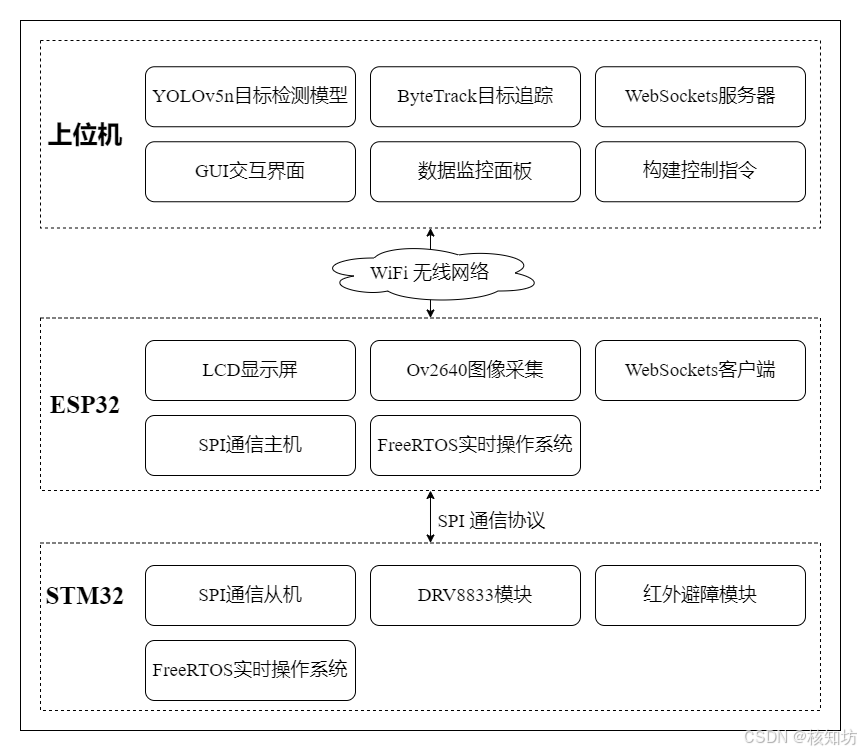
简介:本项目使用ESP32-CAM采集图像上传至上位机进行手部目标检测与追踪,使用了YOLOv5.6(注意力机制ECA,CBAM)+ByteTrack
博主同款迅雷链接:
链接:https://pan.xunlei.com/s/VOSO1EIzmXhBb_BIKM58cM5cA1#
提取码:8ms6
需要付费指导的查看简介联系我!
项目拉取:
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git环境准备:
Python3.10:https://mirrors.aliyun.com/python-release/windows/python-3.10.8.exe
进入Yolov5根目录创建虚拟环境:
python -m venv venv
venv\Scripts\activate #激活虚拟环境
pip install -e . #编辑式安装,之后修改Yolov5源码直接运行
数据集准备:
手部数据egohands_data:http://vision.soic.indiana.edu/egohands_files/egohands_data.zip
数据格式转换:https://blog.csdn.net/wukong168/article/details/122783179
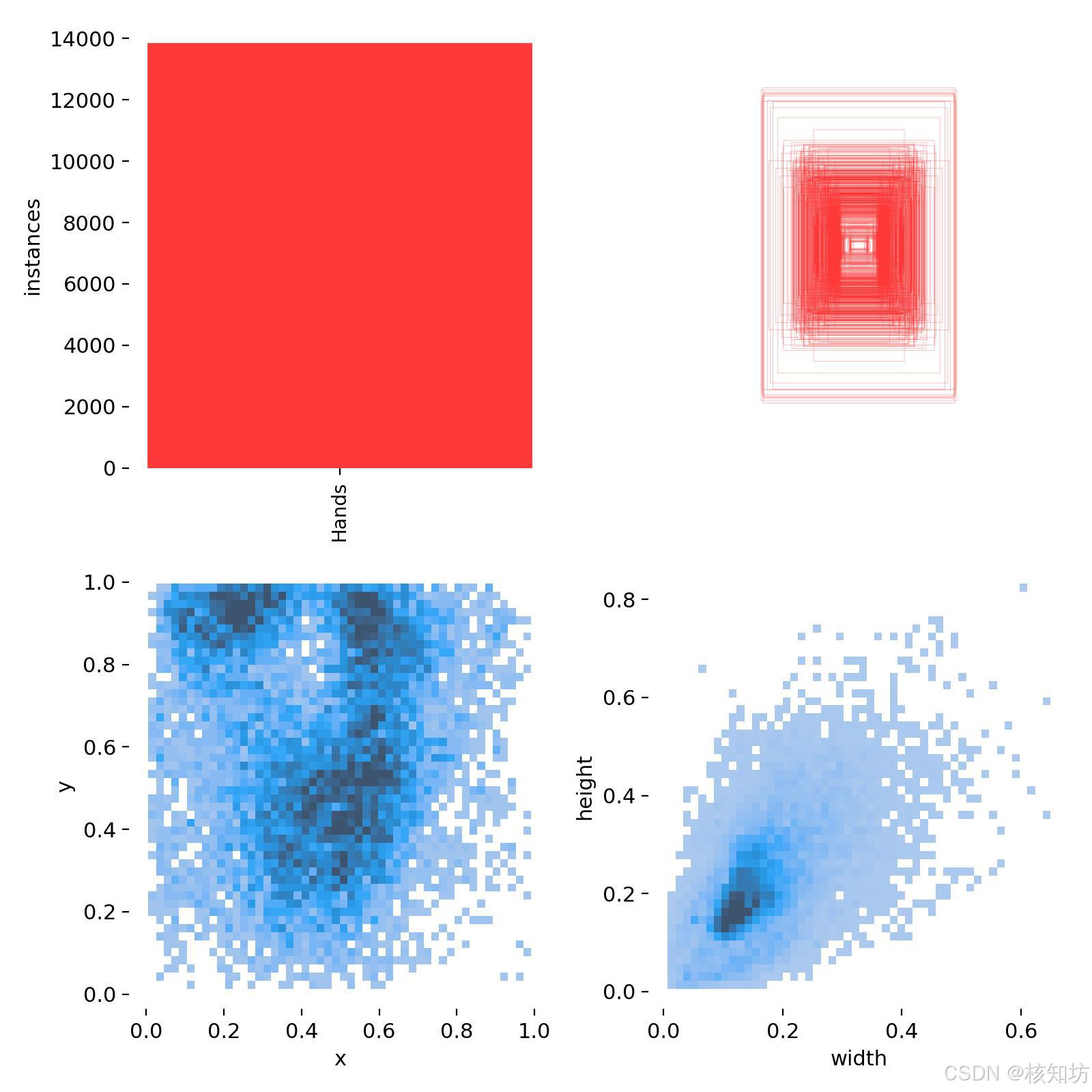
需要添加自定义数据集的可以录制视频,使用脚本提取帧,使用Labelme标注图像。
数据集文件夹目录必须符合一下结构,且图像与标注文件名必须一致:
-images
-train #训练集图片
-val #验证集图片
-labels
-train #训练集标注文件
-val #验证集图片文件coco128.yaml配置是数据集路径:
path: D:/VUE/ModelData/egohands_data/data
train: images/train
val: images/val
test: # test images (optional)
# Classes
names:
0: HandYOLOv5结构:
使用AI简单了解即可。

注意力机制添加:
在Yolov5根目录下的models/common.py文件末尾添加自定义模块,也可以创建一个独立的文件表示一个模块:
CBAM:

import torch
import math
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class BasicConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, relu=True, bn=True, bias=False):
super(BasicConv, self).__init__()
self.out_channels = out_planes
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=bias)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes,eps=1e-5, momentum=0.01, affine=True) if bn else None
self.relu = nn.ReLU() if relu else None
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
if self.bn is not None:
x = self.bn(x)
if self.relu is not None:
x = self.relu(x)
return x
class Flatten(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return x.view(x.size(0), -1)
class ChannelGate(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, gate_channels, reduction_ratio=16, pool_types=['avg', 'max']):
super(ChannelGate, self).__init__()
self.gate_channels = gate_channels
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(
Flatten(),
nn.Linear(gate_channels, gate_channels // reduction_ratio),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(gate_channels // reduction_ratio, gate_channels)
