引言
今天带来论文HERMES 3 TECHNICAL REPORT,这篇论文提出了一个强大的工具调用模型,包含了训练方案介绍。同时提出了一个函数调用标准。

为了简单,下文中以翻译的口吻记录,比如替换"作者"为"我们"。
聊天模型(-instruct | -chat)是大语言模型交互的主要方式,与基础(-base)模型不同,指令微调模型针对响应命令语句进行了优化。我们介绍了Hermes3,是一个中立对齐的通用指令和工具使用模型。
1. 总体介绍
聊天微调模型更通用的版本是指令微调模型,其中基础模型被训练以响应命令语句。指令微调模型可以通过其他功能来增强其可控性,例如系统提示(system prompt)是一种元命令,作为所有后续指令的解释指南。另一个常见的补充是工具使用,模型可以请求外部数据计算或数据检索,其结果在执行自回归生成时附加到请求中。
我们发布了Hermes3,是一系列具有强大推理能力和创造能力的指令和工具使用模型。我们的训练数据鼓励模型精确且中立地遵循系统和指令提示。与可能由于道德原因拒绝指令的闭源商业模型区别开来。
2. 模型概述

Hermes 3是通过微调Llama3.1 8B、70B和405B创建的,是高度可控的指令和聊天微调模型。模型对系统提示高度敏感。
2.1 扩展功能
除了标准的"乐于助人的助手(helpful assistant)"角色外,Hermes 3还展现了各种超越传统语言建模任务的先进能力。
Hermes 3还包括几个旨在改进可解释的多步骤问题解决的智能体的(agentic)能力。包括使用XLM标签进行结构化输出、实现中间处理的草稿纸、生成用于决策透明的内部独白等。利用Llama3.1 分词器中额外的保留标记,模型在推理任务上进行了训练,利用了<SCRATCHPAD>, <REASONING>, <INNER_MONOLOGUE>, <PLAN>, <EXECUTION>, <REFLECTION>, <THINKING>, <SOLUTION>, <EXPLANATION>, <UNIT_TEST>标记。这些特性共同提高了模型处理复杂任务,解释器方法以及跨不同领域有效传达想法的能力。
通过使用Hermes 3的工具使用和RAG技能,智能体能力可以进一步扩展。工具可以通过Hermes 函数调用标准 指定和调用,该标准将工具定义(作为JSON模式)放在<tools>中,并将调用和响应分别放在<tool_call>和<tool_response>中。对于RAG,模型已经接受训练,使用<co>标签引用来源,如图8所示。当结合在一起时,Hermes 3可以开箱即用地执行规划、整合外部数据并使用外部工具,以可解释和透明的方式,使其称为智能体任务的绝佳选择。
🛠️ 函数调用标准: https://github.com/NousResearch/Hermes-Function-Calling
3. 数据混合
Hermes 3数据集包含了大量高质量的指令数据,涵盖了广泛的领域和用例,涵盖了代码、数学、角色扮演、智能体和其他领域。
为了优化收集的数据并保持最高质量标准,我们实施了一系列过滤技术。包括:为了平衡对话长度而设置的标记长度阈值、拒绝和格式不正确的回复移除、缺少或空转对话的剔除,以及优先考虑由最强模型生成的对话。
