给你单链表的头指针 head 和两个整数 left 和 right ,其中 left <= right 。请你反转从位置 left 到位置 right 的链表节点,返回 反转后的链表 。
示例 1:
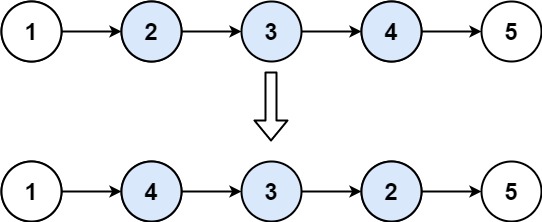
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4
输出:[1,4,3,2,5]示例 2:
输入:head = [5], left = 1, right = 1
输出:[5]提示:
- 链表中节点数目为
n 1 <= n <= 500-500 <= Node.val <= 5001 <= left <= right <= n
进阶: 你可以使用一趟扫描完成反转吗?
答案&测试代码:
cpp
void testLeeCode92(void) { // LeeCode92.反转链表II
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode* next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode* next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
class Solution {
private:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { // 反转整个链表
if (!head) return nullptr;
ListNode* next = head->next;
if (!next) {
return head;
}
head->next = nullptr; // 断开联系
ListNode* newHead = reverseList(next); // 将后面的链表排序好
next->next = head; // 该节点添加到最后
return newHead;
}
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int left, int right) { // LeeCode92.反转链表II
// 将整个链表拆分为3部分,中间那部分用于反转
ListNode *fistHead = nullptr; // 第一段链表的头节点
ListNode *firstLast = nullptr; // 第一段链表的尾节点
// 把第一段链表拆出来
for (int i = 1; i < left; i++) {
if (!fistHead) {
fistHead = head;
}
if (!firstLast) {
firstLast = head;
}
else {
firstLast = firstLast->next;
}
}
// 再把中间要反转的那段链表拆出来
ListNode* midFirst = firstLast? firstLast->next : head;
if (firstLast) {
firstLast->next = nullptr;
}
ListNode* midLast = midFirst;
int midLen = right - left + 1;
for (int i = 1; i < midLen; i++) {
midLast = midLast->next;
}
// 再把最后一段链表拆出来
ListNode* foot = midLast? midLast->next : nullptr;
if (midLast)
midLast->next = nullptr;
// 再反转中间那部分
ListNode *mid_ = reverseList(midFirst);
// 再拼接
ListNode* newHead = mid_;
if (firstLast) {
firstLast->next = newHead;
newHead = fistHead;
}
if (foot && midFirst) {
midFirst->next = foot; // // 中间部分反转后,尾节点为原来的头节点
}
return newHead;
}
};
Solution solution;
ListNode node1 = ListNode(1);
ListNode node2 = ListNode(2);
ListNode node3 = ListNode(3);
ListNode node4 = ListNode(4);
ListNode node5 = ListNode(5);
node1.next = &node2;
node2.next = &node3;
node3.next = &node4;
node4.next = &node5;
ListNode* res = solution.reverseBetween(&node1, 2, 4);
// 打印链表
std::cout << "链表:";
for (ListNode* p = res; p;p = p->next) {
std::cout << p->val << " ";
}
std::cout << endl;
}打印:
ok. 提交到LeeCode:
ok.