题目描述
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
输入输出示例
输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)
解决方案:
基本思想:
1.初始化 ans = 0。
2.从左到右遍历 height:
初始化 left_max= 0,right max = 0。
从 height[0]到当前位置寻找最大值left_max = max(height[j],left_max)。
从当前位置到 height 末端寻找最大值right max= max(height[j],right max)。
ans = ans +min(left max,right max)-height[i]。
方式一:动态规划
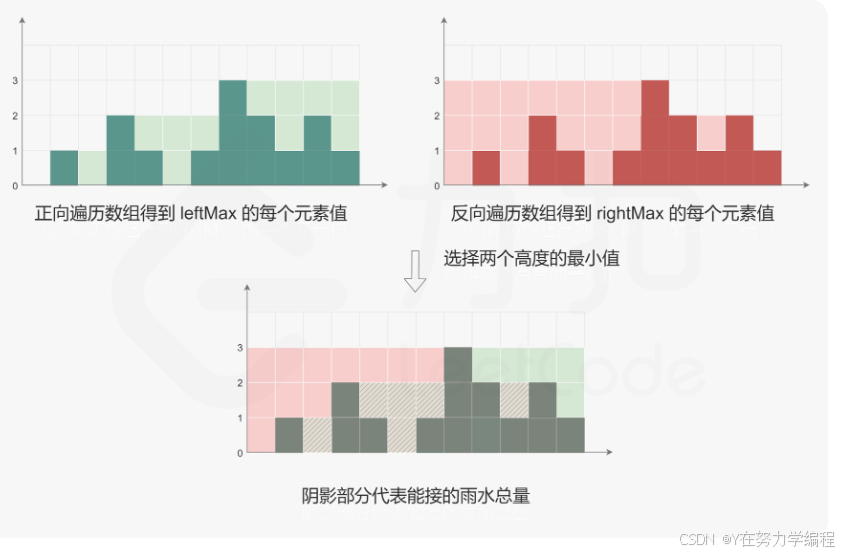
算法思路: 提前储存每个位置上所有左边柱子高度的最大值和所有右边柱子高度的最大值
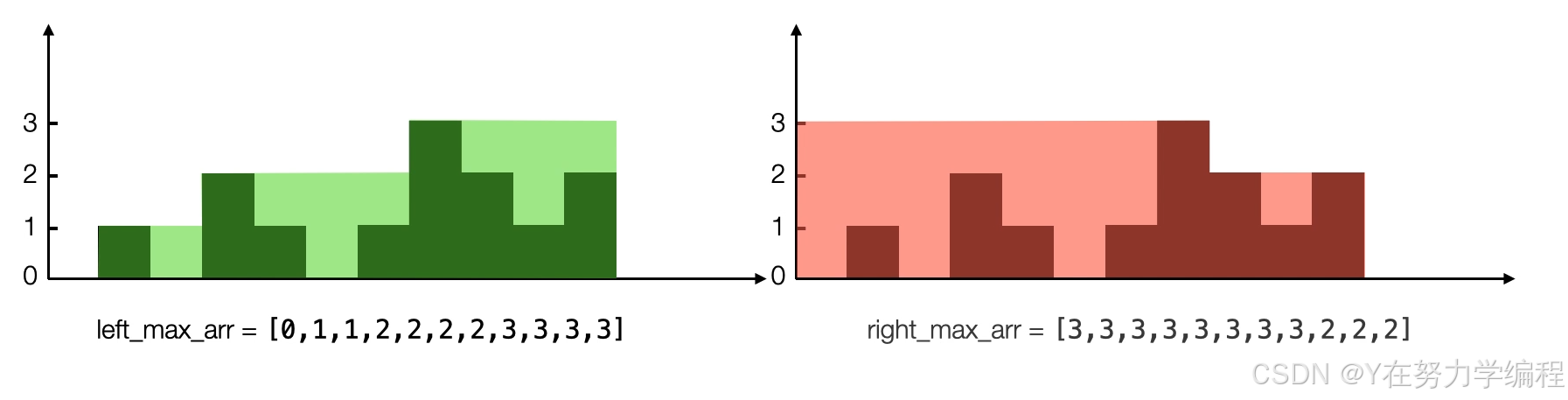
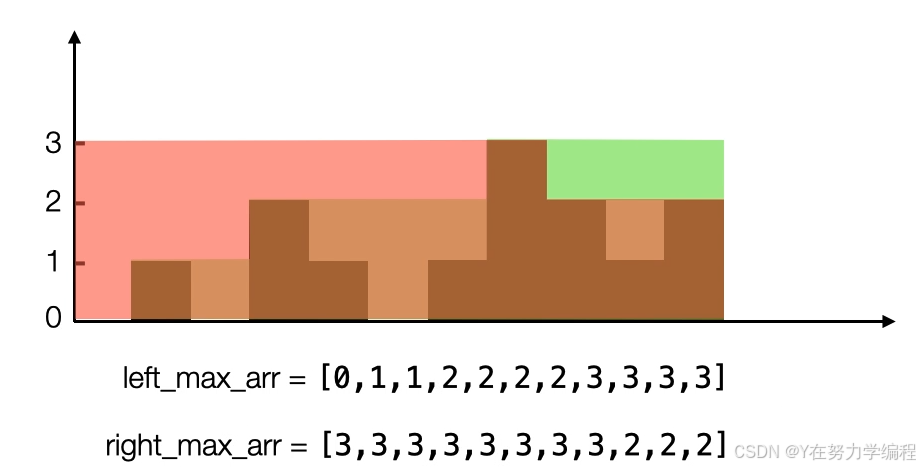
