mongodb的复制集整理
- [1. MongoDB 复制集概念](#1. MongoDB 复制集概念)
-
- [1.1 什么是复制集](#1.1 什么是复制集)
- [1.2 复制集成员角色](#1.2 复制集成员角色)
- [2. 复制集工作原理](#2. 复制集工作原理)
-
- [2.1 数据同步流程](#2.1 数据同步流程)
- [2.2 Oplog(操作日志)](#2.2 Oplog(操作日志))
- [3. 详细部署流程](#3. 详细部署流程)
-
- [3.1 环境准备](#3.1 环境准备)
- [3.2 安装 MongoDB](#3.2 安装 MongoDB)
- [3.3 配置 MongoDB](#3.3 配置 MongoDB)
- [3.4 创建密钥文件(认证)](#3.4 创建密钥文件(认证))
- [3.5 启动 MongoDB 服务](#3.5 启动 MongoDB 服务)
- [3.6 初始化复制集](#3.6 初始化复制集)
- [3.7 创建管理员用户](#3.7 创建管理员用户)
- [. 验证复制集功能](#. 验证复制集功能)
-
- [4.1 检查复制集状态](#4.1 检查复制集状态)
- [4.2 测试数据同步](#4.2 测试数据同步)
- [5. 高级配置选项](#5. 高级配置选项)
-
- [5.1 成员优先级配置](#5.1 成员优先级配置)
- [5.2 隐藏节点和延迟节点](#5.2 隐藏节点和延迟节点)
- 读偏好设置
- [6. 监控和维护](#6. 监控和维护)
-
- [6.1 监控命令](#6.1 监控命令)
- [6.2 备份策略](#6.2 备份策略)
- [7. 故障排除](#7. 故障排除)
-
- [7.1 常见问题解决](#7.1 常见问题解决)
- [8. MongoDB副本集与Redis哨兵模式的关键差异](#8. MongoDB副本集与Redis哨兵模式的关键差异)
-
- [🔄 MongoDB版本与复制模式](#🔄 MongoDB版本与复制模式)
- [🗳️ 仲裁节点详解与配置建议](#🗳️ 仲裁节点详解与配置建议)
- [📝 总结与行动建议](#📝 总结与行动建议)
- [9. 主2从模式的工作机制](#9. 主2从模式的工作机制)
- [10. MongoDB选举机制详解](#10. MongoDB选举机制详解)
-
- [1. 选举资格条件](#1. 选举资格条件)
- [2. 优先级相同时的选举规则](#2. 优先级相同时的选举规则)
- [3. 实际选举过程示例](#3. 实际选举过程示例)
- [4. 如何保证一定能选出主节点](#4. 如何保证一定能选出主节点)
- [5. 查看选举相关信息的命令](#5. 查看选举相关信息的命令)
- [6. 生产环境最佳实践](#6. 生产环境最佳实践)
- [11. 复制集进行主从切换时业务中的解决方案(示例基于lua-skynet版本)](#11. 复制集进行主从切换时业务中的解决方案(示例基于lua-skynet版本))
-
- [1. MongoDB驱动自动故障转移(推荐)](#1. MongoDB驱动自动故障转移(推荐))
- [2. Skynet框架中的具体实现](#2. Skynet框架中的具体实现)
- [3. 在业务中使用MongoDB服务](#3. 在业务中使用MongoDB服务)
- [4. 配置和启动](#4. 配置和启动)
1. MongoDB 复制集概念
1.1 什么是复制集
MongoDB 复制集是一组维护相同数据集的 mongod 进程,提供:
- 数据冗余:防止数据丢失
- 高可用性:自动故障转移
- 读扩展:支持从节点读取
1.2 复制集成员角色
bash
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ PRIMARY │◄───│ SECONDARY │◄───│ SECONDARY │
│ (主节点) │ │ (从节点) │ │ (从节点) │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘
│ │ │
└───────────────────┼───────────────────┘
│
┌─────────┴─────────┐
│ ARBITER │
│ (仲裁节点) │
└───────────────────┘成员类型:
- Primary:唯一接收写操作的节点
- Secondary:复制主节点数据,可处理读查询
- Arbiter:不存储数据,只参与选举投票
2. 复制集工作原理
2.1 数据同步流程
bash
应用写入 ──────► Primary ──────► Oplog ──────► Secondary
│ │
│ 异步复制
▼ ▼
确认写入 ◄──────────────── 应用操作2.2 Oplog(操作日志)
- 存储位置:local 数据库的 oplog.rs 集合
- 内容:所有修改数据库的操作记录
- 格式:
bash
{
"ts" : Timestamp(1503110518, 1), // 时间戳
"h" : NumberLong("232325232322"), // 操作ID
"v" : 2, // 版本
"op" : "i", // 操作类型(i=插入,u=更新,d=删除)
"ns" : "test.users", // 命名空间
"o" : { "_id" : 1, "name" : "Alice" } // 操作文档
}3. 详细部署流程
3.1 环境准备
系统要求:
- 3台服务器(最小复制集配置)
- MongoDB 4.0+ 版本
- 网络互通
服务器规划:
| 主机名 | IP地址 | 端口 | 角色 |
|---|---|---|---|
