🧠前言
在分布式系统中,服务节点的增删是常态操作,例如缓存节点扩容、数据库分片或服务实例上线下线。传统的取模方式(如key.hashCode() % N)虽然简单,但一旦节点数量发生变化,会导致大量数据迁移,严重影响系统性能与可用性。
为了解决这个问题,一致性哈希(Consistent Hashing) 应运而生。
🎯 一致性哈希的核心思想
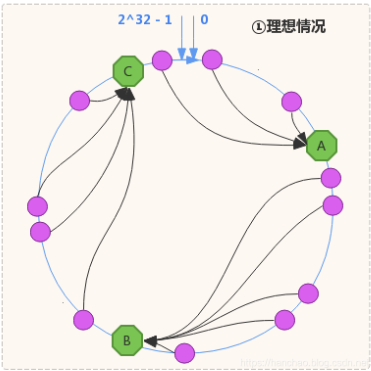
- 将整个哈希值空间(通常是
0 ~ 2^32-1)看作一个闭合的圆环(hash ring) - 每个节点(或虚拟节点)根据其哈希值被放置在环上的某个位置
- 每个数据项(例如 key)也通过哈希函数映射到环上
- 数据顺时针存储在第一个"比自己大的节点"处(tailMap 策略)
- 节点上下线时,仅影响其前一个节点负责的数据范围,最大限度减少数据迁移
📌 tailMap(h) 在一致性哈希中的用途
在一致性哈希中,我们将 key 映射到一个环上(Hash Ring),所有虚拟节点按哈希值顺时针排列。
当我们查找一个 key 要路由到哪个节点时,需要:
-计算该 key 的 hash 值(比如为 h)
-从哈希环中找出第一个 >= h 的节点(即"顺时针第一个")
-如果找不到(即 h 超过了最大值),就"回到"环的最开始(第一个节点)
这正是 tailMap(h) 的用途,源码当中的用法
🧱 核心结构实现:哈希环
我们使用 Java 的 TreeMap 来实现一个有序的哈希环:
java
SortedMap<Long, VirtualNode<T>> hashRing = new TreeMap<>();-
✅ 为什么使用
TreeMap?特性 作用 有序(按 key 排序) 模拟顺时针哈希环结构 tailMap(k) 快速找到下一个最近节点 firstKey() + 环形跳转 实现哈希环首尾相连 插入/删除 O(log n) 动态变更节点效率高
每个 VirtualNode< T > 对象代表一个逻辑上的虚拟节点,它映射到实际服务节点(如缓存服务器、数据库分片等)。
🔁 数据定位逻辑:顺时针查找
java
public T getNode(String key) {
long hash = hash(key); // 计算 key 的哈希值
SortedMap<Long, VirtualNode<T>> tailMap = hashRing.tailMap(hash);
Long nodeHash = tailMap.isEmpty() ? hashRing.firstKey() : tailMap.firstKey();
return hashRing.get(nodeHash).getRealNode();
}这段逻辑实现了"一致性哈希的顺时针最近原则":
- 如果 key 落在节点间空白区,自动跳到下一个最近节点
- 如果超过最大值,自动跳回环起点🧩 虚拟节点的设计(VirtualNode)
虚拟节点通过引入多个副本,将一个真实节点映射到多个位置,提高数据分布的均衡性
通常,我们会为每个真实节点创建 100~200 个虚拟节点,提升分布均匀度,避免热点。
📊 设计亮点小结
- ✅ 高可用性:节点上下线仅影响相邻数据区域,降低迁移量
- ✅ 高均衡性:虚拟节点+哈希环保证数据分布更均匀
- ✅ 高性能查找:TreeMap 支持 O(log n) 顺时针定位
- ✅ 高扩展性:轻松支持节点扩缩容,不影响全局状态
🚀 实际应用场景
-
✅ 场景一:分布式缓存(如 Redis / Memcached)
问题: 多个缓存节点如何分配数据键(key),避免频繁数据迁移?
