1 Redis 缓存架构基础实现
java
@Service
public class ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductDao productDao; // 数据访问层,用于数据库操作
@Autowired
private RedisUtil redisUtil; // Redis工具类,用于缓存操作
/**
* 创建产品
*/
@Transactional
public Product create(Product product) {
Product productResult = productDao.create(product); // 插入数据库
// 将新增产品存入Redis缓存,使用产品ID作为key的一部分
redisUtil.set(RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productResult.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(productResult));
return productResult;
}
/**
* 更新产品信息
*/
@Transactional
public Product update(Product product) {
Product productResult = productDao.update(product); // 更新数据库
// 更新Redis缓存中的产品信息,保持缓存与数据库一致
redisUtil.set(RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productResult.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(productResult));
return productResult;
}
/**
* 根据产品ID获取产品信息
* 先查缓存,缓存不存在再查数据库
*/
public Product get(Long productId){
Product product = null;
String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; // 构造缓存key
String productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); // 从Redis获取缓存数据
// 如果缓存中存在数据,直接返回
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) {
product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); // 反序列化为Product对象
return product;
}
// 缓存不存在,查询数据库
product = productDao.get(productId);
if (product != null) {
// 数据库存在数据,写入缓存,设置随机过期时间防止缓存雪崩
redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product));
}
return product;
}
}2 增加缓存过期时间
-
对于大厂来说,比如京东、淘宝,其商品数量是数以亿计,将这些商品都放入缓存是不现实的。其次,即使有这么多的商品数量,但几乎只有 1% 左右的商品是会被频繁访问的,而剩余的不怎么被频繁访问的 99% 的商品也被放入了缓存中,何尝不是一种资源浪费。所以可以在代码中,对于每一件商品的缓存都可以加一个缓存过期时间:
javapublic static final Integer PRODUCT_CACHE_TIMEOUT = 60 * 60 * 24; // 商品缓存过期时间:24小时 @Transactional public Product update(Product product) { Product productResult = productDao.update(product); redisUtil.set(RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productResult.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(productResult), PRODUCT_CACHE_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 增加缓存过期时间 return productResult; } public Product get(Long productId){ Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; String productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) { product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); return product; } product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), PRODUCT_CACHE_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 增加缓存过期时间 } return product; }
3 缓存数据的冷热分离
-
冷热数据:根据数据的访问频率将数据分为热数据(频繁访问)和冷数据(较少访问),并采用不同的缓存策略;
- 冷数据:设置较短的过期时间;
- 热数据:设置较长的过期时间;
javapublic Product get(Long productId){ Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; String productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) { product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); // 热数据:设置较长的过期时间 redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, PRODUCT_CACHE_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS); return product; } product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), PRODUCT_CACHE_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS); } return product; } -
