目录
[1. 旋转数组](#1. 旋转数组)
[1.1. 题目描述](#1.1. 题目描述)
[1.2. 解题思路](#1.2. 解题思路)
[2. 螺旋矩阵](#2. 螺旋矩阵)
[2.1. 题目描述](#2.1. 题目描述)
[2.2. 解题思路](#2.2. 解题思路)
[3. 顺时针旋转矩阵](#3. 顺时针旋转矩阵)
[3.1. 题目描述](#3.1. 题目描述)
[3.2. 解题思路](#3.2. 解题思路)
[4. 设计LFU缓存结构](#4. 设计LFU缓存结构)
[4.1. 题目描述](#4.1. 题目描述)
[4.2. 解题思路](#4.2. 解题思路)
[5. 顺时针打印矩阵](#5. 顺时针打印矩阵)
[5.1. 题目描述](#5.1. 题目描述)
[5.2. 解题思路](#5.2. 解题思路)
[6. 验证图书取出顺序](#6. 验证图书取出顺序)
[6.1. 题目描述](#6.1. 题目描述)
[6.2. 解题思路](#6.2. 解题思路)
1. 旋转数组
1.1. 题目描述
1.2. 解题思路
方法一:三次翻转(推荐使用)

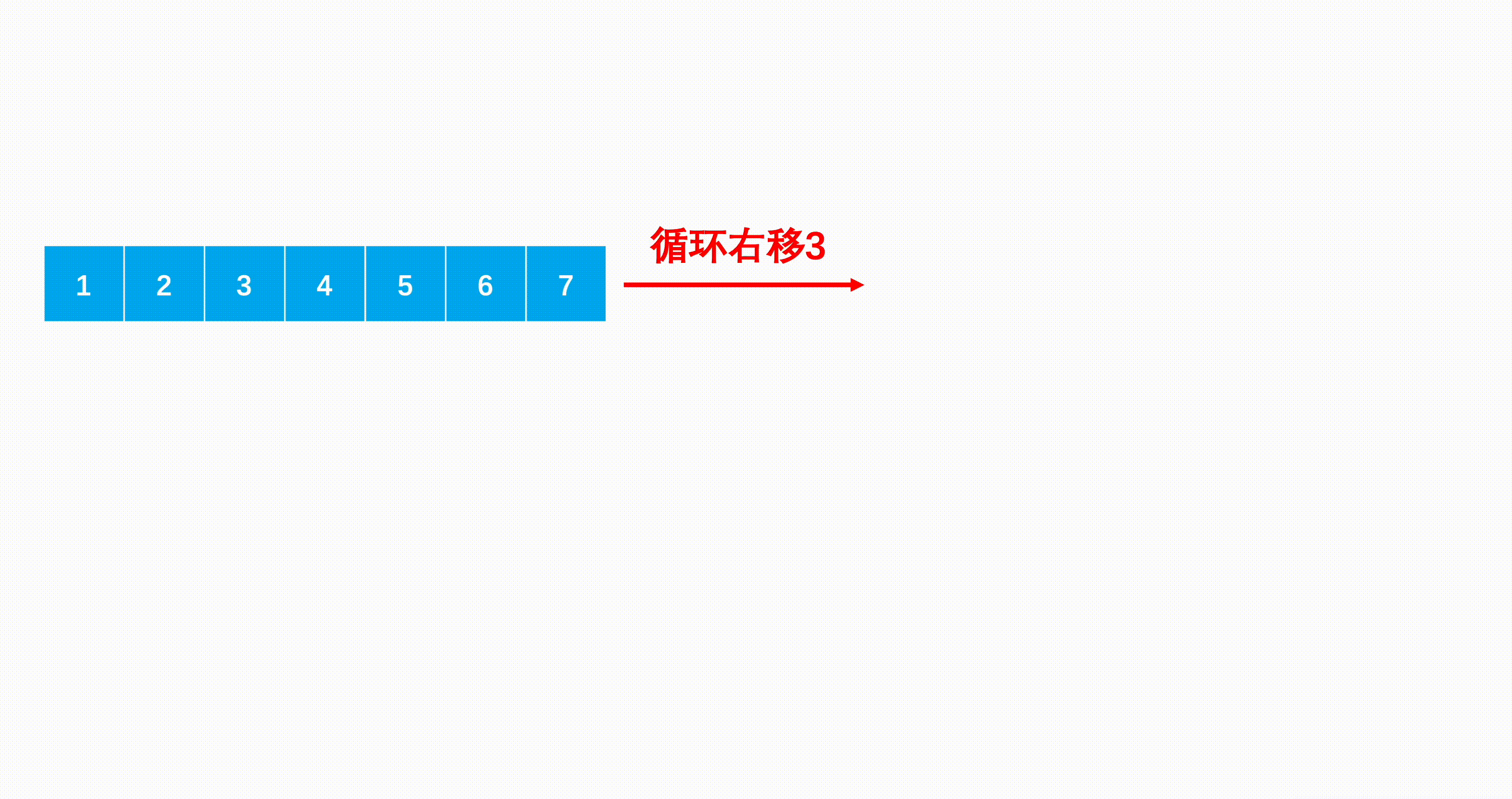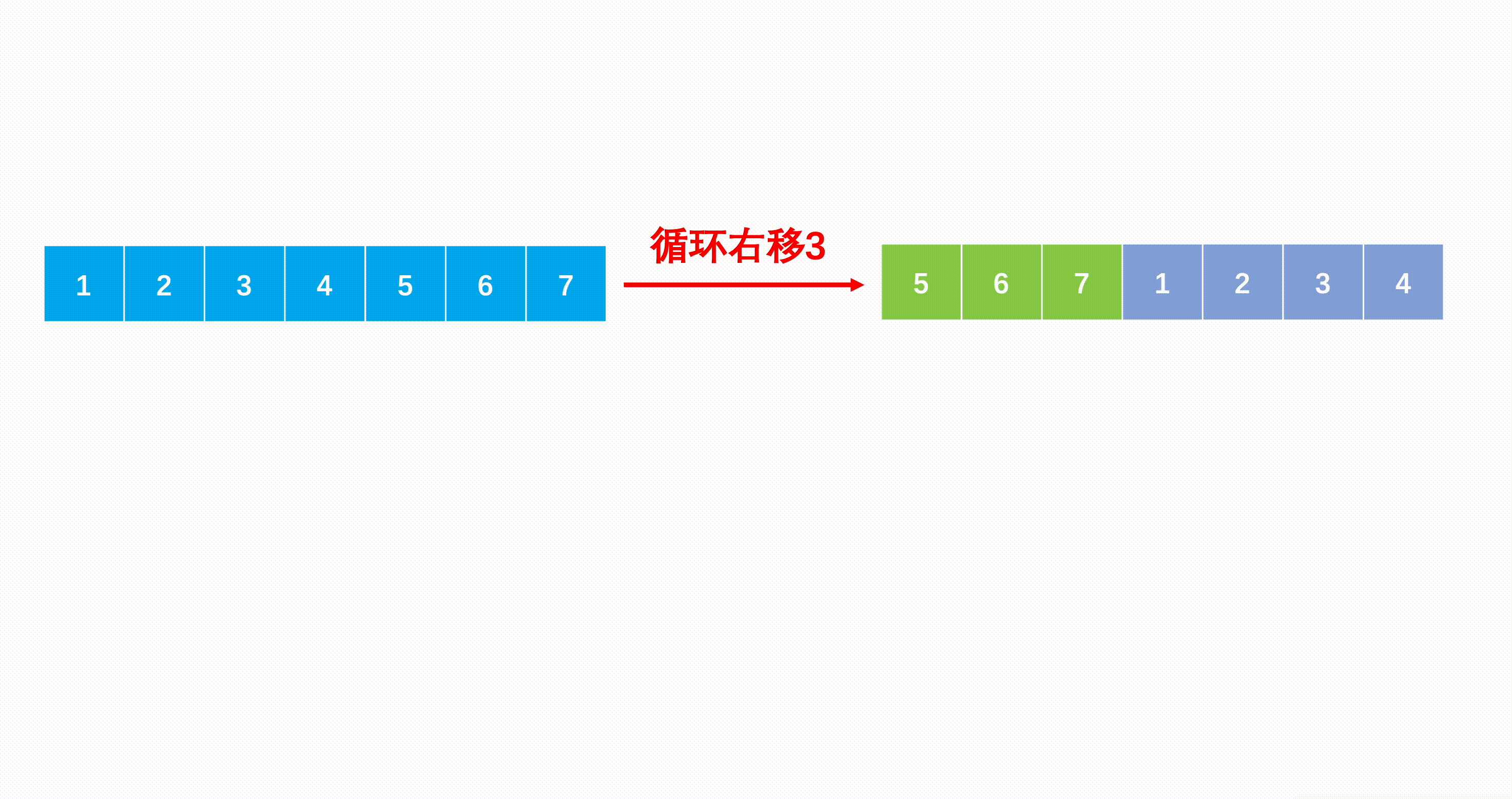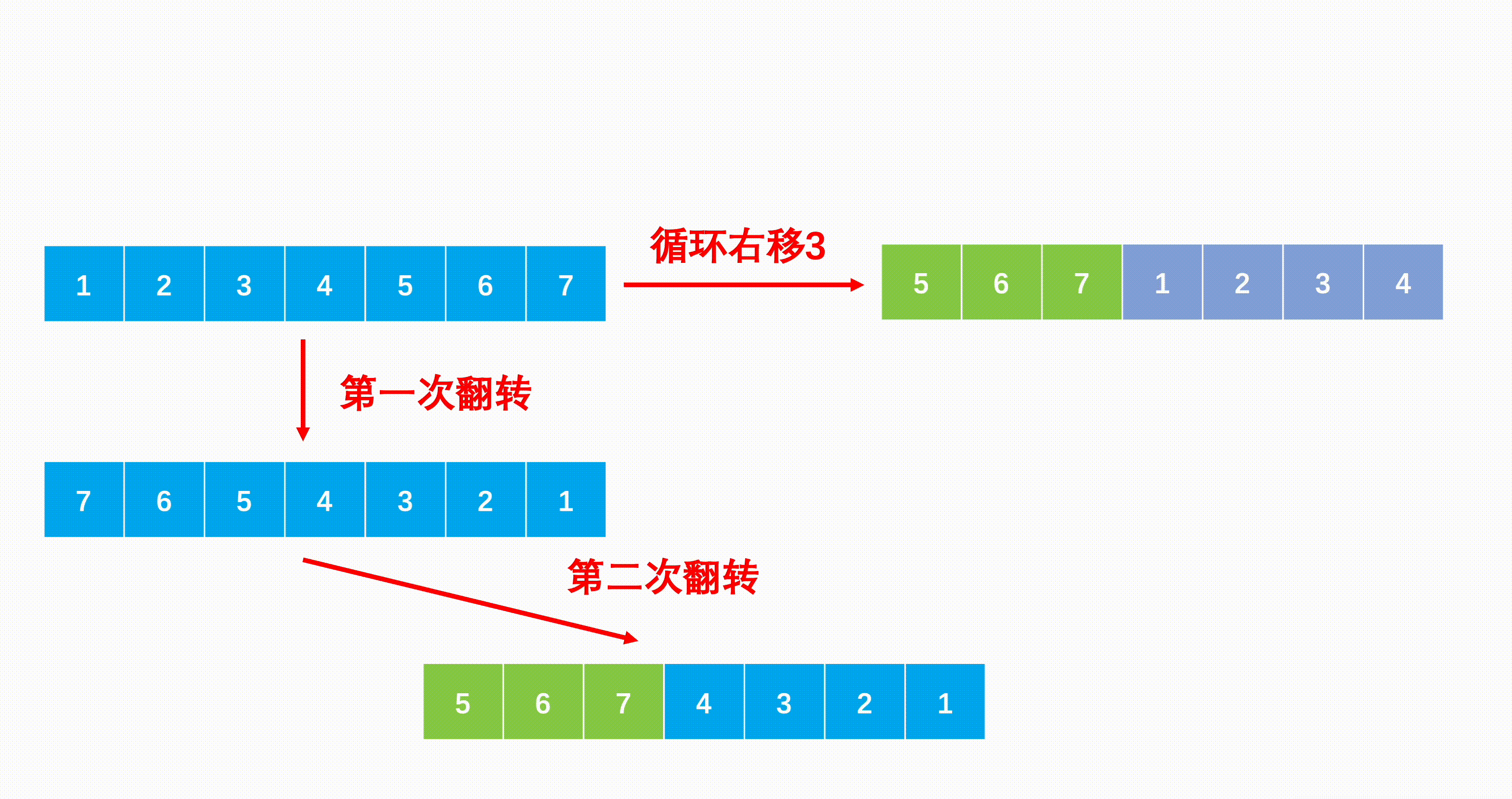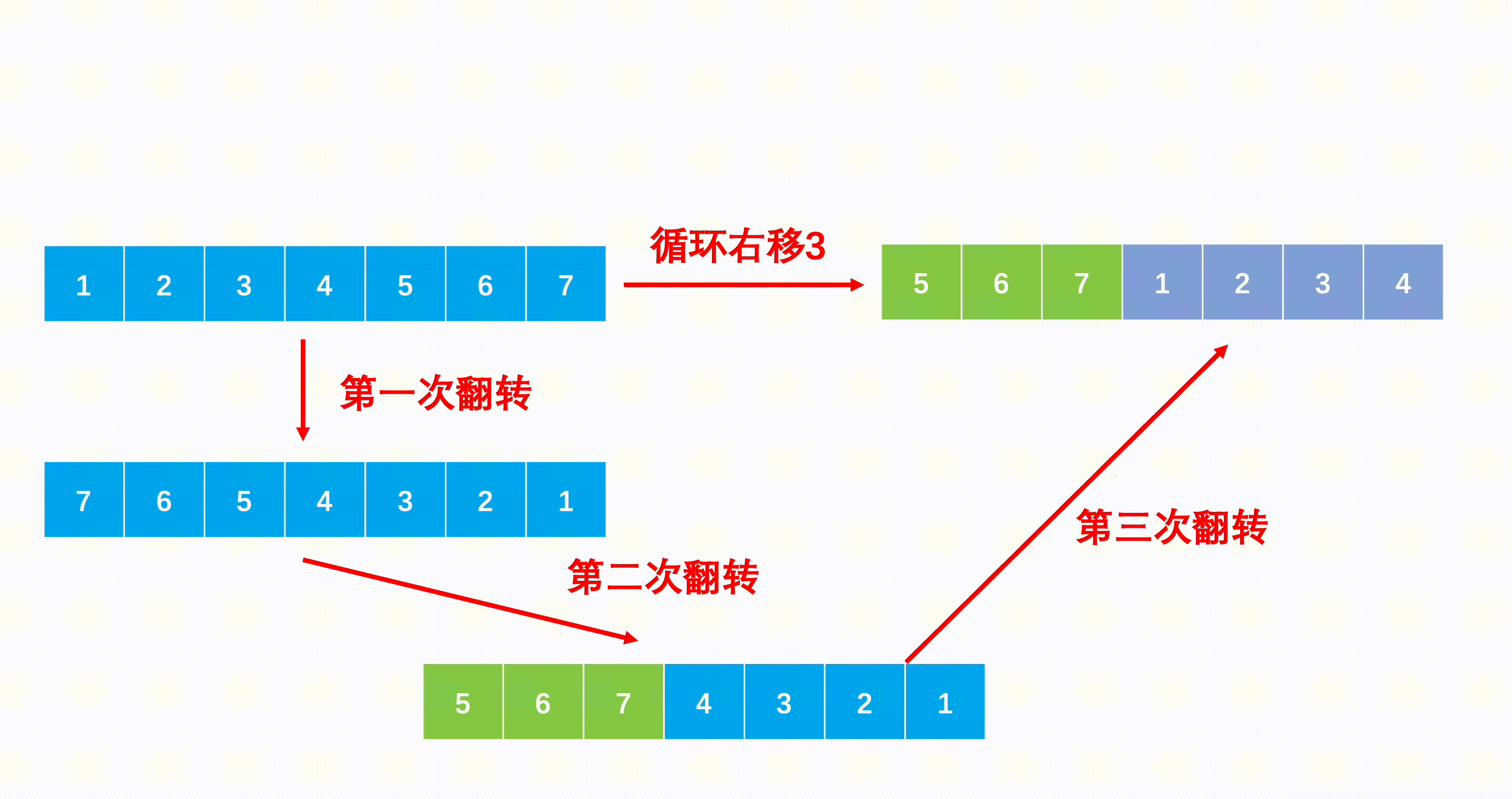
Java代码实现:
public class Solution {
public int[] solve (int n, int m, int[] a) {
//取余,因为每次长度为n的旋转数组相当于没有变化
m = m % n;
//第一次逆转全部数组元素
reverse(a, 0, n - 1);
//第二次只逆转开头m个
reverse(a, 0, m - 1);
//第三次只逆转结尾m个
reverse(a, m, n - 1);
return a;
}
//反转函数