使用方法:- 每个缓存服务器作为一个 Node
- 使用 ConsistentHashRouter.routeNode(key) 来决定 key 存在哪个服务器上
示例:
javaConsistentHashRouter<CacheServer> router = new ConsistentHashRouter<>(serverList, 100); String key = "user:123456"; CacheServer server = router.routeNode(key); server.set(key, value);优点: 增加/删除缓存节点时,只影响极少数数据迁移,比传统 hash(key) % N 更稳定。
-
✅ 场景二:MQ 消费者负载均衡(如 RocketMQ / Kafka)
问题: 多个消费者如何均匀处理消息,且保证特定 key 的消息总落到同一消费者?使用方法:
- 每个消费实例作为一个 Node
- 对消息中的某个字段(如订单号、用户 ID)做 routeNode,路由给固定消费者
示例:
javaConsistentHashRouter<ConsumerInstance> router = new ConsistentHashRouter<>(consumerList, 128); String messageKey = msg.getUserId(); // 一致路由同一用户的消息 ConsumerInstance consumer = router.routeNode(messageKey); consumer.process(msg); -
✅ 场景三:分布式存储 / Sharding(如 MySQL 分库分表)
问题: 将数据分配到多个数据库或表上,支持扩容、容灾使用方法:
- 每个数据库实例或分表作为一个 Node
- 使用一致性哈希选择表名或数据库名
示例:
javaConsistentHashRouter<ShardNode> router = new ConsistentHashRouter<>(shardNodes, 50); String orderId = "ORD123456"; ShardNode db = router.routeNode(orderId); db.insertOrder(order); -
✅ 场景四:分布式文件系统节点选择(如 FastDFS)
问题: 上传文件时,如何选择合适的存储节点且支持节点变更后不迁移所有文件?
使用方法:- 文件名作为 key,节点列表作为 Node 集合
- 使用一致性哈希路由选择目标节点
-
✅ 场景五:微服务调用路由(服务治理)
问题: 同一个用户的请求希望落到同一实例上,便于会话/缓存/限流等操作
示例:javaConsistentHashRouter<ServiceInstance> router = new ConsistentHashRouter<>(instances, 160); String userId = request.getUserId(); ServiceInstance instance = router.routeNode(userId); instance.call(request);
总结:适合一致性哈希的场景
| 场景 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 分布式缓存 | 缓存 key 映射到节点 |
| 分库分表 / 存储节点 | 数据均衡路由、减少数据迁移 |
| MQ 消费者路由 | 按 key 保证消息顺序或一致消费 |
| 文件分布式存储 | 根据文件名分布存储,支持节点上下线 |
| 微服务路由 | 保证同用户请求落到相同服务实例上 |
注意:如你系统中有"按某个 key 做分配、还希望支持节点平滑上下线",基本都可以考虑这段一致性哈希代码。
最后来看看Apache RocketMQ 一致性哈希算法的实现代码
java
/**
* 将节点对象哈希到带有多个虚拟节点的哈希环上。
* 方法 routeNode 会根据一致性哈希算法返回某个 objectKey 所属的节点。
*/
public class ConsistentHashRouter<T extends Node> {
// 使用 TreeMap 维护有序的哈希环,key 是虚拟节点的哈希值,value 是虚拟节点
