在考研数学中,求解一元高次方程(通常指三次及以上)的实数根是一个常见考点。这类题目往往设计精巧,不会要求考生使用繁琐的求根公式,而是考查对有理根定理 和多项式除法的综合应用能力。掌握这套"组合拳",能让你在考场上快速、准确地解决此类问题。
一、核心武器库:有理根定理
有理根定理为我们提供了寻找方程有理根(如果存在的话)的系统性方法。
- 定理内容: 对于一个一元 n 次整系数多项式方程:
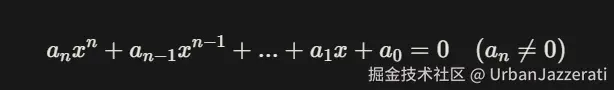
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 其任何可能的有理根 x = p q 必须满足: 其任何可能的有理根x=\frac{p}{q}必须满足: </math>其任何可能的有理根x=qp必须满足:
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> p 是常数项 a 0 的因数。 q 是最高次项系数 a n 的因数。 p是常数项 a_0 的因数。 q是最高次项系数 a_n 的因数。 </math>p是常数项a0的因数。q是最高次项系数an的因数。
- 操作步骤:
-
列出所有候选根 :找出 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a 0 a_0 </math>a0 的所有正负因数( <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> p p </math>p)和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a n a_n </math>an 的所有正负因数( <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> q q </math>q),然后列出所有可能的有理数 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> p q \frac{p}{q} </math>qp(通常需约分为最简形式)。
-
代入验证(试根) :将候选根逐个代入原方程,若满足 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> f ( x ) = 0 , f(x)=0, </math>f(x)=0,则该值即为方程的一个根。
考研应用提示 :考研真题中的方程,其有理根通常是较小的整数,如 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ± 1 , ± 2 , ± 3 ±1,±2,±3 </math>±1,±2,±3优先尝试这些数值可以节省大量时间。
二、降维打击:多项式除法
当我们通过有理根定理找到一个根 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x = k x x=kx </math>x=kx后,就意味着多项式含有因式 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ( x − k ) (x−k) </math>(x−k)。此时,我们需要使用多项式除法 (或综合除法)来降低方程的次数。
-
多项式除法(长除法) : 将原多项式 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> f ( x ) f(x) </math>f(x) 除以因式 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ( x − k ) (x−k) </math>(x−k),得到一个商式 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g ( x ) g(x) </math>g(x)(次数比原式低一次)和一个余数。若 kkk 确实是根,则余数必为0。即有:
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> f ( x ) = ( x − k ) ⋅ g ( x ) f(x)=(x−k)⋅g(x) </math>f(x)=(x−k)⋅g(x)
原方程 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> f ( x ) = 0 就转化为 ( x − k ) ⋅ g ( x ) = 0 。 f(x)=0 就转化为 (x−k)⋅g(x)=0。 </math>f(x)=0就转化为(x−k)⋅g(x)=0。
-
综合除法(快速技巧) : 综合除法是多项式除法的简化版,更适合线性因式 (x−k)(x - k)(x−k),计算更便捷,书写更简洁,是考场上强烈推荐的技巧。
三、实战四步法:解题流程
面对一道一元高次方程求解题,请遵循以下四步:
第一步:观察整理 将方程所有项移到等号一侧,按降幂排列,确保是标准形式 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> f ( x ) = 0 。 f(x)=0。 </math>f(x)=0。
第二步:有理试根
- 列出所有可能的有理根候选。
- 优先尝试 : <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ± 1 , ± 2 ±1,±2 </math>±1,±2等简单整数。
- 找到一个根 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x = k x x=kx </math>x=kx。
第三步:降次分解 利用综合除法 ,用找到的根 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> k k </math>k 对原多项式进行降次,得到商式 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g ( x ) g(x) </math>g(x)。 即: <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> f ( x ) = ( x − k ) ⋅ g ( x ) f(x)=(x−k)⋅g(x) </math>f(x)=(x−k)⋅g(x)
第四步:求解余式 方程转化为:
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ( x − k ) ⋅ g ( x ) = 0 (x−k)⋅g(x)=0 </math>(x−k)⋅g(x)=0