此处只是简单实现了缓存数据的冷热分离,实际上还可以更细化一点,比如:统计一下该商品被访问的次数,当这个次数超过一定阈值的时候,才将该商品数据视为热数据,才给它设置较长的过期时间。
4 缓存击穿(失效)解决
-
有这么一个场景:大批量缓存在同一时间失效,导致大量请求同时穿透缓存直达数据库,造成数据库压力瞬间过大甚至挂掉,这就是缓存击穿(失效);
- 什么情况下会出现大批量缓存在同一时间失效?比如批量添加商品的时候,那么这批商品在缓存中的过期时间就是一样的;
-
对于这种情况:我们在批量增加缓存的时候,可以将这一批数据的缓存过期时间设置为一个时间段内的不同时间;
javapublic static final Integer PRODUCT_CACHE_TIMEOUT = 60 * 60 * 24; // 24小时 @Transactional public Product update(Product product) { Product productResult = productDao.update(product); redisUtil.set(RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productResult.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(productResult), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 缓存击穿(失效)解决 return productResult; } public Product get(Long productId){ Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; String productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) { product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 缓存击穿(失效)解决 return product; } product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 缓存击穿(失效)解决 } return product; } /** * 生成产品缓存随机过期时间 * 基础24小时 + 随机0-4小时,防止大量缓存同时过期 */ private Integer genProductCacheTimeout() { return PRODUCT_CACHE_TIMEOUT + new Random().nextInt(5) * 60 * 60; }
5 缓存穿透解决
-
缓存穿透是指查询一个根本不存在的数据, 缓存层和存储层都不会命中,"穿透"了整个后端。而通常出于容错的考虑, 如果从存储层查不到数据则不写入缓存层。缓存穿透将导致不存在的数据每次请求都要到存储层去查询, 此时缓存就失去了保护后端存储的意义;
-
造成缓存穿透的基本原因有两个:
- 自身业务代码或者数据出现问题;
- 一些恶意攻击、 爬虫等造成大量空命中;
-
解决办法:就算从存储层查询不到数据,也将一个空对象存储到缓存中
javapublic static final String EMPTY_CACHE = "{}"; public Product get(Long productId){ Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; String productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) { if (EMPTY_CACHE.equals(productStr)) { // 如果在缓存中查询到的数据为 EMPTY_CACHE,说明查询的是不存在的数据 return null; // 直接返回空 } product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return product; } product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } else { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, EMPTY_CACHE); // 缓存穿透解决 } return product; } -
如果是恶意攻击造成的缓存穿透,如果每一次攻击都是不同的不存在数据,那么缓存中会存在大量的空对象,占用缓存资源,可以给这些空对象设置一个短一点的过期时间:
javapublic Product get(Long productId){ Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; String productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) { if (EMPTY_CACHE.equals(productStr)) { // 如果在缓存中查询到的数据为 EMPTY_CACHE,说明查询的是不存在的数据 // 如果是访问的不存在数据是一样的,那么对其空对象做一下延期 redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return null; // 直接返回空 } product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return product; } product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } else { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, EMPTY_CACHE, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 缓存穿透解决 } return product; } /** * 生成空值缓存随机过期时间,基础60秒 + 随机0-29秒 */ private Integer genEmptyCacheTimeout() { return 60 + new Random().nextInt(30); }
6 基于DCL机制解决热点缓存并发重建问题
-
看这么一个场景:
- 某个电商平台让一个大V去带货一个冷门商品(该冷门商品在缓存中不存在),当大V喊下"上链接"后,会有千万用户同时涌入系统,查询并下单该商品;
- 假如该商品的缓存重建不能在短时间内完成(可能是一个复杂计算),在缓存失效的瞬间, 会有大量线程来重建缓存,造成后端负载加大,甚至可能会让应用崩溃;
- 这个过程就是突发性热点缓存重建导致系统压力暴增;
-
对于这种场景,可以基于 DCL(Double-Checked Locking,双重检查锁)机制来解决:只允许一个线程重建缓存, 让其它线程等待重建缓存的线程执行完, 然后重新从缓存获取数据即可