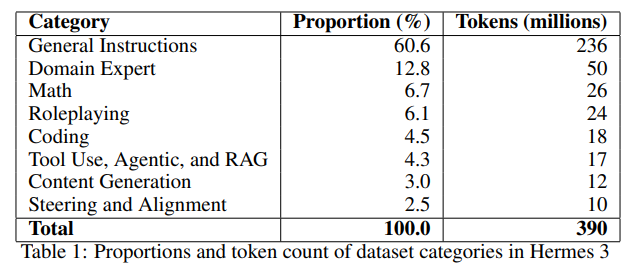
如表 1 所示,最终数据集混合包含约 3.9 亿个标记。这个精心策划和平衡的数据集极大地促进了我们模型的强大性能。
4. 训练方案
我们的训练方案包含两个阶段:监督微调(SFT)和直接偏好优化(DPO)阶段。
4.1 监督微调
SFT 阶段主要由标准指令微调组成。对于基础模型,选择了Llama3.1 Herd of Models。
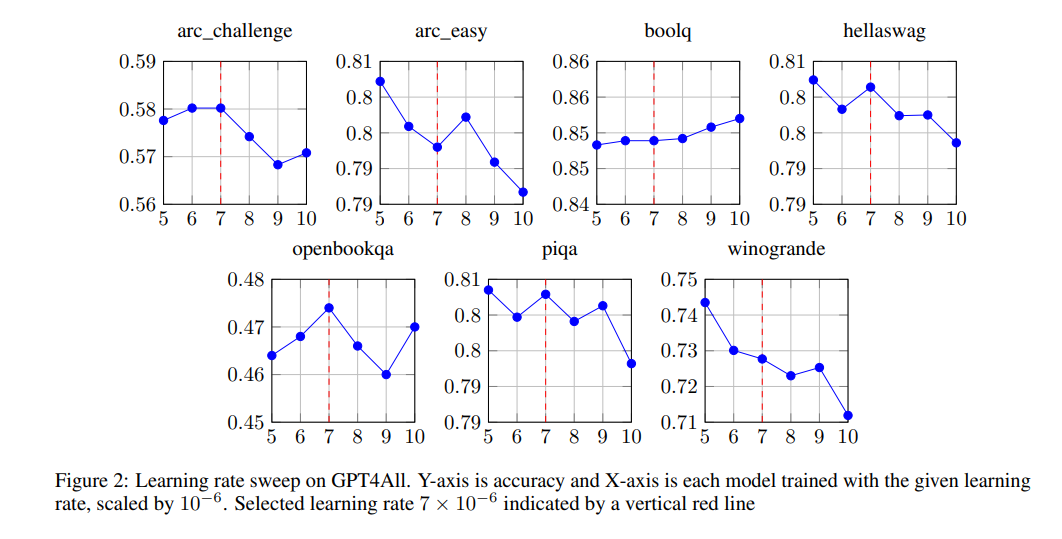
使用AdamW优化器,权重衰退为0.01,峰值学习率为 7 × 1 0 − 6 7\times 10^{-6} 7×10−6,在300步预热后,按照余弦衰减调度进行,一共训练4个epoch。学习率通过超参数搜索选择的,方法是训练8B模型,并在GPT4All基准上进行评估,结果如图2所示。
对于每个数据样本,目标标签在指令和工具输出部分的所有标记中都被设置为特殊的忽略值(-100 Pytorch中),让模型的学习重点集中在指令响应和工具使用上。
多个样本被打包在一个单一序列中,如图3所示。
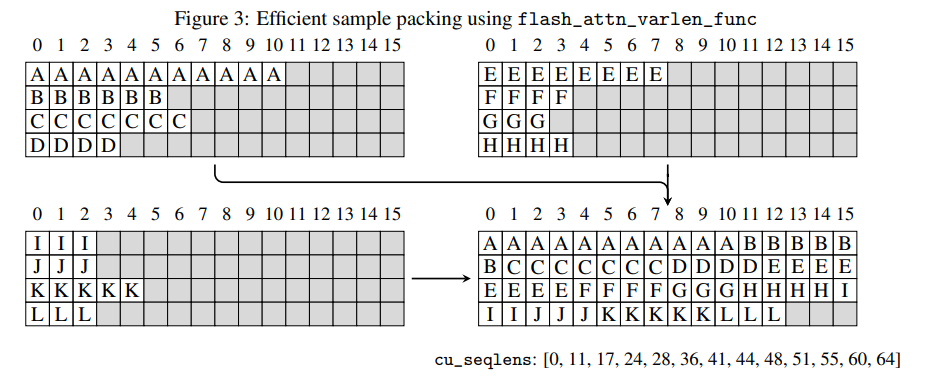
这种样本打包极大地提高了SFT的效率,因为训练数据包含了变长的样本混合。目标序列长度选择8192,以匹配Llama3.1的原生训练上下文窗口。
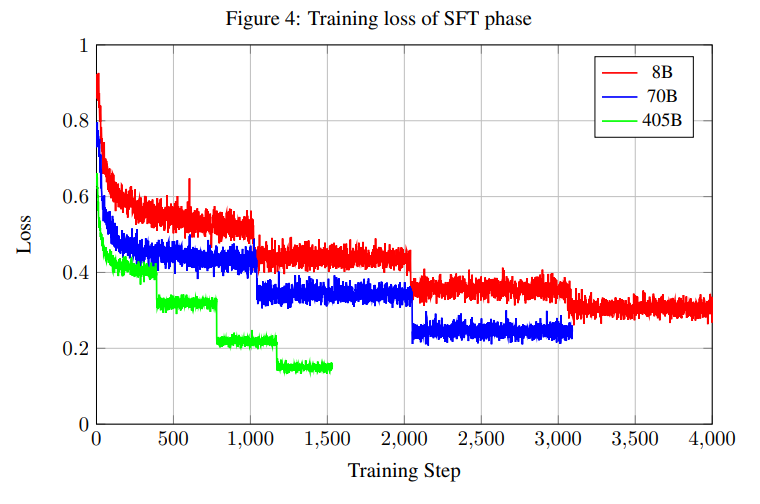
图4显示了不同模型大小的训练损失。
4.2 DPO
当应用DPO而不是调整完整模型时,我们一个LoRA适配器,设置 r = 32 , α = 16 , dropout = 0.05 r=32,\alpha=16,\text{dropout}=0.05 r=32,α=16,dropout=0.05,target是所有线性层。使用RMSProp优化器,峰值学习率为 3 × 1 0 − 6 3\times 10^{-6} 3×10−6,在9个预热步后执行线性衰退调度。此外,应用NEFTune, α = 5 \alpha=5 α=5。
在图5中绘制了奖励边际(即所选样本和被拒绝样本的奖励分数之差)。对于更大的模型尺寸,DPO只提供了微不足道的性能改进,因此只保留SFT阶段的检查点。

函数调用的提示格式
模型在特定的系统提示符和结构上进行了函数调用的训练。
应该在此消息中使用 system 角色,后跟函数签名 json:
py
<|im_start|>system
You are a function calling AI model. You are provided with function signatures within <tools></tools> XML tags. You may call one or more functions to assist with the user query. Don't make assumptions about what values to plug into functions. Here are the available tools: <tools> [{'type': 'function', 'function': {'name': 