public void reverse(int[] nums, int start, int end){
while(start < end){
swap(nums, start++, end--);
}
}
//交换函数
public void swap(int[] nums, int a, int b){
int temp = nums[a];
nums[a] = nums[b];
nums[b] = temp;
}
}
2. 螺旋矩阵
2.1. 题目描述
2.2. 解题思路
方法一:边界模拟法(推荐使用)

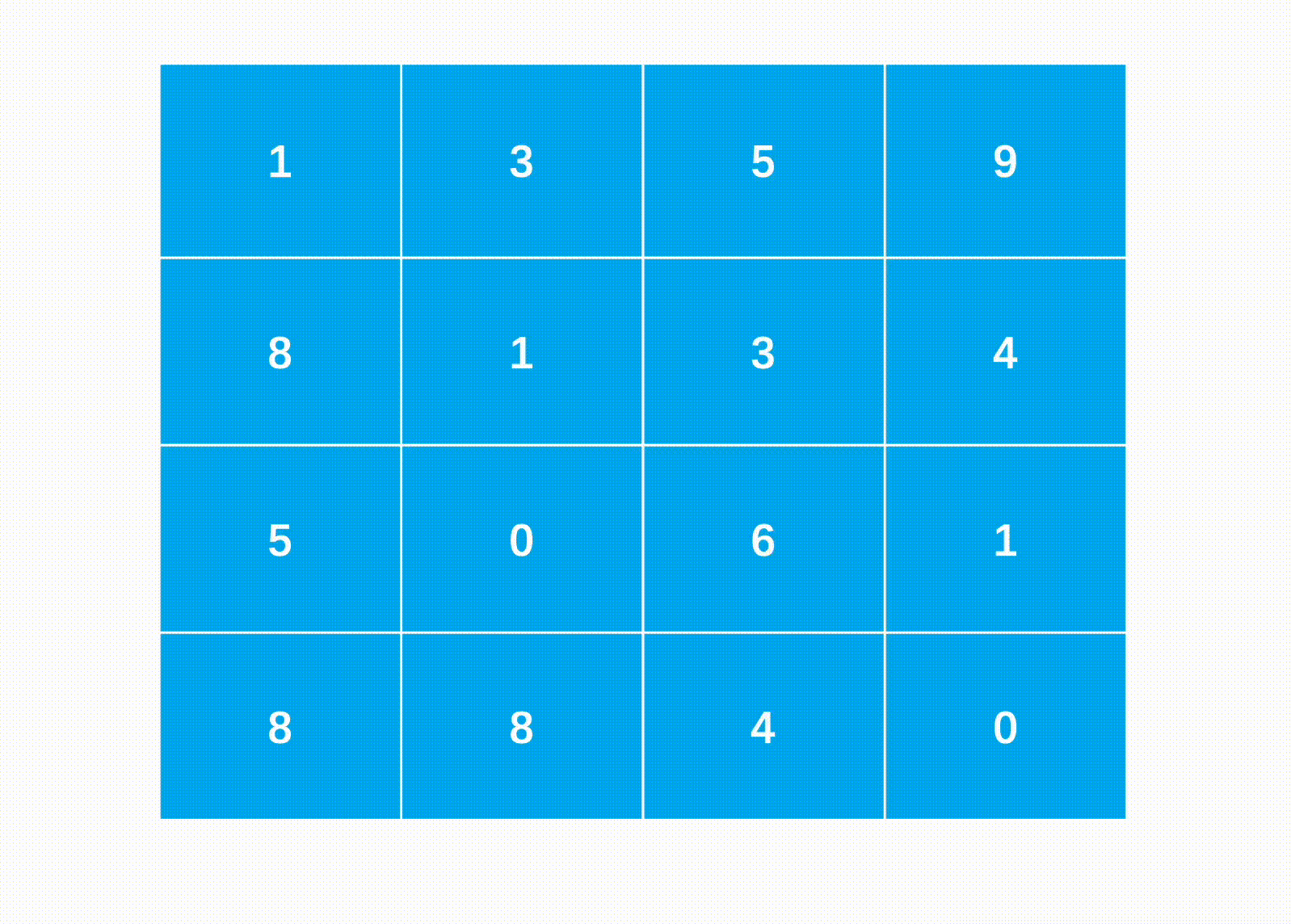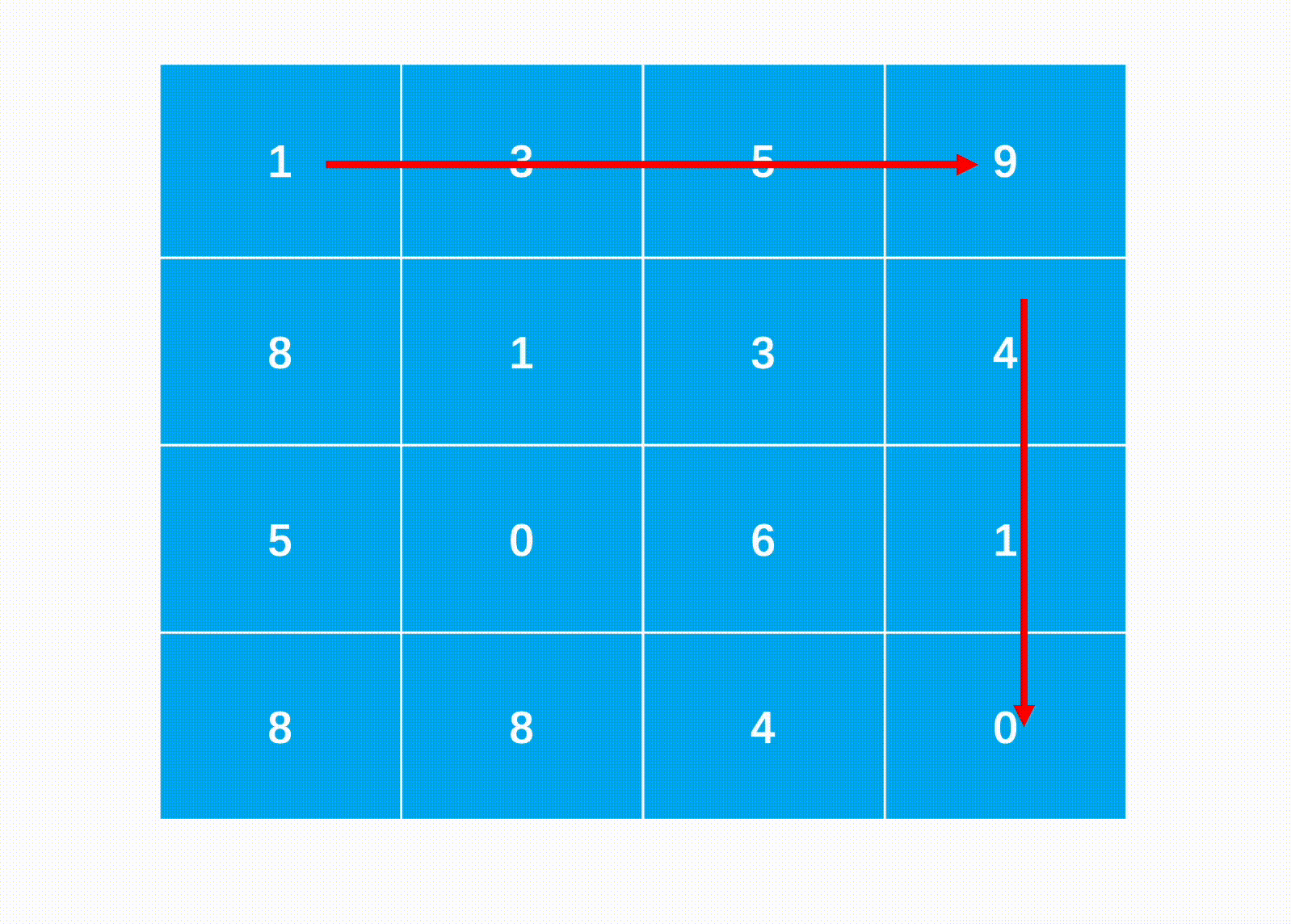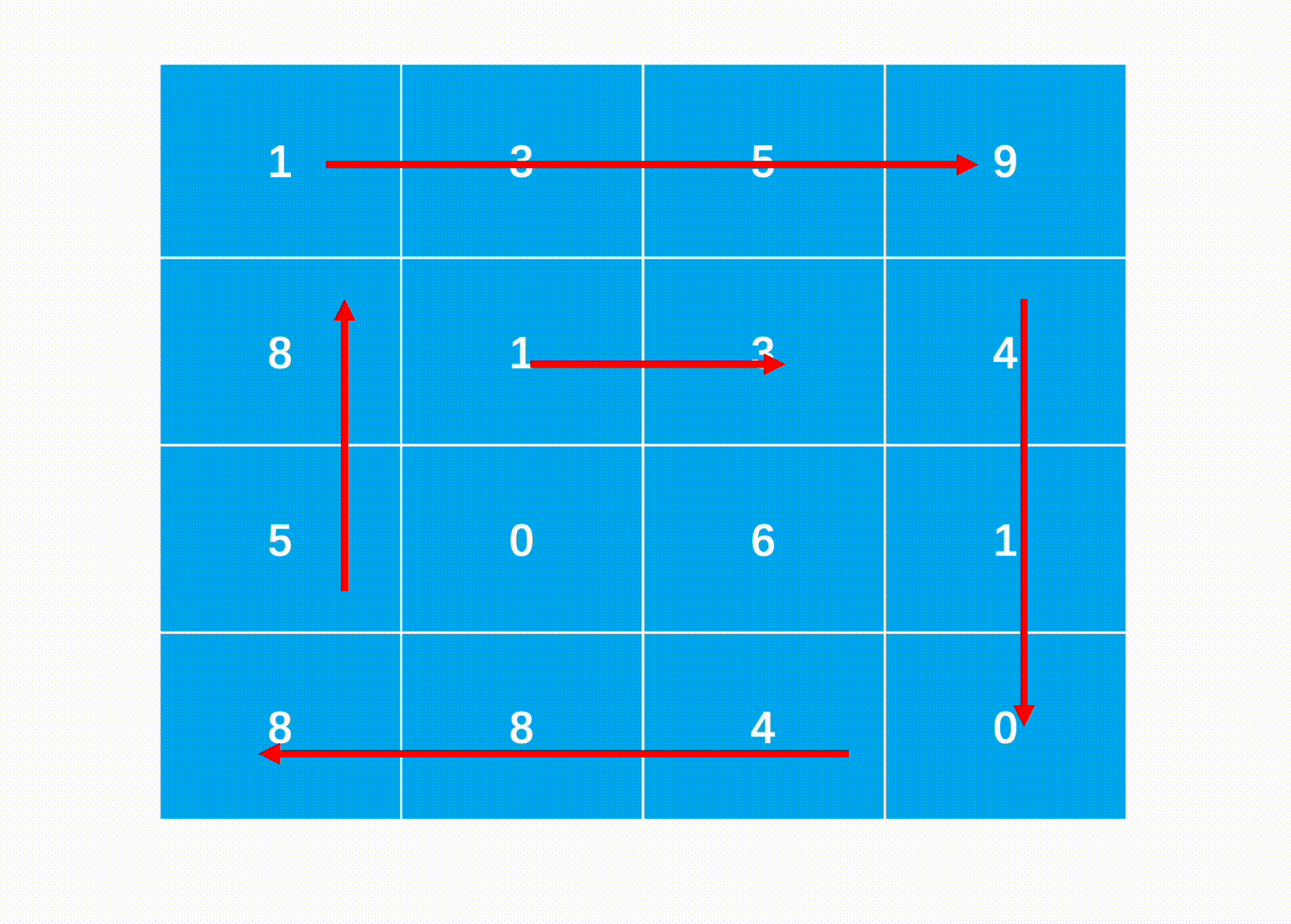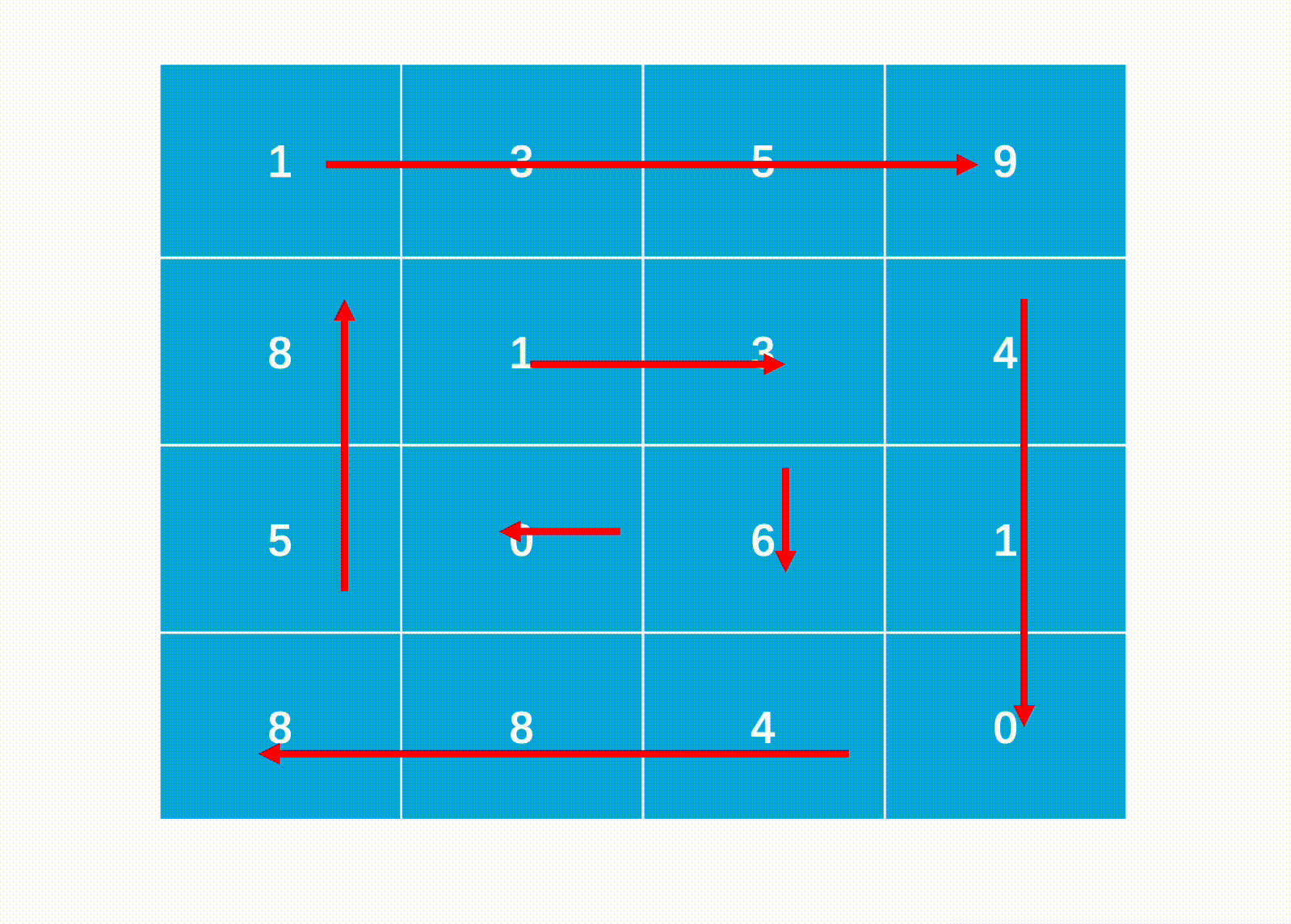
Java代码实现:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
//先排除特殊情况
if(matrix.length == 0) {
return res;
}
//左边界
int left = 0;
//右边界
int right = matrix[0].length - 1;
//上边界
int up = 0;
//下边界
int down = matrix.length - 1;
//直到边界重合
while(left <= right && up <= down){
//上边界的从左到右
for(int i = left; i <= right; i++)
res.add(matrix[up][i]);
//上边界向下
up++;
if(up > down)
break;
//右边界的从上到下
for(int i = up; i <= down; i++)
res.add(matrix[i][right]);
//右边界向左
right--;
if(left > right)
break;
//下边界的从右到左