| mongo1 | 192.168.1.10 | 27017 | Primary |
| mongo2 | 192.168.1.11 | 27017 | Secondary |
| mongo3 | 192.168.1.12 | 27017 | Secondary |
3.2 安装 MongoDB
在所有节点执行:
bash
# 1. 导入MongoDB GPG密钥
wget -qO - https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-6.0.asc | sudo apt-key add -
# 2. 添加MongoDB仓库
echo "deb [ arch=amd64,arm64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu focal/mongodb-org/6.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-6.0.list
# 3. 更新并安装
sudo yum install -y mongodb-org
# 4. 创建数据目录和日志目录
sudo mkdir -p /data/db
sudo mkdir -p /var/log/mongodb
sudo chown -R mongodb:mongodb /data/db /var/log/mongodb3.3 配置 MongoDB
编辑配置文件 /etc/mongod.conf**:
bash
# 网络配置
net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 0.0.0.0 # 生产环境建议使用具体IP
# 存储配置
storage:
dbPath: /data/db
journal:
enabled: true
# 复制集配置
replication:
replSetName: "rs0" # 复制集名称,所有节点必须相同
# 安全配置(可选但推荐)
security:
authorization: enabled
keyFile: /etc/mongodb.keyfile
systemLog:
destination: file
path: /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log
logAppend: true3.4 创建密钥文件(认证)
在主节点创建并分发密钥文件:
bash
# 1. 生成密钥文件
openssl rand -base64 756 > /etc/mongodb.keyfile
chmod 400 /etc/mongodb.keyfile
chown mongodb:mongodb /etc/mongodb.keyfile
# 2. 复制到其他节点
scp /etc/mongodb.keyfile mongo2:/etc/
scp /etc/mongodb.keyfile mongo3:/etc/
# 3. 在其他节点设置权限
# 在 mongo2 和 mongo3 上执行:
chmod 400 /etc/mongodb.keyfile
chown mongodb:mongodb /etc/mongodb.keyfile3.5 启动 MongoDB 服务
在所有节点执行:
bash
# 启动服务
sudo systemctl start mongod
sudo systemctl enable mongod
# 检查状态
sudo systemctl status mongod3.6 初始化复制集
连接到主节点初始化:
bash
# 连接到 mongo1
mongo --host 192.168.1.10 --port 27017在 MongoDB shell 中执行:
javascript
// 初始化复制集配置
rs.initiate({
_id: "rs0",
version: 1,
members: [
{ _id: 0, host: "192.168.1.10:27017", priority: 2 },
{ _id: 1, host: "192.168.1.11:27017", priority: 1 },
{ _id: 2, host: "192.168.1.12:27017", priority: 1 }
]
})
// 检查状态
rs.status()
// 查看配置
rs.conf()3.7 创建管理员用户
javascript
// 切换到admin数据库
use admin
// 创建管理员用户
db.createUser({
user: "admin",
pwd: "your_secure_password",
roles: [
{ role: "root", db: "admin" },
{ role: "clusterAdmin", db: "admin" }
]
})
// 重新认证
db.auth("admin", "your_secure_password"). 验证复制集功能
4.1 检查复制集状态
javascript
// 查看复制集状态
rs.status()
// 查看复制集配置
rs.conf()
// 查看成员状态
rs.isMaster()
// 查看复制集统计信息
db.printReplicationInfo()
db.printSlaveReplicationInfo()4.2 测试数据同步
在主节点插入数据:
javascript
use testdb
// 插入测试数据
for (var i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
db.users.insert({
user_id: i,
name: "User " + i,