)
self.pool_types = pool_types
def forward(self, x):
channel_att_sum = None
for pool_type in self.pool_types:
if pool_type=='avg':
avg_pool = F.avg_pool2d( x, (x.size(2), x.size(3)), stride=(x.size(2), x.size(3)))
channel_att_raw = self.mlp( avg_pool )
elif pool_type=='max':
max_pool = F.max_pool2d( x, (x.size(2), x.size(3)), stride=(x.size(2), x.size(3)))
channel_att_raw = self.mlp( max_pool )
elif pool_type=='lp':
lp_pool = F.lp_pool2d( x, 2, (x.size(2), x.size(3)), stride=(x.size(2), x.size(3)))
channel_att_raw = self.mlp( lp_pool )
elif pool_type=='lse':
# LSE pool only
lse_pool = logsumexp_2d(x)
channel_att_raw = self.mlp( lse_pool )
if channel_att_sum is None:
channel_att_sum = channel_att_raw
else:
channel_att_sum = channel_att_sum + channel_att_raw
scale = F.sigmoid( channel_att_sum ).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(3).expand_as(x)
return x * scale
def logsumexp_2d(tensor):
tensor_flatten = tensor.view(tensor.size(0), tensor.size(1), -1)
s, _ = torch.max(tensor_flatten, dim=2, keepdim=True)
outputs = s + (tensor_flatten - s).exp().sum(dim=2, keepdim=True).log()
return outputs
class ChannelPool(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return torch.cat( (torch.max(x,1)[0].unsqueeze(1), torch.mean(x,1).unsqueeze(1)), dim=1 )
class SpatialGate(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SpatialGate, self).__init__()
kernel_size = 7
self.compress = ChannelPool()
self.spatial = BasicConv(2, 1, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=(kernel_size-1) // 2, relu=False)
def forward(self, x):
x_compress = self.compress(x)
x_out = self.spatial(x_compress)
scale = F.sigmoid(x_out) # broadcasting
return x * scale
class CBAM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, gate_channels, reduction_ratio=16, pool_types=['avg', 'max'], no_spatial=False):
super(CBAM, self).__init__()
self.ChannelGate = ChannelGate(gate_channels, reduction_ratio, pool_types)
self.no_spatial=no_spatial
if not no_spatial:
self.SpatialGate = SpatialGate()
def forward(self, x):
x_out = self.ChannelGate(x)
if not self.no_spatial:
x_out = self.SpatialGate(x_out)
return x_out
class ECA(nn.Module):
"""Constructs a ECA module.