for(int i = right; i >= left; i--)
res.add(matrix[down][i]);
//下边界向上
down--;
if(up > down)
break;
//左边界的从下到上
for(int i = down; i >= up; i--)
res.add(matrix[i][left]);
//左边界向右
left++;
if(left > right)
break;
}
return res;
}
}
3. 顺时针旋转矩阵
3.1. 题目描述
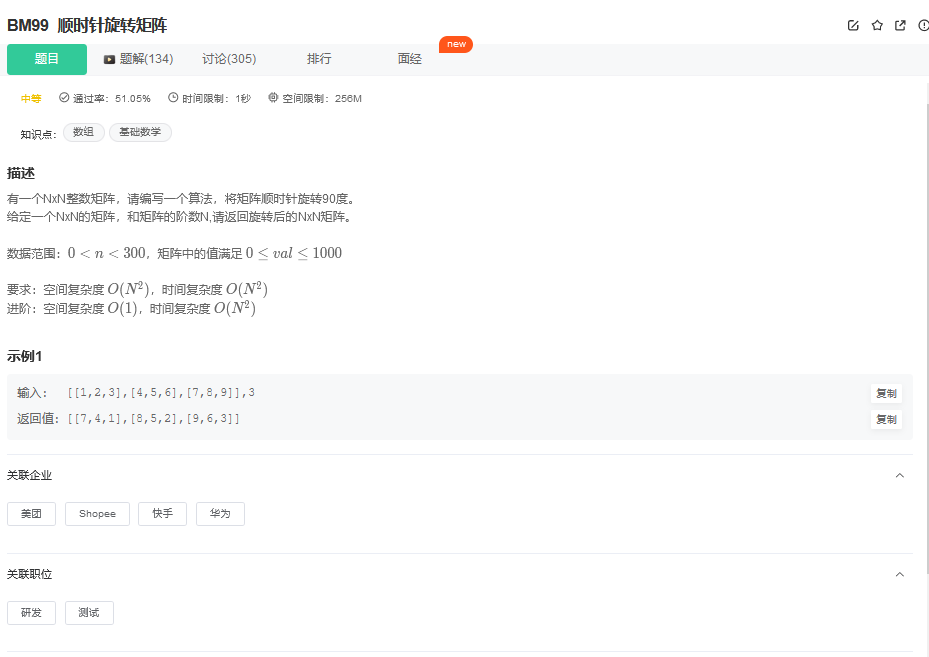
3.2. 解题思路
方法一:倒置翻转(推荐使用)

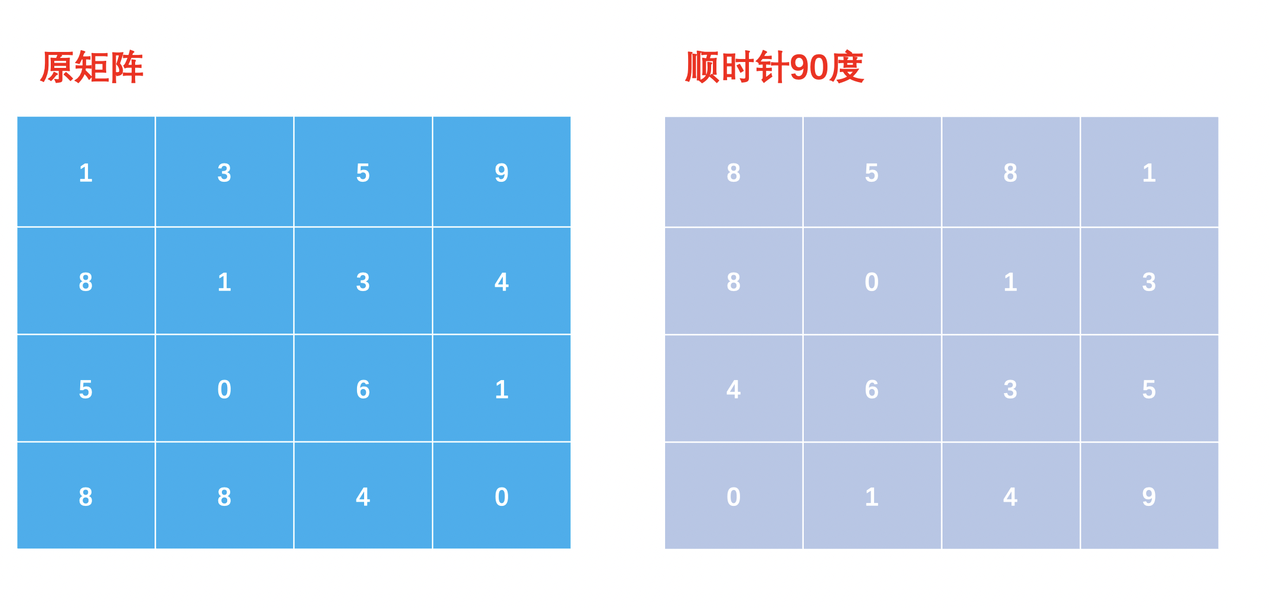
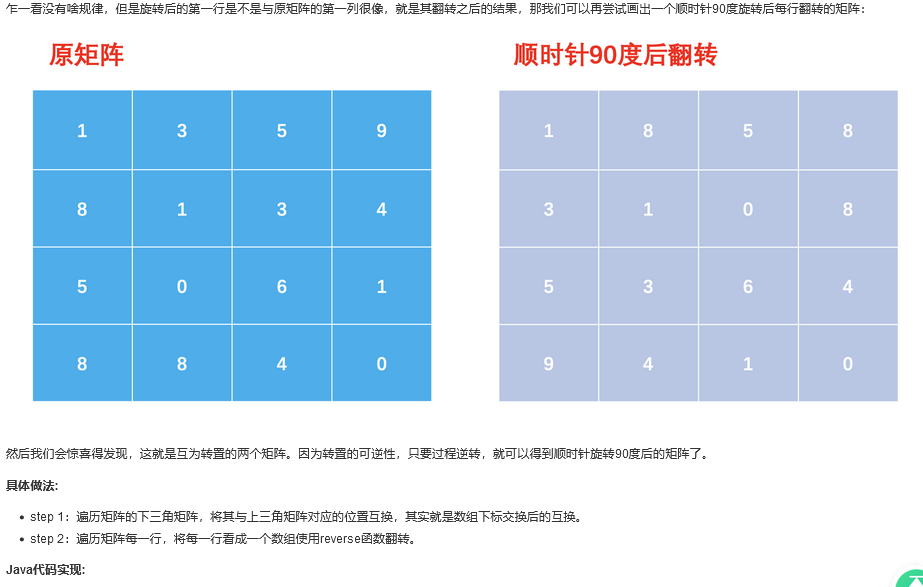
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int[][] rotateMatrix(int[][] mat, int n) {
int length = mat.length;
//矩阵转置
for(int i = 0; i < length; ++i){
for(int j = 0; j < i; ++j){
//交换上三角与下三角对应的元素
int temp = mat[i][j];
mat[i][j] = mat[j][i];
mat[j][i] = temp;
}
}
//每行翻转
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < length/2; j++){
int temp = mat[i][j];
mat[i][j] = mat[i][length - j - 1];
mat[i][length - j - 1] = temp;
}
}
return mat;
}
}
4. 设计LFU缓存结构
4.1. 题目描述
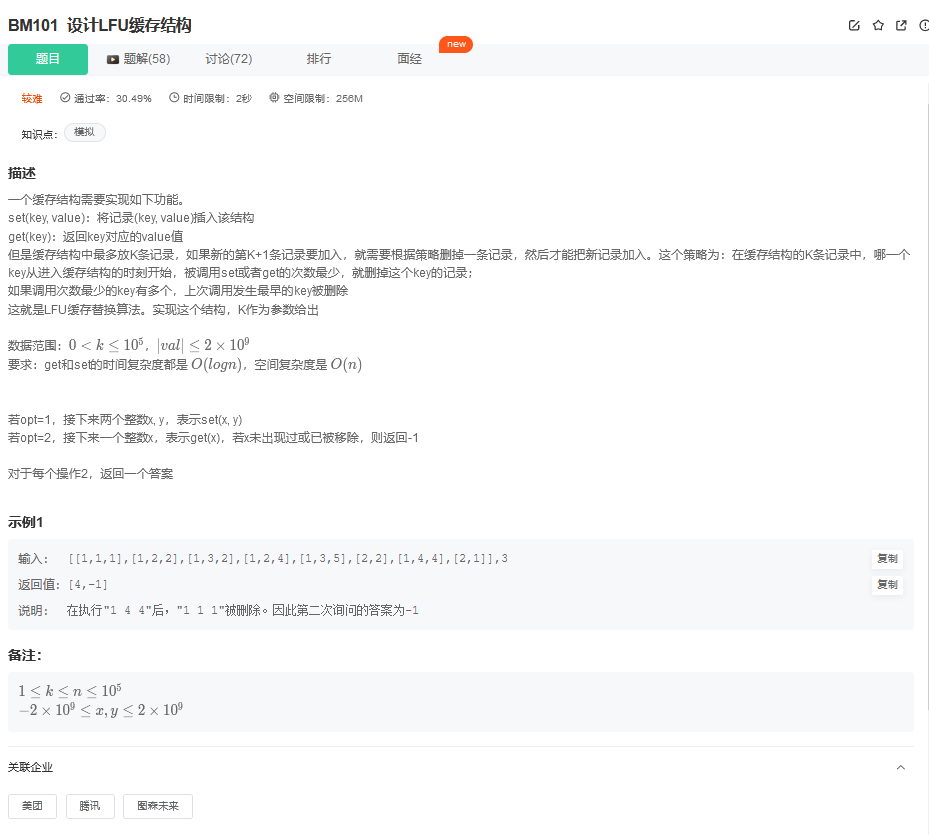