email: "user" + i + "@example.com",
created_at: new Date()
})
}
// 查看数据计数
db.users.count()在从节点验证数据:
bash
# 连接到从节点
mongo --host 192.168.1.11 --port 27017
javascript
// 在从节点执行
rs.slaveOk() // 允许从节点读取
use testdb
db.users.count() // 应该显示100
// 验证数据一致性
db.users.find().sort({_id: -1}).limit(5)`在这里插入代码片`5. 高级配置选项
5.1 成员优先级配置
javascript
// 修改成员配置
var config = rs.conf()
config.members[0].priority = 2 // 主节点优先级最高
config.members[1].priority = 1
config.members[2].priority = 0.5 // 最低优先级
// 应用新配置
rs.reconfig(config)5.2 隐藏节点和延迟节点
javascript
var config = rs.conf()
// 配置隐藏节点(不处理读请求)
config.members[2].hidden = true
config.members[2].priority = 0
// 配置延迟节点(数据延迟1小时)
config.members[2].slaveDelay = 3600
config.members[2].priority = 0
rs.reconfig(config)读偏好设置
在应用连接字符串中配置:
javascript
// 优先从从节点读取
mongodb://username:password@192.168.1.10:27017,192.168.1.11:27017,192.168.1.12:27017/testdb?replicaSet=rs0&readPreference=secondaryPreferred
// 最近节点读取
mongodb://username:password@192.168.1.10:27017,192.168.1.11:27017,192.168.1.12:27017/testdb?replicaSet=rs0&readPreference=nearest6. 监控和维护
6.1 监控命令
javascript
// 监控复制延迟
db.getReplicationInfo()
// 查看操作日志状态
db.getSiblingDB("local").oplog.rs.stats()
// 监控连接数
db.serverStatus().connections
// 查看当前操作
db.currentOp()6.2 备份策略
javascript
# 使用 mongodump 备份
mongodump --host rs0/192.168.1.10:27017,192.168.1.11:27017 \
--username admin --password "your_password" \
--authenticationDatabase admin \
--out /backup/mongodb-$(date +%Y%m%d)7. 故障排除
7.1 常见问题解决
节点无法连接:
bash
# 检查网络连通性
ping 192.168.1.10
telnet 192.168.1.10 27017
# 检查防火墙
sudo ufw status复制延迟:
javascript
// 检查复制状态
rs.printSlaveReplicationInfo()
// 优化方案:
// 1. 增加oplog大小
// 2. 优化网络带宽
// 3. 升级硬件性能重新同步节点:
bash
# 如果节点严重落后,可能需要重新同步
# 停止落后节点
sudo systemctl stop mongod
# 清空数据目录(谨慎操作!)
sudo rm -rf /data/db/*
# 重新启动
sudo systemctl start mongod
# 节点将自动重新同步8. MongoDB副本集与Redis哨兵模式的关键差异
| 特性/方面 | MongoDB 副本集 | Redis 哨兵模式 (Sentinel) |
|---|---|---|
| 架构核心 | 数据节点(Primary, Secondary) + 可选仲裁节点(Arbiter) | Redis数据节点 + 专用哨兵节点集群 |
| 高可用与故障转移 | 内置自动故障转移,节点通过心跳检测和投票协议直接选举新主 | 哨兵节点集群负责监控、发现故障并选举新主 |
| 仲裁/哨兵角色 | Arbiter:不存储数据,仅参与投票 | Sentinel:不存储数据,专用于监控与选举 |
| 仲裁/哨兵数量 | 1个即可,通常用于凑足投票奇数,避免脑裂 | 通常需要至少3个哨兵实例,以形成分布式共识,防止误判 |
🔄 MongoDB版本与复制模式
需要注意一个重要变化:自 MongoDB 4.0 版本开始,旧式的 Master-Slave(主从)复制模式已被完全废弃,不再支持。取而代之的是官方推荐且功能更强大的 Replica Set(副本集) 模式
副本集通过 Primary(主节点) 、Secondary(从节点) 和可选的 Arbiter(仲裁节点) 来提供数据冗余、高可用性和自动故障恢复。直到目前,MongoDB 8.0系列版本仍在持续更新,并对副本集的复制过程进行了性能优化,例如引入了并行的写线程和应用线程
🗳️ 仲裁节点详解与配置建议
仲裁节点(Arbiter) 在副本集中的唯一作用就是参与主节点选举时的投票 。它本身不存储任何数据,因此资源消耗极低
- 为什么一个就够了?