Args:
channel: Number of channels of the input feature map
k_size: Adaptive selection of kernel size
"""
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k_size=3):
super(ECA, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.conv = nn.Conv1d(1, 1, kernel_size=k_size, padding=(k_size - 1) // 2, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
# feature descriptor on the global spatial information
y = self.avg_pool(x)
y = self.conv(y.squeeze(-1).transpose(-1, -2)).transpose(-1, -2).unsqueeze(-1)
# Multi-scale information fusion
y = self.sigmoid(y)
return x * y.expand_as(x)添加到YOLO系统配置输入参数:
在Yolov5根目录下的models/yolo.py文件导入自定义模块:

输入参数配置,此处有大量if语句用于个性化输入通道配置:


修改YOLOv5结构文件:
在Yolov5根目录下的models/yolov5s.yaml文件定义模型结构:
#YOLOv5s_custom summary: 320 layers, 1046153 parameters, 1046153 gradients, 2.5 GFLOPs
#YOLOv5s summary: 214 layers, 7022326 parameters, 7022326 gradients, 15.9 GFLOPs
nc: 1 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.25 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10, 13, 16, 30, 33, 23] # P3/8
- [30, 61, 62, 45, 59, 119] # P4/16
- [116, 90, 156, 198, 373, 326] # P5/32
activation: nn.RReLU() # 激活函数可以自定义
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[
[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2, 1]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]], # 2
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 4, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 1, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, ECA, [1024]], # 添加 ECA 提高小目标检测效果
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 10
]
# YOLOv5 v6.0 head
head: [
# [from, number, module, args]
[-1, 1, GhostConv, [512, 1, 1]], # 11
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], #13 cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 14
[-1, 1, GhostConv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, "nearest"]],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # 17 cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 18 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, ECA, [256]], # 在检测头中添加 ECA
[-1, 1, GhostConv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 14], 1, Concat, [1]], # 21 cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 22 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, GhostConv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [128, False]], # 25 (P5/32-large)
[[18, 22, 25], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]训练:
由于修改了模型结构,建议不加载官方预训练权重yolov5s.pt从0训练,当然可以提前使用遗传算法获取合适的超参数加快收敛速度。
python train.py --data coco128.yaml --weights '' --cfg yolov5s.yaml --img 640ByteTrack引入:
原理:Yolov5模型输出检测框列表,ByteTrack接收预测跟踪目标,最重要的是ID参数。
具体查看博主重新编写的检测函数:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@FileName:YoloModelRun.py
@Description:
@Author: 核知坊,一个激发创造力的网站:http://wwww.CoreKSets.cn
@Time:2025/3/23 20:02
"""
import pathlib
import time
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import torch
from models.common import DetectMultiBackend
from utils.augmentations import letterbox
from utils.general import non_max_suppression
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator
from utils.dataloaders import LoadImages
from utils.general import (
LOGGER,
Profile,
check_img_size,
scale_boxes,
)
from bytetracker import BYTETracker
# 兼容 Windows 下的路径问题
temp = pathlib.PosixPath
pathlib.PosixPath = pathlib.WindowsPath
class YoloModelRun():
"""
@ClassName:YoloModelRun
@Description:
@Author:锦沐Python
"""
def __init__(self, weights="best.onnx", imgsz = (640, 640), conf_thres=0.2, iou_thres=0.45, save_result = False, half=False):
self.weights = weights
self.conf_thres = conf_thres
self.iou_thres = iou_thres
self.save_result = save_result
self.device = torch.device("cpu")
# Load model
LOGGER.info("模型加载中")
self.Model = DetectMultiBackend(weights, device=self.device, dnn=False, fp16=half)
self.Model.eval()
# 追踪系统
self.Tracker = BYTETracker(track_thresh=0.25, track_buffer=10, match_thresh=0.7, frame_rate=8)
