1. 所有的实现迭代器的类都直接或间接的继承实现了 Iterable接口.并在类的内部实现了 Iterator 类
java
/**
* Implementing this interface allows an object to be the target of the enhanced
* {@code for} statement (sometimes called the "for-each loop" statement).
*
* @param <T> the type of elements returned by the iterator
*
* @since 1.5
* @jls 14.14.2 The enhanced {@code for} statement
*/
public interface Iterable<T> {
/**
* Returns an iterator over elements of type {@code T}.
*
* @return an Iterator.
*/
Iterator<T> iterator();
/**
* Performs the given action for each element of the {@code Iterable}
* until all elements have been processed or the action throws an
* exception. Actions are performed in the order of iteration, if that
* order is specified. Exceptions thrown by the action are relayed to the
* caller.
* <p>
* The behavior of this method is unspecified if the action performs
* side-effects that modify the underlying source of elements, unless an
* overriding class has specified a concurrent modification policy.
*
* @implSpec
* <p>The default implementation behaves as if:
* <pre>{@code
* for (T t : this)
* action.accept(t);
* }</pre>
*
* @param action The action to be performed for each element
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified action is null
* @since 1.8
*/
default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (T t : this) {
action.accept(t);
}
}
/**
* Creates a {@link Spliterator} over the elements described by this
* {@code Iterable}.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation creates an
* <em><a href="../util/Spliterator.html#binding">early-binding</a></em>
* spliterator from the iterable's {@code Iterator}. The spliterator
* inherits the <em>fail-fast</em> properties of the iterable's iterator.
*
* @implNote
* The default implementation should usually be overridden. The
* spliterator returned by the default implementation has poor splitting
* capabilities, is unsized, and does not report any spliterator
* characteristics. Implementing classes can nearly always provide a
* better implementation.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements described by this
* {@code Iterable}.
* @since 1.8
*/
default Spliterator<T> spliterator() {
return Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(iterator(), 0);
}
}并在内部实现Iterator接口
java
/*
* Copyright (c) 1997, 2018, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*
*/
package java.util;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
/**
* An iterator over a collection. {@code Iterator} takes the place of
* {@link Enumeration} in the Java Collections Framework. Iterators
* differ from enumerations in two ways:
*
* <ul>
* <li> Iterators allow the caller to remove elements from the
* underlying collection during the iteration with well-defined
* semantics.
* <li> Method names have been improved.
* </ul>
*
* <p>This interface is a member of the
* <a href="{@docRoot}/java.base/java/util/package-summary.html#CollectionsFramework">
* Java Collections Framework</a>.
*
* @apiNote
* An {@link Enumeration} can be converted into an {@code Iterator} by
* using the {@link Enumeration#asIterator} method.
*
* @param <E> the type of elements returned by this iterator
*
* @author Josh Bloch
* @see Collection
* @see ListIterator
* @see Iterable
* @since 1.2
*/
public interface Iterator<E> {
/**
* Returns {@code true} if the iteration has more elements.
* (In other words, returns {@code true} if {@link #next} would
* return an element rather than throwing an exception.)
*
* @return {@code true} if the iteration has more elements
*/
boolean hasNext();
/**
* Returns the next element in the iteration.
*
* @return the next element in the iteration
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the iteration has no more elements
*/
E next();
/**
* Removes from the underlying collection the last element returned
* by this iterator (optional operation). This method can be called
* only once per call to {@link #next}.
* <p>
* The behavior of an iterator is unspecified if the underlying collection
* is modified while the iteration is in progress in any way other than by
* calling this method, unless an overriding class has specified a
* concurrent modification policy.
* <p>
* The behavior of an iterator is unspecified if this method is called
* after a call to the {@link #forEachRemaining forEachRemaining} method.
*
* @implSpec
* The default implementation throws an instance of
* {@link UnsupportedOperationException} and performs no other action.
*
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException if the {@code remove}
* operation is not supported by this iterator
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if the {@code next} method has not
* yet been called, or the {@code remove} method has already
* been called after the last call to the {@code next}
* method
*/
default void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove");
}
/**
* Performs the given action for each remaining element until all elements
* have been processed or the action throws an exception. Actions are
* performed in the order of iteration, if that order is specified.