我们可以看到重叠部分,就是left_max[i]和right_max[i]之间的最小值,如果要获取存水量需要和当前的高度做差
实现代码
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int ans=0;//定义结果集
int len=height.length;
if(len<3){
return 0;//这种情况下,存不住水
}
int[] left_max=new int[len];//每个位置上所有左边柱子高度的最大值
int[] right_max=new int[len];//每个位置上所有右边柱子高度的最大值
left_max[0]=height[0];
right_max[len-1]=height[len-1];
for(int i=1;i<len;i++){
left_max[i]=Math.max(left_max[i-1],height[i]);
}
for(int i=len-2;i>=0;i--){
right_max[i]=Math.max(right_max[i+1],height[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
ans+=Math.min(left_max[i],right_max[i])-height[i];
//left_max[i]和right_max[i]之间的最小值,如果要获取存水量需要和当前的高度做差
}
return ans;
}
}复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n)
其中 n 是数组 height 的长度。计算数组 leftMax 和 rightMax 的元素值各需要遍历数组 height 一次,计算能接的雨水总量还需要遍历一次。
空间复杂度:O(n)
其中 n 是数组 height 的长度。需要创建两个长度为 n 的数组 leftMax 和 rightMax。
方式二:单调栈
**算法思想:**积水只能在低洼处形成,当后面的柱子高度比前面的低时,是无法接雨水的。所以使用单调递减栈储存可能储水的柱子,当找到一根比前面高的柱子,就可以计算接到的雨水。
实现步骤
- 使用栈 st 来存储柱子的索引下标。
- 从左到右遍历 height:
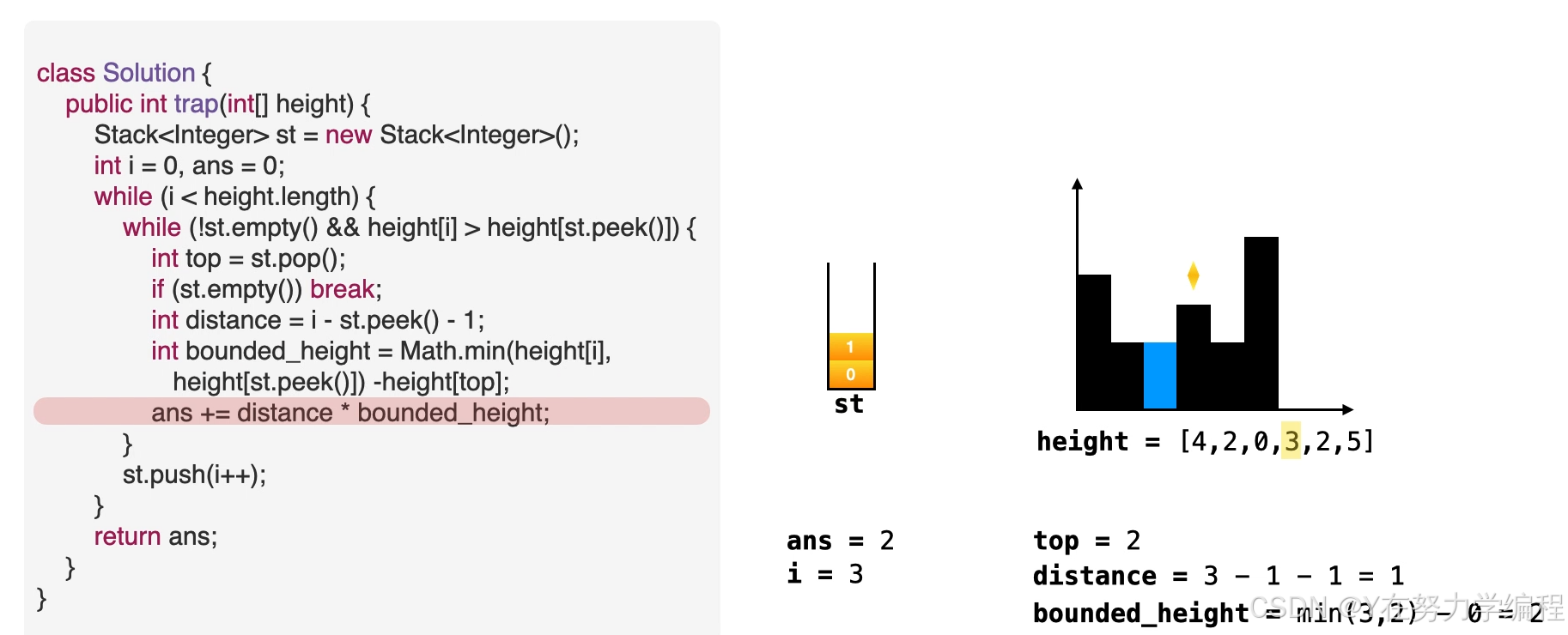
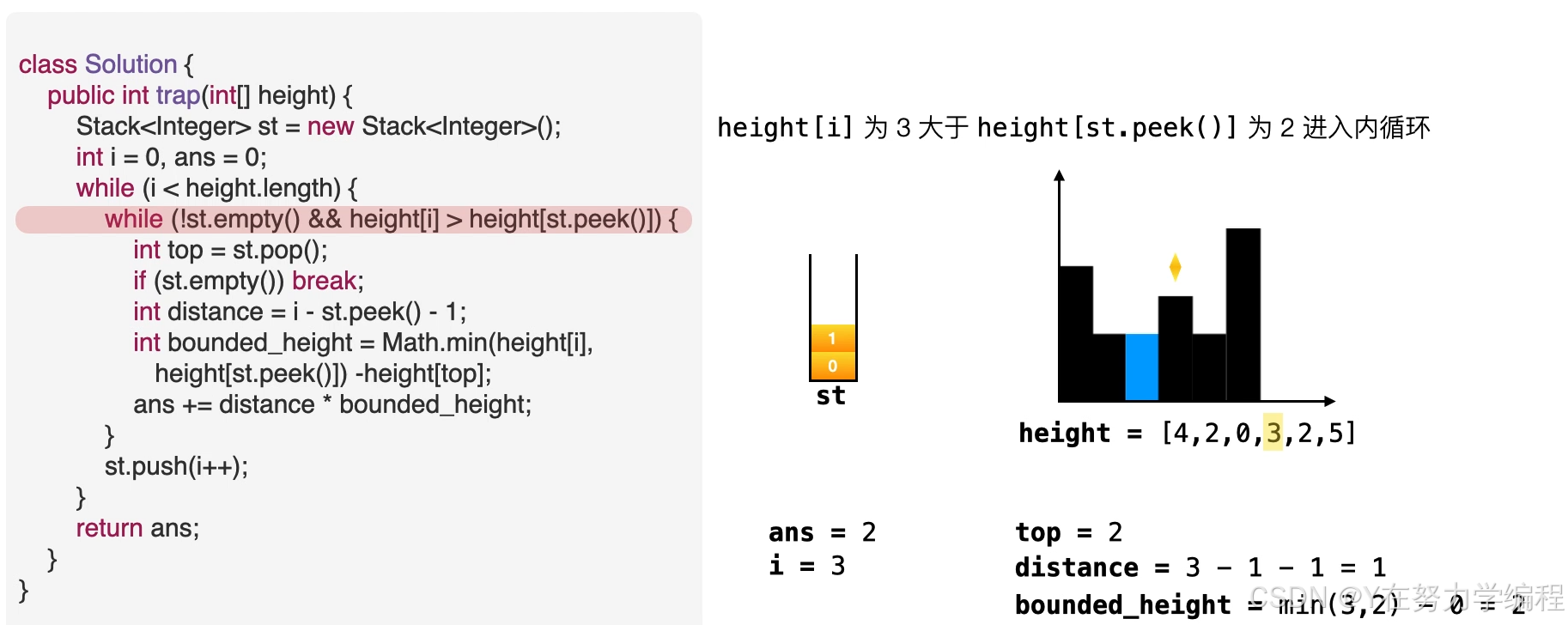
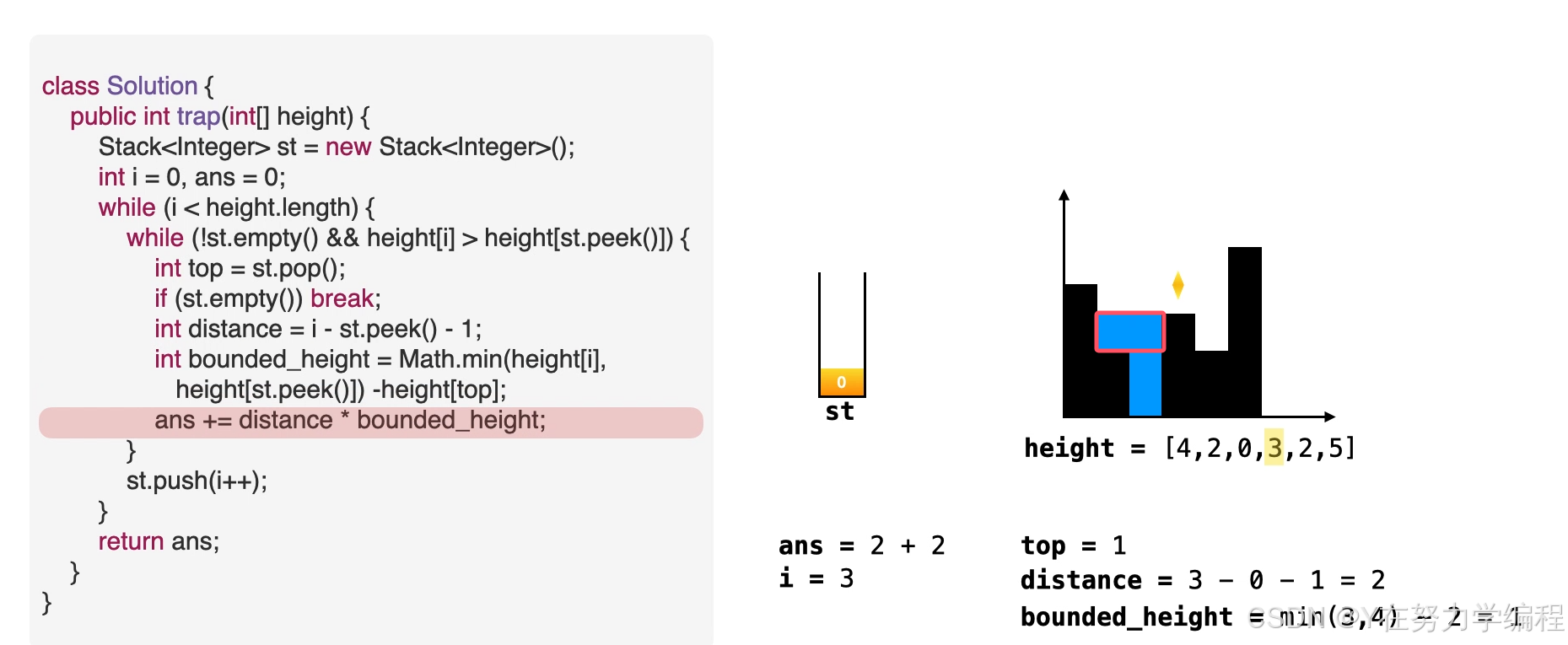
- 当栈非空目height[i]> height[st.peek()]。
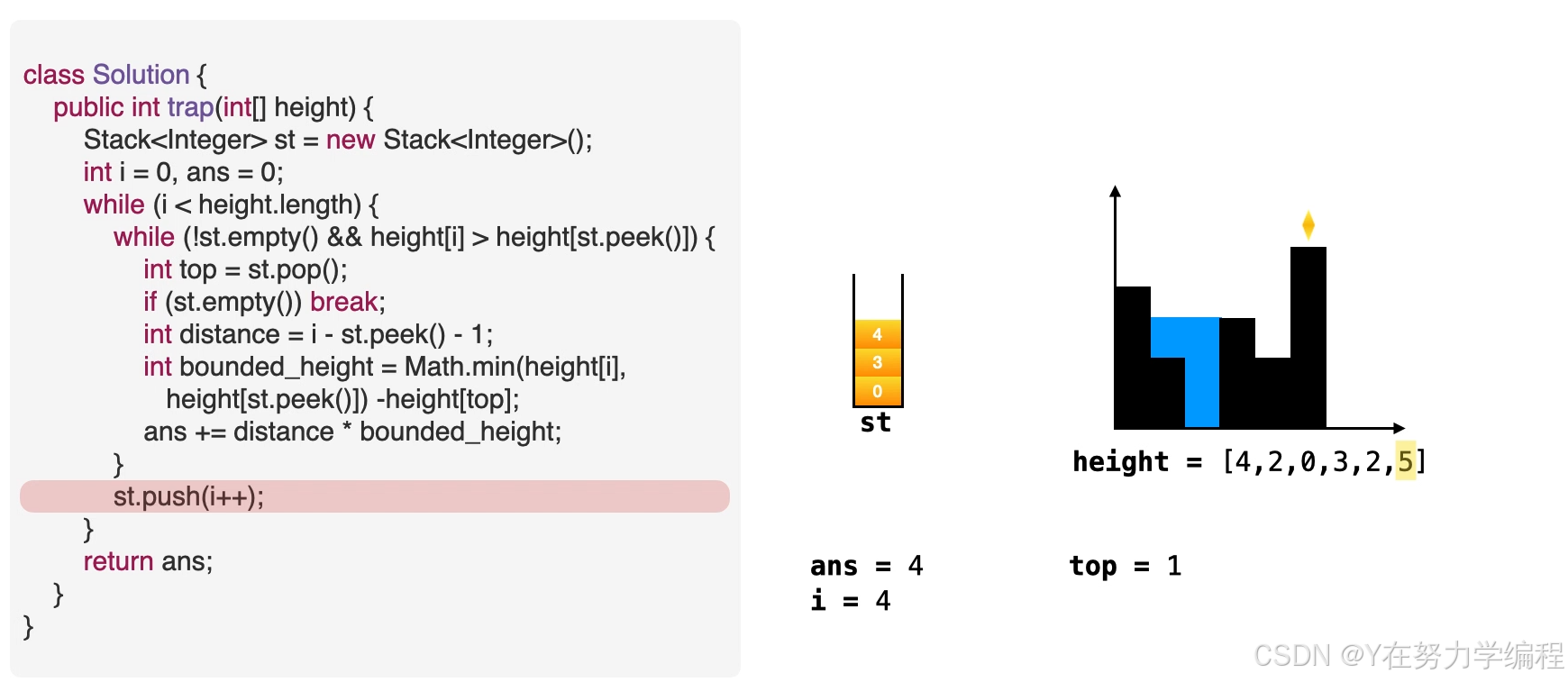
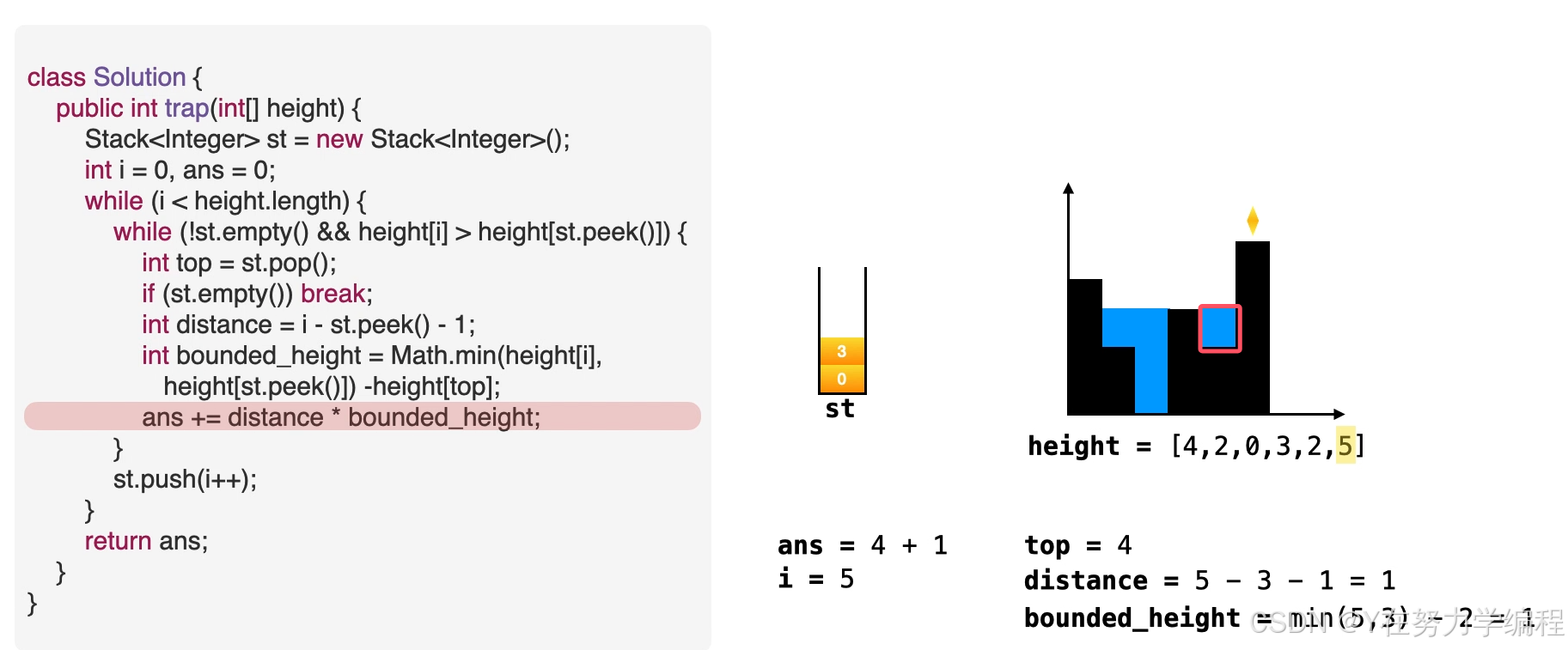
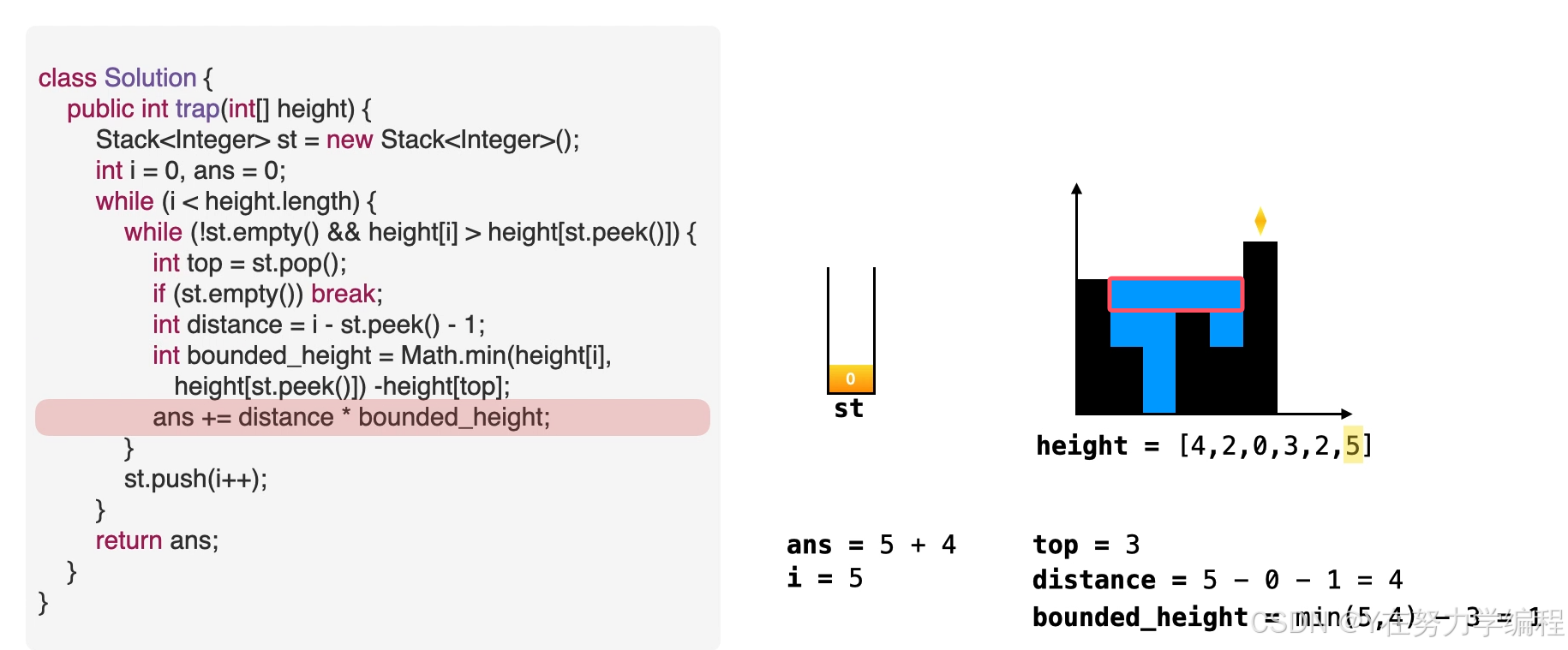
- 意味着栈中元素可以被弹出,弹出栈顶元素。top=st.pop()
- 计算积水宽度,即当前元素和栈顶元素的距离,准备进行填充操作。distance=i-st.peek()-1
- 找出积水高度。water_height = min(height[i],height[st.peek()])- height[top]
- 往答案中累加积水量。ans += distance *bounded_height
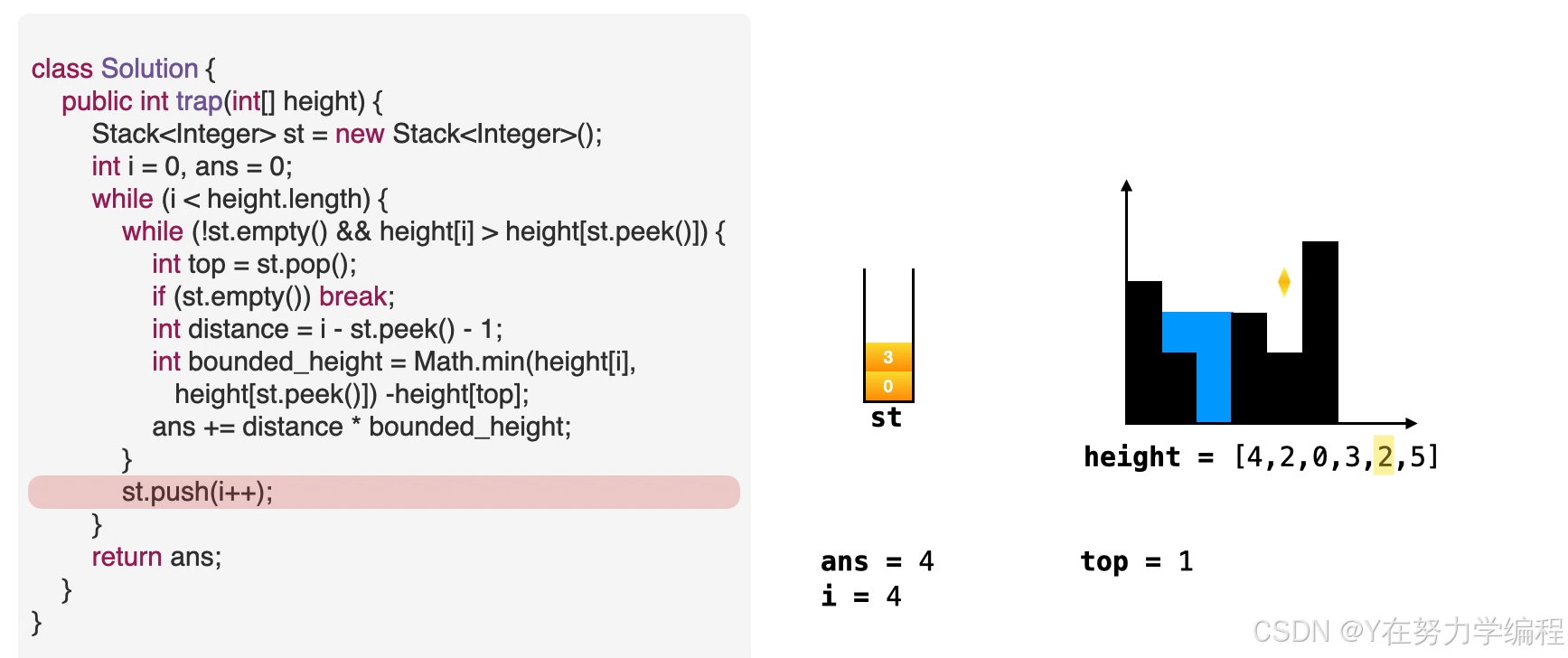
- 将当前索引下标入栈。
