A 二叉树删除子树
编写程序对给定二叉树执行若干次删除子树操作,输出每次删除子树后剩余二叉树的中根序列。二叉树结点的数据域值为不等于0的整数。每次删除操作是在上一次删除操作后剩下的二叉树上执行。
输入格式:
输入第1行为一组用空格间隔的整数,表示带空指针信息的二叉树先根序列,其中空指针信息用0表示。例如1 5 8 0 0 0 6 0 0表示如下图的二叉树。第2行为整数m,表示要进行的删除操作次数。接下来m行,每行一个不等于0的整数K,表示要删除以K为根的子树。m不超过100,二叉树结点个数不超过5000。输入数据保证各结点数据值互不相等,且删除子树后二叉树不为空。
输出格式:
输出为m行,每行为一组整数,表示执行删除操作后剩余二叉树的中根序列(中根序列中每个整数后一个空格)。若要删除的子树不在当前二叉树中,则该行输出0(0后无空格)。
输入样例:
1 5 8 0 0 0 6 0 0 3 5 8 6输出样例:
1 6 0 1
cpp#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<unordered_map> using namespace std; const int N = 1e4; int m; int idx, cnt; bool st[N]; unordered_map<int, int>ma; struct tree { int v; int r, l; int father; }p[N]; int build(int root) { int x; cin>>x; if (x == 0) { return 0; } p[root].v = x; ma[x]=root; p[root].l = build(++idx); p[root].r = build(++idx); return root; } void print(int root) { if (st[root]) { return; } if (root == 0) { return; } print(p[root].l); cout << p[root].v << " "; print(p[root].r); } void Delete(int root) { if (root == 0) { return; } ma[p[root].v] = 0; Delete(p[root].l); Delete(p[root].r); } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0); build(++idx); cin >> m; while (m--) { int k; cin >> k; if (!ma[k]) { cout << 0 << endl; } else { st[ma[k]] = true; print(1); cout << endl; Delete(ma[k]); } } }B 重建二叉树
给定非空二叉树的中根序列和后根序列,请编写程序创建该二叉树,计算其高度和先根序列;如给定的中根和后根序列不合法,则亦能识别。
输入格式:
输入包含多组数据(不超过10组),每组为两行字符串,第一行表示某二叉树的后根序列,第二行表示其中根序列。结点的值均为A-Z的大写字母,故二叉树结点个数不超过26,且保证输入的两个序列都是结点的全排列,但不一定是合法的中根和后根序列。输入保证不是空二叉树。
输出格式:
对于每组数据,如果输入的序列不合法(不是同一棵树的中根序列和后根序列),则输出INVALID;若输入序列合法,输出为两行,第一行为一个整数,表示该二叉树的高度,第二行为一个字符串,表示该二叉树的先根序列。
输入样例1:
CEFDBHGA CBEDFAGH CBEDFAGH CEFDBHGA BCA CAB输出样例1:
3 ABCDEFGH INVALID INVALID
经典先序,后序加中序遍历建树板子,如果有需要可以看看我有关二叉树建树的分享。
这个题外加一个判断是否为一个二叉树。
cpp#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<string> using namespace std; const int N = 100; struct tree { char c; int l, r; }p[N]; char s1[N]; char s2[N]; int cnt; int max_h; int m; bool flag = 1; int build(int al, int ar, int bl, int br,int h) { if (al > ar) { return 0; } int root = ar; char cc = s1[ar]; int k = 0; while (s1[ar] != s2[k]) { k++; } int len = k - bl; p[root].c = cc; cnt++; if (max_h < h) { max_h = h; } if (bl + len - 1 < 0) { return 0; } if (cnt >m ) { flag = 0; return 0; } p[root].l = build(al, al + len - 1, bl, bl + len - 1,h+1); p[root].r = build(al + len, ar - 1, bl + len + 1, br,h+1); return root; } void print(int root) { cout << p[root].c; if (p[root].l > 0) { print(p[root].l); } if (p[root].r > 0) { print(p[root].r); } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0); while (cin >> s1+1 && cin >> s2+1) { flag = 1; m = strlen(s1+1); cnt = 0; max_h = 0; build(1,m,1,m,0); if (cnt < m||!flag) { cout << "INVALID" << endl; } else { cout << max_h << endl; print(m); cout << endl; } } }C 最右子表达式
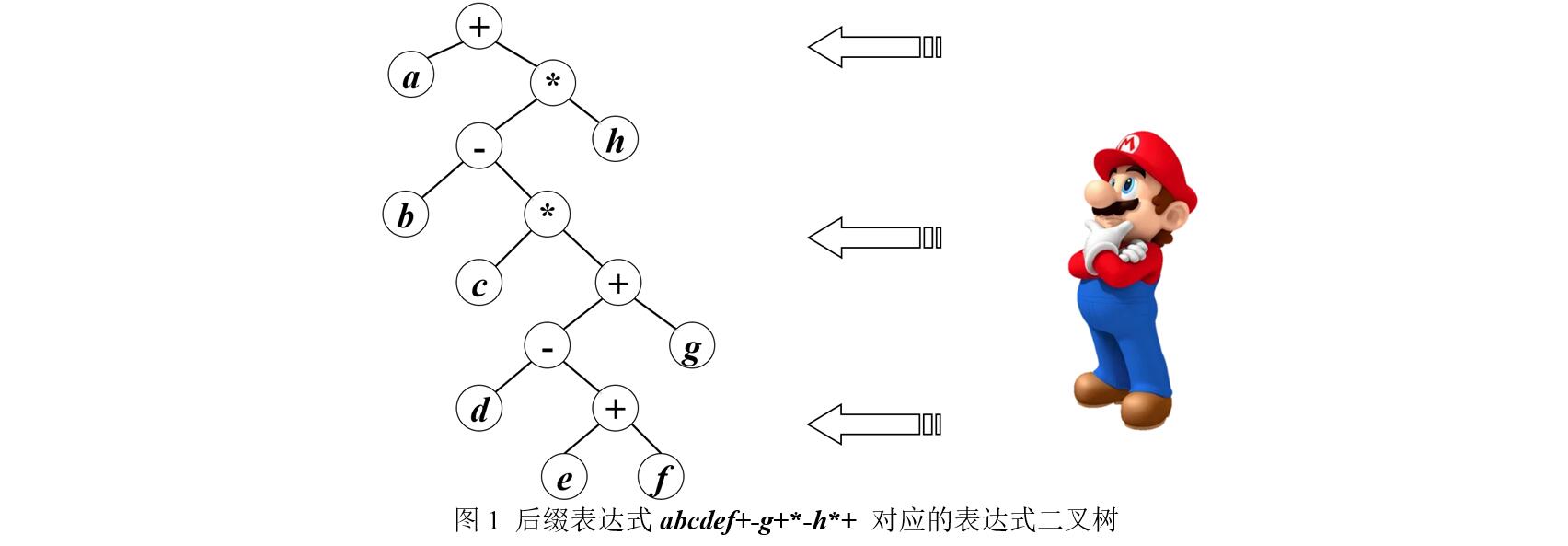
表达式可以对应一个树结构,称为表达式树。其中的叶结点对应表达式中的操作数,非叶结点对应运算符,假定所有运算均为二元运算。根据后缀表达式可以构造出表达式二叉树,方法是:从左向右扫描后缀表达式,每扫描到一个符号就生成一个二叉树结点,该符号作为结点的数据域值;若扫描到的符号是操作数,则将此操作数结点压栈;若扫描到的符号是运算符,则从栈中弹出两个结点,分别作为当前运算符结点的右、左孩子,再将当前运算符结点压栈。表达式扫描完成后,栈顶即为表达式树的根结点。表达式树的后根序列即为后缀表达式。
现给定一个后缀表达式exp,请编写程序求出exp的"最右子表达式"。exp的"最右子表达式"是指从exp对应的表达式树右边看向树,从第0层到最底层所能看到的各结点。例如后缀表达式abcdef+−g+∗−h∗+对应的表达式树如图1所示,其最右子表达式为 +∗h∗+g+f 。
输入格式:
第一行是正整数n ,表示后缀表达式的数目,1<n ≤100。接下来n 行,每行是一个由字母构成的字符串,长度不超过500,表示一个后缀表达式,其中小写字母表示操作数,大写字母表示运算符。所有运算符均为二元运算符。
输出格式:
对每个后缀表达式,输出其"最右子表达式"。
输入样例1:
6 abcdefXYgXZYhZX xyPzwIM abcABdefgCDEF abcMN bcMaN fgCeDdEbcAaBF输出样例1:
XZhZXgXf MIw FEDCg NMc Nac FBacg输入样例2:
6 vesBdtIBU crpNWgaQmGG jhAhRnlCJzU laaKuqBHfzVEJ rngAlKCpwgFIM kcqoDYoDeqiYFDL输出样例1:
UBIt GGma UzClh JEVzq MIFgg LDFYio
这道题主要是按照题目所描述的方式建树,即非递归引入栈建立二叉树。
cpp#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<stack> using namespace std; const int N = 1010; int n, m; bool st[N]; struct tree { char c; int l, r; int h; }p[N]; int idx; char s[N]; int root; void build() { stack<char> q; stack<int> in; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { char c = s[i]; if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') { q.push(c); p[++idx].c = c; in.push(idx); } else { char x = q.top(); q.pop(); char y = q.top(); q.pop(); int a = in.top(); in.pop(); int b = in.top(); in.pop(); p[++idx].c = c; p[idx].r = a; p[idx].l = b; q.push(c); in.push(idx); } } root = in.top(); } void