一个副本集只需要配置一个仲裁节点 。它的价值在于,当设置的数据节点(Primary + Secondary)是偶数个 时,加入一个仲裁节点可以使总的投票成员数变为奇数 。这确保了在故障发生时,副本集总能产生一个"大多数"(majority)来成功选举出新的主节点,避免因票数相同而陷入选举僵局(脑裂)。如果数据节点本身已是奇数个,则不需要仲裁节点
- 如何配置仲裁节点?
仲裁节点的配置过程与数据节点相似,但更轻量
1. 启动节点 :像启动普通mongod实例一样启动它,使用相同的replSet名称
2. 添加到副本集:通过MongoDB Shell连接到当前的主节点,使用 rs.addArb() 命令将其添加为仲裁节点。例如:rs.addArb("hostname:port")
一个经典的三节点部署架构:
- 1个主节点 + 2个从节点
- 1个主节点 + 1个从节点 + 1个仲裁节点 (这是一种高性价比且具备自动故障转移能力的方案)
📝 总结与行动建议
1. 使用副本集 :请务必使用副本集(Replica Set) 而非过时的 Master-Slave 架构
2. 规划节点数 :确保副本集中拥有投票权的成员(包括仲裁节点)总数为奇数
3. 生产环境配置 :对于重要的生产环境,更推荐的稳健配置是 1个主节点 + 2个从节点,这样可以同时提供数据冗余和读扩展能力
9. 主2从模式的工作机制
架构示意图
bash
正常状态:
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ PRIMARY │◄───│ SECONDARY │◄───│ SECONDARY │
│ (Node A) │ │ (Node B) │ │ (Node C) │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘
│ │ │
└───── 心跳检测 ──────┴───── 心跳检测 ──────┘
主节点故障后:
┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐
│ DOWN │ │ NEW │ │ SECONDARY │
│ (Node A) │ │ PRIMARY │ │ (Node C) │
│ │ │ (Node B) │◄───│ │
└─────────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────────┘故障转移过程详解
1. 心跳检测机制
javascript
// 每个节点每2秒向其他节点发送心跳
// 配置示例(在mongo shell中查看)
rs.conf().settings
{
"heartbeatIntervalMillis" : 2000, // 心跳间隔:2秒
"heartbeatTimeoutSecs" : 10, // 超时时间:10秒
"electionTimeoutMillis" : 10000 // 选举超时:10秒
}2. 主节点故障检测流程
bash
时间线:
T+0秒 主节点停止响应
T+2秒 从节点发送心跳,未收到主节点回复
T+4秒 连续两次心跳失败
T+10秒 选举超时,从节点开始选举新主
T+12秒 新主节点选举完成3. 选举过程
javascript
// 选举条件检查(伪代码逻辑)
function canBecomePrimary(secondary) {
return (
secondary.isHealthy() && // 节点健康
secondary.isUpToDate() && // 数据最新
secondary.priority > 0 && // 优先级>0
!secondary.hidden && // 不是隐藏节点
secondary.votes > 0 // 有投票权
);
}
// 投票规则:需要获得大多数票数
// 在3节点环境中:大多数 = 2票10. MongoDB选举机制详解
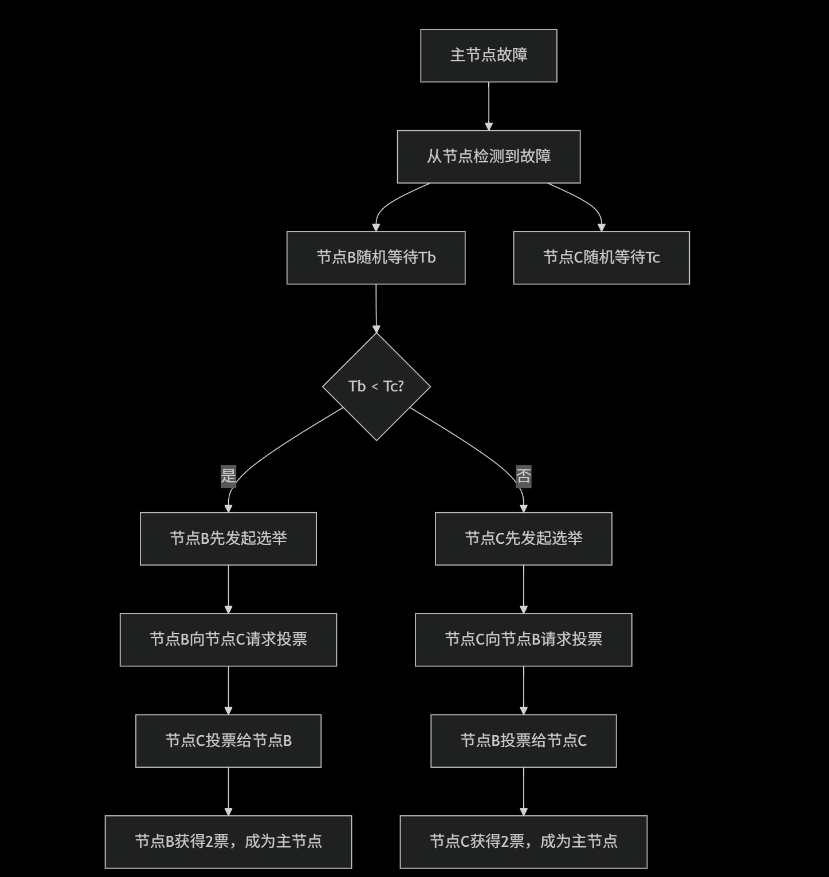
选举过程不仅仅是根据优先级 ,而是结合了多个因素的综合决策
选举的核心机制
1. 选举资格条件
节点要成为主节点,必须满足以下所有条件:
javascript
// 选举资格检查逻辑
function isEligibleForPrimary(node) {
return (
node.priority > 0 && // 优先级 > 0
!node.hidden && // 不是隐藏节点
node.state === "SECONDARY" && // 当前是从节点
node.health === 1 && // 节点健康
isUpToDate(node) && // 数据是最新的
canReachMajority(node) // 能连接到大多数节点
);
}2. 优先级相同时的选举规则
当两个从节点优先级相同时,选举按以下决策顺序进行:
bash
选举决策树:
1. 数据最新程度 (optime) ← 最重要的因素
├── 如果A的数据比B新 → A胜出
└── 如果数据相同新 → 进入下一步
2. 节点运行时间 (uptime)
├── 如果A运行更稳定 → A胜出
└── 如果运行时间相近 → 进入下一步
3. 节点ID (_id字段)
├── _id较小的节点胜出
└── 这是最终的决胜条件3. 实际选举过程示例
场景:1主2从,优先级相同
javascript
// 初始状态
节点A: PRIMARY (优先级=1, optime=100)
节点B: SECONDARY (优先级=1, optime=99) // 数据稍旧
节点C: SECONDARY (优先级=1, optime=100) // 数据最新
// 节点A故障后的选举过程:
1. 节点B和C检测到A故障
2. 检查选举资格:
- 节点B: optime=99 (落后) → 无资格
- 节点C: optime=100 (最新) → 有资格
3. 节点C发起选举,请求投票
4. 投票结果:
- 节点B投票给C (因为C数据更新)