private final SortedMap<Long, VirtualNode<T>> ring = new TreeMap<>();
private final HashFunction hashFunction;
/**
* 构造函数,使用默认 MD5 哈希函数
*/
public ConsistentHashRouter(Collection<T> pNodes, int vNodeCount) {
this(pNodes, vNodeCount, new MD5Hash());
}
/**
* @param pNodes 物理节点集合
* @param vNodeCount 每个物理节点所对应的虚拟节点数量
* @param hashFunction 哈希函数,用于计算节点哈希值
*/
public ConsistentHashRouter(Collection<T> pNodes, int vNodeCount, HashFunction hashFunction) {
if (hashFunction == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("Hash Function is null");
}
this.hashFunction = hashFunction;
if (pNodes != null) {
for (T pNode : pNodes) {
addNode(pNode, vNodeCount); // 将物理节点添加到哈希环
}
}
}
/**
* 添加一个物理节点及其虚拟节点到哈希环中
*
* @param pNode 要添加的物理节点
* @param vNodeCount 虚拟节点的数量,必须 >= 0
*/
public void addNode(T pNode, int vNodeCount) {
if (vNodeCount < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("illegal virtual node counts :" + vNodeCount);
int existingReplicas = getExistingReplicas(pNode);
for (int i = 0; i < vNodeCount; i++) {
// 为物理节点生成第 i 个虚拟节点
VirtualNode<T> vNode = new VirtualNode<>(pNode, i + existingReplicas);
ring.put(hashFunction.hash(vNode.getKey()), vNode); // 添加到哈希环
}
}
/**
* 从哈希环中移除某个物理节点及其所有虚拟节点
*/
public void removeNode(T pNode) {
Iterator<Long> it = ring.keySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Long key = it.next();
VirtualNode<T> virtualNode = ring.get(key);
if (virtualNode.isVirtualNodeOf(pNode)) {
it.remove(); // 移除匹配的虚拟节点
}
}
}
/**
* 根据给定 key,从哈希环中路由到最近的节点
*
* @param objectKey 要路由的 key
* @return 路由到的物理节点
*/
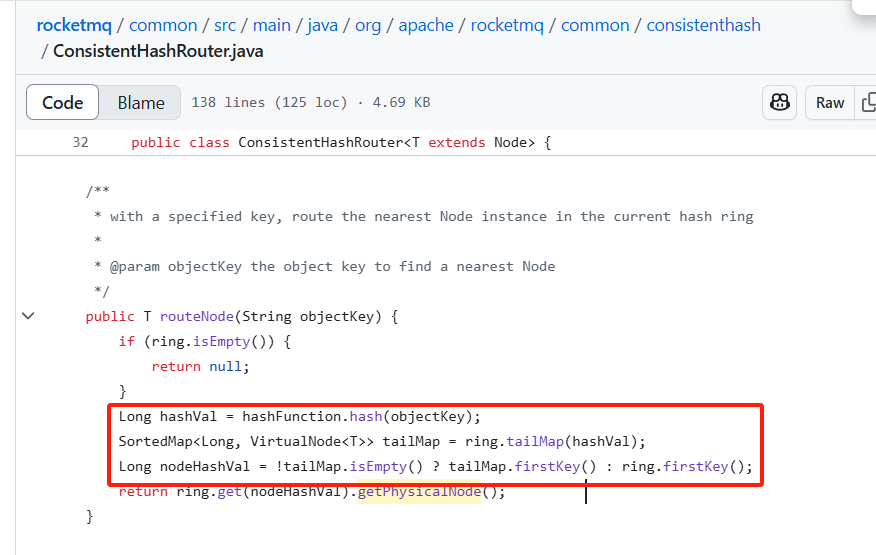
public T routeNode(String objectKey) {
if (ring.isEmpty()) {
return null; // 没有节点
}
Long hashVal = hashFunction.hash(objectKey); // 计算 key 的哈希值
// 获取大于等于 hashVal 的子哈希环
SortedMap<Long, VirtualNode<T>> tailMap = ring.tailMap(hashVal);
// 如果 tailMap 不为空,选择第一个;否则回环到 ring 的第一个节点
Long nodeHashVal = !tailMap.isEmpty() ? tailMap.firstKey() : ring.firstKey();