- 解 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x − k = 0 ,得 x 1 = k 。 x−k=0,得 x_1=k。 </math>x−k=0,得x1=k。
- 解 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g ( x ) = 0 。如果 g ( x ) g(x)=0。如果 g(x) </math>g(x)=0。如果g(x) 是二次式,可直接用求根公式;若次数仍较高,则对 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g ( x ) g(x) </math>g(x) 重复第二步 和第三步,直至所有根都被求出。
四、真题演练
例题 :求解方程 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> f ( x ) = x 4 − 2 x 3 − 3 x 2 + 4 x + 4 = 0 f(x) = x^4 - 2x^3 - 3x^2 + 4x + 4 = 0 </math>f(x)=x4−2x3−3x2+4x+4=0
解:
-
试根 :常数项为4,系数为1。可能有理根: <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ± 1 , ± 2 , ± 4 。 ±1,±2,±4。 </math>±1,±2,±4。
- 试 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x = − 1 : f ( − 1 ) = 1 + 2 − 3 − 4 + 4 = 0 x=−1: f(−1)=1+2−3−4+4=0 </math>x=−1:f(−1)=1+2−3−4+4=0 ✅ 找到第一个根 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x 1 = − 1 x_1=−1 </math>x1=−1。
-
综合除法(降次) :用 −1-1−1 对多项式进行综合除法。
lua系数: | 1 -2 -3 4 4 根 -1 | -1 3 0 -4 | -------------------------- | 1 -3 0 4 0
商式为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x 3 − 3 x 2 + 4 ,余数为 0 。 ∴ f ( x ) = ( x + 1 ) ( x 3 − 3 x 2 + 4 ) . x^3 - 3x^2 + 4,余数为0。 ∴ f(x) = (x + 1)(x^3 - 3x^2 + 4). </math>x3−3x2+4,余数为0。∴f(x)=(x+1)(x3−3x2+4).
-
对商式 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g ( x ) = x 3 − 3 x 2 + 4 g(x) = x^3 - 3x^2 + 4 </math>g(x)=x3−3x2+4重复过程。
-
试根 : <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 可能根 ± 1 , ± 2 , ± 4 可能根 ±1,±2,±4 </math>可能根±1,±2,±4。h
- 试 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x = 2 : g ( 2 ) = 8 − 12 + 4 = 0 x=2: g(2)=8−12+4=0 </math>x=2:g(2)=8−12+4=0 ✅ 找到第二个根 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x 2 = 2 x_2 =2 </math>x2=2。
-
综合除法 :用 2 对 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> g ( x ) g(x) </math>g(x) 进行综合除法。
lua系数:| 1 -3 0<-不要漏 4 根 2 | 2 -2 -4 | -------------------- 1 -1 -2 0新的商式为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x 2 − x − 2 x^2 - x - 2 </math>x2−x−2,余数为0。 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ∴ g ( x ) = ( x − 2 ) ( x 2 − x − 2 ) 综上: f ( x ) = ( x + 1 ) ( x − 2 ) ( x 2 − x − 2 ) ∴ g(x) = (x - 2)(x^2 - x - 2) 综上:f(x) = (x + 1)(x - 2)(x^2 - x - 2) </math>∴g(x)=(x−2)(x2−x−2)综上:f(x)=(x+1)(x−2)(x2−x−2)
-
-
解低次方程 :分解 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x 2 − x − 2 = ( x − 2 ) ( x + 1 ) 。 ∴ f ( x ) = ( x + 1 ) 2 ( x − 2 ) 2 = 0 x^2 - x - 2 = (x - 2)(x + 1)。 ∴ f(x) = (x + 1)^2 (x - 2)^2 = 0 </math>x2−x−2=(x−2)(x+1)。∴f(x)=(x+1)2(x−2)2=0
-
最终解:
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ( x + 1 ) 2 = 0 或 ( x − 2 ) 2 = 0 (x + 1)^2 = 0 \quad \text{或} \quad (x - 2)^2 = 0 </math>(x+1)2=0或(x−2)2=0
得方程的解为: <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> x 1 = x 2 = − 1 , x 3 = x 4 = 2 (二重根)。 \boxed{x_1 = x_2 = -1,\quad x_3 = x_4 = 2}(二重根)。 </math>x1=x2=−1,x3=x4=2(二重根)。
五、总结与备考建议
- 核心思维:有理根定理是"探测器",多项式除法是"拆解器",二者结合,将高次方程拆解为我们会解的低次方程。
- 效率优先 :在考场上,综合除法远比多项式长除法快捷,务必熟练掌握。
- 练习重点 :多找考研真题中的类似题目进行练习,尤其注意方程有重根 、根为分数等稍复杂的情况,做到熟能生巧。