i对应的数值在nums中出现过,代码会根据当前的index和arr[i]的值来计算部分结果:
((index + 1) % 2 + arr[i]) / 2这个表达式与确定中位数位置相关,它用于决定是否将该数值纳入res的计算。
(i - 10000)将索引i转换回原来的数值范围(因为我们之前对nums的数值进行了偏移处理)。最后,
index = index + arr[i]用于更新累计的数值个数。
((index + 1) % 2 + arr[i]) / 2这个表达式的作用是用于控制在遍历过程中,是否选择将当前i对应的数值 (即i - 10000) 贡献给最终的res结果。让我们一步一步拆解它的含义:
index + 1
index是用来记录遍历到当前位置之前,总共处理过的元素的个数。index + 1表示当前的元素是所有已经遍历过的元素中的第几个。
% 2对
index + 1取模 2 的作用是确定当前这个元素是偶数还是奇数。它会返回两种情况:
当
index + 1是奇数时,(index + 1) % 2 = 1。当
index + 1是偶数时,(index + 1) % 2 = 0。这个结果决定了后续表达式的一个偏移调整。
arr[i]
arr[i]表示当前索引i对应的数值在nums数组中出现的次数。
((index + 1) % 2 + arr[i])这一步是把
(index + 1) % 2和arr[i]的值加起来:
如果当前是奇数个元素 (
(index + 1) % 2 = 1),那么结果就是1 + arr[i]。如果当前是偶数个元素 (
(index + 1) % 2 = 0),那么结果就是0 + arr[i]。这相当于调整了
arr[i]的数值,使得某些条件下它多加 1 或不变,这和计算中位数的位置有关系。
/ 2这一步是对整个表达式进行除以 2:
如果
arr[i]是偶数或者(index + 1) % 2是 0,那么(index + 1) % 2 + arr[i]是偶数,除以 2 后返回一个整数。如果
arr[i]是奇数,并且(index + 1) % 2 = 1,这会使得奇数变为偶数的一半。总体意义
这个表达式的作用在于,在遍历过程中,根据当前遍历的元素顺序(
index)以及该元素的出现次数(arr[i]),判断要不要取一半的数值(除以 2),这样就可以控制贡献给res的数值。在处理中位数相关的算法时,这个操作可以帮助判断中位数所在位置以及应取多少值。举例
假设:
arr[i] = 3表示当前这个数出现了 3 次,
index + 1 = 5表示当前是第 5 个元素,那么:
(index + 1) % 2 = 1,所以((index + 1) % 2 + arr[i]) = 1 + 3 = 4,
/ 2后结果是2,表示将当前的数值贡献 2 次。这个操作对中位数或者其他与位置相关的统计操作有帮助。
java
class Solution {
public int arrayPairSum(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length <= 1800) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i = i + 2) {
sum = sum + nums[i];
}
return sum;
} else {
// 在该用数组排序的时候又把这件事忘了个干净
int[] arr = new int[20001];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
arr[nums[i] + 10000]++;
}
int index = 0;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > 0) {
res = res + ((index + 1) % 2 + arr[i]) / 2 * (i - 10000);
index = index + arr[i];
}
}
return res;
}
}
}455. 分发饼干(简单)
假设你是一位很棒的家长,想要给你的孩子们一些小饼干。但是,每个孩子最多只能给一块饼干。
对每个孩子
i,都有一个胃口值g[i],这是能让孩子们满足胃口的饼干的最小尺寸;并且每块饼干j,都有一个尺寸s[j]。如果s[j] >= g[i],我们可以将这个饼干j分配给孩子i,这个孩子会得到满足。你的目标是满足尽可能多的孩子,并输出这个最大数值。
