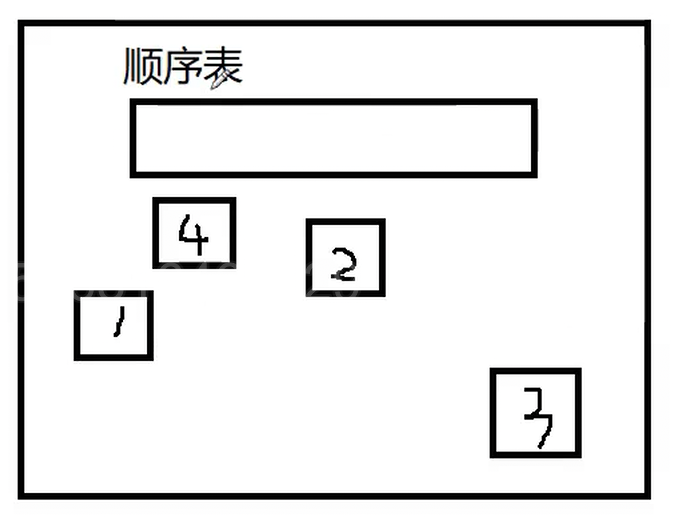
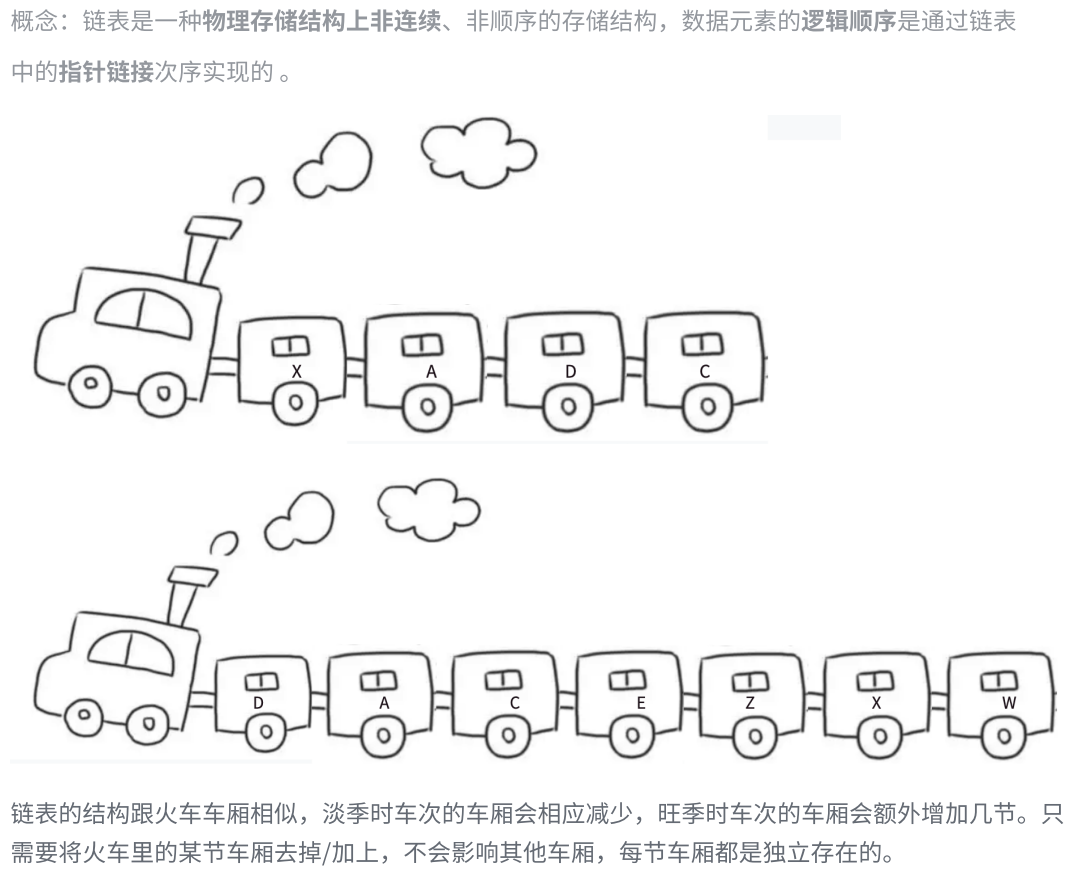
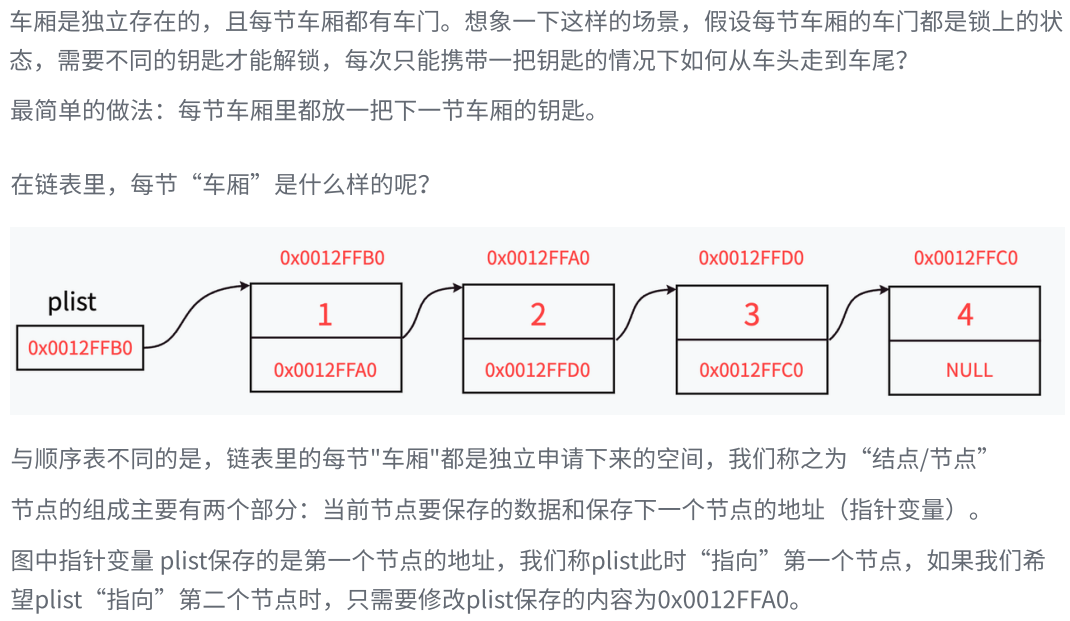
一.链表的概念及结构


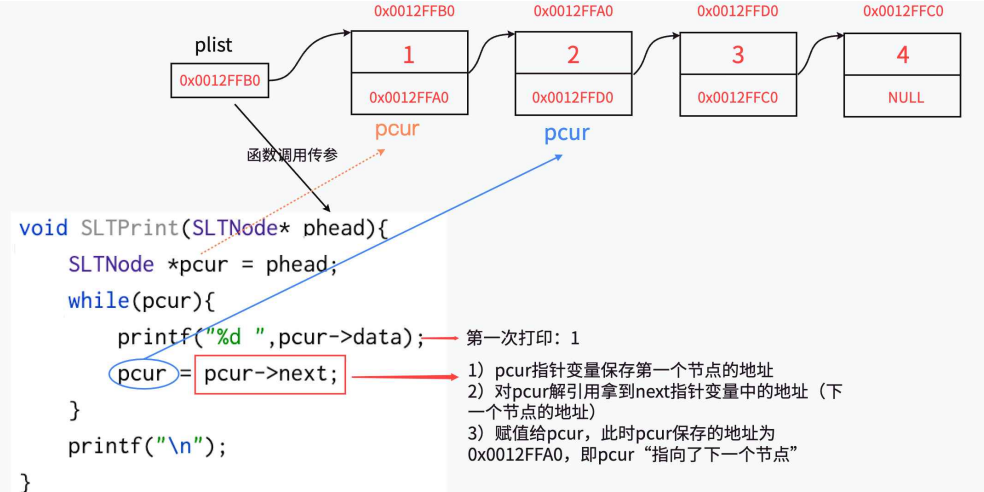


二.list测试
cpp
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLTDataType;
//链表是由节点组成
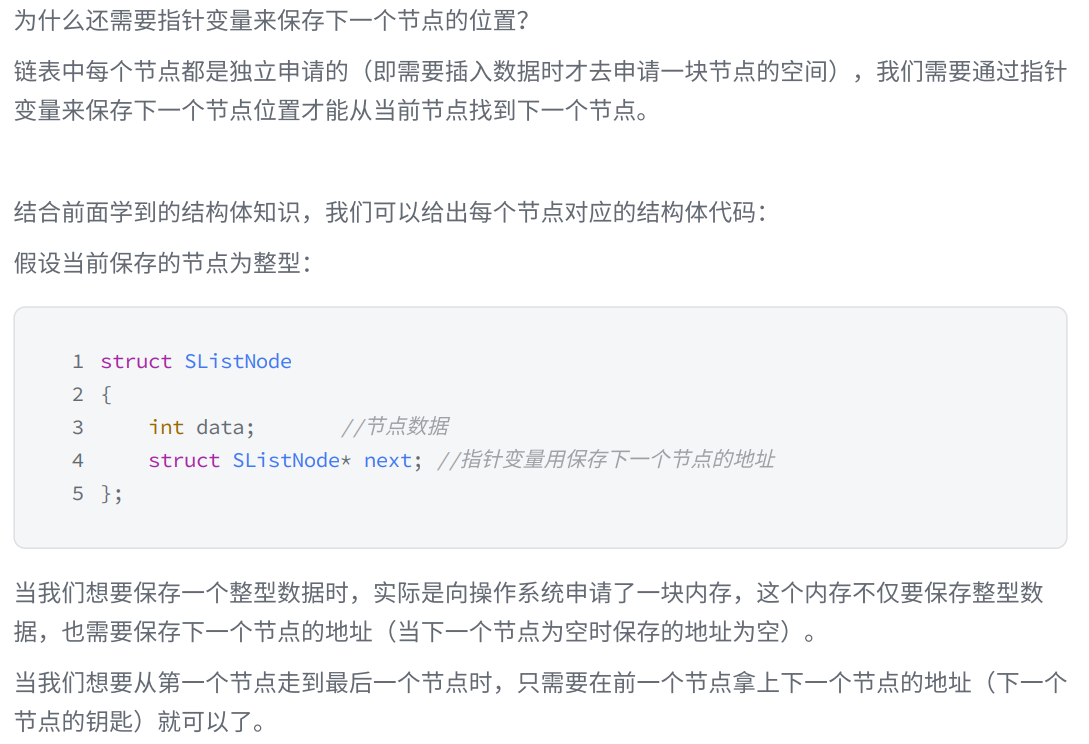
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
cpp
#include"SList.h"
void SlistTest01() {
//一般不会这样去创建链表,这里只是为了给大家展示链表的打印
SLTNode* node1 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
node1->data = 1;
SLTNode* node2 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
node2->data = 2;
SLTNode* node3 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
node3->data = 3;
SLTNode* node4 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
node4->data = 4;
node1->next = node2;
node2->next = node3;
node3->next = node4;
node4->next = NULL;
SLTNode* plist = node1;
SLTPrint(plist);
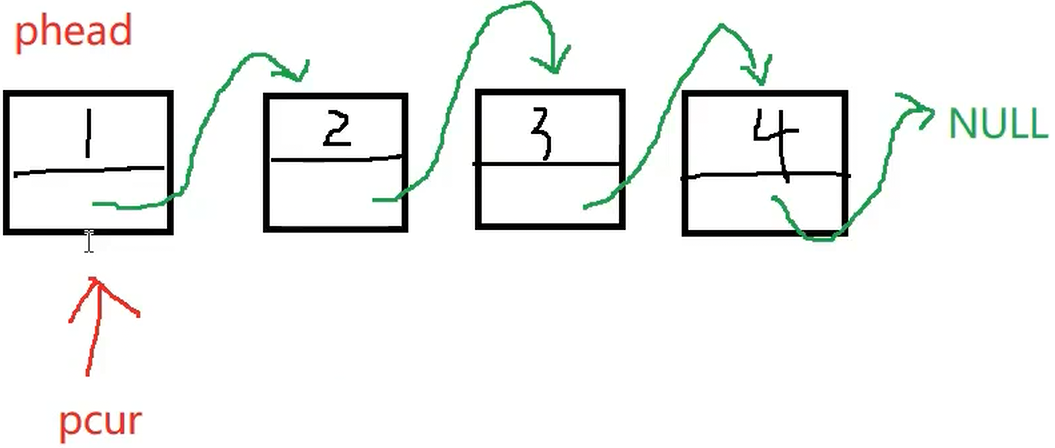
}
cpp
#include"SList.h"
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead) {
SLTNode* pcur = phead;
while (pcur)
{
printf("%d->", pcur->data);
pcur = pcur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
三.链表的模拟实现
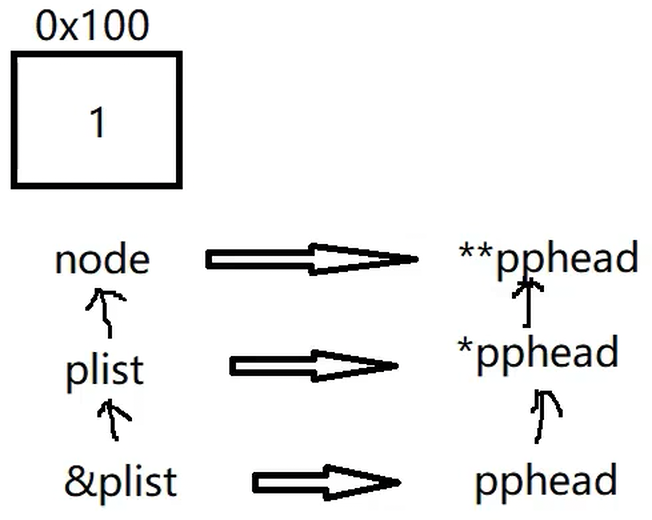
我们要改变ListNode*,就要传递ListNode*的地址
1.SList.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int SLTDataType;
//链表是由节点组成
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
//typedef struct SListNode SLTNode;
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead);
//链表的头插、尾插
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
//链表的头删、尾删
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);