fh(int r,int hh) { p[r].h = hh; if (p[r].l) { fh(p[r].l, hh + 1); } if (p[r].l) { fh(p[r].r, hh + 1); } } void print(int r) { if (!st[p[r].h]) { cout << p[r].c; st[p[r].h] = true; } if (p[r].r) { print(p[r].r); } if (p[r].l) { print(p[r].l); } } void init() { for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) { p[i].c = 0; p[i].l = 0; p[i].r = 0; p[i].h = 0; } root = 0; idx = 0; memset(st, false, sizeof(st)); } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0); cin >> m; while (m--) { cin >> s + 1; init(); n = strlen(s + 1); build(); fh(root, 0); print(root); cout << endl; } }D 哈夫曼树
编写一个哈夫曼编码译码程序。针对一段文本,根据文本中字符出现频率构造哈夫曼树,给出每个字符的哈夫曼编码,并进行译码,计算编码前后文本大小。
为确保构建的哈夫曼树唯一,本题做如下限定:
- 选择根结点权值最小的两棵二叉树时,选取权值较小者作为左子树。
- 若多棵二叉树根结点权值相等,则先生成的作为左子树,后生成的作为右子树,具体来说:i) 对于单结点二叉树,优先选择根结点对应字母在文本中最先出现者,如文本为cba,三个字母均出现1次,但c在文本中最先出现,b第二出现,故则选择c作为左子树,b作为右子树。ii) 对于非单结点二叉树,先生成的二叉树作为左子树,后生成的二叉树作为右子树。iii. 若单结点和非单结点二叉树根结点权值相等,优先选择单结点二叉树。
- 生成哈夫曼编码时,哈夫曼树左分支标记为0,右分支标记为1。
输入格式:
输入为3行。第1行为一个字符串,包含不超过5000个字符,至少包含两个不同的字符,每个字符为a-z的小写字母。第2、3行为两个由0、1组成的字符串,表示待译码的哈夫曼编码。
输出格式:
输出第一行为用空格间隔的2个整数,分别为压缩前后文本大小,以字节为单位,一个字符占1字节,8个二进制位占1字节,若压缩后文本不足8位,则按1字节算。输出从第二行开始,每行为1个字符的哈夫曼编码,按各字符在文本中出现次数递增顺序输出,若多个字符出现次数相同,则按其在文本出现先后排列。每行格式为"字母:编码"。最后两行为两行字符串,表示译码结果,若译码失败,则输出INVALID。
输入样例:
cbaxyyzz 0100 011输出样例:
8 3 c:100 b:101 a:110 x:111 y:00 z:01 zy INVALID
这是本次作业的难题了,但是它本身没有难度,主要是熟练哈夫曼建树的模板(有兴趣的可以看看我关于哈夫曼树建树的分享),再加上对一些优先级的限定,我这里采用的是优先队列,目的是省去比较函数,但是如果不熟练的话自己写一个结构体的比较函数就好了。
cpp#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<unordered_map> using namespace std; const int N = 5010; typedef pair<int, int>PII; typedef pair<int, char>PLL; string str; string s1, s2; int nu[200]; int idx, cnt; bool st[200]; unordered_map<char, string>ma; priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>>q; priority_queue < pair<int, PLL>, vector < pair<int, PLL>>, greater<pair<int, PLL>>>qq; struct tree { char c; int num; int l, r; }p[N]; void get_map(int root,string s) { if (p[root].c) { ma[p[root].c] = s; return; } get_map(p[root].l, s + '0'); get_map(p[root].r, s + '1'); } void get_ma(string s) { int r = idx; string ans1 = ""; int root = idx; for (int i = 0;i < s.size();i++) { if (s[i] == '0') { root = p[root].l; } else { root = p[root].r; } if (p[root].c) { ans1 += p[root].c; if (i == s.size() - 1) { cout << ans1 << endl; } root = idx; } else { if (i == s.size() - 1) { cout << "INVALID" << endl; } } } } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0); cin >> str >> s1 >> s2; int n1 = str.size(); for (int i = 0;i < str.size();i++) { char c = str[i]; if (!nu[c]) { p[++idx].c = c; cnt++; } nu[c]++; } for (int i = 1;i <= idx;i++) { char cc = p[i].c; qq.push({ nu[cc],{i,cc} }); } for (int i = 1;i < 200;i++) { if (nu[i]) { for (int j = 1;j <= idx;j++) { if (p[j].c == (char)i) { p[j].num = nu[i]; //cout << p[j].c << " " << p[j].num << endl; q.push({ nu[i],j }); } } } } while (q.size() > 1) { auto x = q.top(); q.pop(); auto y = q.top(); q.pop(); p[++idx].num = p[x.second].num + p[y.second].num; p[idx].l = x.second; p[idx].r = y.second; q.push({ p[idx].num,idx }); //cout << p[idx].num << endl; } get_map(idx, ""); int n2 = 0; for (int i = 0;i < str.size();i++) { int x = ma[str[i]].size(); n2 += x; } if (n2 % 8) { n2 = n2 / 8 + 1; } else { n2 = n2 / 8; } cout << n1 << " "<<n2 << endl; //cout << cnt << endl; while (qq.size()) { auto t = qq.top(); qq.pop(); char cc = t.second.second; cout << cc << ":" << ma[cc] << endl; } get_ma(s1); get_ma(s2); }E 罪犯帮派
Tabu市的警察局决定结束混乱,因此要采取行动根除城市中的几大帮派。目前的问题是,给出两个罪犯,他们是属于同一帮派么?城市里一共有多少个帮派?假设在Tabu市现有n名罪犯,编号为1到n,给出m条消息表示属于同一帮派的两个罪犯编号。请基于这些不完全的信息帮助警方计算出他们想要的信息。
输入格式:
输入第一行为三个正整数,n、m和q。n为罪犯数;m为给出的已知信息数量;q为查询数。接下来m行,每行2个正整数a和b,表示罪犯a和罪犯b属于同一帮派。接下来q行,每行2个正整数c和d,即查询罪犯c和d是否属于同一帮派。每行输入的整数以空格间隔,n、m、q均不超过1000。
输出格式:
输出为q+1行,前q行对应于输入的q个查询的结果,如果属于同一帮派,则输出"In the same gang.",否则输出"In different gangs."。最后一行为一个整数,表示帮派数目。
输入样例:
3 2 1 1 2 2 3 1 3输出样例:
In the same gang. 1
并查集没什么好说的。。
cpp#include<iostream> using namespace std; const int N = 1010; int p[N]; int n, m, q; int cnt; int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) { p[x] = find(p[x]); } return p[x]; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0); cin >> n >> m >> q; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { p[i] = i; } cnt = n; for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; int x = find(a); int y = find(b); if (x != y) { p[x] = y; cnt--; } } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { p[i] = find(p[i]); } for (int i = 1; i <= q; i++) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; if (p[a] == p[b]) { cout << "In the same gang." << endl; } else { cout << "In different gangs." << endl; } } cout << cnt; }F 二叉树路径和II
编写程序找出非空二叉树中和最大的路径,二叉树结点为不等于0的整数。本题的"路径"定义为二叉树中的结点序列vi,...,vj,序列中前一个结点是后一个结点的父结点,但路径不一定是以根结点为起点,也不一定是以叶结点为终点。路径的和定义为该路径所包含的所有结点的数据值之和。
输入格式:
输入为一组用空格间隔的整数,个数不超过100个,表示带空指针信息的二叉树先根序列。
输出格式:
输出为两行,第一行为该二叉树路径和的最大值,第二行为一组整数,每个整数后一个空格,表示该最大路径包含的结点值(按所在层数递增顺序输出)。如果存在多条满足条件的路径,则输出最短(包含结点个数最少)者,如果存在多条最短的路径,则输出最靠左上者。
输入样例1:
1 2 0 0 3 0 0输出样例1:
4 1 3输入样例2:
-1 2 0 0 3 4 0 0 0输出样例2:
7 3 4输入样例3:
3 2 0 0 -1 4 0 0 0输出样例3:
6 3 -1 4
这道题还是有点恶心到我了。。
cpp#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N = 210; int idx; int max_num=-0x3f3f3f3f; int min_cn=0x3f3f3f3f; int ans[N]; bool flag; struct tree { int v; int l, r; int num; }p[N]; int build(int root) { int val; cin >> val; if (val == 0) { return 0; } p[root].v = val; p[root].l = build(++idx); p[root].r = build(++idx); return root; } void get_maxnum(int root,int num){ if(root==0){ return ; } p[root].num=num+p[root].v; if(p[root].num>max_num){ max_num=p[root].num; } if(p[root].num<=0){ get_maxnum(p[root].l,0); get_maxnum(p[root].r,0); }else{ get_maxnum(p[root].l,p[root].num); get_maxnum(p[root].r,p[root].num); } } void get_mincn(int root,int h1,int h2){ if(root==0){ return; } if(p[root].num==max_num){ min_cn=min(min_cn,h2-h1); } if(p[root].num<=0){ h1=h2+1; } get_mincn(p[root].l,h1,h2+1); get_mincn(p[root].r,h1,h2+1); } void print(int root,int h1,int h2){ if(root==0){ return; } ans[h2]=p[root].v; if(p[root].num==max_num&&h2-h1==min_cn){ for(int i=h1;i<=h2;i++){ cout<<ans[i]<<" "; } return ; } if(p[root].num<=0){ h1=h2+1; } print(p[root].l,h1,h2+1); print(p[root].r,h1,h2+1); } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0); build(++idx); get_maxnum(1,0); get_mincn(1,0,0); cout<<max_num<<endl; print(1,0,0); }