前言
Redis中提供多种数据结构:string、list、map、set、zset等,关于上述多种数据类型的底层实现原理,Redis针对不同的数据类型对应的不同使用场景从时间和空间上进行平衡选择不同的对象编码方式。本文大致介绍一些Redis对象编码方式以及在上述五种数据类型上的应用。
一、统一对象结构:redisObject
在Redis中所有的数据都通过redisObject结构体封装,其核心字段定义如下:
cpp
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4; // 数据类型(string/list/hash/set/zset)
unsigned encoding:4; // 底层编码(如int/ziplist/skiplist)
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
// 内存淘汰信息
int refcount; // 引用计数
void *ptr; // 指向实际数据的指针
} robj;通过redisObject结构体中type字段和encoding字段分离,实现对不同的数据类型动态适配合适的编码方式。用户使用方式上,无需考虑底层编码方式只需要按照需求选择对应数据类型。
二、核心数据类型
1、简单动态字符串(Simple Dynamic String - SDS)
Redis中描述字符串使用SDS,对比C语言传统字符串,SDS在获取字符串长度上有更快的速度优势,同时保证二进制安全。C语言字符串以'\0'结尾,SDS通过len字段标识字符串长度,因此在存储二进制数据时保证二进制安全。并且SDS兼容C语言字符串,在buf字段末尾保留'\0',可以兼容部分C语言字符串操作函数。具体实现如下:
cpp
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};-
len :已使用字节长度(字符串实际长度,不包括'\0')
-
alloc:分配的总字节长度(不包括header)
-
flags:SDS类型标识
-
buf[]:柔性数组,存放具体的字符串 + '\0'
2、字典(Dict)
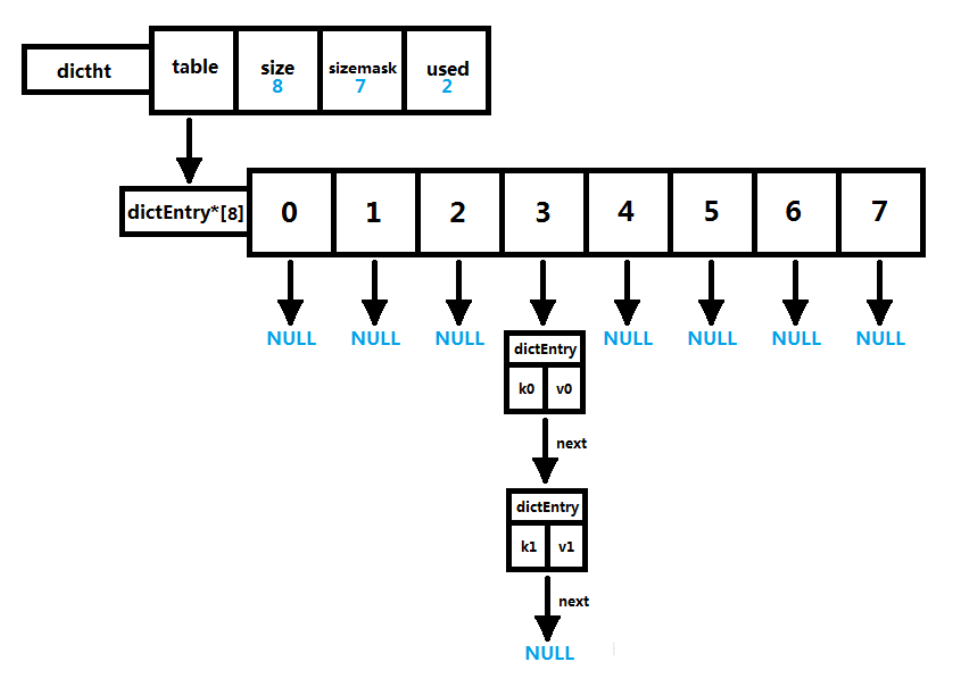
Redis中dict数据类型是使用拉链法处理hash冲突的hash表结构。其中关键数据结构为:dict、dictht、dictEntry。具体实现以及层级结构如下:
cpp
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key; // key值
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v; // value值
struct dictEntry *next; // 指向下个元素,拉链法处理hash冲突
} dictEntry; // 元素
typedef struct dictType {
uint64_t (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType; // dict操作函数集合
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table; // 元素数组
unsigned long size; // hash表长度
unsigned long sizemask; // 用于映射位置的掩码,值永远等于 (size - 1),索引值=Hash值&掩码值
unsigned long used; // hash表当前包含的节点数量
} dictht; // 具体hash表结构
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type; // 该字典对应的特定操作函数 (hash, keyDup, keyCompare, ...)