javapublic Product get(Long productId){ Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; String productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); // 第一重检查:大多数情况下缓存命中直接返回 if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) { if (EMPTY_CACHE.equals(productStr)) { redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return null; } product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return product; } // DCL机制:同步代码块,确保只有一个线程进入临界区,防止多个线程同时查询数据库和重建缓存 synchronized (this){ // 第二重检查:获取锁后再次检查缓存是否已被其他线程重建,避免在等待锁期间缓存已被重建,造成重复查询 productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) { if (EMPTY_CACHE.equals(productStr)) { redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return null; } product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return product; } // 临界区:只有一个线程执行实际的数据库查询,根据查询结果设置正常数据或空值缓存 // 当该线程查询到数据并将其缓存后,后续的其它线程就可以直接在缓存中命中 product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } else { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, EMPTY_CACHE, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } return product; } -
synchronized(this)是单机锁,在分布式环境下需要改用分布式锁(如 Redisson)才能保证集群级别的线程安全:java@Autowired private Redisson redisson; public static final String LOCK_PRODUCT_HOT_CACHE_PREFIX = "lock:product:hot_cache:"; public static final Integer PRODUCT_CACHE_TIMEOUT = 60 * 60 * 24; // 24小时 @Transactional public Product update(Product product) { Product productResult = productDao.update(product); redisUtil.set(RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productResult.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(productResult), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 缓存击穿(失效)解决 return productResult; } public Product get(Long productId){ Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; String productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); // 第一重检查:大多数情况下缓存命中直接返回 if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) { if (EMPTY_CACHE.equals(productStr)) { redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return null; } product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return product; } // 第二重检查:获取锁后再次检查缓存是否已被其他线程重建,避免在等待锁期间缓存已被重建,造成重复查询 RLock hotCacheLock = redisson.getLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_HOT_CACHE_PREFIX + productId); hotCacheLock.lock(); try { productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) { if (EMPTY_CACHE.equals(productStr)) { redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return null; } product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); redisUtils.expire(productCacheKey, genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return product; } // 临界区:只有一个线程执行实际的数据库查询,根据查询结果设置正常数据或空值缓存 // 当该线程查询到数据并将其缓存后,后续的其它线程就可以直接在缓存中命中 product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } else { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, EMPTY_CACHE, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } finally { hotCacheLock.unlock(); } return product; }
将代码重构整理一下
java
@Service
public class ProductServiceNew {
@Autowired
private ProductDao productDao;
@Autowired
private RedisUtil redisUtil;
@Autowired
private Redisson redisson;
public static final Integer PRODUCT_CACHE_TIMEOUT = 60 * 60 * 24;