- 将 i移动到下个位置。
实现代码
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
Stack<Integer> st=new Stack<Integer>();//使用栈 st 来存储柱子的索引下标。
int i=0,ans=0;
while(i<height.length){
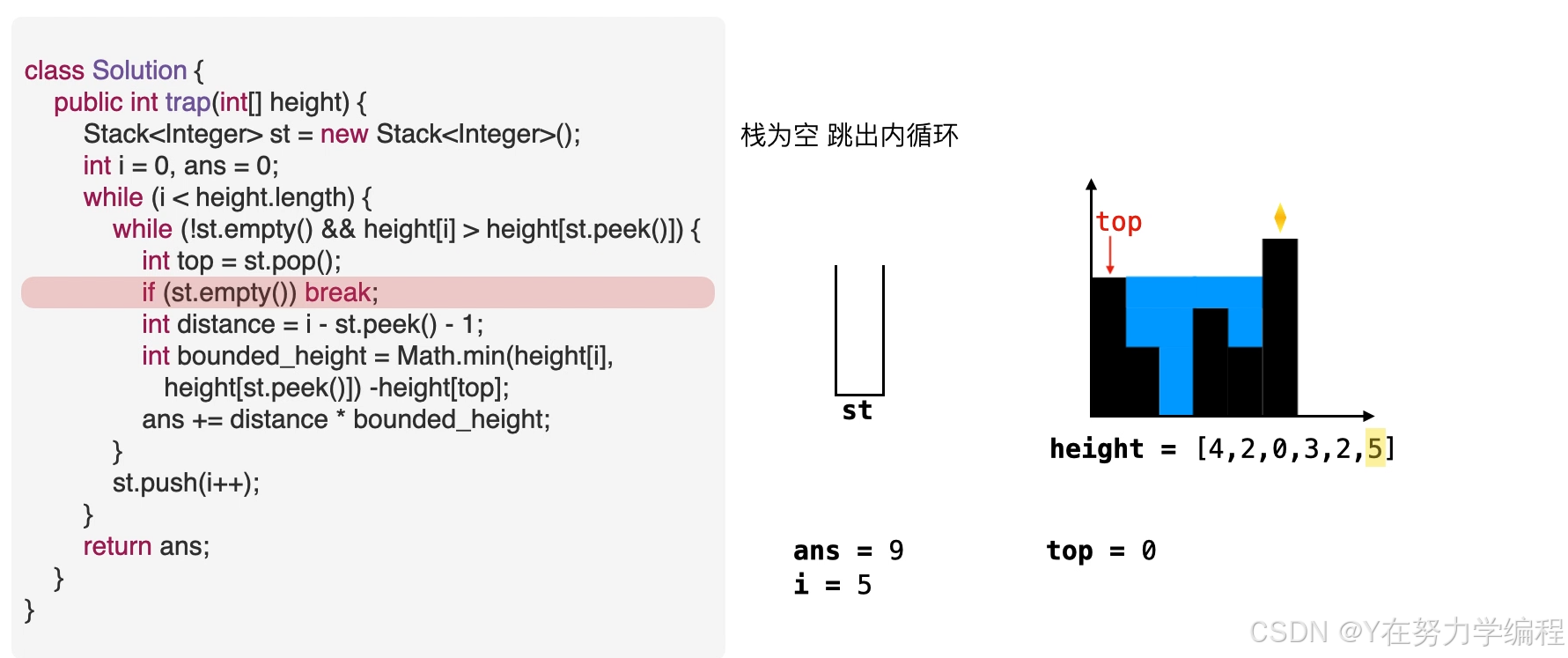
while(!st.empty()&&height[i]>height[st.peek()]){
int top=st.pop();//
if(st.empty()) break;
int width=i-st.peek()-1;
int water_height=Math.min(height[i],height[st.peek()])-height[top];
ans+=width*water_height;
}
st.push(i++);
}
return ans;
}
}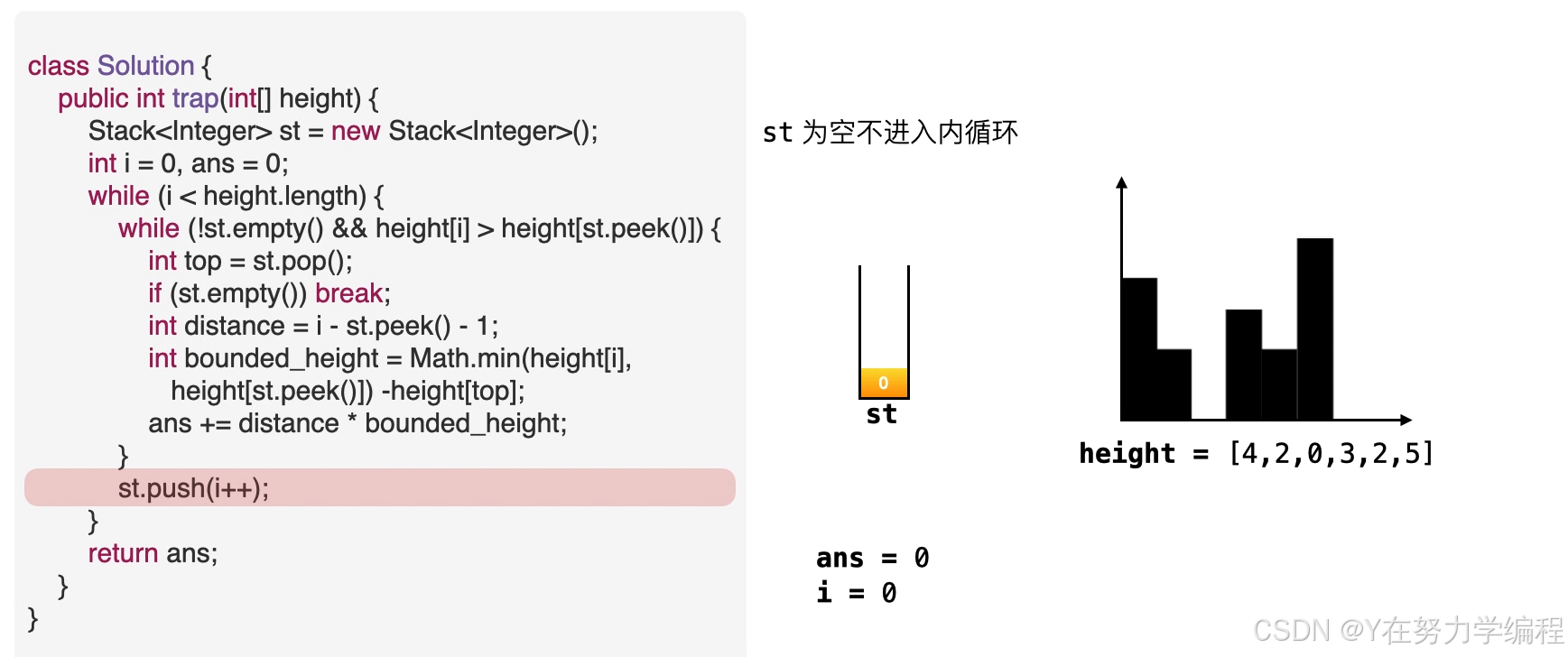
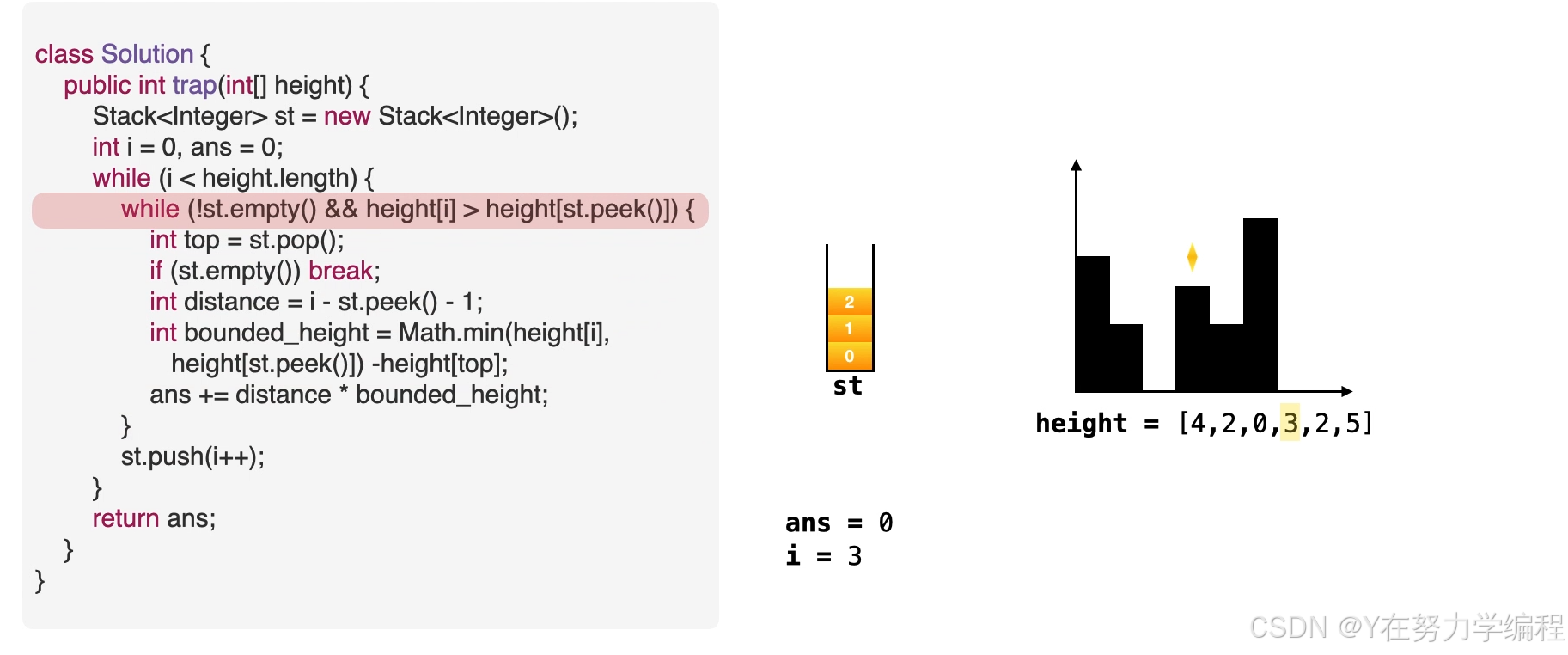