void *privdata; // 上述类型函数对应的可选参数
dictht ht[2]; // 两张hash表,方便rehah操作
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */ // rehash标识
unsigned long iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */ // 当前运行的迭代器数量
} dict; // hash表3、双向链表(list)
实现结构同数据结构中双向链表。具体实现如下:
cpp
typedef struct listNode {
struct listNode *prev;
struct listNode *next;
void *value;
} listNode;
typedef struct list {
listNode *head;
listNode *tail;
void *(*dup)(void *ptr);
void (*free)(void *ptr);
int (*match)(void *ptr, void *key);
unsigned long len;
} list;4、压缩列表(ziplist)- Redis 7.0 起替换为 listpack
ziplist结构是一块连续内存存储一个字节数组,其中顺序存储多个元素,每个节点元素存储一个字节数组或者一个整数。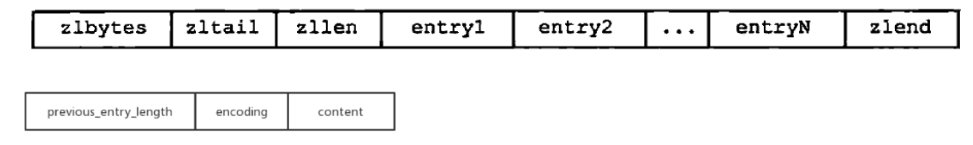
-
zlbytes: 4 字节,列表总字节数(字节长度)。
-
zltail: 4 字节,列表尾节点偏移量。
-
zllen: 2 字节,节点数量 (超过 65535 时需遍历)。
-
entry: 若干节点。每个节点包含:
-
prevlen: 前一个节点的长度 (1 或 5 字节)。
-
encoding: 内容编码 (类型和长度,1/2/5 字节)。
-
content: 实际数据。
-
-
zlend: 1 字节,结束标志 0xFF(255)
对于节点的数据结构中prevlen记录的是前一个节点的长度,此时如果调整当前节点,会影响后面一个节点的prevlen,此时如果是发生的扩展操作,那么可能会导致连续重新分配多个节点。此时该数据结构效率严重下降。因此这也是listpack替代它的主要原因。
5、紧凑列表(listpack) - Redis5.0引入,7.0开始列表/哈希/有序集合的ziplist实现替换为listpack
listpack是对ziplist的优化。其结构也是一块连续内存。与ziplist的主要不同点为在节点元素中ziplist的节点长度信息保存的是前一个节点的长度,而ziplist保存的是自身的长度信息。
6、整数集合(intSet)
整数集合是一块连续内存,其元素保存的是一个整数,其中通过encoding字段中标识了当前元素的整数类型,length保存了当前的元素数量,然后后续就挨个保存每个元素。
7、快速列表(quicklist)
快速列表是结合list与ziplist/listpack。list是一个双向链表,ziplist/listpack是一块连续的内存区域高效的保存数据。list每个节点的值保存一个ziplist/listpack结构。在具体操作时,插入/删除操作多数集中在list节点内部,即ziplist/listpack中。当节点过大/过小时进行节点分裂/合并操作。
cpp
typedef struct quicklistNode {
struct quicklistNode *prev;
struct quicklistNode *next;
unsigned char *zl;
unsigned int sz; /* ziplist size in bytes */
unsigned int count : 16; /* count of items in ziplist */
unsigned int encoding : 2; /* RAW==1 or LZF==2 */
unsigned int container : 2; /* NONE==1 or ZIPLIST==2 */
unsigned int recompress : 1; /* was this node previous compressed? */
unsigned int attempted_compress : 1; /* node can't compress; too small */
unsigned int extra : 10; /* more bits to steal for future usage */
} quicklistNode;
typedef struct quicklist {
quicklistNode *head;
quicklistNode *tail;
unsigned long count; /* total count of all entries in all ziplists */
unsigned long len; /* number of quicklistNodes */
int fill : QL_FILL_BITS; /* fill factor for individual nodes */
unsigned int compress : QL_COMP_BITS; /* depth of end nodes not to compress;0=off */
unsigned int bookmark_count: QL_BM_BITS;
quicklistBookmark bookmarks[];
} quicklist;8、跳表(skiplist)
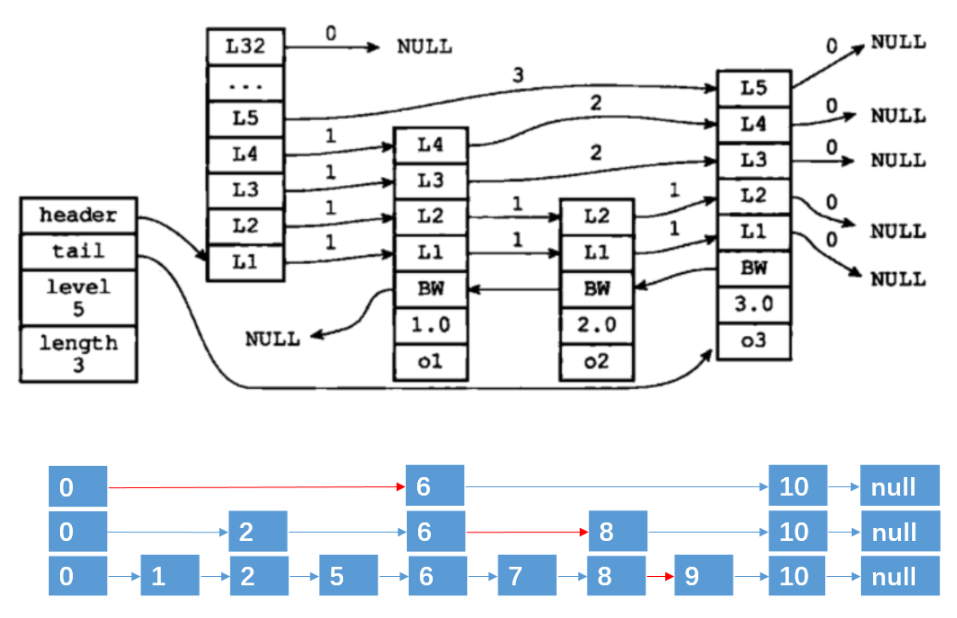
Redis中跳表主要用在zset的实现中。跳表数据结构是对时间和空间上的综合。跳表是在链表基础上提供更高效的查找效率(O(logN)),并且在实现上更简单。
更多资料:0voice · GitHub