//查找
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
//在指定位置之前插入数据
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
//在指定位置之后插入数据
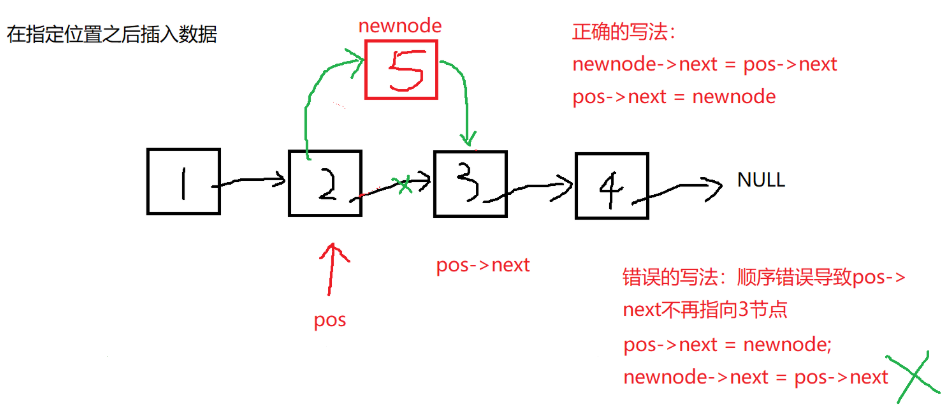
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
//删除pos节点
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);
//删除pos之后的节点
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);
//销毁链表
void SListDesTroy(SLTNode** pphead);2.SList.c
cpp
#include"SList.h"
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead) {
SLTNode* pcur = phead;
while (pcur)
{
printf("%d->", pcur->data);
pcur = pcur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
SLTNode* SLTBuyNode(SLTDataType x) {
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
if (newnode == NULL) {
perror("malloc fail!");
exit(1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
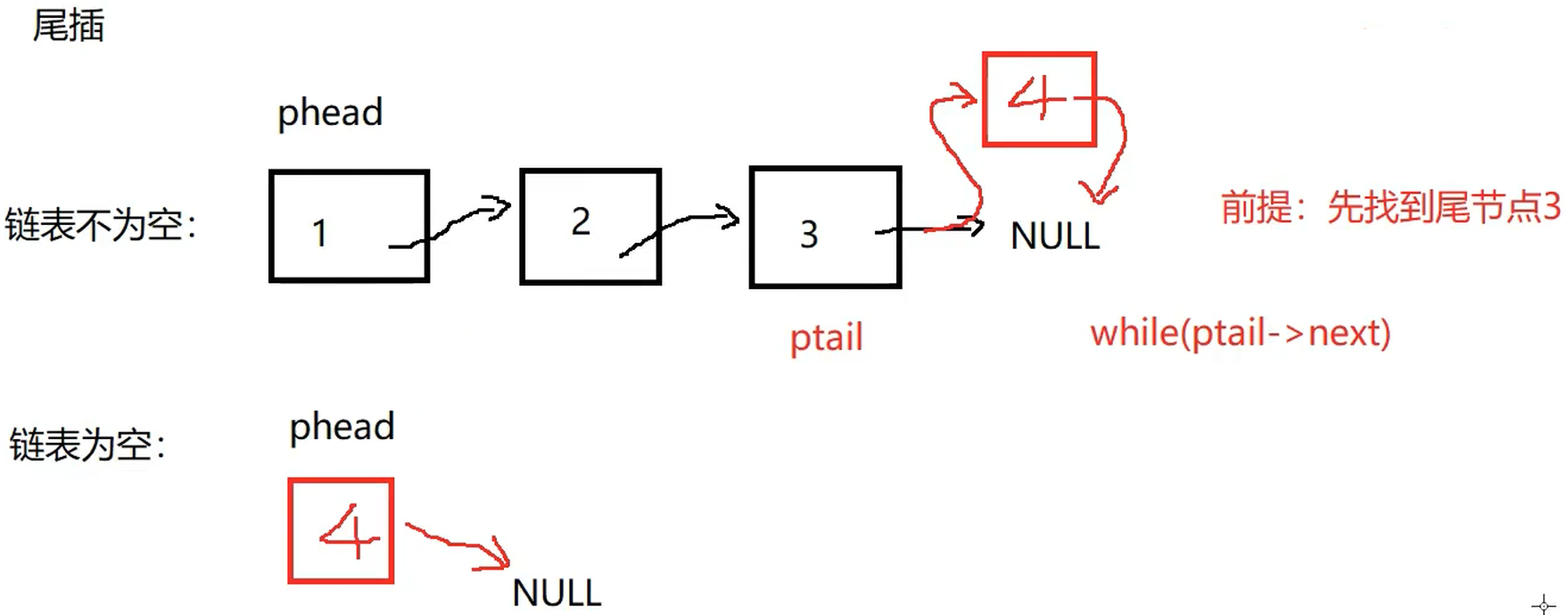
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x) {
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newnode = SLTBuyNode(x);
//链表为空,新节点作为phead
if (*pphead == NULL) {
*pphead = newnode;
return;
}
//链表不为空,找尾节点
SLTNode* ptail = *pphead;
while (ptail->next)
{
ptail = ptail->next;
}
//ptail就是尾节点
ptail->next = newnode;
}
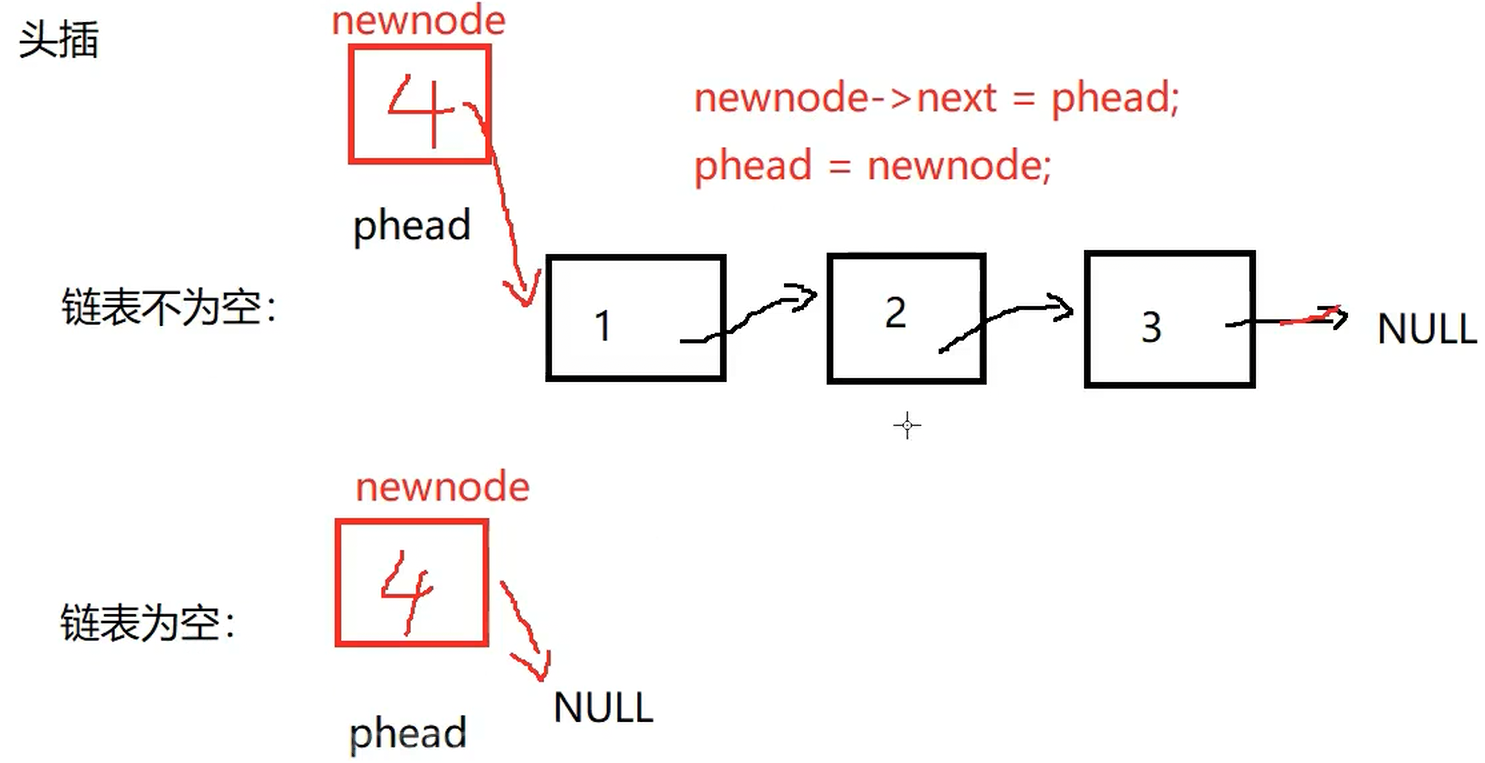
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x) {
assert(pphead);
SLTNode* newnode = SLTBuyNode(x);
//newnode *pphead
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
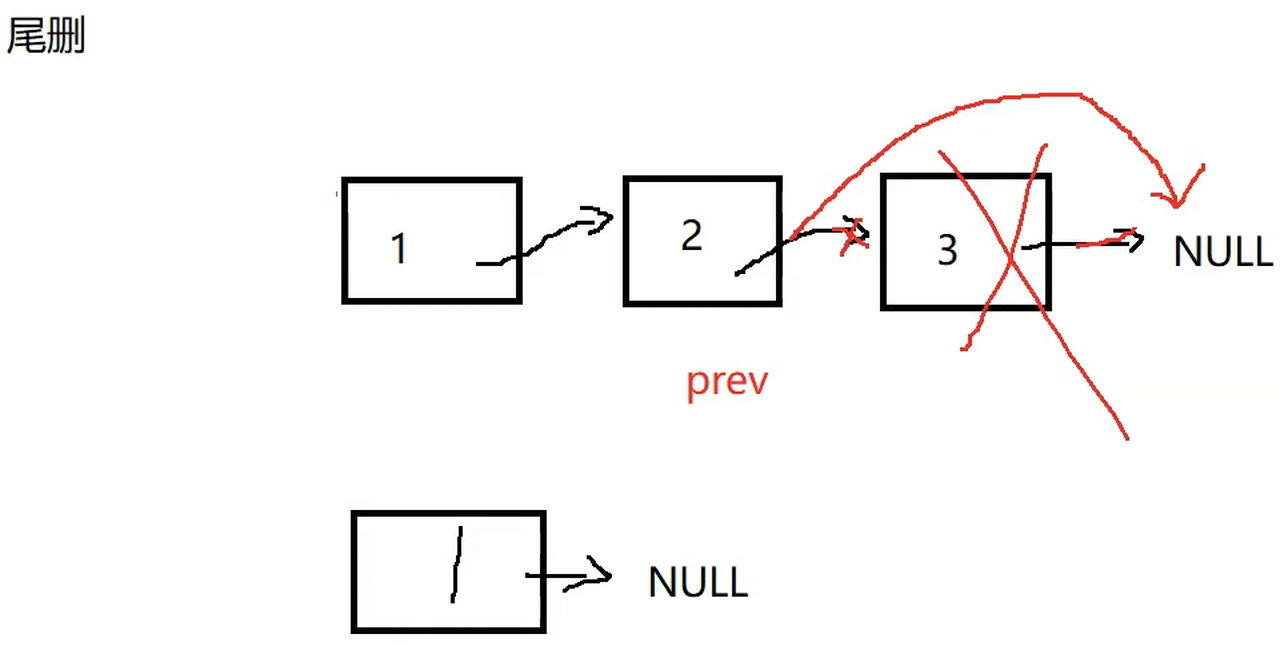
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead) {
assert(pphead);
//链表不能为空
assert(*pphead);