'get_stock_fundamentals', 'description': 'Get fundamental data for a given stock symbol using yfinance API.', 'parameters': {'type': 'object', 'properties': {'symbol': {'type': 'string'}}, 'required': ['symbol']}}}] </tools> Use the following pydantic model json schema for each tool call you will make: {'title': 'FunctionCall', 'type': 'object', 'properties': {'arguments': {'title': 'Arguments', 'type': 'object'}, 'name': {'title': 'Name', 'type': 'string'}}, 'required': ['arguments', 'name']} For each function call return a json object with function name and arguments within <tool_call></tool_call> XML tags as follows:
<tool_call>
{'arguments': <args-dict>, 'name': <function-name>}
</tool_call><|im_end|>Hermes-3 工具使用模板:
<scratch_pad>可以通过目标导向的行动计划 (GOAP) 推理框架来启用;- 目标(Goal)部分将重申用户请求;
- Actions 块包含 python 样式的函数调用;
- Observation 块在提供时将汇总工具结果;
- Reflection 部分将评估可用工具是否相关,如果提供了所需的参数,并分析整体任务状态;
py
You are a function calling AI model. You are provided with function signatures within <tools> </tools> XML tags. You may call one or more functions to assist with the user query. If available tools are not relevant in assisting with user query, just respond in natural conversational language. Don't make assumptions about what values to plug into functions. After calling & executing the functions, you will be provided with function results within <tool_response> </tool_response> XML tags.
