目录
[1. 安装 Pandas](#1. 安装 Pandas)
[(3.)Series 的索引和切片](#(3.)Series 的索引和切片)
[(1.)创建 DataFrame](#(1.)创建 DataFrame)
[(2.)DataFrame 的属性](#(2.)DataFrame 的属性)
[(3.)DataFrame 的排序和值替换](#(3.)DataFrame 的排序和值替换)
[1. 标签索引(.loc)](#1. 标签索引(.loc))
[2. 位置索引(.iloc)](#2. 位置索引(.iloc))
[5. Pandas 的条件筛选](#5. Pandas 的条件筛选)
[6. Pandas 中处理重复值](#6. Pandas 中处理重复值)
[7. Pandas 中处理缺失值](#7. Pandas 中处理缺失值)
简介
在当今这个数据爆炸的时代,数据处理已经成为了各个领域中不可或缺的一环。无论是数据分析、机器学习还是人工智能,都需要对大量的数据进行清洗、转换和分析。而 Pandas 作为 Python 中最流行的数据处理库之一,凭借其强大的功能和简洁的 API,成为了数据科学家们的首选工具。无论你是数据科学的新手还是有一定经验的从业者,都能从本文中获得有价值的信息。
这篇文章并没有把pandas所有内容说完,但是为后面机器学习、深度学习已经足够使用了,学习太多容易混乱
1. 安装 Pandas
Pandas 是一个开源的 Python 库,专为数据处理和分析而设计。它提供了高性能、易用的数据结构和数据分析工具,使数据处理变得更加简单和高效。Pandas 的主要数据结构是 Series(一维数组)和 DataFrame(二维表格),它们提供了强大的索引功能和数据操作能力。
安装 Pandas 非常简单,只需要使用 pip 命令即可:
python
pip install pandas==1.3.5 -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
2.基本数据结构
Pandas 有两种主要的数据结构:Series 和 DataFrame。
1.Series
(1.)创建Series
Series 是一个一维的带标签数组,可以容纳任何数据类型(整数、字符串、浮点数、Python 对象等)。它由两部分组成:索引(index)和值(values)。
python
import pandas as pd
# 创建一个Series
s_1 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(s_1)
# 创建自定义索引的 Series
s_2 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
print(s_2)
#创建字符串类型的 Series
s_3 = pd.Series(['Lily', "Rose", "Jack"])
print(s_3)输出结果:
python
#s_1
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
dtype: int64
#s_2
a 1
b 2
c 3
d 4
e 5
dtype: int64
#s_3
0 Lily
1 Rose
2 Jack
dtype: object(2.)Series的属性
.index:获取索引对象.values:获取底层 NumPy 数组
python
print(s_1.index)
print(s_2.index)
print(s_1.values)
print(s_3.values)
# 运行结果:RangeIndex(start=0, stop=5, step=1)
# Index(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'], dtype='object')
# [1 2 3 4 5]
# ['Lily' 'Rose' 'Jack'](3.)Series 的索引和切片
创建 Series 对象
python
import pandas as pd
s_1 = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
s_2 = pd.Series(['lily', 'rose', 'jack'])
# a 1
# b 2
# c 3
# d 4
# e 5
# dtype: int64
# 0 lily
# 1 rose
# 2 jack
# dtype: object基于标签的索引(自定义索引)
python
# 访问单个元素(标签索引)
print(s_1['d']) # 输出:4
# 访问多个元素(标签切片)
# print(s_1['a':'d']) # 输出:a到d的元素(含d)
# 访问不连续的元素
print(s_1[['a', 'd']]) # 输出:a和d的元素基于位置的索引(默认索引)
python
print(s_2[2]) # 输出:jack(位置2的元素)