//链表不为空
//链表只有一个节点,有多个节点
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL) {
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
return;
}
SLTNode* ptail = *pphead;
SLTNode* prev = NULL;
while (ptail->next)
{
prev = ptail;
ptail = ptail->next;
}
prev->next = NULL;
//销毁尾结点
free(ptail);
ptail = NULL;
}
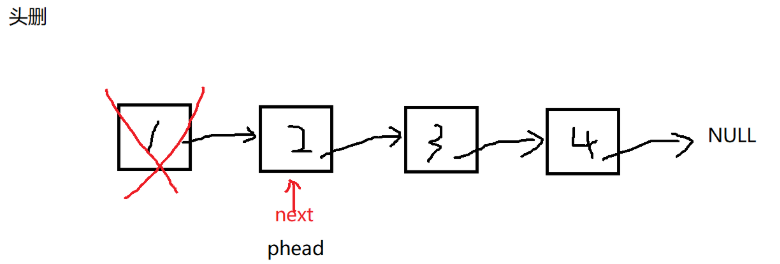
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead) {
assert(pphead);
//链表不能为空
assert(*pphead);
//让第二个节点成为新的头
//把旧的头结点释放掉
SLTNode* next = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = next;
}
//查找
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x) {
assert(pphead);
//遍历链表
SLTNode* pcur = *pphead;
while (pcur) //等价于pcur != NULL
{
if (pcur->data == x) {
return pcur;
}
pcur = pcur->next;
}
//没有找到
return NULL;
}
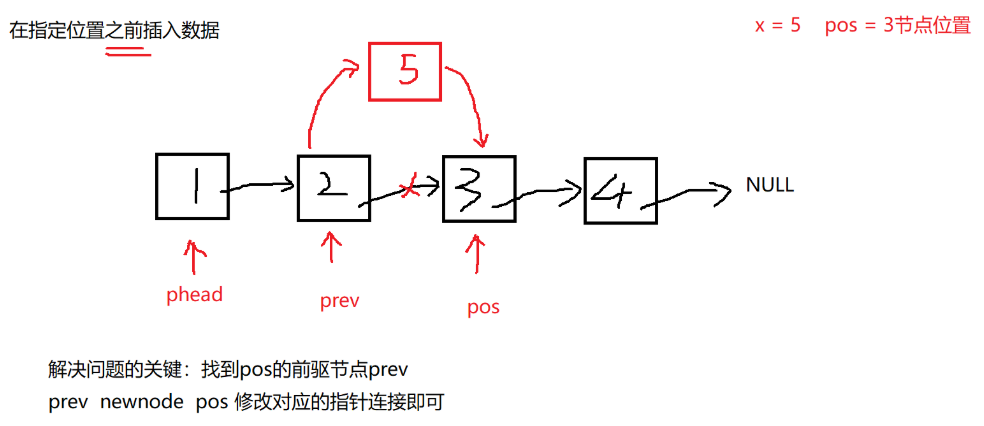
//在指定位置之前插入数据
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x) {
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
//要加上链表不能为空
assert(*pphead);
SLTNode* newnode = SLTBuyNode(x);
//pos刚好是头结点
if (pos == *pphead) {
//头插
SLTPushFront(pphead, x);
return;
}
//pos不是头结点的情况
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
//prev -> newnode -> pos
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
//在指定位置之后插入数据
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x) {
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newnode = SLTBuyNode(x);
//pos newnode pos->next
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
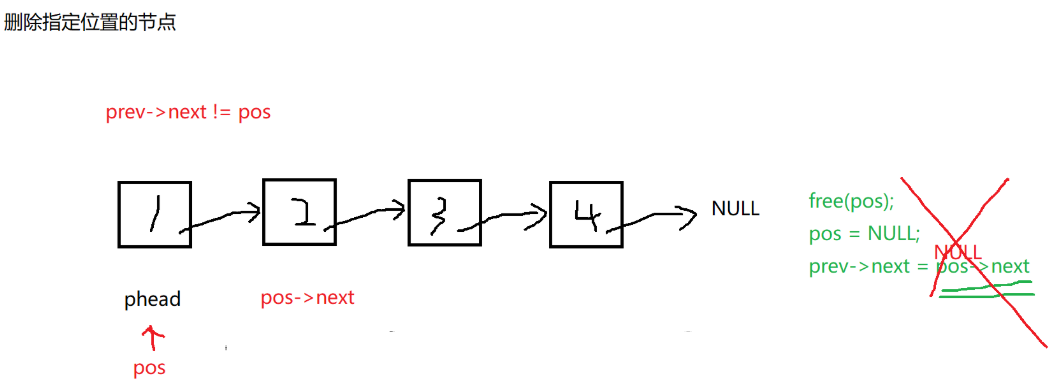
//删除pos节点
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos) {