4.2. 解题思路
方法一:双哈希表(推荐使用)




Java代码实现:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
//设置节点结构
static class Node{
int freq;
int key;
int val;
//初始化
public Node(int freq, int key, int val) {
this.freq = freq;
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
//频率到双向链表的哈希表
private Map<Integer, LinkedList<Node> > freq_mp = new HashMap<>();
//key到节点的哈希表
private Map<Integer, Node> mp = new HashMap<>();
//记录缓存剩余容量
private int size = 0;
//记录当前最小频次
private int min_freq = 0;
public int[] LFU (int[][] operators, int k) {
//构建初始化连接
//链表剩余大小
this.size = k;
//获取操作数
int len = (int)Arrays.stream(operators).filter(x -> x[0] == 2).count();
int[] res = new int[len];
//遍历所有操作
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < operators.length; i++){
if(operators[i][0] == 1)
//set操作
set(operators[i][1], operators[i][2]);
else
//get操作
res[j++] = get(operators[i][1]);
}
return res;
}
//调用函数时更新频率或者val值
private void update(Node node, int key, int value) {
//找到频率
int freq = node.freq;
//原频率中删除该节点
freq_mp.get(freq).remove(node);
//哈希表中该频率已无节点,直接删除
if(freq_mp.get(freq).isEmpty()){
freq_mp.remove(freq);
//若当前频率为最小,最小频率加1
if(min_freq == freq)
min_freq++;
}
if(!freq_mp.containsKey(freq + 1))
freq_mp.put(freq + 1, new LinkedList<Node>());
//插入频率加一的双向链表表头,链表中对应:freq key value
freq_mp.get(freq + 1).addFirst(new Node(freq + 1, key, value));
mp.put(key, freq_mp.get(freq + 1).getFirst());
}
//set操作函数
private void set(int key, int value) {
//在哈希表中找到key值
if(mp.containsKey(key))
//若是哈希表中有,则更新值与频率
update(mp.get(key), key, value);
else{
//哈希表中没有,即链表中没有
if(size == 0){
//满容量取频率最低且最早的删掉
int oldkey = freq_mp.get(min_freq).getLast().key;
//频率哈希表的链表中删除
freq_mp.get(min_freq).removeLast();
if(freq_mp.get(min_freq).isEmpty())
freq_mp.remove(min_freq);
//链表哈希表中删除
mp.remove(oldkey);
}
//若有空闲则直接加入,容量减1
else
size--;
//最小频率置为1