print(s_2[0:2]) # 输出:位置0和1的元素(不含2)
print(s_2[[0, 2]]) # 输出:位置0和2的元素混合索引的注意事项
python
print(s_1[4]) # 输出:5(位置4的元素,即索引'e'对应的值)- 当自定义索引是标签时,
s_1[4]会被解释为位置索引 - 但这种用法容易混淆,建议明确使用
.loc(标签)或.iloc(位置)
2.DataFrame
DataFrame 是一个二维的带标签数据结构,类似于 Excel 表格或 SQL 表。它可以被看作是由多个 Series 组成的字典,每个 Series 共享相同的索引。
(1.)创建 DataFrame
创建带自定义索引的 DataFrame
python
df_1 = pd.DataFrame({'age': [10, 11, 12],
'name': ['tim', 'tom', 'rose'],
'income': [100, 200, 300]},
index=['person1', 'person2', 'person3'])
print(df_1)- 使用字典创建 DataFrame,键为列名,值为列数据
- 通过
index参数指定行索引
python
age name income
person1 10 tim 100
person2 11 tom 200
person3 12 rose 300创建带默认索引的 DataFrame
python
df_1 = pd.DataFrame({'age': [10, 11, 12],
'name': ['tim', 'tom', 'rose'],
'income': [100, 200, 300]})
print(df_1)- 不指定索引时,默认生成整数索引(0 到 2)
python
age name income
0 10 tim 100
1 11 tom 200
2 12 rose 300(2.)DataFrame 的属性
python
# 行索引
df_1.index # 输出:Index(['person1', 'person2', 'person3'], dtype='object')
# 列名
df_1.columns # 输出:Index(['age', 'name', 'income'], dtype='object')
# 值(NumPy数组)
df_1.values # 输出:
# array([[10, 'tim', 100],
# [11, 'tom', 200],
# [12, 'rose', 300]], dtype=object)访问DataFrame 的列(Series)
python
print(df_1.name)- 通过属性访问
name列,返回 Series 对象 - 输出结果:
python
0 tim
1 tom
2 rose
Name: name, dtype: object(3.)DataFrame 的排序和值替换
创建 DataFrame
python
dic = {'name': ['kiti', 'beta', 'peter', 'tom'],
'age': [20, 18, 35, 21],
'gender': ['f', 'f', 'm', 'm']}
df = pd.DataFrame(dic)
print(df)- 使用字典创建 DataFrame,默认索引为 0 到 3
python
name age gender
0 kiti 20 f
1 beta 18 f
2 peter 35 m
3 tom 21 m按照年龄列排序
python
# 升序排序(默认)
df = df.sort_values(by=['age'])
# 降序排序
df = df.sort_values(by=['age'], ascending=False)- 最终结果(降序):
python
name age gender
2 peter 35 m
3 tom 21 m
0 kiti 20 f
1 beta 18 f值替换
python
df['gender'] = df['gender'].replace(['m', 'f'], ['male', 'female'])replace()方法替换 Series 中的值['m', 'f']:要替换的值['male', 'female']:替换后的值
python
name age gender
2 peter 35 male
3 tom 21 male
0 kiti 20 female
1 beta 18 female3.pandas的选取与修改
创建 DataFrame
python
df = pd.DataFrame(
{'age': [10, 11, 12],
'name': ['tim', 'tom', 'rose'],
'income': [100, 200, 300]},
index=['person1', 'person2', 'person3'])
python
age name income
person1 10 tim 100
person2 11 tom 200
person3 12 rose 300添加列