- 节点C投票给自己
- 总票数: 2票 (达到大多数)
5. 节点C成为新的PRIMARY4. 如何保证一定能选出主节点
投票机制保证:
javascript
// 在3节点环境中
总投票权 = 3票
大多数要求 = 2票
// 可能的投票分布:
场景1: 1个候选节点获得2票 → 选举成功
场景2: 无候选节点获得2票 → 选举失败,等待重试
// 重试机制:选举会持续进行直到成功
// 随机延迟:节点在发起选举前会随机等待0-1秒,避免同时发起5. 查看选举相关信息的命令
javascript
// 查看副本集状态(重点关注optime)
rs.status()
// 输出关键字段示例:
{
"members": [
{
"name": "nodeB:27017",
"stateStr": "SECONDARY",
"optime": { "ts": Timestamp(1621000000, 1), "t": 1 },
"optimeDate": ISODate("2024-01-15T10:00:00Z"),
"lastHeartbeat": ISODate("2024-01-15T10:00:05Z")
},
{
"name": "nodeC:27017",
"stateStr": "PRIMARY",
"optime": { "ts": Timestamp(1621000005, 1), "t": 1 },
"optimeDate": ISODate("2024-01-15T10:00:05Z")
}
]
}
// 查看选举统计
db.adminCommand({replSetGetStatus: 1}).electionCandidateMetrics6. 生产环境最佳实践
合理设置优先级:
javascript
// 建议:设置不同的优先级,引导选举方向
var config = rs.conf()
config.members[0].priority = 3 // 首选主节点
config.members[1].priority = 2 // 备选主节点
config.members[2].priority = 1 // 最后选择
rs.reconfig(config)监控选举健康:
bash
# 检查选举次数和原因
mongo --eval "
db.adminCommand({replSetGetStatus: 1}).elections &&
db.adminCommand({replSetGetStatus: 1}).lastElectionReason
"
# 检查复制延迟
mongo --eval "db.printSlaveReplicationInfo()"- 投票不只看优先级:数据新旧程度(optime)是首要决定因素
- 保证选举成功:通过数据新旧比较 + 运行时间 + 节点ID 的层级决策
- 获得2票的保证:数据最新的节点会自动获得其他落后节点的投票
- 绝对能选出主节点:重试机制 + 随机延迟确保最终会成功选举
在1主2从相同优先级的情况下,数据最新的从节点一定会成为新的主节点,因为另一个数据较旧的节点会主动投票给它。这就是MongoDB复制集高可用性的核心保证
11. 复制集进行主从切换时业务中的解决方案(示例基于lua-skynet版本)
常见的解决方案对比
| 方案 | 原理 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 连接字符串 | 在URI中列出所有节点 | 简单,驱动自动处理 | 依赖驱动支持 |
| 服务发现 | 通过中间件发现主节点 | 灵活,可自定义逻辑 | 增加架构复杂度 |
| 健康检查 | 业务层定期检查主节点 | 完全可控 | 实现复杂,有延迟 |
1. MongoDB驱动自动故障转移(推荐)
大多数MongoDB驱动都支持自动故障转移,只需在连接字符串中正确配置:
lua
-- Lua MongoDB驱动连接配置(以lua-mongo为例)
local mongo = require("mongo")
local uri = "mongodb://192.168.1.10:27017,192.168.1.11:27017,192.168.1.12:27017/testdb?replicaSet=rs0&readPreference=primaryPreferred"
local client = mongo.Client(uri)
local db = client:getDatabase("testdb")连接字符串关键参数:
- replicaSet=rs0:指定复制集名称
- readPreference=primaryPreferred:优先读主节点,主不可用时读从节点
- w=majority:写确认需要大多数节点确认
- maxStalenessSeconds=90:从节点数据最大延迟时间
2. Skynet框架中的具体实现
方案一:基于lua-resty-mongol驱动的自动重连
lua
-- mongodb_pool.lua
local skynet = require "skynet"
local mongol = require "resty.mongol"
local MongoDB = {}
local conn_pool = {}
local current_primary = nil
function MongoDB:init()
-- 初始化连接池,包含所有节点
local nodes = {
{host = "192.168.1.10", port = 27017},
{host = "192.168.1.11", port = 27017},
{host = "192.168.1.12", port = 27017}
}
for _, node in ipairs(nodes) do
local conn = mongol:new()
local ok, err = conn:connect(node.host, node.port)
if ok then
table.insert(conn_pool, {