* Exceptions thrown by the action are relayed to the caller.
* <p>
* The behavior of an iterator is unspecified if the action modifies the
* collection in any way (even by calling the {@link #remove remove} method
* or other mutator methods of {@code Iterator} subtypes),
* unless an overriding class has specified a concurrent modification policy.
* <p>
* Subsequent behavior of an iterator is unspecified if the action throws an
* exception.
*
* @implSpec
* <p>The default implementation behaves as if:
* <pre>{@code
* while (hasNext())
* action.accept(next());
* }</pre>
*
* @param action The action to be performed for each element
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified action is null
* @since 1.8
*/
default void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (hasNext())
action.accept(next());
}
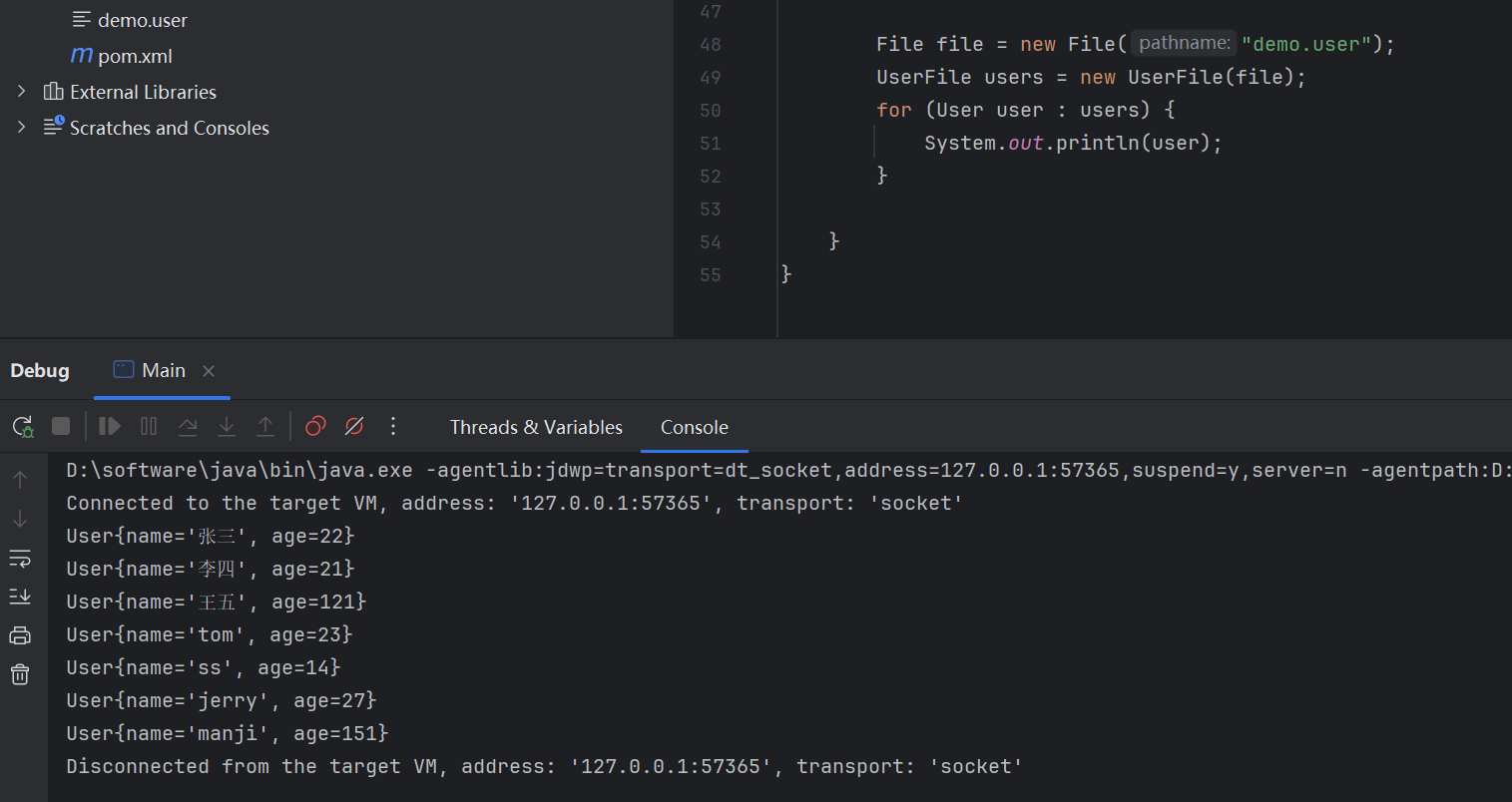
}部分List 的继承关系图可以清晰的看到
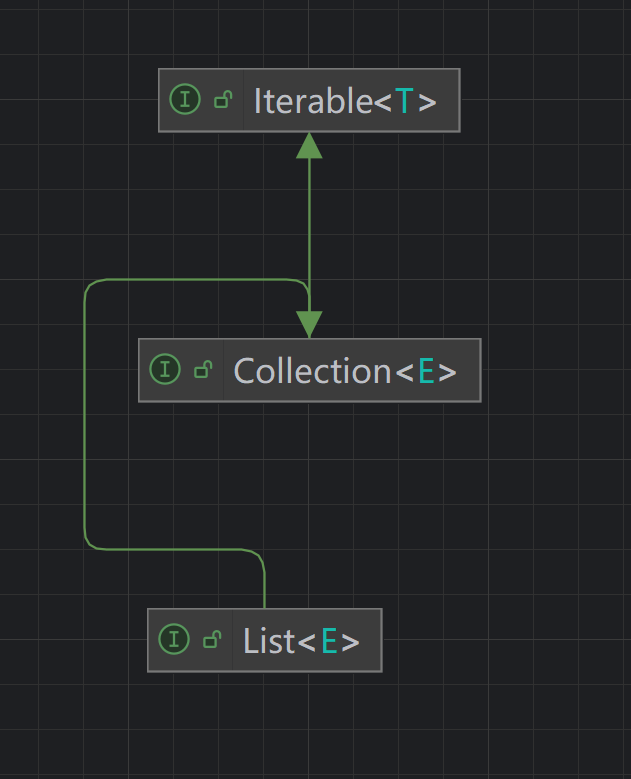
具体的实战案例,将对User对象遍历内部的属性进行遍历。在Itreator接口中实现 hasNext方法判断是否有一个元素。用next方法获取下一个元素。
java
package org.example;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
public class User implements Iterable<String> {
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
private String name;
private Integer age;
@Override
public Iterator<String> iterator() {
return new UserIterator();
}
class UserIterator implements Iterator<String> {
public int count = 2 ;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return count > 0;