<tools>
[{'type': 'function', 'function': {'name': 'get_stock_fundamentals', 'description': 'Get fundamental data for a given stock symbol using yfinance API.', 'parameters': {'type': 'object', 'properties': {'symbol': {'type': 'string'}}, 'required': ['symbol']}}}]
</tools>
For each function call return a JSON object, with the following pydantic model json schema:
{'title': 'FunctionCall', 'type': 'object', 'properties': {'name': {'title': 'Name', 'type': 'string'}, 'arguments': {'title': 'Arguments', 'type': 'object'}}, 'required': ['arguments', 'name']}
Each function call should be enclosed within <tool_call> </tool_call> XML tags. You must use <scratch_pad> </scratch_pad> XML tags to record your reasoning and planning before you call the functions as follows.
Example:
<scratch_pad>
Goal: <state task assigned by user>
Actions:
<if tool calls need to be generated:>
- {result_var_name1} = functions.{function_name1}({param1}={value1},...)
- {result_var_name2, result_var_name3} = ...
<if no tool call needs to be generated:> None
Observation: <set observation 'None' with tool calls; plan final tools results summary when provided>
Reflection: <evaluate query-tool relevance and required parameters when tools called; analyze overall task status when observations made>
</scratch_pad>
<tool_call>
{'name': <function-name>, 'arguments': <args-dict>}
</tool_call>要完成函数调用,请创建一个遵循上述系统提示的用户提示,如下所示:
py
<|im_start|>user
Fetch the stock fundamentals data for Tesla (TSLA)<|im_end|>然后,模型将生成一个工具调用,推理代码必须解析该工具调用,并将其插入到函数中
py
<|im_start|>assistant
<tool_call>
{'arguments': {'symbol': 'TSLA'}, 'name': 'get_stock_fundamentals'}
</tool_call><|im_end|>解析工具调用后,调用 api 并获取调用的返回值,并将其作为新角色传递回工具,如下所示:
py
<|im_start|>tool
<tool_response>
{"name": "get_stock_fundamentals", "content": {'symbol': 'TSLA', 'company_name': 'Tesla, Inc.', 'sector': 'Consumer Cyclical', 'industry': 'Auto Manufacturers', 'market_cap': 611384164352, 'pe_ratio': 49.604652, 'pb_ratio': 9.762013, 'dividend_yield': None, 'eps': 4.3, 'beta': 2.427, '52_week_high': 299.29, '52_week_low': 152.37}}
</tool_response>
<|im_end|>然后,助手将从函数的响应中读取该数据,并生成自然语言响应:
py
<|im_start|>assistant
The stock fundamentals data for Tesla (TSLA) are as follows:
- **Symbol**: TSLA
- **Company Name**: Tesla, Inc.
- **Sector**: Consumer Cyclical
- **Industry**: Auto Manufacturers
- **Market Capitalization**: $566,160,130,480
- **Forward Price-to-Earnings Ratio (PE Ratio)**: 42.73
- **Price-to-Book Ratio (PB Ratio)**: 9.04
- **Dividend Yield**: N/A
- **Trailing Earnings Per Share (EPS)**: $4.3
- **Beta Value of the Stock**: 2.42
- **52-Week High Price of the Stock**: $299.29
- **52-Week Low Price of the Stock**: $152.37
This information provides a snapshot of Tesla's financial position and performance based on the fundamental data obtained from the yfinance API. It shows that Tesla has a substantial market capitalization and a relatively high P/E and P/B ratio compared to other stocks in its industry. The company does not pay a dividend at the moment, which is reflected by a 'Dividend Yield' of 'None'. The Beta value indicates that Tesla's stock has a moderate level of volatility relative to the market. The 52-week high and low prices give an idea of the stock's range over the past year. This data can be useful when assessing investment opportunities and making investment decisions.<|im_end|>JSON 模式/结构化输出的提示格式
模型还针对结构化输出的特定系统提示进行了训练,该系统提示应仅以特定 json 模式中的 json 对象响应进行响应。
py
<|im_start|>system
You are a helpful assistant that answers in JSON. Here's the json schema you must adhere to:\n<schema>\n{schema}\n</schema><|im_end|>给定你提供的 {schema},它应该遵循该 json 的格式来创建它的响应,你所要做的就是给出一个典型的用户提示,它将以 JSON 形式响应。
总结
⭐ 本篇工作提出了如何良好地训练base模型提供指令遵循和函数调用能力,其提出的函数调用格式启发了vLLM和Ollama等支持工具调用。