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
//pos刚好是头结点,没有前驱节点,执行头删
if (*pphead == pos) {
//头删
SLTPopFront(pphead);
return;
}
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
//prev pos pos->next
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
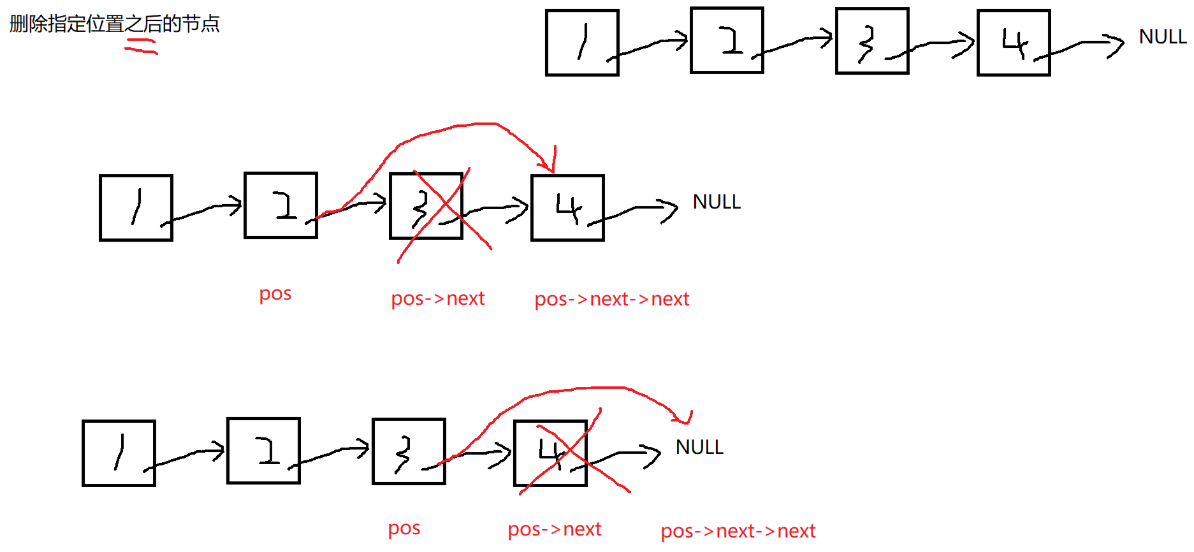
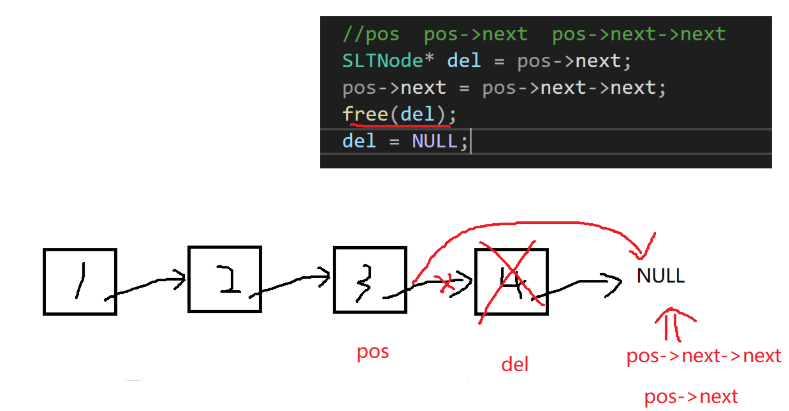
//删除pos之后的节点
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos) {
assert(pos);
//pos->next不能为空
assert(pos->next);
//pos pos->next pos->next->next
SLTNode* del = pos->next;
pos->next = pos->next->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
//销毁链表
void SListDesTroy(SLTNode** pphead) {
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
SLTNode* pcur = *pphead;
while (pcur)
{
SLTNode* next = pcur->next;
free(pcur);
pcur = next;
}
*pphead = NULL;
}3.Test.c
cpp
#include"SList.h"
//void SlistTest01() {
// //一般不会这样去创建链表,这里只是为了给大家展示链表的打印
// SLTNode* node1 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
// node1->data = 1;
// SLTNode* node2 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
// node2->data = 2;
// SLTNode* node3 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
// node3->data = 3;
// SLTNode* node4 = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
// node4->data = 4;
//
// node1->next = node2;
// node2->next = node3;
// node3->next = node4;
// node4->next = NULL;
//
// SLTNode* plist = node1;
// SLTPrint(plist);
//}
void SlistTest02() {
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
SLTPrint(plist); //1->2->3->4->NULL
//SLTPushFront(&plist, 5);
//SLTPrint(plist); //5->1->2->3->4->NULL
//SLTPushFront(&plist, 6);