}
//拿到下一个元素
@Override
public String next() {
count--;
if(count == 1) {
return User.this.name;
}
if(count == 0) {
return User.this.age.toString();
}
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
}2. 使用迭代器模式 编写方法实现对demo.user文件的添加。(特别使用于demo.user 文件较大的情况下)
核心代码逻辑,使用 IO流读取文件并进行文件的分割操作,并实现将属性封装成java的对象。实现对文件。UserFile作为一个可迭代的对象。里面实现一个内部类继承迭代器类,实现 迭代器的具体方法
java
package org.example;
import java.io.File;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class UserFile implements Iterable<User> {
private final File file;
@Override
public Iterator<User> iterator() {
return new UserIterator();
}
public UserFile(File file) {
this.file = file;
}
class UserIterator implements Iterator<User> {
List<User> userList = loadUserFromFile( );
int cursor = 0;
private List<User> loadUserFromFile( ) {
try {
// 组装 user 对象
return Files.readAllLines(file.toPath()).stream().map(line->{
String midStr = line.substring(1,line.length()-1);
String[] split = midStr.split(",");
return new User(split[0], Integer.parseInt(split[1]));
}).collect(Collectors.toList()) ;
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
// 判断 下一个元素是否存在
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor!=userList.size();
}
// 返回下一个元素
@Override
public User next() {
if(cursor >= userList.size()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return userList.get(cursor ++);
}
}
}执行结果: 可以看到具体的代码实现结果