min_freq = 1;
//在频率为1的双向链表表头插入该键
if(!freq_mp.containsKey(1))
freq_mp.put(1, new LinkedList<Node>());
freq_mp.get(1).addFirst(new Node(1, key, value));
//哈希表key值指向链表中该位置
mp.put(key, freq_mp.get(1).getFirst());
}
}
//get操作函数
private int get(int key) {
int res = -1;
//查找哈希表
if(mp.containsKey(key)){
Node node = mp.get(key);
//根据哈希表直接获取值
res = node.val;
//更新频率
update(node, key, res);
}
return res;
}
}
5. 顺时针打印矩阵
5.1. 题目描述
5.2. 解题思路
方法一:模拟

class Solution {
public int[] spiralArray(int[][] array) {
if (array == null || array.length == 0 || array[0].length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
int rows = array.length, columns = array[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rows][columns];
int total = rows * columns;
int[] order = new int[total];
int row = 0, column = 0;
int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
int directionIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++) {
order[i] = array[row][column];
visited[row][column] = true;
int nextRow = row + directions[directionIndex][0], nextColumn = column + directions[directionIndex][1];
if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= rows || nextColumn < 0 || nextColumn >= columns || visited[nextRow][nextColumn]) {
directionIndex = (directionIndex + 1) % 4;
}
row += directions[directionIndex][0];
column += directions[directionIndex][1];
}
return order;
}
}
方法二:按层模拟

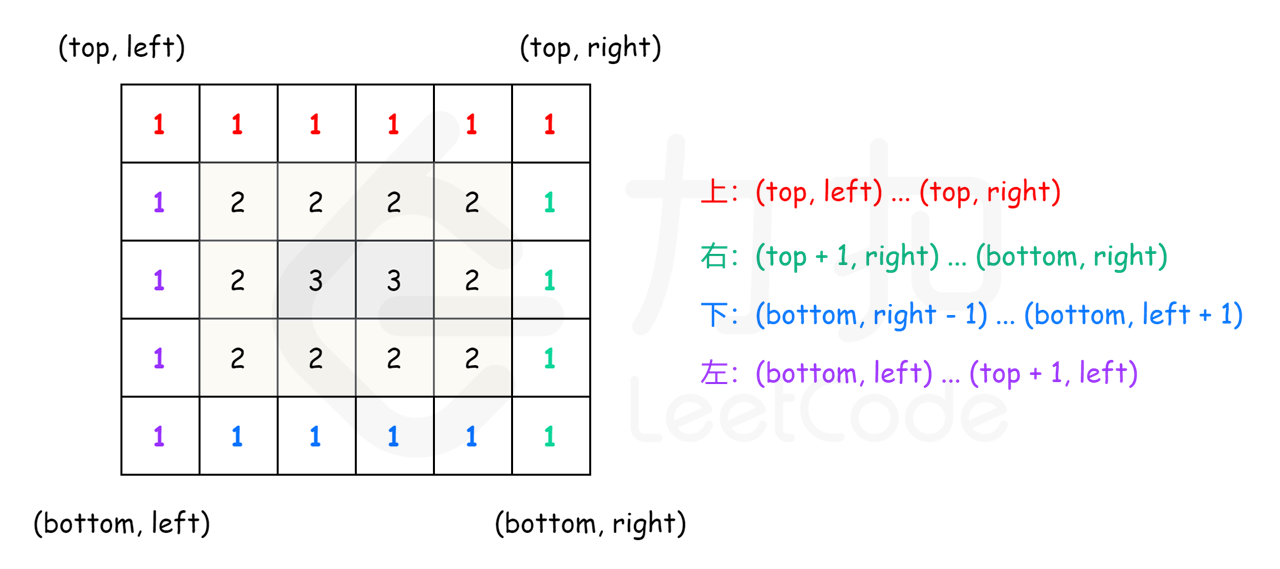
class Solution {
public int[] spiralArray(int[][] array) {
if (array == null || array.length == 0 || array[0].length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
int rows = array.length, columns = array[0].length;
int[] order = new int[rows * columns];
int index = 0;
int left = 0, right = columns - 1, top = 0, bottom = rows - 1;
while (left <= right && top <= bottom) {