解法一、排序+双指针
先排序。如果饼干比当前孩子胃口值小,那么饼干值往后挑。否则,i++,j++,计入结果。
java
class Solution {
public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
int i = 0,j = 0,res = 0;
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
while(i < g.length && j < s.length){
while(i < g.length && j < s.length && s[j] < g[i])j++;
if(i < g.length && j < s.length && s[j] >= g[i]){
i++;
j++;
res++;
}
}
return res;
}
}稍微改善一些(2ms)的情况。在这次的循环里,以孩子都吃到为前提条件,如果饼干用完,则结束,减少了反复判断。
java
public int findContentChildren0(int[] g, int[] s) {
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
int result = 0;
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < g.length; i++) {
while (j < s.length && g[i] > s[j]) {
j++;
}
if (j >= s.length) {
break;
}
j++;
result++;
}
return result;
}575. 分糖果(简单)
Alice 有
n枚糖,其中第i枚糖的类型为candyType[i]。Alice 注意到她的体重正在增长,所以前去拜访了一位医生。医生建议 Alice 要少摄入糖分,只吃掉她所有糖的
n / 2即可(n是一个偶数)。Alice 非常喜欢这些糖,她想要在遵循医生建议的情况下,尽可能吃到最多不同种类的糖。给你一个长度为
n的整数数组candyType,返回: Alice 在仅吃掉n / 2枚糖的情况下,可以吃到糖的 最多种类数。
解法一、枚举
只要品种不同就过,如果达到满值就break
java
class Solution {
public int distributeCandies(int[] candyType) {
int res = 0,n2 = candyType.length;
Arrays.sort(candyType);
for(int i = 0;i < n2;i++){
if(res == n2/2)return n2/2;
res++;
while(i < n2-1 && candyType[i]==candyType[i+1])i++;
}
return res;
}
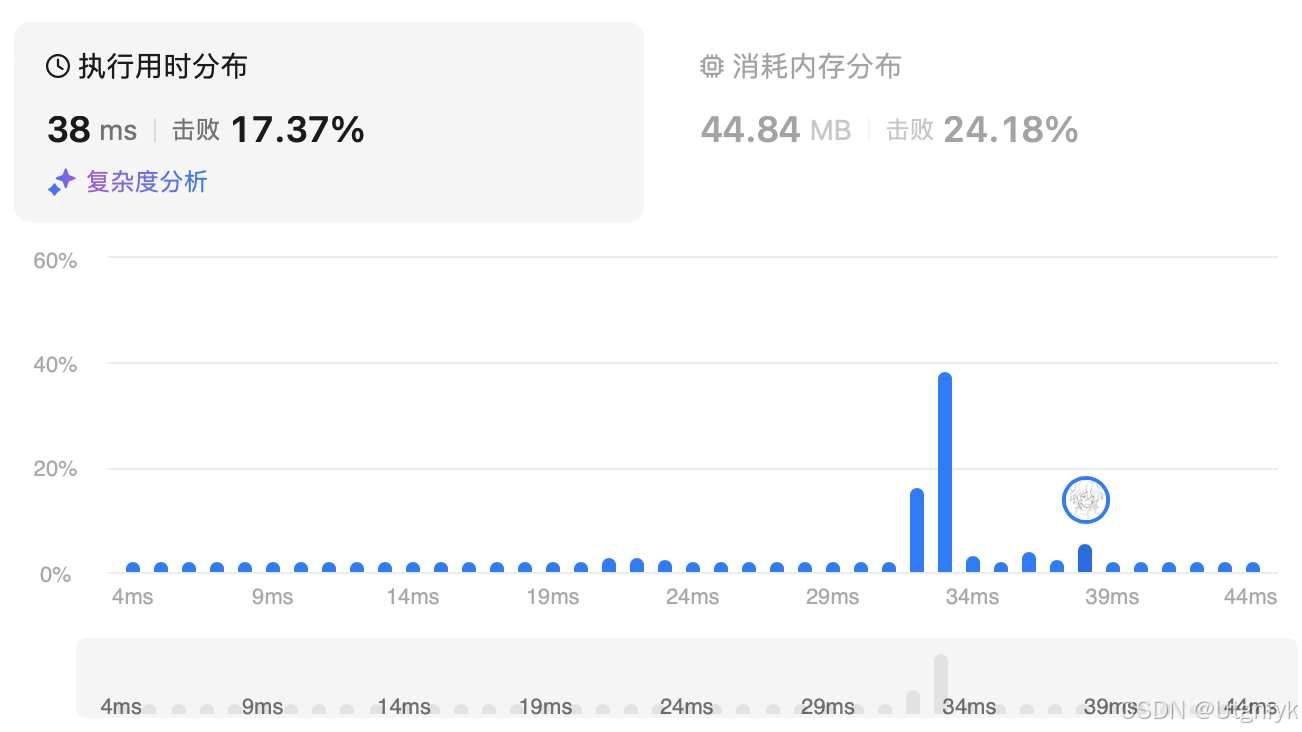
}
解法二、数据结构去重
本质上就是统计种类,然后返回Math.min(n/2,m)的东西,只要能够统计种类,什么方法都可以。
java
class Solution {
public int distributeCandies(int[] candyType) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int candy : candyType) {
set.add(candy);
}
return Math.min(set.size(), candyType.length / 2);
}
}
作者:力扣官方题解
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/distribute-candies/solutions/1072396/fen-tang-guo-by-leetcode-solution-l4f6/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。碎碎念
- 605需要转换思维,121、122是一个系列,考察dp还蛮有意思的。其中122的贪心做法比其他想法都要简单。感觉贪心里目前用到排序的次数很多