conn = conn,
host = node.host,
port = node.port,
is_primary = false
})
skynet.error(string.format("MongoDB connected: %s:%d", node.host, node.port))
else
skynet.error(string.format("MongoDB connect failed: %s:%d - %s",
node.host, node.port, err))
end
end
-- 启动主节点检测
self:start_primary_detection()
end
function MongoDB:start_primary_detection()
skynet.fork(function()
while true do
self:detect_primary()
skynet.sleep(500) -- 每5秒检测一次
end
end)
end
function MongoDB:detect_primary()
for _, node_info in ipairs(conn_pool) do
local conn = node_info.conn
local ok, result = pcall(function()
return conn:run_command("admin", {isMaster = 1})
end)
if ok and result and result.ismaster then
if current_primary ~= node_info.host then
skynet.error(string.format("Primary changed to: %s:%d",
node_info.host, node_info.port))
current_primary = node_info.host
end
node_info.is_primary = true
else
node_info.is_primary = false
end
end
end
function MongoDB:get_primary_connection()
-- 优先返回已知的主节点
for _, node_info in ipairs(conn_pool) do
if node_info.is_primary then
local ok, err = pcall(function()
-- 简单ping测试连接是否有效
node_info.conn:run_command("admin", {ping = 1})
return true
end)
if ok then
return node_info.conn
else
skynet.error(string.format("Primary connection failed: %s", err))
node_info.is_primary = false
end
end
end
-- 如果没有已知主节点,重新检测
self:detect_primary()
-- 再次尝试获取主节点
for _, node_info in ipairs(conn_pool) do
if node_info.is_primary then
return node_info.conn
end
end
-- 如果仍然没有主节点,抛出错误或返回第一个可用连接(用于读操作)
skynet.error("No primary node available!")
return conn_pool[1].conn -- 降级到从节点读取
end
function MongoDB:insert(collection, document)
local conn = self:get_primary_connection()
local ok, result = pcall(function()
local db = conn:get_db("testdb")
local col = db:get_col(collection)
return col:insert(document)
end)
if not ok then
skynet.error("Insert failed: " .. tostring(result))
-- 可以在这里实现重试逻辑
return false
end
return true
end
function MongoDB:find(collection, query)
local conn = self:get_primary_connection()
local ok, result = pcall(function()
local db = conn:get_db("testdb")
local col = db:get_col(collection)
return col:find(query)
end)
if not ok then
skynet.error("Find failed: " .. tostring(result))
return nil
end
return result
end
return MongoDB方案二:使用连接池和故障转移的完整服务
lua
-- mongodb_service.lua
local skynet = require "skynet"
local snax = require "snax"
local mongol = require "resty.mongol"
local MongoDBService = {}
function MongoDBService:init()
self.nodes = {
{host = "192.168.1.10", port = 27017, priority = 3},
{host = "192.168.1.11", port = 27017, priority = 2},
{host = "192.168.1.12", port = 27017, priority = 1}