//SLTPrint(plist); //6->5->1->2->3->4->NULL
//SLTPushFront(&plist, 7);
//SLTPrint(plist); //7-6->5->1->2->3->4->NULL
SLTPopBack(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);//1->2->3->NULL
SLTPopBack(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);//1->2->3->NULL
SLTPopBack(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);//1->2->3->NULL
SLTPopBack(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);//1->2->3->NULL
SLTPopBack(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);//1->2->3->NULL
}
void SlistTest03() {
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTPushBack(&plist, 1);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 2);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 3);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 4);
SLTPrint(plist); //1->2->3->4->NULL
SListDesTroy(&plist);
////头删
//SLTPopFront(&plist);
//SLTPrint(plist); //2->3->4->NULL
//SLTPopFront(&plist);
//SLTPrint(plist); //3->4->NULL
//SLTPopFront(&plist);
//SLTPrint(plist); //4->NULL
//SLTPopFront(&plist);
//SLTPrint(plist); //NULL
//SLTPopFront(&plist);
//SLTPrint(plist); //assert
//
//SLTNode* FindRet = SLTFind(&plist, 3);
//if (FindRet) {
// printf("找到了!\n");
//}
//else {
// printf("未找到!\n");
//}
//SLTInsert(&plist, FindRet, 100);
//SLTInsertAfter(FindRet, 100);
//
//删除指定位置的节点
//SLTErase(&plist, FindRet);
//SLTPrint(plist); //1->2->3->NULL
}
int main() {
//SlistTest01();
//SlistTest02();
SlistTest03();
return 0;
}四.链表的分类
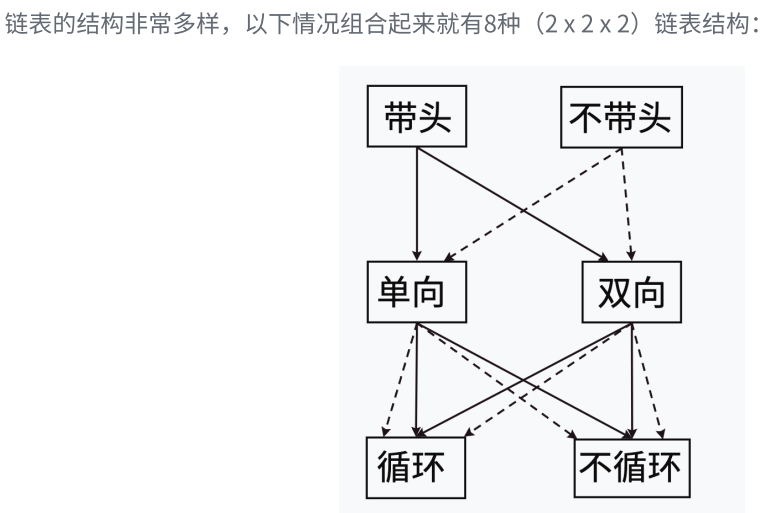
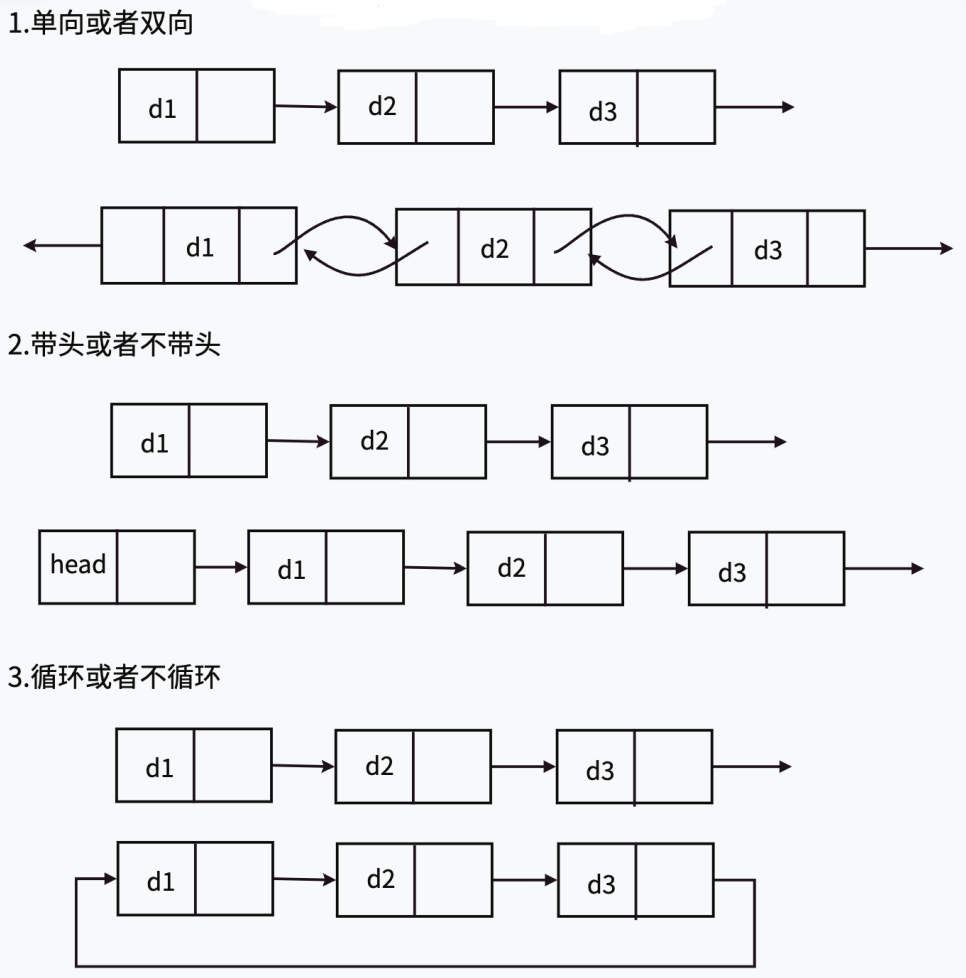

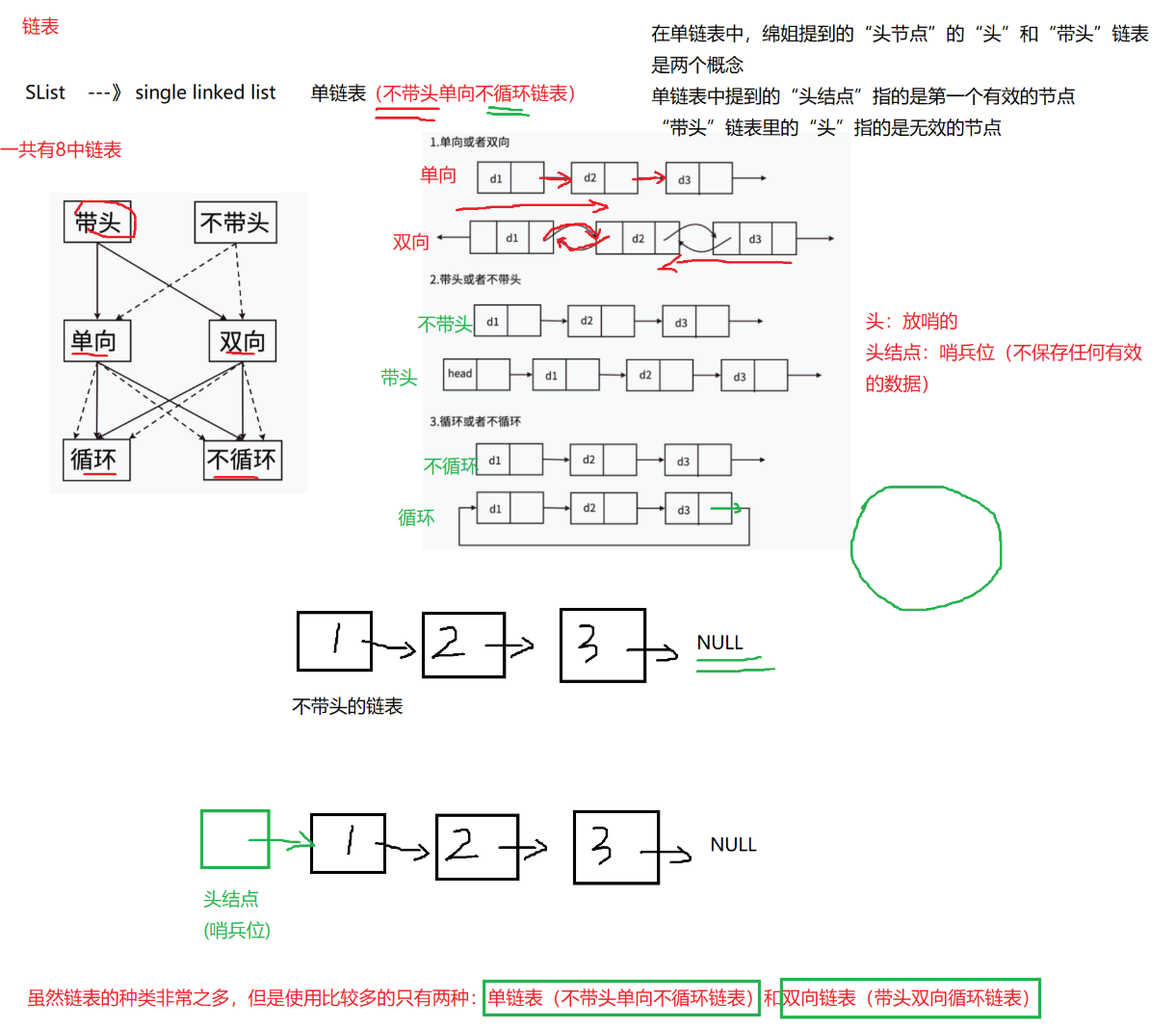
五.单链表的应用
1.题目1
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
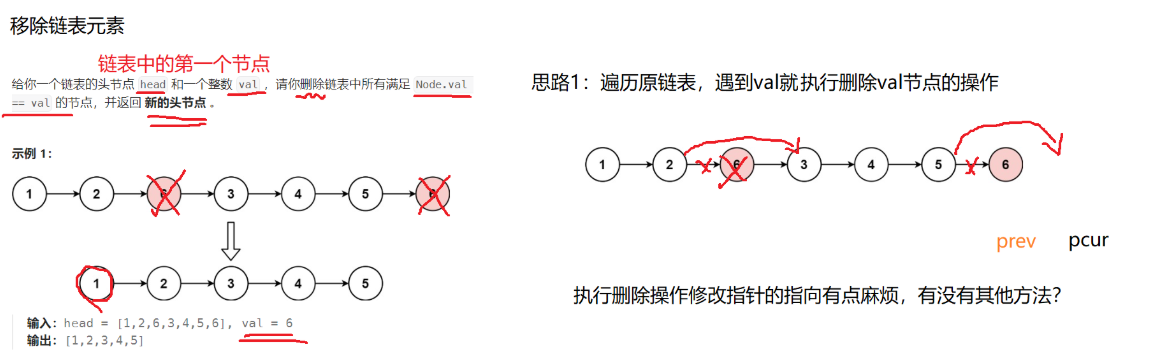
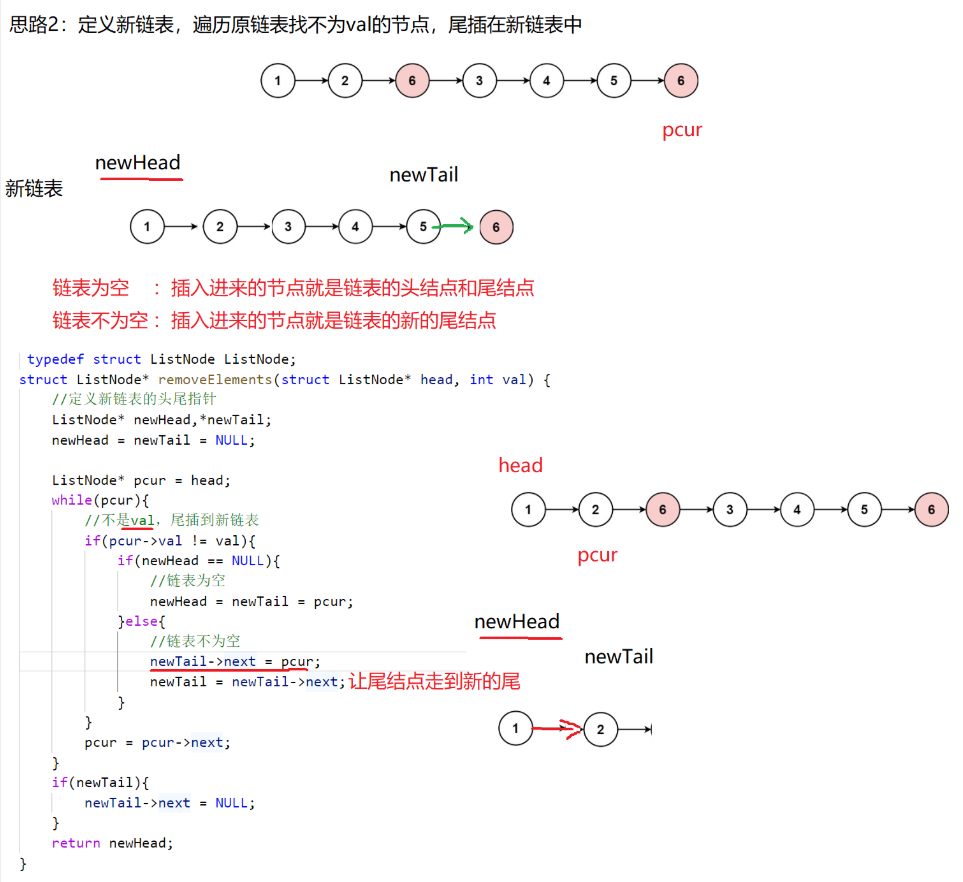
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* newhead=NULL;
struct ListNode* newtail=NULL;
struct ListNode* pcur=head;
while(pcur)
{
if(pcur->val != val)
{
if(newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = pcur;
}
else
{
newtail->next = pcur;
newtail = newtail->next;
}
}
pcur = pcur->next;
}
if(newtail)
{
newtail->next=NULL;
}
return newhead;
}2.题目2
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/https://leetcode.cn/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/description/https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
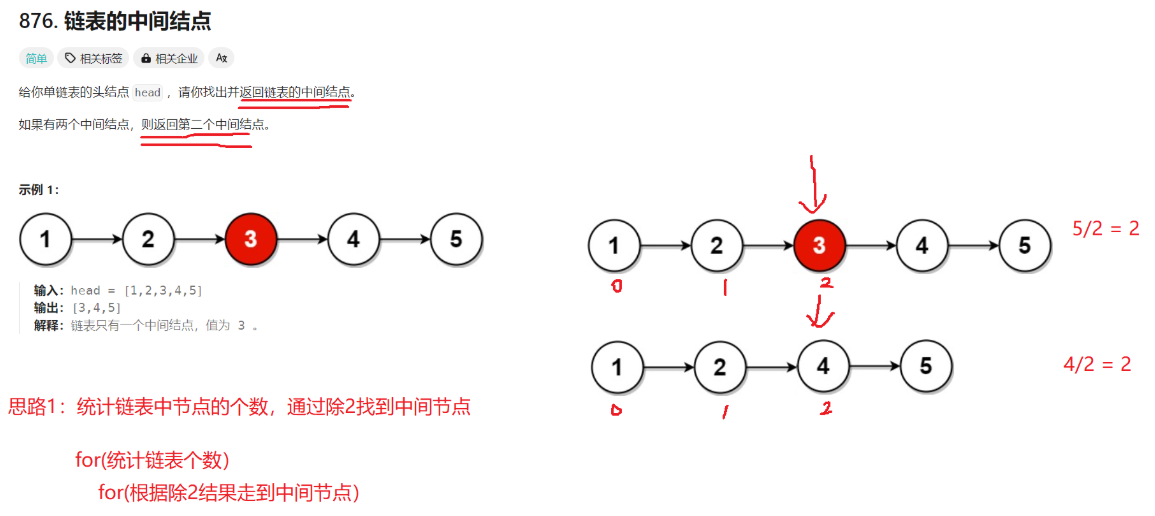
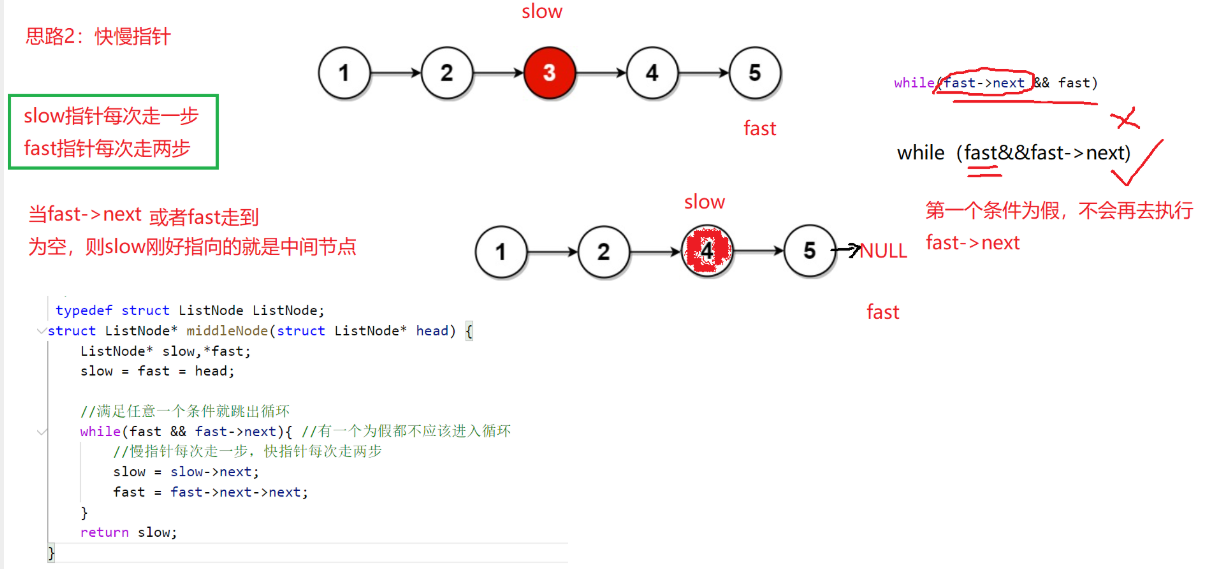
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode*slow=head,*fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}3.题目3
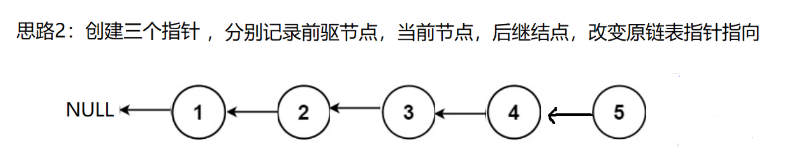
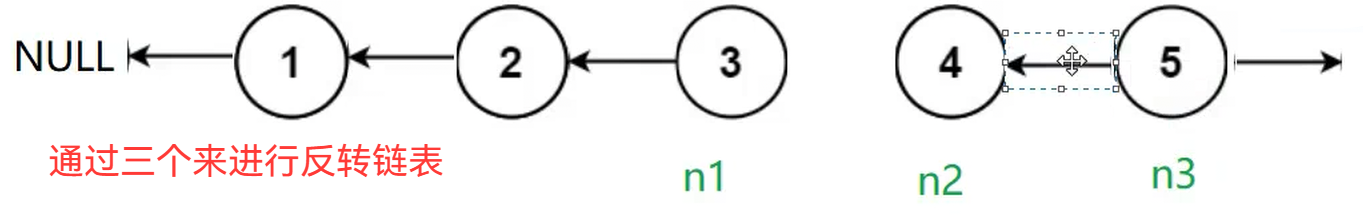
题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
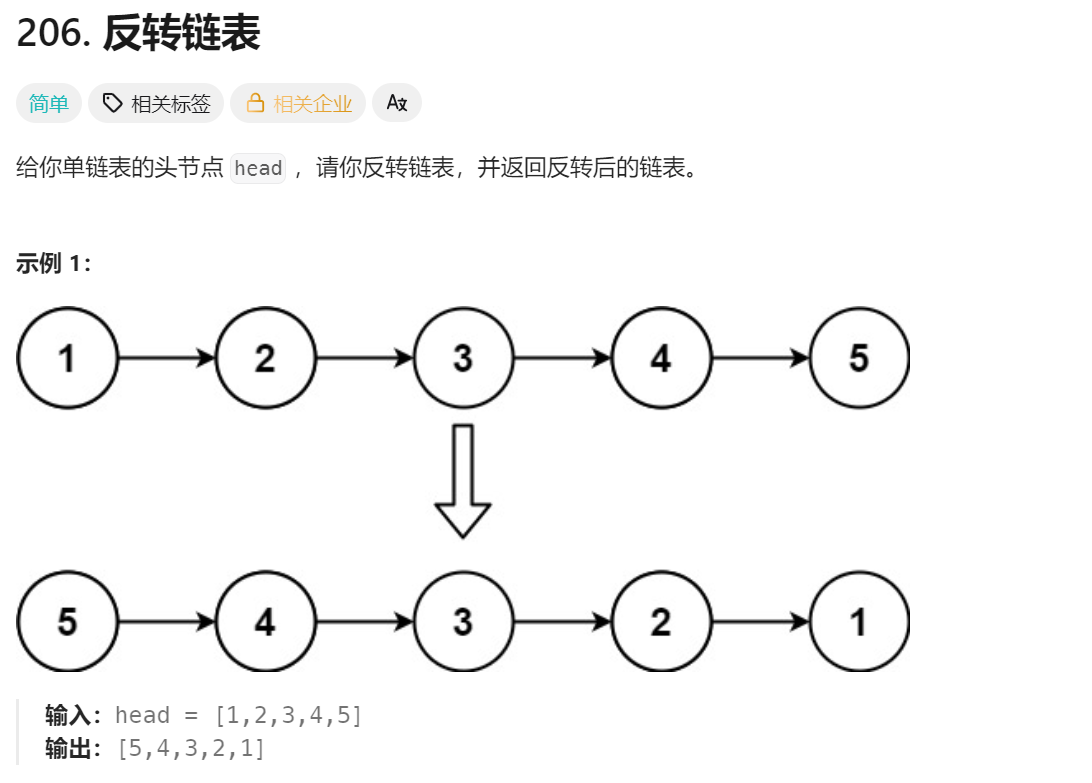
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
ListNode* n1,* n2,* n3;
if(head == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
n1 = NULL,n2 = head,n3 = head->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
{
n3 = n3->next;
}
}
return n1;
}4.题目4
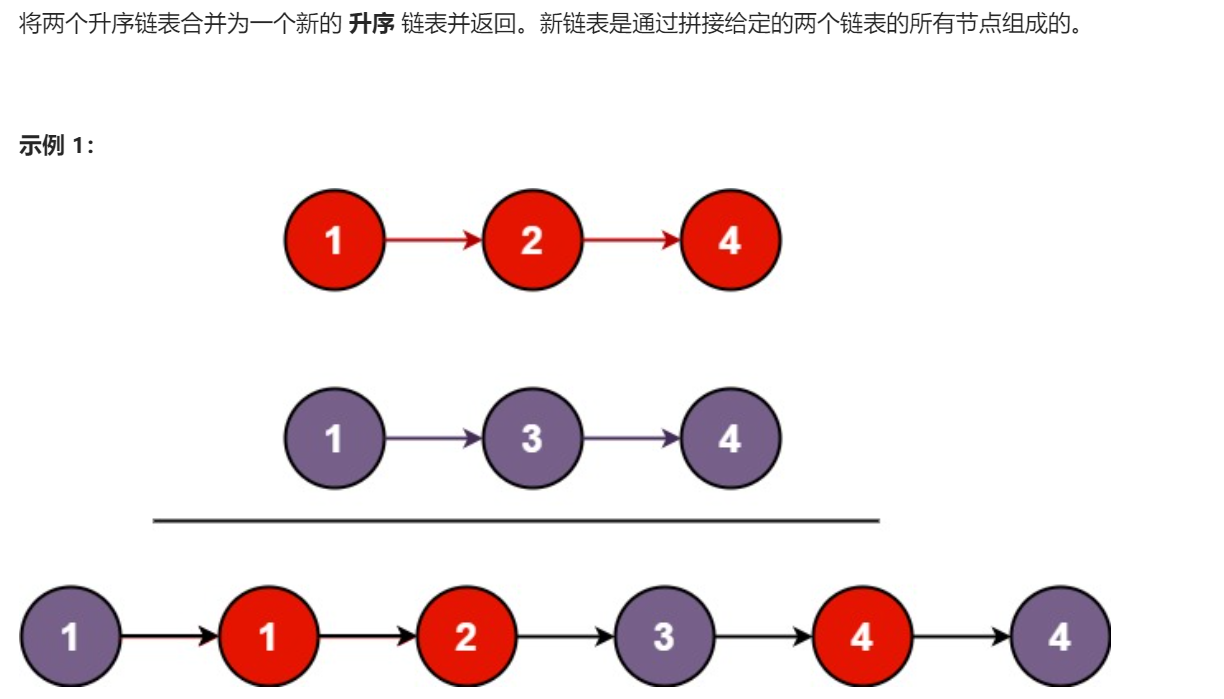
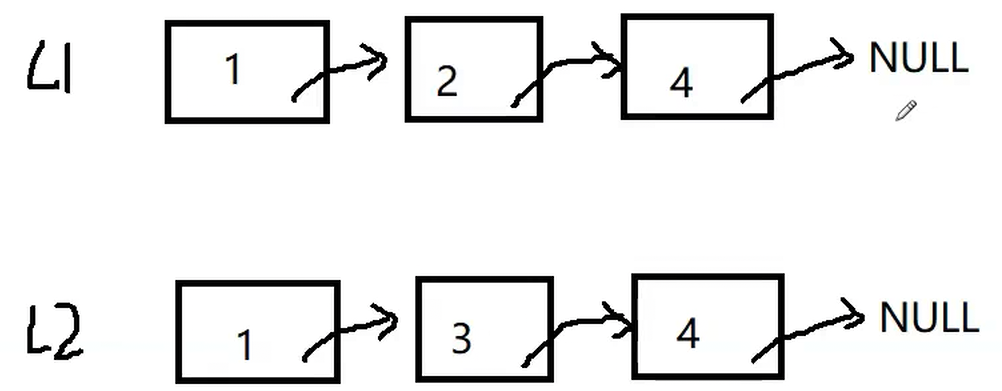
题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/description/
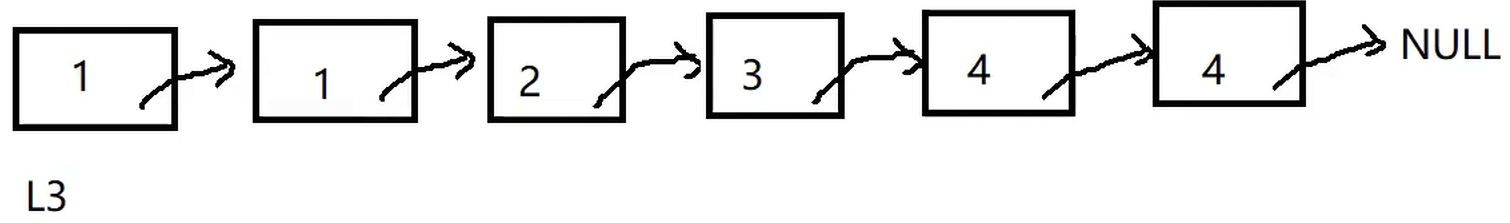
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
if(list1==NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if(list2==NULL)
{
return list1;
}
struct ListNode* l1=list1;
struct ListNode* l2=list2;
struct ListNode* newhead=NULL,*newtail=NULL;
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->val>l2->val)
{
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newtail=newhead=l2;
}
else
{
newtail->next=l2;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
l2=l2->next;
}
else
{
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newtail=newhead=l1;
}
else
{
newtail->next=l1;
newtail=newtail->next;
}
l1=l1->next;
}
}
if(l1)
{
newtail->next=l1;
}
if(l2)
{
newtail->next=l2;
}
return newhead;
}代码优化(增加一个头节点)
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
if(list1==NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if(list2==NULL)
{
return list1;
}
struct ListNode* l1=list1;
struct ListNode* l2=list2;
struct ListNode* newhead,*newtail;
newhead = newtail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->val>l2->val)
{
newtail->next=l2;
newtail=newtail->next;
l2=l2->next;
}
else
{
newtail->next=l1;
newtail=newtail->next;
l1=l1->next;
}
}
if(l1)
{
newtail->next=l1;
}
if(l2)
{
newtail->next=l2;
}
struct ListNode* ret = newHead->next;
free(newHead);
return ret;
}5.题目5
题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/partition-list-lcci/description/
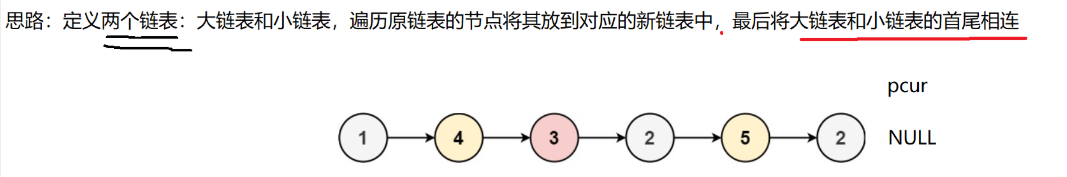
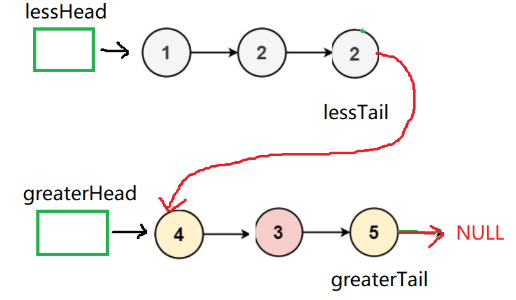
cpp
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* partition(struct ListNode* head, int x){
if(head==NULL)
{
return head;
}
struct ListNode*pcur=head;
struct ListNode*new1head,*new1tail,*new2head,*new2tail;
new1head=new1tail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
new2head=new2tail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
while(pcur)
{
if(pcur->val>=x)
{
new1tail->next=pcur;
new1tail=new1tail->next;
}
else
{
new2tail->next=pcur;
new2tail=new2tail->next;
}
pcur=pcur->next;
}
new1tail->next=NULL;
new2tail->next=new1head->next;
struct ListNode* ret=new2head->next;
free(new1head);
free(new2head);
return ret;
}6.题目6
题目链接: https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/41c399fdb6004b31a6cbb047c641ed8a
cpp
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param n int整型
* @param m int整型
* @return int整型
*/
// 创建单个节点
ListNode* BuyNode(int x) {
ListNode* newNode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
newNode->val = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// 创建包含n个节点的单向循环链表
ListNode* createList(int n) {
ListNode* phead = BuyNode(1);
ListNode* ptail = phead;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
ptail->next = BuyNode(i);
ptail = ptail->next;
}
// 首尾相连形成循环链表
ptail->next = phead;
return ptail;
}
// 核心逻辑:约瑟夫环问题(逢m删除节点,返回最后剩余节点的值)
int ysf(int n, int m) {
// 创建不带头单向循环链表
ListNode* prev = createList(n);
ListNode* pcur = prev->next;
int count = 1;
// 逢m删除节点(循环到只剩一个节点)
while (pcur->next != pcur) {
if (count == m) {
// 删除当前节点pcur
prev->next = pcur->next;
free(pcur);
// 删除后更新pcur位置,重置count
pcur = prev->next;
count = 1;
} else {
// pcur往后移动
prev = pcur;
pcur = pcur->next;
count++;
}
}
// 此时pcur是最后剩余的节点
return pcur->val;
}
};