取出栈顶元素,因为是单调递减栈,所以之前的元素比栈顶元素高,当前元素也比栈顶元素高,因此在栈顶元素top会形成低洼
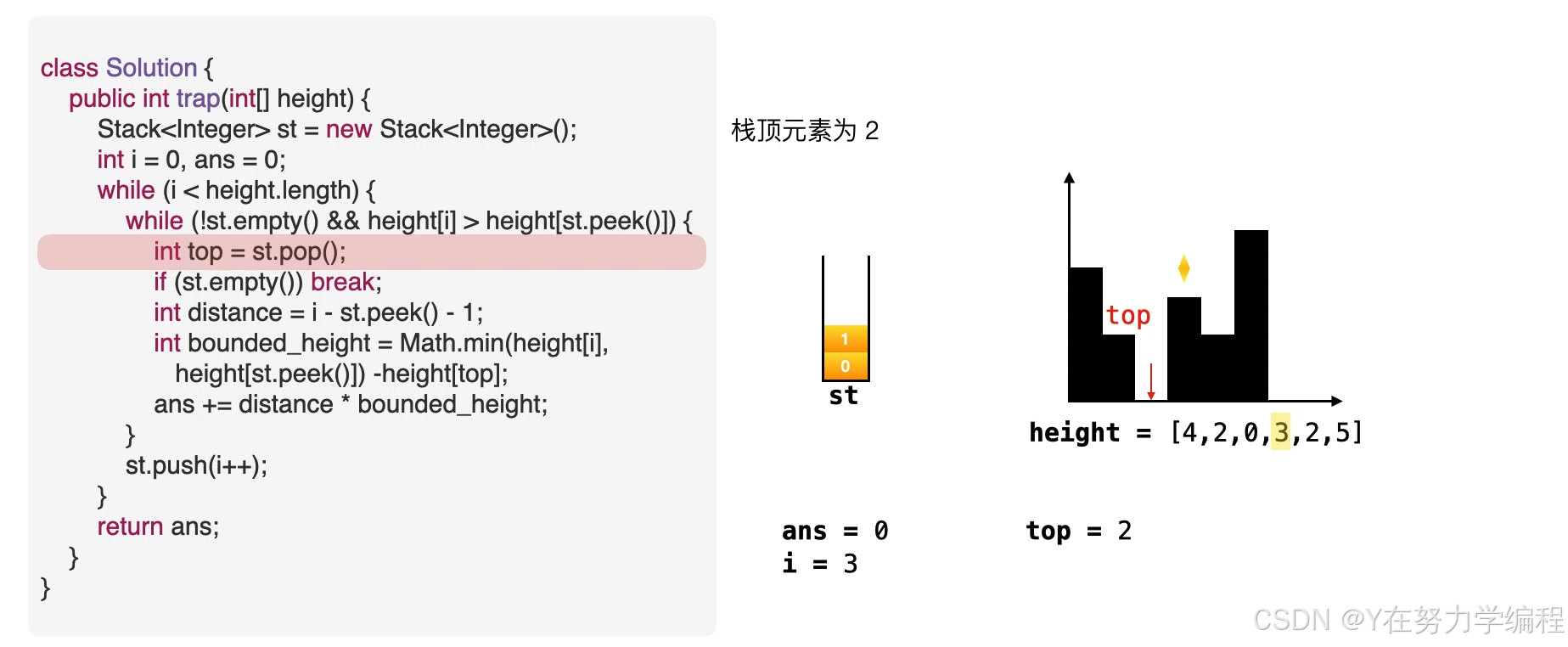
我们可以求出现在的存水量
求宽度
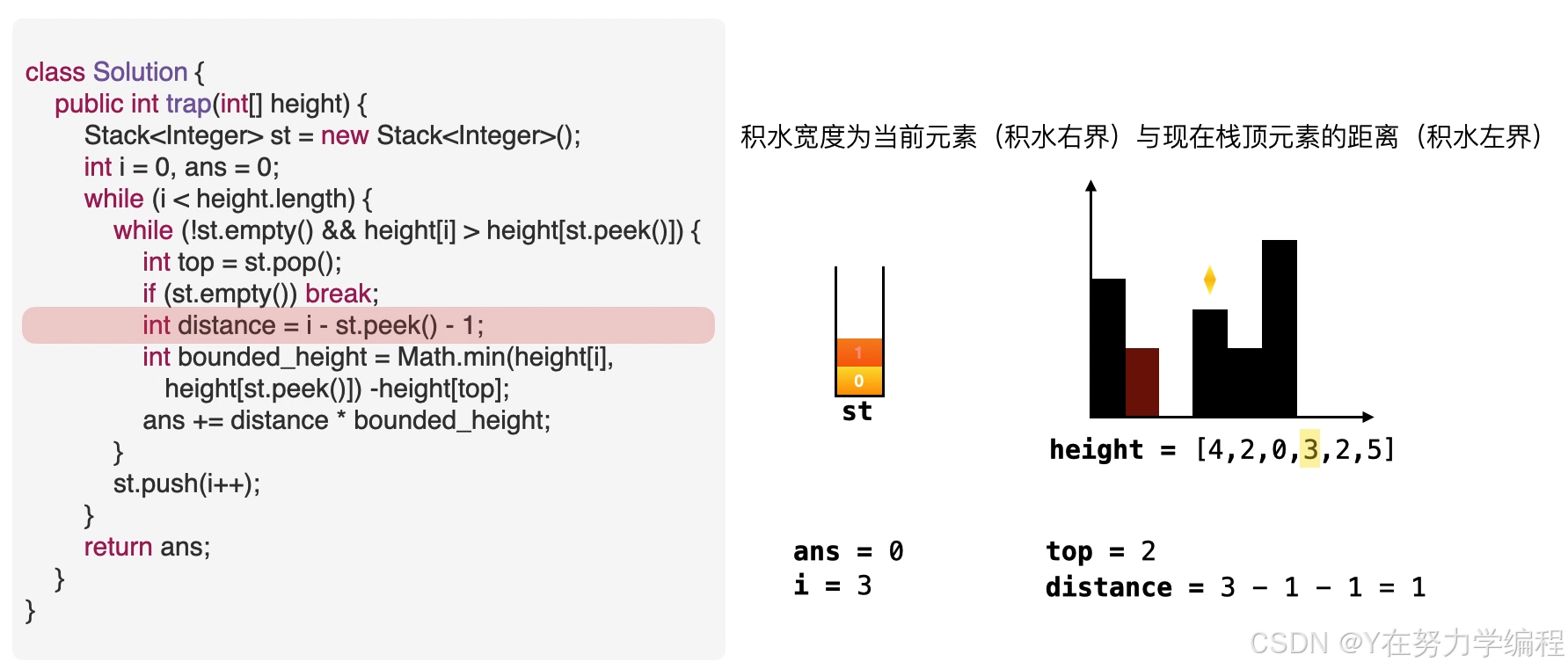
当前元素为低洼地区的右边界,而此时的栈顶元素为低洼的左边界,因而可以求出低洼处的宽度,
求高度
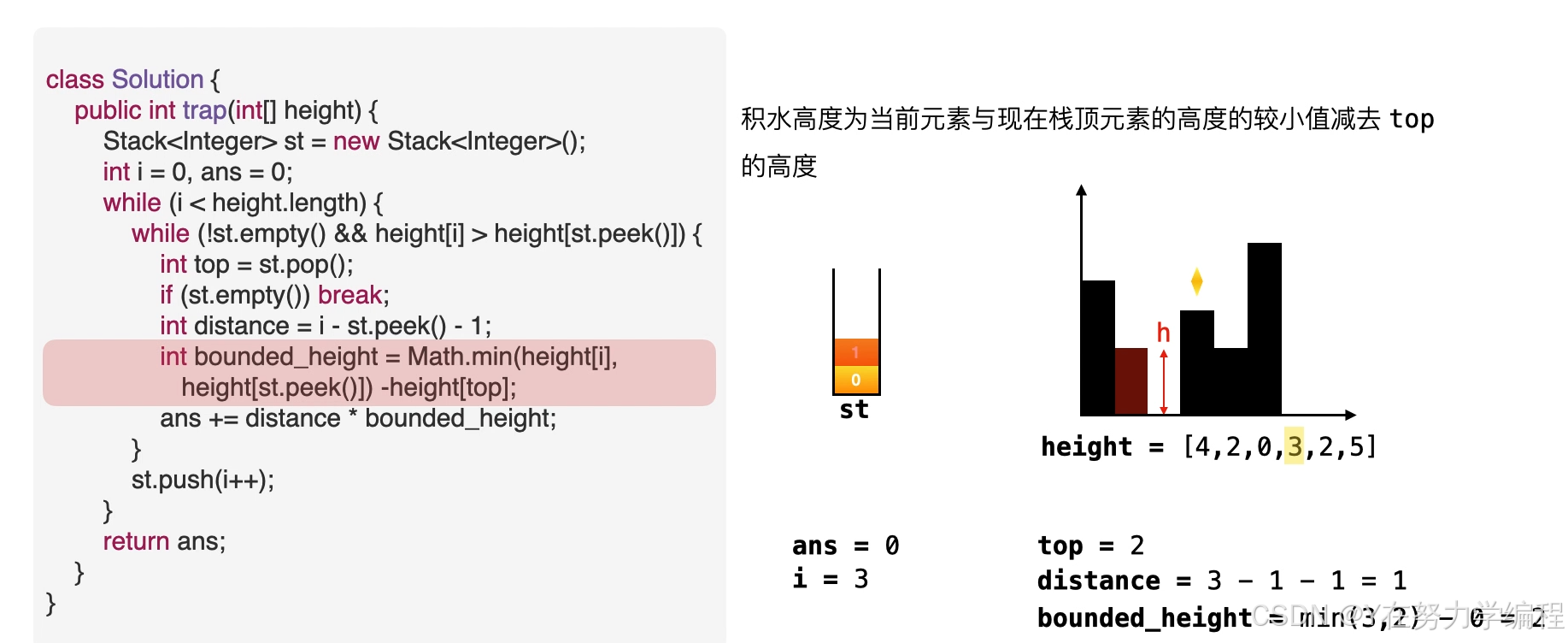
高度应为两个边界高度的较小值减去低洼处的高度
求面积
方法三: 双指针
算法思想:
从动态规划方法的示意图中我们注意到只要 left_max[i]>right_max[i],积水的高度将由
right_max决定,同理如果 right_max[i]>left_max[i],积水的高度将由left_max决定
所以我们可以认为如果右端有更高的条形块,积水的高度依赖于当前方向的高度(从左到
右),即左边这些柱子的高度决定。当我们发现左侧有更高的条形块,我们则开始从相反的方向遍历(从右到左),即积水的高度由右边这些柱子的高度决定。