self.stride=self.Model.stride
self.names=self.Model.names
self.pt = self.Model.pt
self.imgsz = check_img_size(imgsz, s=self.stride) # check image size
self.Model.warmup(imgsz=(1 , 3, *self.imgsz)) # warmup
# [[x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, cls], [x1, y1, x2, y2, conf, cls],....]
self.detect_results = []
LOGGER.info("模型准备就绪")
def detect_image(self,source)->(list[[float,float,float,float,float,int,int]],Image.Image):
self.detect_results.clear()
# 处理不同类型的输入
if isinstance(source, str):
# 如果输入是图片路径,使用 LoadImages 进行加载
dataset = LoadImages(source, img_size=self.imgsz, stride=self.stride, auto=self.pt, vid_stride=1)
path, im, im0s, vid_cap, s = next(iter(dataset)) # 读取一张图片
elif isinstance(source, Image.Image):
im0s = np.array(source) # 原始图像 (RGB)
im0s = im0s[..., ::-1] # 转换为 BGR 格式(因为 OpenCV 使用 BGR)
# **使用与 LoadImages 类似的预处理**
im = letterbox(im0s, self.imgsz, stride=self.stride, auto=self.pt)[0] # 调整大小
im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC -> CHW, BGR -> RGB
im = np.ascontiguousarray(im) # 确保数据连续
else:
raise ValueError("输入必须是图片路径 (str) 或 PIL.Image 对象!")
# Run inference
detect_time_tuble = (Profile(device=self.device), Profile(device=self.device), Profile(device=self.device), Profile(device=self.device))
# 图像预处理
with detect_time_tuble[0]:
im = torch.from_numpy(im).to(self.Model.device)
im = im.half() if self.Model.fp16 else im.float() # uint8 to fp16/32
im /= 255 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
if len(im.shape) == 3:
im = im[None] # expand for batch dim
# Inference 预测
with detect_time_tuble[1]:
pred = self.Model(im, augment=False, visualize=False)
# NMS
with detect_time_tuble[2]:
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, self.conf_thres, self.iou_thres, None, False, max_det=10)
# 目标绘制
im0 = im0s.copy()
annotator = Annotator(im0, line_width=3, example=str(self.names[0]))
# Process predictions
with detect_time_tuble[3]:
det = pred[0]
# print(det)
s = ""
if len(det):
det = self.Tracker.update(det)
# 没有跟踪到物体直接返回
if not det:
return [], None
det = torch.tensor(det, dtype=torch.float32)
# print(det)
# Rescale boxes from img_size to im0 size
det[:, :4] = scale_boxes(im.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round()
# Print results
for c in det[:, 5].unique():
n = (det[:, 5] == c).sum() # detections per class
s += f"{n} {self.names[int(c)]}{'s' * (n > 1)}, " # add to string
for *xyxy, conf, cls, id in reversed(det):
x1,y1,x2,y2 = xyxy
c = int(cls) # integer class
label = f"{self.names[c]} {conf:.2f}"
annotator.box_label(xyxy, label, color= (255, 36, 125))
# 添加检测结果
w = 640
h = 480
self.detect_results.append([
round(x1.item() / w, 6), # 归一化 x1,保留6位小数
round(y1.item() / h, 6), # 归一化 y1,保留6位小数
round(x2.item() / w, 6), # 归一化 x2,保留6位小数
round(y2.item() / h, 6), # 归一化 y2,保留6位小数
round(conf.item(), 6), # 置信度,保留6位小数
self.names[c], # 类别名称
int(id)
])
# Stream results
if self.save_result:
timestamp = int(time.time())
annotator.save(f"{timestamp}_result.jpg")
show_img = Image.fromarray(np.asarray(annotator.im)[..., ::-1])
# Print time (inference-only)
LOGGER.info(f"{s}{'' if len(det) else '(没有检测到目标), '}{detect_time_tuble[1].dt * 1e3:.1f}ms")
# Print results
LOGGER.info(f"Speed: %.1fms 预处理, %.1fms 识别, %.1fms NMS ,%d.1ms ByteTrack 每张图像 {(1, 3, *self.imgsz)}" %
(detect_time_tuble[0].dt * 1e3,
detect_time_tuble[1].dt * 1e3,
detect_time_tuble[2].dt * 1e3,
detect_time_tuble[3].dt * 1e3))
return self.detect_results, show_img结果: