目录
[深度学习 DL](#深度学习 DL)
[DL4 Log Softmax函数的实现](#DL4 Log Softmax函数的实现)
[DL7 两个正态分布之间的KL散度](#DL7 两个正态分布之间的KL散度)
[DL15 实现自注意力机制](#DL15 实现自注意力机制)
[DL16 RNN 简化版](#DL16 RNN 简化版)
[DL17 实现长短期记忆(LSTM)网络](#DL17 实现长短期记忆(LSTM)网络)
[机器学习 ML](#机器学习 ML)
[ML2 使用梯度下降的线性回归](#ML2 使用梯度下降的线性回归)
[ML3 标准化缩放和最大最小缩放](#ML3 标准化缩放和最大最小缩放)
[ML5 损失函数](#ML5 损失函数)
[ML6 鸢尾花分类](#ML6 鸢尾花分类)
深度学习 DL
DL4 Log Softmax函数的实现
先减去最大值,再对softmax 结果取log
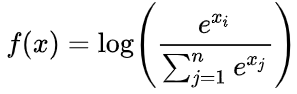
题目让返回 np.ndarray 的结果,先转化为 np.array() 利用 numpy 的广播性。
python
import numpy as np
def log_softmax(scores: list) -> np.ndarray:
arr = np.array(scores)
arr = arr - np.max(arr)
return arr - np.log(sum(np.exp(arr)))
if __name__ == "__main__":
scores = eval(input())
print(log_softmax(scores))DL7 两个正态分布之间的KL散度
KL散度 衡量两个分布的差异
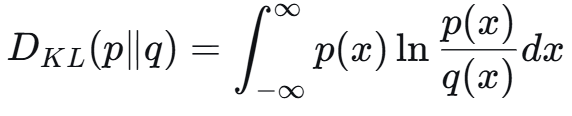
对于正态分布:
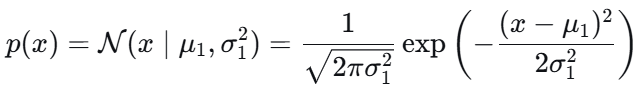
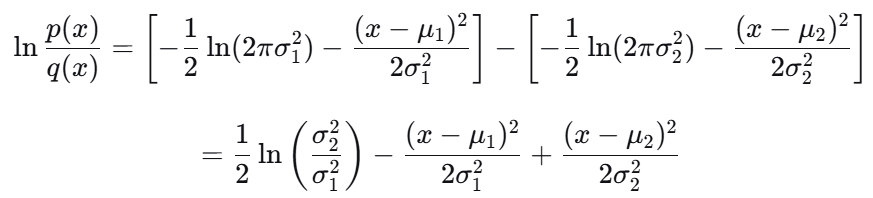
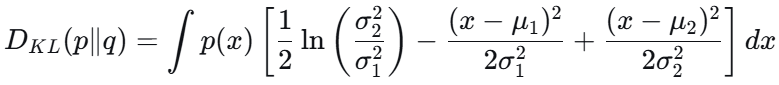

最终结果:
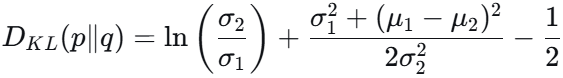
DL15 实现自注意力机制
# Q: [序列长度, 特征维度], K: [序列长度, 特征维度]
# scores = Q @ K.T / sqrt(d_k) → [序列长度, 序列长度]得到矩阵:每个位置对其他位置的注意力分数(n*n矩阵);
对每行(每个token对其他)softmax(axis = 0 竖着一列操作;axis = 1 横着一行操作)
在sum求和的时候,会把 (n*n)的矩阵 变成长度为n的向量,删掉一维,导致除法维度不对应。
keepdims=True,使得最后一维保留为1,变成 (n,1)。
python
import numpy as np
def compute_qkv(X, W_q, W_k, W_v):
return X @ W_q, X @ W_k, X @ W_v
def self_attention(Q, K, V):
# Q * K
d_k = np.sqrt(Q.shape[1]) # 缩放点积,防止梯度消失
scores = Q @ K.T / d_k
# softmax 并对求和保持后一维度
weights = np.exp(scores) / np.sum(np.exp(scores), axis=1, keepdims=True)
return weights @ V
if __name__ == "__main__":
X = np.array(eval(input()))
W_q = np.array(eval(input()))
W_k = np.array(eval(input()))
W_v = np.array(eval(input()))
Q, K, V = compute_qkv(X, W_q, W_k, W_v)
print(self_attention(Q, K, V))DL16 RNN 简化版
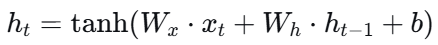
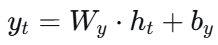
简化版题:给定Wx,Wh,b;最初的h以及从前到后的 input_sequence
只要求最后的隐藏层 h;
python
def rnn_forward(input_sequence, h, Wx, Wh, b):
for x in input_sequence:
h = np.tanh(np.dot(Wx,x) + np.dot(Wh,h) + b)
return np.round(h, 4).tolist()DL17 实现长短期记忆(LSTM)网络
三态门 + 细胞状态 => 隐状态 h;处理时将 前一个h和x 拼在一起。
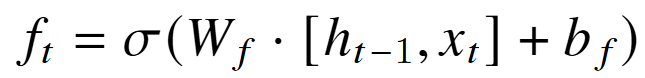
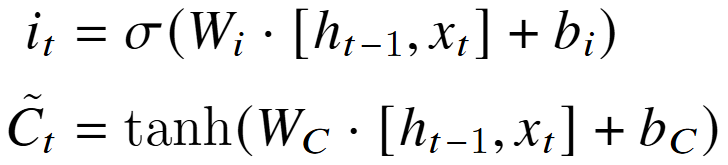
新细胞状态C:遗忘门 f 和输入门 i;对之前与候选 细胞状态进行加权。
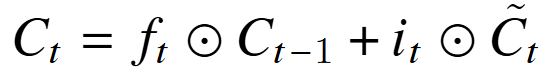
输出门并更新隐状态 h。
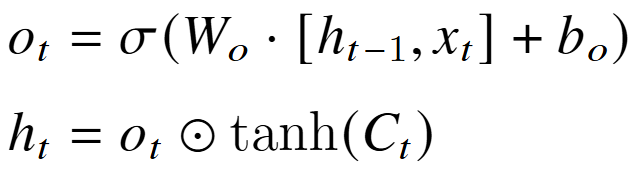
python
def sigmoid(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def forward(self, x, h, c):
outputs = []
for t in range(len(x)):
# 拿出t时间的x转化为列向量 最后一列加上xt变为 (h,xt)
xt = x[t].reshape(-1,1)
concat = np.vstack((h, xt))
# 遗忘门
ft = self.sigmoid(np.dot(self.Wf, concat) + self.bf)
# 输入门
it = self.sigmoid(np.dot(self.Wi, concat) + self.bi)
c_tilde = np.tanh(np.dot(self.Wc, concat) + self.bc)
# 细胞状态更新
c = ft * c + it * c_tilde
# 输出门
ot = self.sigmoid(np.dot(self.Wo, concat) + self.bo)
# 隐状态更新
h = ot * np.tanh(c)
outputs.append(h)
return np.array(outputs), h, c机器学习 ML
ML2 使用梯度下降的线性回归
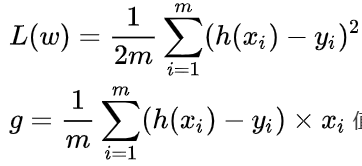 h(x) = x @ θ
h(x) = x @ θ
| 步骤 | 运算 | 输入形状 | 输出形状 |
| 预测 | X @ theta | (m,n)@(n,1) | (m,1) |
| 误差 | predictions - y | (m,1)-(m,1) | (m,1) |
| 梯度 | X.T @ errors | (n,m)@(m,1) | (n,1) |
| 更新 | theta - α×updates | (n,1)-(n,1) | (n,1) |
|---|
python
import numpy as np
def linear_regression_gradient_descent(X, y, alpha, iterations):
m, n = X.shape
theta = np.zeros((n,1))
for _ in range(iterations):
pre = X @ theta
errors = pre - y.reshape(-1,1) # 把y变成列向量
theta -= alpha * (X.T @ errors) / m
return np.round(theta.flatten(),4) # 把(n,1)二维的拉直为 长度为n的列表ML3 标准化缩放和最大最小缩放
对每列进行两种缩放。 axis = 0 并广播机制。
python
def feature_scaling(data):
# 标准化
mean = np.mean(data, axis=0)
std = np.std(data, axis=0)
standardized_data = (data - mean) / std
# 最大最小
min_val = np.min(data, axis=0)
max_val = np.max(data, axis=0)
normalized_data = (data - min_val) / (max_val - min_val)
return np.round(standardized_data,4).tolist(), np.round(normalized_data,4).tolist()sklearn 版本 预处理库的两种Scaler
python
def feature_scaling(data):
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler, MinMaxScaler
return np.round(StandardScaler().fit_transform(data),4).tolist(), np.round(MinMaxScaler().fit_transform(data),4).tolist()ML5 损失函数

numpy的使用,mse mae 按规则计算取平均 np.mean()
np.where起到条件选择的作用;np.dot np.norm 进行点积和二范数
python
import numpy as np
def calculate_loss(real, pre, delta):
mse = np.mean((real-pre)**2)
mae = np.mean(np.abs(real-pre))
huber_loss = np.where(np.abs(real-pre)<=delta, mse, mae)
cosine_loss = 1 - np.dot(real,pre) / np.linalg.norm(real) / np.linalg.norm(pre)
return round(mse, 6), round(mae, 6), round(np.mean(huber_loss), 6), round(cosine_loss, 6)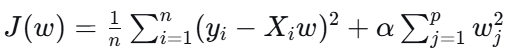
python
# 岭回归
def ridge_loss(X, w, y_true, alpha):
return np.mean( (y_true-X@w)**2 ) + alpha*np.sum(w**2)ML7 数据集洗牌 np.random.shuffle
对索引 [0,n) 进行shuffle洗牌; 对np.random 设定随机种子
python
import numpy as np
def shuffle_data(X, y, seed=None):
if seed:
np.random.seed(seed) # 为np.random 设定随机种子
# 索引shuffle
idx = np.arange(X.shape[0])
np.random.shuffle(idx)
return X[idx], y[idx]
if __name__ == "__main__":
X = np.array(eval(input()))
y = np.array(eval(input()))
print(shuffle_data(X, y, 42))ML6 鸢尾花分类
你的任务是用sklearn的LogisticsRegression模型对鸢尾花类别进行预测,模型请指定参数max_iter=200以减少训练用时。
1.读入数据集
2.对数据集进行一次随机洗牌(索引顺序shuffle)
3.数据分成训练集与测试集(后n为测试)
输出预测类别;最大概率。
分别用predict 和 predict_proba。
python
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
import numpy as np
import random
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
n = int(input())
random.seed(42)
indices = list(range(len(X))) # 创建索引列表
random.shuffle(indices) # 洗牌
X = X[indices] # 根据洗牌后的索引重新排列数据
y = y[indices] # 根据洗牌后的索引重新排列标签
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = X[:-n], X[-n:], y[:-n], y[-n:]
# 3. 使用逻辑回归算法进行训练
model = LogisticRegression(max_iter=200)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 4. 进行预测
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
y_prob = model.predict_proba(X_test)
# 5. 输出预测的类别以及对应的概率
for i in range(len(y_pred)):
print(f'{iris.target_names[y_pred[i]]} {y_prob[i][y_pred[i]]:.2f}')