public static final String EMPTY_CACHE = "{}";
public static final String LOCK_PRODUCT_HOT_CACHE_PREFIX = "lock:product:hot_cache:";
public static final String LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX = "lock:product:update:";
@Transactional
public Product create(Product product) {
Product productResult = productDao.create(product);
redisUtil.set(RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productResult.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(productResult),
genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return productResult;
}
@Transactional
public Product update(Product product) {
Product productResult = productDao.update(product);
redisUtil.set(RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productResult.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(productResult),
genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return productResult;
}
public Product get(Long productId) {
Product product = null;
String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId;
product = getProductFromCache(productCacheKey);
if (product != null) {
return product;
}
RLock hotCacheLock = redisson.getLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_HOT_CACHE_PREFIX + productId);
hotCacheLock.lock();
try {
product = getProductFromCache(productCacheKey);
if (product != null) {
return product;
}
product = productDao.get(productId);
if (product != null) {
redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product),
genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} else {
redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, EMPTY_CACHE, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
} finally {
hotCacheLock.unlock();
}
return product;
}
private Integer genProductCacheTimeout() {
return PRODUCT_CACHE_TIMEOUT + new Random().nextInt(5) * 60 * 60;
}
private Integer genEmptyCacheTimeout() {
return 60 + new Random().nextInt(30);
}
private Product getProductFromCache(String productCacheKey) {
Product product = null;
String productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) {
if (EMPTY_CACHE.equals(productStr)) { // 如果在缓存中查询到的数据为 EMPTY_CACHE,说明查询的是不存在的数据
redisUtil.expire(productCacheKey, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return new Product(); // 返回一个空的商品对象,要与实际上查询不到商品返回的null做区分,所以此处不返回null
}
product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class);
redisUtil.expire(productCacheKey, genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
return product;
}
}7 分布式锁解决缓存与数据库双写不一致问题
-
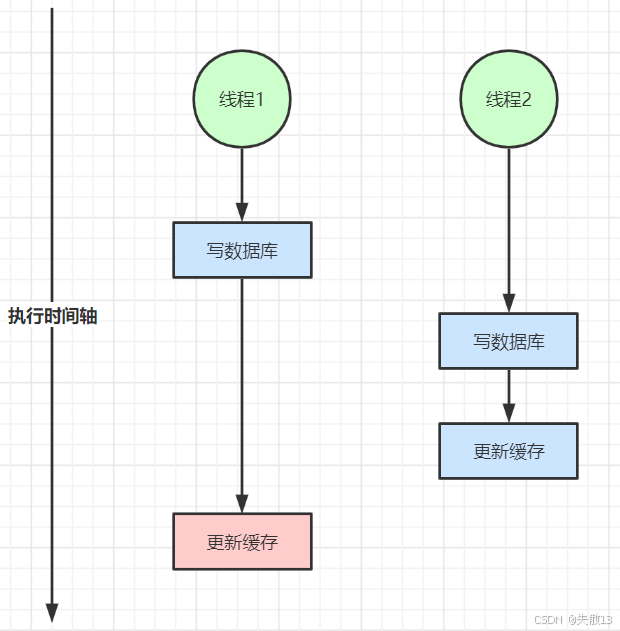
双写不一致:
- 线程 2 在线程 1 后写数据库,所以线程 2 的数据应该更"新";
- 但最终缓存会被线程 1 的旧逻辑覆盖,导致缓存值与数据库最新值(线程 2 写入的)不一致;
-
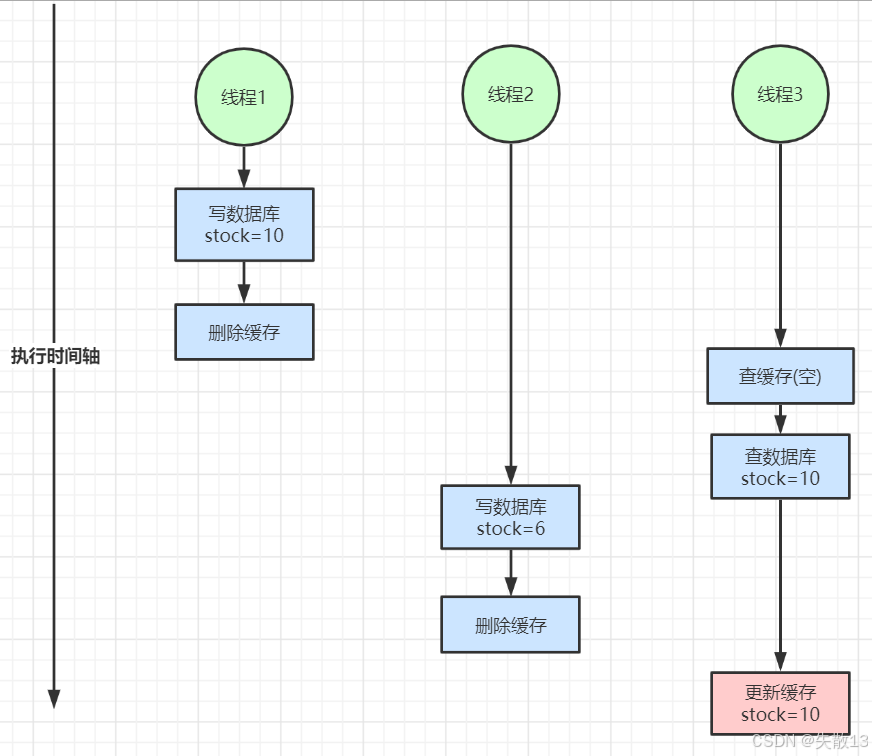
读写并发不一致:
- 线程 1 将数据写入数据库,然后删除缓存;
- 线程 3 查询缓存为空,就去查询数据库,得到 stock = 10;
- 线程 2 将新的 stock 写入数据库,然后删除缓存;
- 在线程 2 执行完后,线程 3 才将查询到的 stock 写入缓存,但是此时缓存中存储的是旧值 stock =10,而数据库中却为新值 stock = 6;
-
可以用 Redisson 分布式锁解决:
create方法也要做处理,此处省略;javapublic static final String LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX = "lock:product:update:"; @Transactional public Product update(Product product) { Product productResult = null; // 分布式锁解决缓存与数据库双写不一致问题 RLock updateProductLock = redisson.getLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX + product.getId()); updateProductLock.lock(); try { productResult = productDao.update(product); redisUtil.set(RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productResult.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(productResult), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } finally { updateProductLock.unlock(); } return productResult; } public Product get(Long productId) { Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; product = getProductFromCache(productCacheKey); if (product != null) { return product; } RLock hotCacheLock = redisson.getLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_HOT_CACHE_PREFIX + productId); hotCacheLock.lock(); try { product = getProductFromCache(productCacheKey); if (product != null) { return product; } // 分布式锁解决缓存与数据库双写不一致问题 RLock updateProductLock = redisson.getLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX + productId); updateProductLock.lock(); try { product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } else { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, EMPTY_CACHE, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } finally { updateProductLock.unlock(); } } finally { hotCacheLock.unlock(); } return product; }
8 ReadWriteLock 读写锁(锁优化)
-
在大多数分布式场景下,都是读多写少。Redisson 提供的
RReadWriteLock是基于 Redis 实现的分布式读写锁,遵循"读共享、写独占"的原则,就适用于读多写少的分布式场景; -
核心特性:
- 读写分离
- 读锁(
RLock):允许多个线程同时获取,适合查询操作。 - 写锁(
RLock):同一时间只允许一个线程获取,获取时会阻塞所有读锁和其他写锁,适合更新操作。
- 读锁(
- 分布式特性:锁的状态存储在 Redis 中,所有分布式节点共享锁状态,确保跨服务、跨进程的锁一致性;
- 自动续期:类似 Redisson 的普通分布式锁,读写锁也支持 "看门狗" 机制:若持有锁的线程未完成操作,会自动延长锁的过期时间,避免因锁超时导致的并发问题;
- 可重入性:支持同一线程多次获取读锁或写锁(需遵循 "写锁可降级为读锁,但读锁不能升级为写锁" 的规则);
- 公平锁 / 非公平锁:可通过配置实现公平锁(按请求顺序获取锁)或非公平锁(默认,允许 "插队" 提高效率);
- 读写分离
-
代码实现:
java@Transactional public Product update(Product product) { Product productResult = null; //RLock updateProductLock = redisson.getLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX + product.getId()); //updateProductLock.lock(); // 加写锁 RReadWriteLock readWriteLock = redisson.getReadWriteLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX + product.getId()); RLock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock(); writeLock.lock(); try { productResult = productDao.update(product); redisUtil.set(RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productResult.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(productResult), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } finally { writeLock.unlock(); } return productResult; } public Product get(Long productId) { Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; product = getProductFromCache(productCacheKey); if (product != null) { return product; } RLock hotCacheLock = redisson.getLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_HOT_CACHE_PREFIX + productId); hotCacheLock.lock(); try { product = getProductFromCache(productCacheKey); if (product != null) { return product; } //RLock updateProductLock = redisson.getLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX + productId); //updateProductLock.lock(); // 加读锁 RReadWriteLock readWriteLock = redisson.getReadWriteLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX + productId); RLock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock(); readLock.lock(); try { product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } else { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, EMPTY_CACHE, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } finally { readLock.unlock(); } } finally { hotCacheLock.unlock(); } return product; }
9 tryLock()优化串行争用分布式锁
-
是否可以对在
6 基于DCL机制解决热点缓存并发重建问题中加的 Redisson 锁进行优化呢?- 这个 Redisson 锁的作用是:让一个线程获取到该锁后去执行缓存重建,后续的所有线程都在等待获取这个分布式锁,这就是串行争用分布式锁;
- 可以使用
tryLock()方法取代原本的lock(),进行优化,其实就是串行争用分布式锁 >> 并发;
javapublic Product get(Long productId) throws InterruptedException { Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; // 第一重缓存检查 product = getProductFromCache(productCacheKey); if (product != null) { return product; } RLock hotCacheLock = redisson.getLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_HOT_CACHE_PREFIX + productId); // hotCacheLock.lock(); // 尝试获取分布式锁,最多等待3秒 // 3秒后如果【没有获取】到锁,就返回false(意味着负责缓存重建的线程在3秒内没有完成缓存重建),无需等待获取锁,继续向下执行代码 // 3秒后如果【获取】到锁,就返回true,成为负责缓存重建的线程 hotCacheLock.tryLock(3, TimeUint.SECONDS); try { // 第二重缓存检查 product = getProductFromCache(productCacheKey); if (product != null) { return product; } RReadWriteLock readWriteLock = redisson.getReadWriteLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX + productId); RLock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock(); readLock.lock(); try { product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } else { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, EMPTY_CACHE, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } finally { readLock.unlock(); } } finally { hotCacheLock.unlock(); } return product; }- 第一重缓存检查:缓存不存在 → 继续
- 尝试获取锁 :
tryLock(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS),如果返回false - 第二重缓存检查 :再次检查缓存(此时可能已被其他线程重建)
- 如果缓存已存在:直接返回缓存数据
- 如果缓存仍不存在:继续执行下面的代码
- 执行数据库查询 :无论是否获取到锁,都会执行
productDao.get(productId)
10 缓存雪崩问题解决
-
来看这么一个场景:
- 某顶流明星突然发布了一条爆炸性新闻(例如官宣恋情、结婚、离婚等),数百万甚至数千万粉丝和吃瓜群众在极短时间内(几分钟内)同时打开手机微博:他们刷新首页 ,想看明星的动态;点击该微博 ,导致该条微博的读请求 激增;转发、评论、点赞 ,导致写请求激增;
- 所有这些用户操作,最终都会转化为对微博后端服务器的 HTTP 请求,像海啸一样涌向服务器集群。每个进入的 HTTP 请求都需要一个 Tomcat 的工作线程(Thread)来处理,而 Tomcat 的线程池大小是有限的。海量请求瞬间到达,Tomcat 开始快速创建线程(直到达到最大值)来处理这些请求。每个处理"读微博"请求的线程,都需要去调用 Redis 获取数据。由于请求量远超平时,线程池中的所有线程很快被全部占用。此时,新的用户请求到达 Tomcat 时,发现没有空闲线程可用,开始排队等待。用户端感受到的就是加载缓慢、转圈;
- Redis虽然是内存操作,性能极高,但其处理能力也有上限(通常受限于网络带宽、CPU和单线程模型)。它每秒能处理的命令数(QPS)是有限的(例如10万-几十万)。所有被占用的 Tomcat 线程都在同时、疯狂地向 Redis 发送请求。Redis 的请求队列瞬间被塞满,开始过载运行。Redis 的 CPU 占用率达到 100%,处理每个命令的响应时间(RT)从微秒级暴增到几十甚至几百毫秒。Tomcat线程在等待Redis响应时会被阻塞(Blocked)。Redis 响应越慢,Tomcat 线程被占用的时间就越长。这导致 Tomcat 线程回收和释放的速度变得极其缓慢;
- 因为 Redis 处理不过来,所有 Tomcat 线程都在等待 Redis 的响应,几乎全部被阻塞。它们既无法处理完当前请求,也无法被释放。Tomcat内部的请求等待队列也被塞满。此时,系统已经达到极限。新的请求到达服务器时,Tomcat 既没有空闲线程来处理,也没有队列空间来存放。操作系统或 Tomcat 本身会开始拒绝新的连接 。用户看到的是**"服务器繁忙,请稍后再试"、"网络连接错误"** 或者一个完全空白的页面。**微博,崩了。**如果 Redis 中缓存失效(例如缓存穿透),部分请求会直接打到数据库上。在如此巨大的流量下,数据库会瞬间被压垮,导致更严重的数据层面故障;
- 这就是缓存雪崩;
-
解决:
- 保证缓存层服务高可用性,比如使用 Redis Sentinel 或 Redis Cluster;
- 依赖隔离组件为后端限流熔断并降级。比如使用 Sentinel 或 Hystrix 限流降级组件。比如服务降级,我们可以针对不同的数据采取不同的处理方式:
- 当业务应用访问的是非核心数据(例如电商商品属性,用户信息等)时,暂时停止从缓存中查询这些数据,而是直接返回预定义的默认降级信息、空值或是错误提示信息;
- 当业务应用访问的是核心数据(例如电商商品库存)时,仍然允许查询缓存,如果缓存缺失,也可以继续通过数据库读取;
-
下面使用多级缓存来解决一下:将商品信息存储到 JVM 缓存(可支持百万级别的并发)中
javapublic static Map<String, Product> productMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); // JVM 缓存 @Transactional public Product update(Product product) { Product productResult = null; RReadWriteLock readWriteLock = redisson.getReadWriteLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX + product.getId()); RLock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock(); writeLock.lock(); try { productResult = productDao.update(product); redisUtil.set(RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productResult.getId(), JSON.toJSONString(productResult), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); productMap.put(LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX + product.getId(), product); // 将商品放入 JVM 缓存 } finally { writeLock.unlock(); } return productResult; } public Product get(Long productId) throws InterruptedException { Product product = null; String productCacheKey = RedisKeyPrefixConst.PRODUCT_CACHE + productId; product = getProductFromCache(productCacheKey); if (product != null) { return product; } RLock hotCacheLock = redisson.getLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_HOT_CACHE_PREFIX + productId); hotCacheLock.tryLock(3, TimeUint.SECONDS); try { product = getProductFromCache(productCacheKey); if (product != null) { return product; } RReadWriteLock readWriteLock = redisson.getReadWriteLock(LOCK_PRODUCT_UPDATE_PREFIX + productId); RLock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock(); readLock.lock(); try { product = productDao.get(productId); if (product != null) { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, JSON.toJSONString(product), genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); productMap.put(productCacheKey, product); // 将商品放入 JVM 缓存 } else { redisUtil.set(productCacheKey, EMPTY_CACHE, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } } finally { readLock.unlock(); } } finally { hotCacheLock.unlock(); } return product; } private Product getProductFromCache(String productCacheKey) { Product product = productMap.get(productCacheKey); // 先查 JVM 缓存 if (product != null) { return product; } String productStr = redisUtil.get(productCacheKey); if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(productStr)) { if (EMPTY_CACHE.equals(productStr)) { redisUtil.expire(productCacheKey, genEmptyCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); return new Product(); } product = JSON.parseObject(productStr, Product.class); redisUtil.expire(productCacheKey, genProductCacheTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS); } return product; } -
虽然 JVM 缓存可以抗百万级别的并发,但是也有缺点:
- 对于一些大厂来说,其商品数以亿计,即使就将 1% 的热点商品放入 JVM 缓存中,所占用的空间也是非常大的;
- 有的商品可能只是当下是热点,如果没有及时清理,就会造成内存泄漏,所以真实场景不能像上面那样随意的使用
ConcurrentHashMap,应该使用一些缓存框架,比如:Guava Cache 、Caffeine等,其会有一些数据淘汰策略; - 如果 Web 应用是集群部署,JVM 缓存更新的是当前的 Web 应用所在的机器,对于集群中其他的机器并没有同步更新,解决:
- 消息队列(可能会有短时的不一致,但是要做取舍,不然整个系统架构过于复杂,会难以维护);
- 一般来说,是专门用一个系统来处理热点缓存(分布式实时计算来判断什么数据是热点),而且处理的一般是热点中的热点,其它 Web 应用就监听该系统。当有数据成为热点中的热点需要被各个 Web 应用本地缓存的时候,该系统就会通知各个 Web 应用,将相应的数据缓存到本地缓存中。