return ring.get(nodeHashVal).getPhysicalNode(); // 返回物理节点
}
/**
* 获取某个物理节点当前已有的虚拟节点数
*/
public int getExistingReplicas(T pNode) {
int replicas = 0;
for (VirtualNode<T> vNode : ring.values()) {
if (vNode.isVirtualNodeOf(pNode)) {
replicas++;
}
}
return replicas;
}
/**
* 默认的 MD5 哈希函数实现
*/
private static class MD5Hash implements HashFunction {
MessageDigest instance;
public MD5Hash() {
try {
instance = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
// 忽略异常
}
}
@Override
public long hash(String key) {
instance.reset();
instance.update(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
byte[] digest = instance.digest();
// 使用前4字节构造 long 类型的哈希值
long h = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
h <<= 8;
h |= ((int) digest[i]) & 0xFF;
}
return h;
}
}
}
java
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.rocketmq.common.consistenthash;
/**
* Hash String to long value
*/
public interface HashFunction {
long hash(String key);
}
java
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.rocketmq.common.consistenthash;
/**
* Represent a node which should be mapped to a hash ring
*/
public interface Node {
/**
* @return the key which will be used for hash mapping
*/
String getKey();
}
java
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.rocketmq.common.consistenthash;
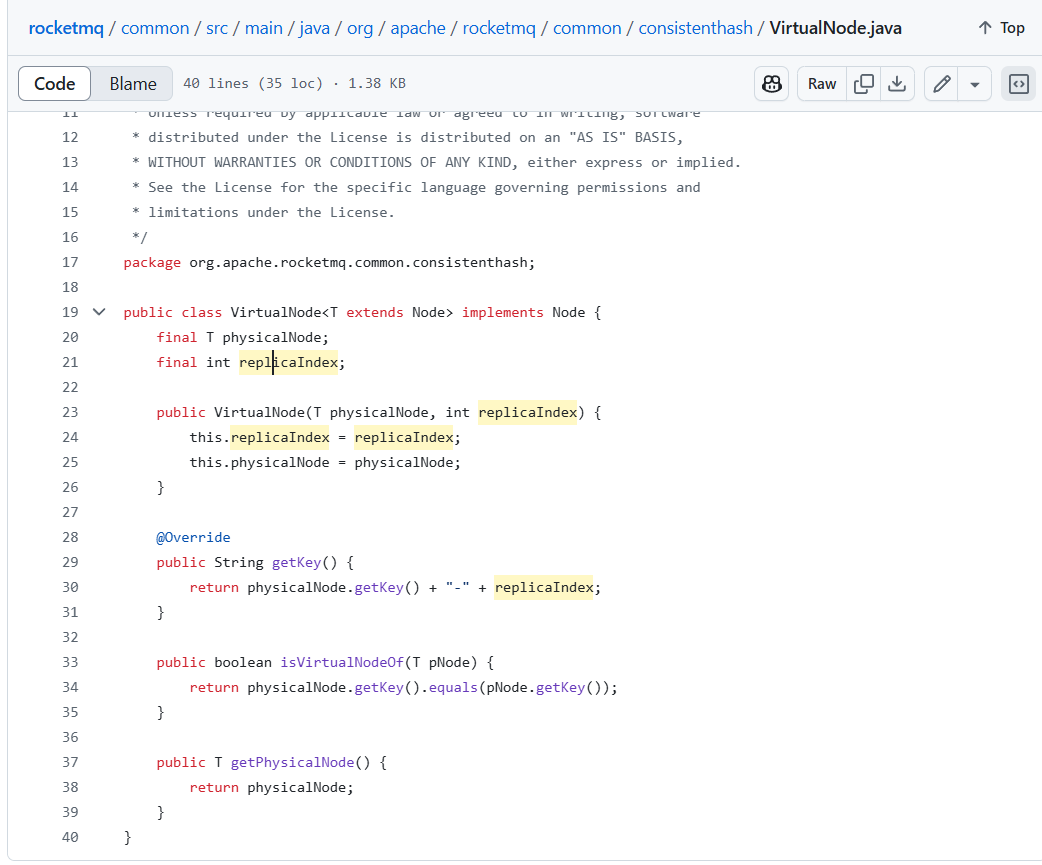
public class VirtualNode<T extends Node> implements Node {
final T physicalNode;
final int replicaIndex;
public VirtualNode(T physicalNode, int replicaIndex) {
this.replicaIndex = replicaIndex;
this.physicalNode = physicalNode;
}
@Override
public String getKey() {
return physicalNode.getKey() + "-" + replicaIndex;
}
public boolean isVirtualNodeOf(T pNode) {
return physicalNode.getKey().equals(pNode.getKey());
}
public T getPhysicalNode() {
return physicalNode;
}
}最后 今天的分享就到这里,有问题发私信交流
顺便说下 这是腾讯的一道面试题
虚拟节点通过"将一个物理节点映射为多个散布在哈希环上的点",显著提高了 key 到节点的均衡性,从而提高系统的负载均衡能力和可扩展性。