for (int column = left; column <= right; column++) {
order[index++] = array[top][column];
}
for (int row = top + 1; row <= bottom; row++) {
order[index++] = array[row][right];
}
if (left < right && top < bottom) {
for (int column = right - 1; column > left; column--) {
order[index++] = array[bottom][column];
}
for (int row = bottom; row > top; row--) {
order[index++] = array[row][left];
}
}
left++;
right--;
top++;
bottom--;
}
return order;
}
}
6. 验证图书取出顺序
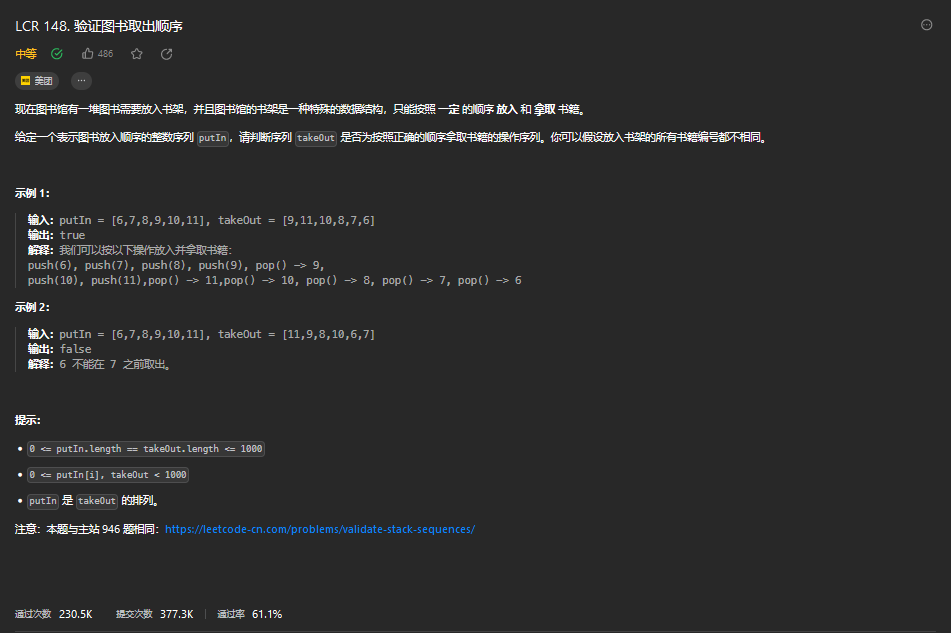
6.1. 题目描述
6.2. 解题思路
方法一:栈

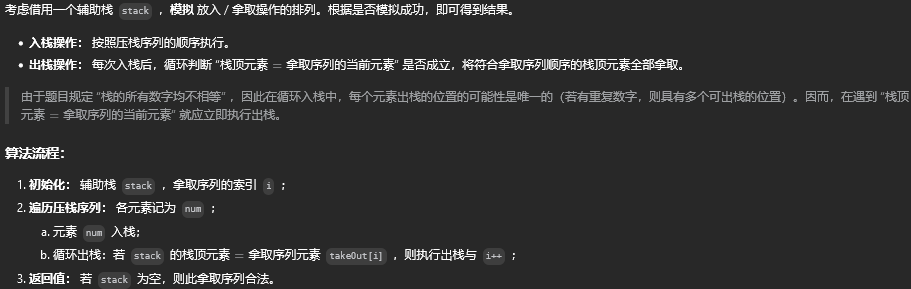

class Solution {
public boolean validateBookSequences(int[] putIn, int[] takeOut) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int i = 0;
for(int num : putIn) {
stack.push(num); // num 入栈
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == takeOut[i]) { // 循环判断与出栈
stack.pop();
i++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}