python
df['pay'] = [20, 30, 40]- 在末尾添加
pay列
python
age name income pay
person1 10 tim 100 20
person2 11 tom 200 30
person3 12 rose 300 40添加行
python
df.loc['person4', ['age', 'name', 'income']] = [20, 'kitty', 200]- 使用
.loc在person4位置添加新行
python
age name income pay
person1 10 tim 100 20
person2 11 tom 200 30
person3 12 rose 300 40
person4 20 kitty 200 NaN数据访问
python
# 访问列
print(df.name) # 通过属性访问
# 访问多列
print(df[['age', 'name']])
# 访问行(位置切片)
print(df[0:2]) # 位置0到1(不含2)
# 访问行(标签索引)
print(df.loc[['person1', 'person3']])
# 访问单个值
print(df.loc['person1', 'name']) # 输出:tim删除操作
python
# 直接删除列(原地操作)
del df['age']
# 删除列(返回新DataFrame)
data = df.drop('name', axis=1, inplace=False)
# 删除行(原地操作)
df.drop('person3', axis=0, inplace=True)时间序列 DataFrame
python
datas = pd.date_range('20180101', periods=5)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(30).reshape(5, 6),
index=datas,
columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'])
python
A B C D E F
2018-01-01 0 1 2 3 4 5
2018-01-02 6 7 8 9 10 11
2018-01-03 12 13 14 15 16 17
2018-01-04 18 19 20 21 22 23
2018-01-05 24 25 26 27 28 294.pandas的索引
创建 DataFrame
python
df = pd.DataFrame(
np.arange(30).reshape(5, 6),
index=['20180101', '20180102', '20180103', '20180104', '20180105'],
columns=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F']
)- 使用 NumPy 数组创建 DataFrame
- 行索引为日期字符串,列索引为字母
python
A B C D E F
20180101 0 1 2 3 4 5
20180102 6 7 8 9 10 11
20180103 12 13 14 15 16 17
20180104 18 19 20 21 22 23
20180105 24 25 26 27 28 291. 标签索引(.loc)
python
# 获取某列(全部行的B列)
print(df.loc[:, 'B'])
# 输出:
# 20180101 1
# 20180102 7
# 20180103 13
# 20180104 19
# 20180105 25
# Name: B, dtype: int64
# 获取单个值(20180103行的B列)
print(df.loc['20180103', 'B']) # 输出:13
# 获取某行的多列(20180103行的B列和D列)
print(df.loc['20180103', ['B', 'D']])
# 输出:
# B 13
# D 15
# Name: 20180103, dtype: int64
# 获取整行(20180101行的所有列)
print(df.loc['20180101', :])
# 输出:
# A 0
# B 1
# C 2
# D 3
# E 4
# F 5
# Name: 20180101, dtype: int642. 位置索引(.iloc)
python
# 获取单个值(第2行第3列,索引从0开始)
print(df.iloc[1, 2]) # 输出:8
# 获取某列(所有行的第3列)
print(df.iloc[:, 2])
# 输出:
# 20180101 2
# 20180102 8
# 20180103 14
# 20180104 20
# 20180105 26
# Name: C, dtype: int64
# 获取整行(第2行的所有列)
print(df.iloc[1, :])
# 输出:
# A 6
# B 7
# C 8
# D 9
# E 10
# F 11
# Name: 20180102, dtype: int645. Pandas 的条件筛选
读取数据
python
df = pd.read_csv("data2.csv", encoding='gbk', engine='python')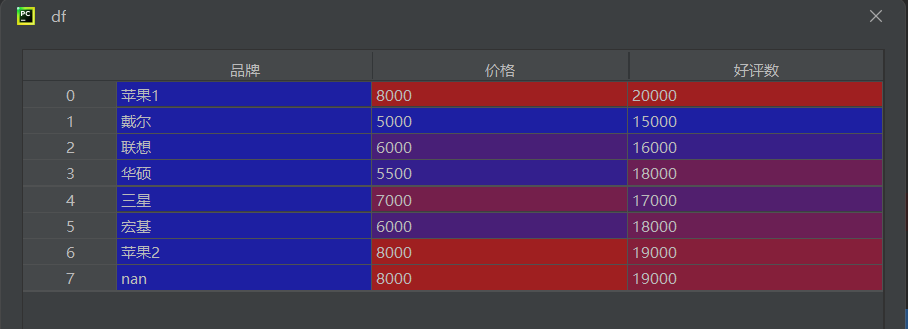
数值条件筛选
python
# 筛选好评数>17000的记录
df_1 = df[df['好评数'] > 17000]
# 筛选好评数在15000-17000之间的记录
df_2 = df[df['好评数'].between(15000, 17000)]df['好评数'] > 17000:生成布尔 Seriesbetween(a, b):等效于(x >= a) & (x <= b)
字符串条件筛选
python
# 筛选品牌包含"苹果"且非空的记录
df_3 = df[df['品牌'].str.contains('苹果', na=False)]
# 筛选品牌包含"苹果"或为空值的记录
df_4 = df[df['品牌'].str.contains('苹果', na=True)]str.contains('苹果'):判断字符串是否包含子串na=False:将 NaN 视为 False(排除空值)na=True:将 NaN 视为 True(包含空值)
多条件组合筛选
python
# 筛选价格<7000且好评数>16000的记录
df_5 = df[(df['价格'] < 7000) & (df['好评数'] > 16000)]
# 筛选价格<6000或好评数>18000的记录
df_6 = df[(df['价格'] < 6000) | (df['好评数'] > 18000)]- 使用
&(逻辑与)和|(逻辑或)组合条件 - 每个条件必须用括号
()包裹 - 最终结果
df_6包含所有满足任一条件的记录
6. Pandas 中处理重复值
读取数据
python
df = pd.read_csv(r"data1.csv", encoding='gbk', engine='python')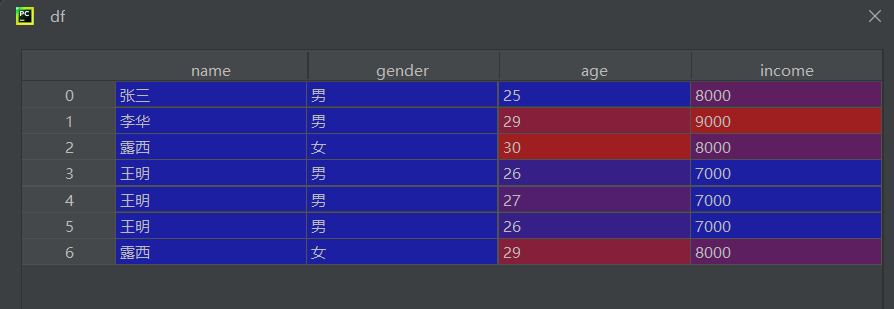
判断重复值
python
# 判断全量重复行(所有列值相同)
result1 = df.duplicated()
# 判断基于单列的重复行
result2 = df.duplicated('gender')
# 判断基于多列组合的重复行
result3 = df.duplicated(['gender', 'name'])duplicated()返回布尔 Series,标记每行是否为重复行keep='first'(默认):首次出现的行标记为 False,后续重复行标记为 True- 多列判断时,只有所有指定列的值都相同才算重复
提取重复行
python
a = df[result1] # 全量重复行
b = df[result2] # gender列重复的行
c = df[result3] # gender和name都重复的行
# 手动布尔索引(示例)
d = df[[True, False, False, True, True, False, False]]- 通过布尔索引提取对应行
- 手动指定布尔列表时,长度必须与 DataFrame 行数一致
删除重复行
python
# 删除全量重复行(保留首次出现的行)
new_df1 = df.drop_duplicates()
# 删除基于多列组合的重复行
new_df2 = df.drop_duplicates(['name', 'gender'])7. Pandas 中处理缺失值
读取数据
python
df = pd.read_csv(r"data.csv", encoding='gbk', engine='python')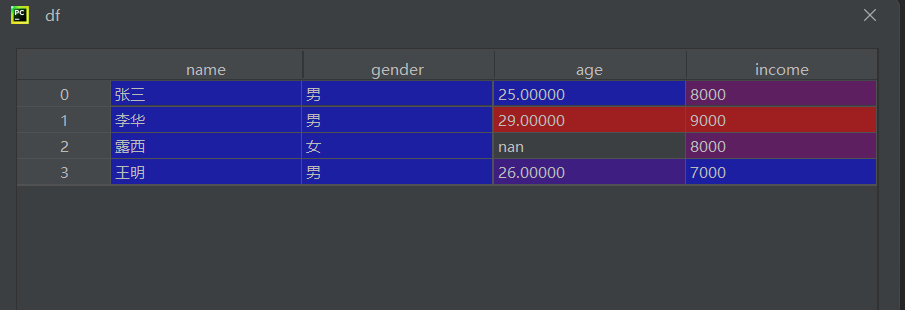
检测缺失值
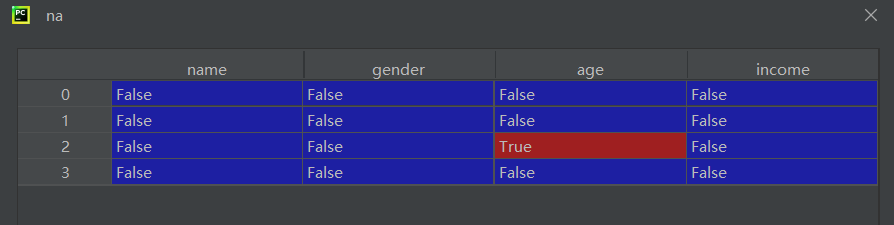
python
na = df.isnull()isnull()返回布尔 DataFrame- 每个元素标记是否为缺失值(
NaN或None)
填充缺失值
python
df1 = df.fillna('1')fillna('1'):用字符串'1'填充所有缺失值- 其他常用填充方式:
python
df.fillna(0) # 用0填充
df.fillna(method='ffill') # 用前一个有效值填充
df.fillna({'col1': 0, 'col2': 100}) # 按列指定填充值删除缺失值
python
df2 = df.dropna()dropna()默认删除包含任何缺失值的行- 参数说明
python
df.dropna(axis=0) # 删除行(默认)
df.dropna(axis=1) # 删除列
df.dropna(how='all') # 只删除全为缺失值的行
df.dropna(thresh=2) # 保留至少有2个非缺失值的行