目录
[2.1 单应性变换](#2.1 单应性变换)
[2.2 RANSAC算法](#2.2 RANSAC算法)
一、实验内容
- 理解单应性变换中各种变换的原理(自由度),并实现图像平移、旋转、仿射变换等操作,输出对应的单应性矩阵。
- 利用RANSAC算法优化关键点匹配,比较优化前后图像拼接和所生成全景图的差别,输出RANSAC前后匹配点数量、单应性矩阵。
二、实验过程及结果
2.1 单应性变换
(1)实验代码
python
import cv2
from networkx import center
import numpy as np
from scipy.fft import dst
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img=cv2.imread("D:/Computer vision/test1 picture/picture3.png")
x=100
y=50
M0=np.float32([[1,0,x],[0,1,y]])
translated=cv2.warpAffine(img,M0,(img.shape[1],img.shape[0]))
print("平移变换单应性矩阵:\n",M0)
img_center=(img.shape[1]/2,img.shape[0]/2)
M1=cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(img_center,45,1)
rotated=cv2.warpAffine(img,M1,(img.shape[1],img.shape[0]))
print("旋转变换单应性矩阵:\n",M1)
M2=cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(img_center,0,0.5)
scaled=cv2.warpAffine(img,M2,(img.shape[1],img.shape[0]))
print("缩放变换单应性矩阵:\n",M2)
rows,cols,ch=img.shape
src_points=np.float32([[0,0],[cols-1,0],[0,rows-1]])
dst_points=np.float32([[0,rows*0.33],[cols*0.85,rows*0.25],[cols*0.15,rows*0.7]])
M3=cv2.getAffineTransform(src_points,dst_points)
warped=cv2.warpAffine(img,M3,(cols,rows))
print("扭曲变换单应性矩阵:\n",M3)
rows,cols=img.shape[:2]
pts1=np.float32([[150,50],[400,50],[60,450],[310,450]])
pts2=np.float32([[50,50],[rows-50,50],[50,cols-50],[rows-50,cols-50]])
M4=cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1,pts2)
img_dst=cv2.warpPerspective(img,M4,(cols,rows))
print("透视变换单应性矩阵:\n",M4)
plt.figure("Processed Images")
plt.subplot(2,3,1)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.title("Original Image")
plt.subplot(2,3,2)
plt.imshow(translated)
plt.title("Translated Image")
plt.subplot(2,3,3)
plt.imshow(rotated)
plt.title("Rotated Image")
plt.subplot(2,3,4)
plt.imshow(scaled)
plt.title("Scaled Image")
plt.subplot(2,3,5)
plt.imshow(warped)
plt.title("Warped Image")
plt.subplot(2,3,6)
plt.imshow(img_dst)
plt.title("Dst Image")
plt.show()
plt.savefig("D:/Computer vision/ransac_picture/processed_images.png")
plt.show()(2)实验结果截图
图1为输出的单应性矩阵结果截图:
平移变换:两个自由度(两个平移参数),单应性矩阵为2*3的矩阵
旋转变换:一个自由度(一个旋转角度参数),单应性矩阵为2*3的矩阵
缩放变换:一个自由度(一个缩放因子),单应性矩阵为2*3的矩阵
扭曲变换有六个自由度(两个旋转参数 一个缩放因子),单应性矩阵为2*3的矩阵
透视变换有八个自由度(5个是仿射变换参数,3个是透视变换参数),单应性矩阵为3*3的矩阵
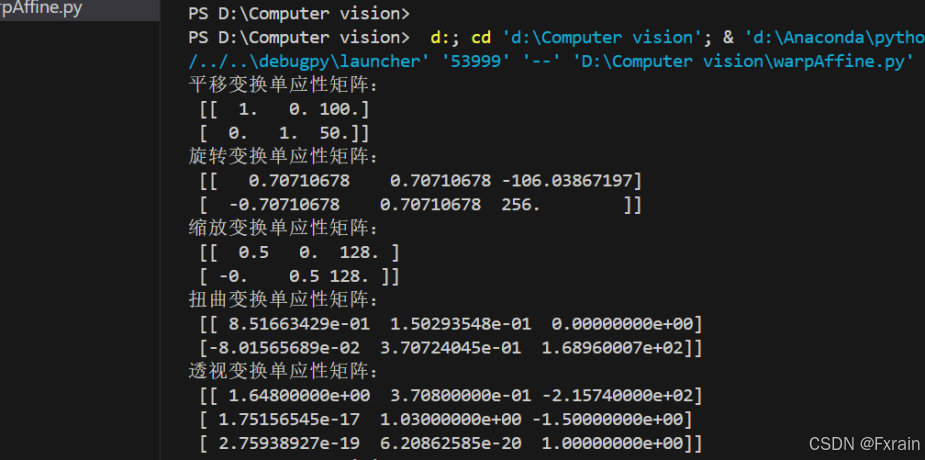 图1
图1
图2为输出的单应性变换的结果图:
可以看到,平移变换的图像在x方向上平移100个像素,在y方向上平移50个像素。旋转变换的图像绕图像中心旋转45度。缩放变换的图像在x方向上缩小到原来的一半,在y方向上缩小到原来的一半。扭曲变换的图像进行仿射变换,包括旋转、缩放、平移和剪切。透视变换的图像进行了透视变换,包括旋转、缩放、平移和透视变形。
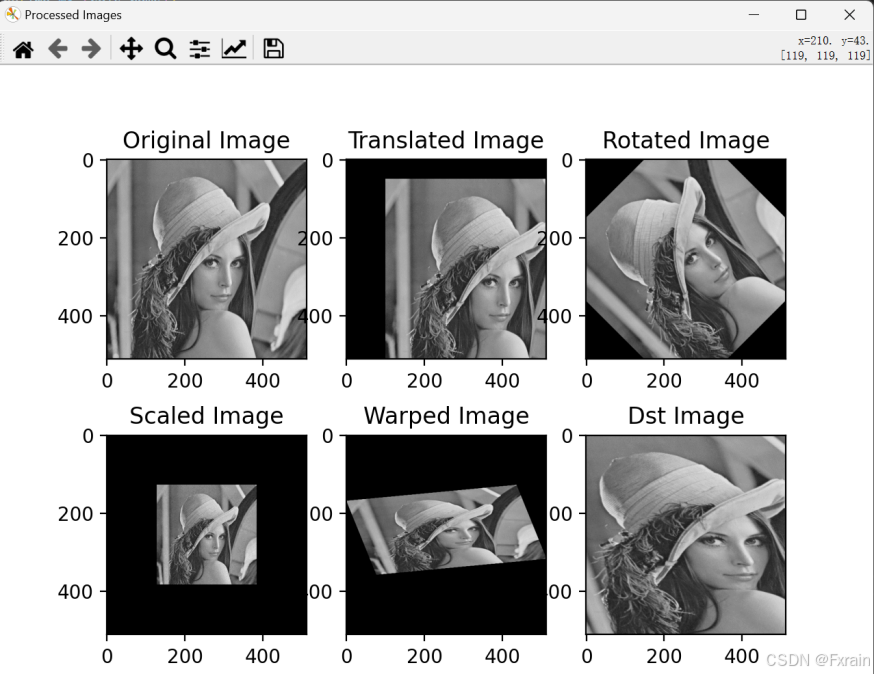 图2
图2
2.2 RANSAC算法
(1)实验代码
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
def detectAndCompute(image):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
sift = cv2.SIFT_create()
keypoints, descriptors = sift.detectAndCompute(gray, None)
return keypoints, descriptors
def matchKeyPoints(kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio=0.75, reprojThresh=4.0):
matcher = cv2.BFMatcher()
rawMatches = matcher.knnMatch(featuresA, featuresB, 2)
matches = []
for m in rawMatches:
if len(m) == 2 and m[0].distance < ratio * m[1].distance:
matches.append((m[0].queryIdx, m[0].trainIdx))
ptsA = np.float32([kpsA[i].pt for (i, _) in matches])
ptsB = np.float32([kpsB[i].pt for (_, i) in matches])
(M, status) = cv2.findHomography(ptsA, ptsB, cv2.RANSAC, reprojThresh)
return (M, matches, status)
def drawMatches(imgA, imgB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status):
(hA, wA) = imgA.shape[:2]
(hB, wB) = imgB.shape[:2]
result = np.zeros((max(hA, hB), wA + wB, 3), dtype="uint8")
result[0:hA, 0:wA] = imgA
result[0:hB, wA:] = imgB
for ((trainIdx, queryIdx), s) in zip(matches, status):
if s == 1:
ptA = (int(kpsA[queryIdx].pt[0]), int(kpsA[queryIdx].pt[1]))
ptB = (int(kpsB[trainIdx].pt[0]) + wA, int(kpsB[trainIdx].pt[1]))
cv2.line(result, ptA, ptB, (0, 255, 0), 1)
return result
def stitchImages(imageA, imageB, M):
(hA, wA) = imageA.shape[:2]
(hB, wB) = imageB.shape[:2]
result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageA, M, (wA + wB, hA))
result[0:hB, 0:wB] = imageB
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
imageA = cv2.imread("D:\Computer vision/ransac_picture/ransac1.jpg")
imageB = cv2.imread("D:/Computer vision/ransac_picture/ransac2.jpg")
kpsA, featuresA = detectAndCompute(imageA)
kpsB, featuresB = detectAndCompute(imageB)
M, matches, status = matchKeyPoints(kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB)
initial_matches = sum(status)
final_matches = len(matches)
print(f"RANSAC前匹配点数量: {initial_matches}")
print(f"RANSAC后匹配点数量: {final_matches}")
print("单应性矩阵为:\n", M)
drawImgBeforeRANSAC = drawMatches(imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status)
cv2.imshow("drawMatches Before RANSAC", drawImgBeforeRANSAC)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
stitchedImage = stitchImages(imageA, imageB, M)
cv2.imshow("Stitched Image", stitchedImage)
cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
cv2.imwrite("D:/Computer vision/ransac_picture/stitched_image.jpg", stitchedImage)
cv2.imwrite("D:/Computer vision/ransac_picture/drawMatchesBeforeRANSAC.jpg", drawImgBeforeRANSAC)(2)数据集(待拼接)

(3)实验结果截图
图3为输出的单应性矩阵结果截图:
如图所示,在运行SIFT特征检测和描述符提取后,通过BFMatcher进行特征匹配,初始匹配点的数量是198对。经过RANSAC算法去除错误匹配后,剩余的匹配点数量为1074对。这表明RANSAC算法有效地保留了正确的匹配点并去除了错误的匹配点。
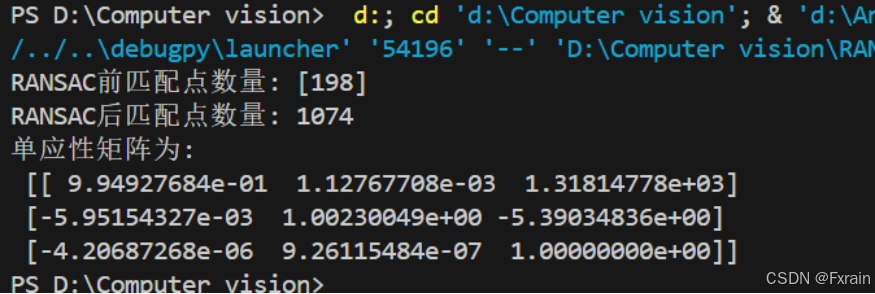 图3
图3
图4为在应用RANSAC算法之前绘制的匹配结果图像:
如图所示,绘制两幅图像的匹配结果并显示特征点之间的匹配关系。通过可视化匹配结果,可以直观地看到哪些特征点被成功匹配。
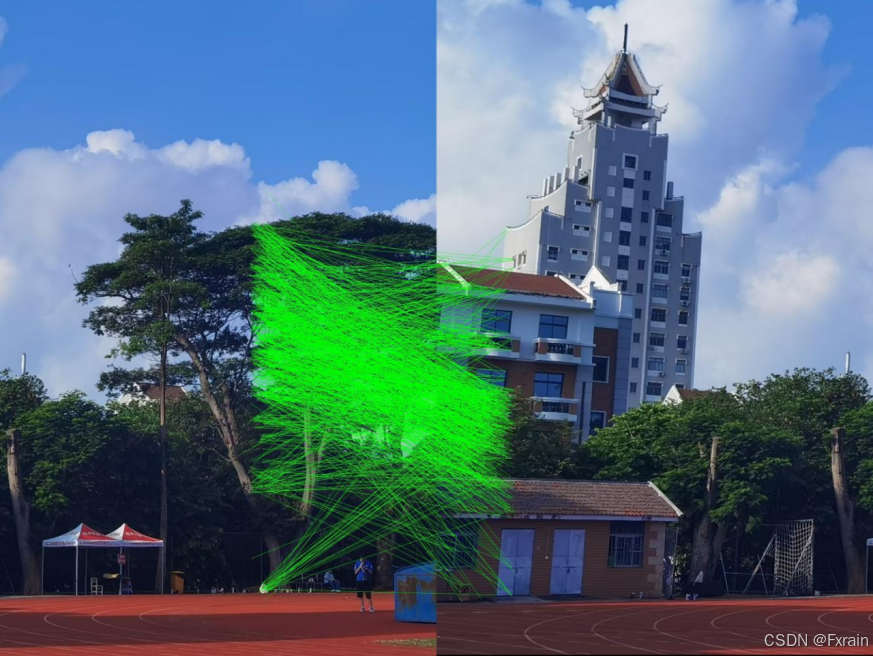 图4
图4
图5为最终拼接后的图像:
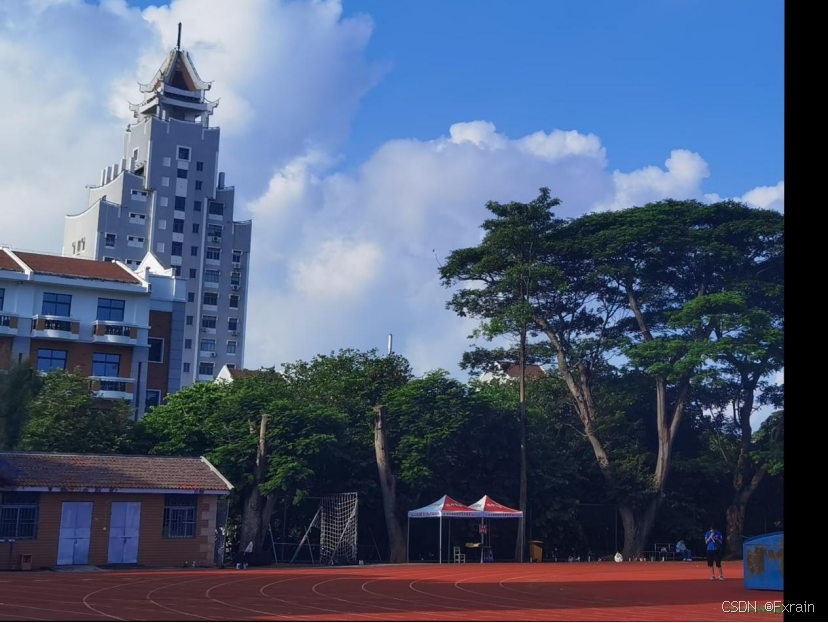 图5
图5
三、实验小结
图像拼接是计算机视觉领域的一个重要研究方向,通过将多张重叠的图像拼接在一起,实现更大、更全面的图像展示。实验中通过使用opencv中的相关函数实现图像的单应性变换,并使用BFMatcher和RANSAC算法进行了特征点匹配以及图像拼接。使用RANSAC算法后拼接效果良好,没有出现明显的错位或重叠问题。