}
self.connections = {}
self.current_primary = nil
self.retry_count = 0
self.max_retries = 3
self:init_connections()
self:start_health_check()
end
function MongoDBService:init_connections()
for _, node in ipairs(self.nodes) do
local conn = mongol:new()
conn:set_timeout(500) -- 5秒超时
local ok, err = conn:connect(node.host, node.port)
if ok then
self.connections[node.host] = {
conn = conn,
host = node.host,
port = node.port,
priority = node.priority,
healthy = true,
last_check = skynet.time()
}
skynet.error(string.format("MongoDB connected: %s:%d", node.host, node.port))
else
skynet.error(string.format("MongoDB connect failed: %s:%d - %s",
node.host, node.port, err))
end
end
end
function MongoDBService:start_health_check()
skynet.fork(function()
while true do
self:check_primary_status()
skynet.sleep(300) -- 每3秒检查一次
end
end)
end
function MongoDBService:check_primary_status()
local candidates = {}
for host, info in pairs(self.connections) do
if info.healthy then
local ok, result = pcall(function()
return info.conn:run_command("admin", {isMaster = 1})
end)
if ok and result and result.ismaster then
table.insert(candidates, {
host = host,
priority = info.priority,
optime = result.lastWrite and result.lastWrite.opTime or {ts = 0}
})
if self.current_primary ~= host then
skynet.error(string.format("Primary switched to: %s", host))
self.current_primary = host
self.retry_count = 0 -- 重置重试计数
end
else
info.healthy = false
skynet.error(string.format("Node %s is unhealthy", host))
if self.current_primary == host then
self.current_primary = nil
end
end
end
end
-- 如果没有主节点,选择优先级最高的健康节点
if not self.current_primary and #candidates > 0 then
table.sort(candidates, function(a, b)
if a.priority ~= b.priority then
return a.priority > b.priority
else
return a.optime.ts > b.optime.ts
end
end)
self.current_primary = candidates[1].host
skynet.error(string.format("Elected new primary: %s", self.current_primary))
end
end
function MongoDBService:get_connection()
if self.current_primary and self.connections[self.current_primary].healthy then
return self.connections[self.current_primary].conn
end
-- 降级策略:返回任意健康连接
for host, info in pairs(self.connections) do
if info.healthy then
skynet.error(string.format("Using fallback connection: %s", host))
return info.conn
end
end
error("No available MongoDB connections")
end
-- 业务方法
function MongoDBService:insert(collection, data)
local conn = self:get_connection()
for i = 1, self.max_retries do
local ok, result = pcall(function()
local db = conn:get_db("testdb")
local col = db:get_col(collection)
return col:insert(data)
end)
if ok then
return true, result
else
