netbuf结构体
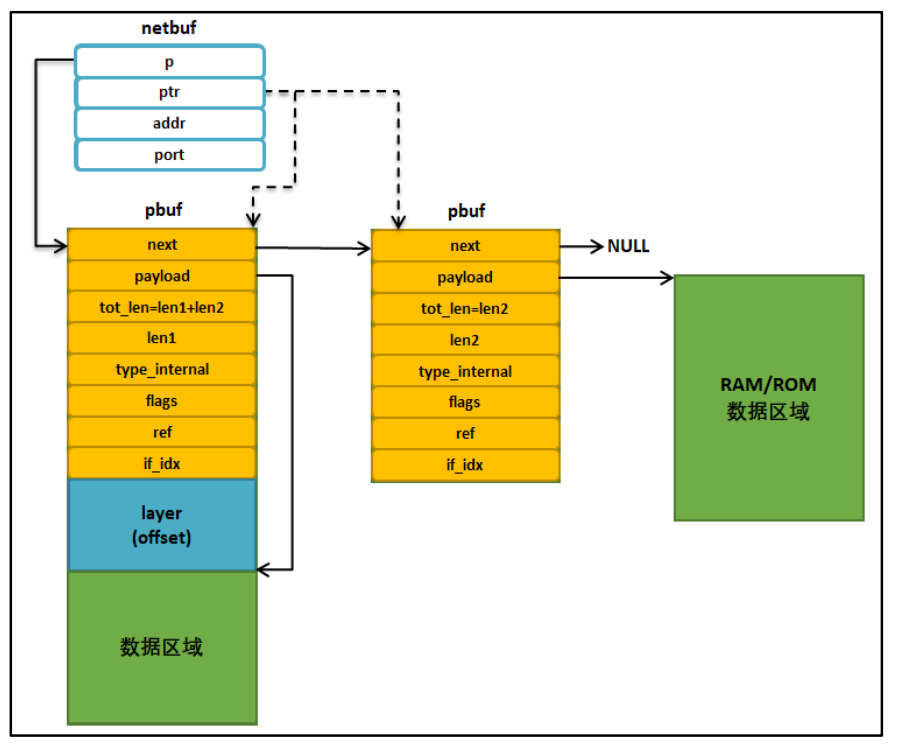
netbuf是lwip中对接收和发送数据的更高一层封装,记录了数据发送方的IP地址和端口号,netbuf结构体如下:
c
/** "Network buffer" - contains data and addressing info */
struct netbuf {
struct pbuf *p, *ptr;
ip_addr_t addr;
u16_t port;
};其中addr是ip地址,port是端口号,ip地址对应的是一个设备,端口号对应一个设备里的一个线程。
指针p指向首个pbuf,是不可改变的,指针ptr可以通过函数netbuf_next()和函数netbuf_first()来移动。用函数netbuf_data(struct netbuf *buf, void **dataptr, u16_t *len)获取ptr指向的pbuf中数据的地址dataptr,并获取其数据量len。
netbuf_new()
申请一个新的netbuf结构体内存空间并返回。
c
struct
netbuf *netbuf_new(void)
{
struct netbuf *buf;
buf = (struct netbuf *)memp_malloc(MEMP_NETBUF);
if (buf != NULL) {
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(struct netbuf));
}
return buf;
}netbuf_delete()
删除一个netbuf结构体内存空间,如果删除的netbuf中ptr或p指向的pbuf有数据,那么将对应的pbuf也释放掉。
c
void
netbuf_delete(struct netbuf *buf)
{
if (buf != NULL) {
if (buf->p != NULL) {
pbuf_free(buf->p);
buf->p = buf->ptr = NULL;
}
memp_free(MEMP_NETBUF, buf);
}
}netbuf_alloc()
为netbuf中ptr或p指向的pbuf申请一块指定大小的内存空间。如果当前netbuf中的pbuf存在数据,则先把数据释放掉。
c
void *
netbuf_alloc(struct netbuf *buf, u16_t size)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_alloc: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return NULL;);
/* Deallocate any previously allocated memory. */
if (buf->p != NULL) {
pbuf_free(buf->p);
}
buf->p = pbuf_alloc(PBUF_TRANSPORT, size, PBUF_RAM);
if (buf->p == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
LWIP_ASSERT("check that first pbuf can hold size",
(buf->p->len >= size));
buf->ptr = buf->p;
return buf->p->payload;
}netbuf_free()
将netbuf中的pbuf的内存空间释放掉。
c
void
netbuf_free(struct netbuf *buf)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_free: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return;);
if (buf->p != NULL) {
pbuf_free(buf->p);
}
buf->p = buf->ptr = NULL;
#if LWIP_CHECKSUM_ON_COPY
buf->flags = 0;
buf->toport_chksum = 0;
#endif /* LWIP_CHECKSUM_ON_COPY */
}netbuf_ref()
与netbuf_alloc()类似,只不过这个是申请一个空的pbuf,然后pbuf的数据指针payload指向用户传入的数据地址。
reference:引用,指向。
c
err_t
netbuf_ref(struct netbuf *buf, const void *dataptr, u16_t size)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_ref: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
if (buf->p != NULL) {
pbuf_free(buf->p);
}
buf->p = pbuf_alloc(PBUF_TRANSPORT, 0, PBUF_REF);
if (buf->p == NULL) {
buf->ptr = NULL;
return ERR_MEM;
}
((struct pbuf_rom *)buf->p)->payload = dataptr;
buf->p->len = buf->p->tot_len = size;
buf->ptr = buf->p;
return ERR_OK;
}netbuf_chain()
将指针tail指向的pbuf添加到h指向的head链表的末尾,然后tail会被释放
pbuf_cat()的cat是Concatenate的缩写,中文意思是 "连接" 或 "拼接"。
c
void
netbuf_chain(struct netbuf *head, struct netbuf *tail)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_chain: invalid head", (head != NULL), return;);
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_chain: invalid tail", (tail != NULL), return;);
pbuf_cat(head->p, tail->p);
head->ptr = head->p;
memp_free(MEMP_NETBUF, tail);
}netbuf_data()
将netbuf中ptr指向的pbuf里数据的起始地址填写到dataptr,并将数据长度填写到len。
netbuf中的p指向的是pbuf链表的首个pbuf,ptr指向的是当前pbuf,如果想移动ptr可以用netbuf_next()函数或者netbuf_first()函数。
c
err_t
netbuf_data(struct netbuf *buf, void **dataptr, u16_t *len)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_data: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_data: invalid dataptr", (dataptr != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_data: invalid len", (len != NULL), return ERR_ARG;);
if (buf->ptr == NULL) {
return ERR_BUF;
}
*dataptr = buf->ptr->payload;
*len = buf->ptr->len;
return ERR_OK;
}netbuf_next()
将netbuf的ptr移动到pbuf链表的下一个pbuf。
c
s8_t
netbuf_next(struct netbuf *buf)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_next: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return -1;);
if (buf->ptr->next == NULL) {
return -1;
}
buf->ptr = buf->ptr->next;
if (buf->ptr->next == NULL) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}netbuf_first()
将netbuf的ptr指向pbuf链表的首个pbuf,也就是p指向的pbuf。
c
void
netbuf_first(struct netbuf *buf)
{
LWIP_ERROR("netbuf_first: invalid buf", (buf != NULL), return;);
buf->ptr = buf->p;
}