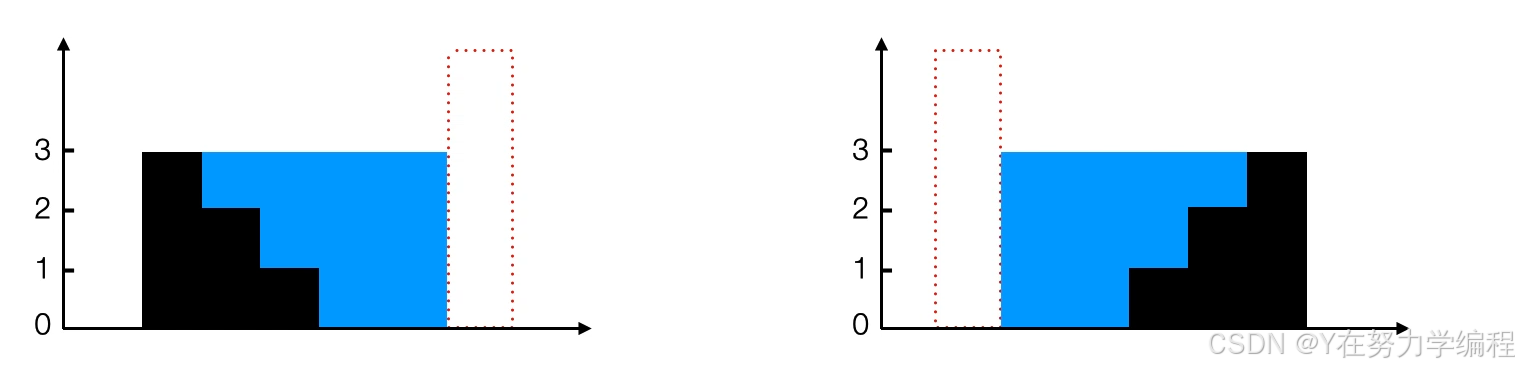
实现步骤
初始化两个指针left=0和right= height.length - 1。
当 left < right时向中间移动两个指针:
- 如果 height [left]< height[right] 说明储水量依赖于 height[left]的高度(可能构成低洼的右边界很大)
- 如果 height[left]> left max 说明没有或超出左边边界,不构成低洼,left max= height[left]。
- 如果 height[left]
- 前进 left。left ++
- 如果 height[left]>= height[right]说明储水量依赖于 height[right]的高度(可能构成低洼的左边界很大)
- 如果 height[right]> right max说明没有或超出右边边界,不构成低洼,right max= height[right]
- 如果 height[right]
- height[right]
- 前进 right。right --
实现代码:
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
int left=0,right=height.length-1;
int left_max=0,right_max=0,ans=0;
while(left<right){
if(height[left]<height[right]){//高的在右边,正向遍历,找存储的
if(height[left]>left_max){
left_max=height[left];
}else{
ans+=left_max-height[left];
}
left++;
}else{
if(height[right]>right_max){
right_max=height[right];//更新右侧最高点
}else{
ans+=right_max-height[right];
}
right--;
}
}
return ans;
}
}复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n)
其中 n 是数组 height 的长度。两个指针的移动总次数不超过 n。
空间复杂度:O(1)
只需要使用常数的额外空间。