skynet.error(string.format("Insert attempt %d failed: %s", i, result))
if i < self.max_retries then
skynet.sleep(100) -- 等待1秒后重试
self:check_primary_status() -- 重新检查状态
conn = self:get_connection()
end
end
end
return false, "All retry attempts failed"
end
function MongoDBService:find(collection, query, options)
local conn = self:get_connection()
local ok, result = pcall(function()
local db = conn:get_db("testdb")
local col = db:get_col(collection)
return col:find(query, options or {})
end)
if ok then
return result
else
skynet.error("Find failed: " .. tostring(result))
return nil
end
end
-- Snax服务接口
function response.insert(collection, data)
return MongoDBService:insert(collection, data)
end
function response.find(collection, query, options)
return MongoDBService:find(collection, query, options)
end
function response.get_primary_info()
local primary = MongoDBService.current_primary
if primary then
return {
host = primary,
healthy = MongoDBService.connections[primary].healthy
}
end
return nil
end
function init()
MongoDBService:init()
end
function exit()
-- 清理连接
for _, info in pairs(MongoDBService.connections) do
if info.conn then
info.conn:close()
end
end
end3. 在业务中使用MongoDB服务
lua
-- user_service.lua
local skynet = require "skynet"
local UserService = {}
function UserService:init()
-- 通过snax调用MongoDB服务
self.mongo = snax.uniqueservice("mongodb_service")
end
function UserService:create_user(user_data)
local ok, result = self.mongo.req.insert("users", user_data)
if not ok then
skynet.error("Failed to create user: " .. tostring(result))
return false, "Database error"
end
return true, "User created"
end
function UserService:get_user(user_id)
local result = self.mongo.req.find("users", {_id = user_id})
if result and result:has_next() then
return result:next()
end
return nil
end
function UserService:get_all_users()
local result = self.mongo.req.find("users", {})
local users = {}
while result and result:has_next() do
table.insert(users, result:next())
end
return users
end
return UserService4. 配置和启动
lua
-- config.lua
-- MongoDB配置
config.mongodb = {
nodes = {
{host = "192.168.1.10", port = 27017, priority = 3},
{host = "192.168.1.11", port = 27017, priority = 2},
{host = "192.168.1.12", port = 27017, priority = 1}
},
db_name = "testdb",
timeout = 500,
max_retries = 3,
health_check_interval = 300 -- 3秒
}
lua
-- main.lua
local skynet = require "skynet"
skynet.start(function()
-- 启动MongoDB服务
local mongo_service = skynet.uniqueservice("mongodb_service")
-- 启动业务服务
skynet.uniqueservice("user_service")
skynet.error("MongoDB replication-aware service started")
end)1. 首选方案 :使用支持自动故障转移的驱动和连接字符串
2. 备选方案:在业务层实现健康检查和连接管理