Xilinx FIFO的两种读模式
目标
本文主要是对 Xilinx FIFO中的两种读模式:Standard 与 FWFT 模式进行简单的分析。弄清楚在设置不同的读写长度下,两种模式内部信号是如何变化的,有什么差异。便于后续使用这个IP
FWFT模式相比Strandard模式的特点
在First-Word-Fall-Through(FWFT)读模式下,用户可以预先的查看FIFO中下一个数据内容。读潜伏期为0
而在Standard模式下,用户在发起读使能后,经过1个或者2个读潜伏期后,才能读取数据。读潜伏期>1
实验配置
实验环境在Vivado 2021. 1 下进行,使用modelsim 作为仿真工具
本文设置FIFO数据宽度为 16 位,数据深度为256 , 同时设置了一些常用的信号,具体配置如下:
对于 FWFT模式的实验配置如下
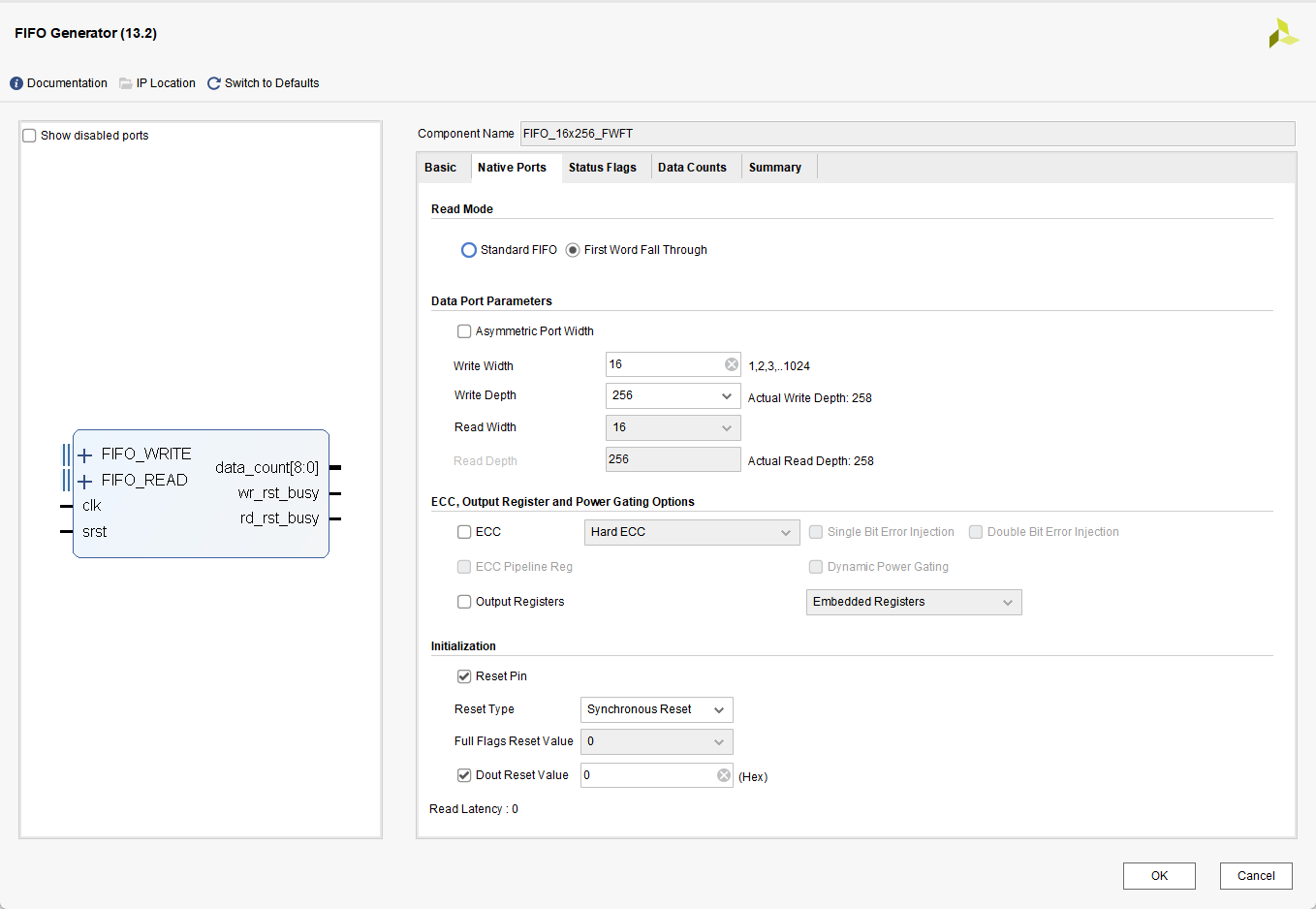
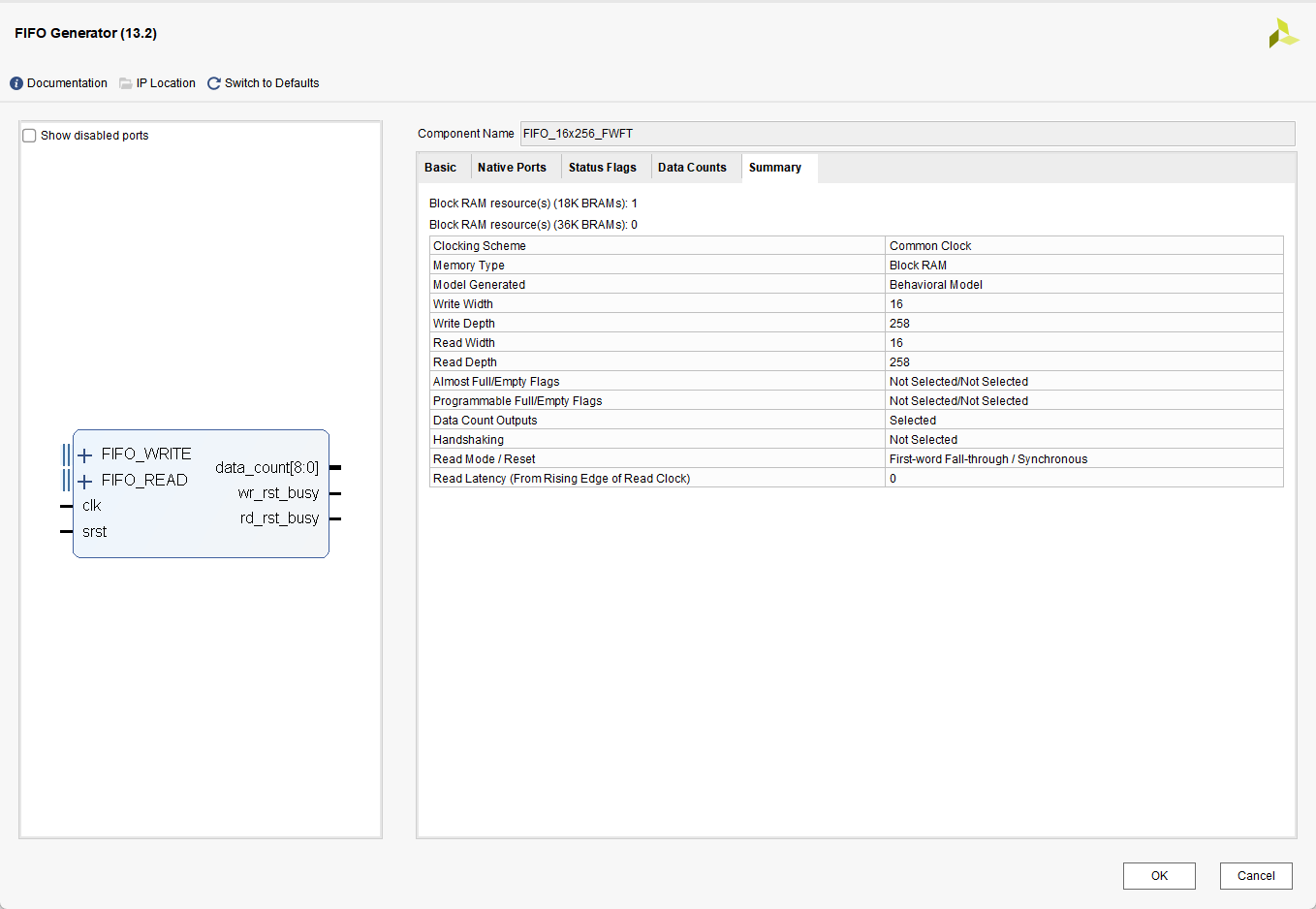
对于 Standard模式的实验配置如下
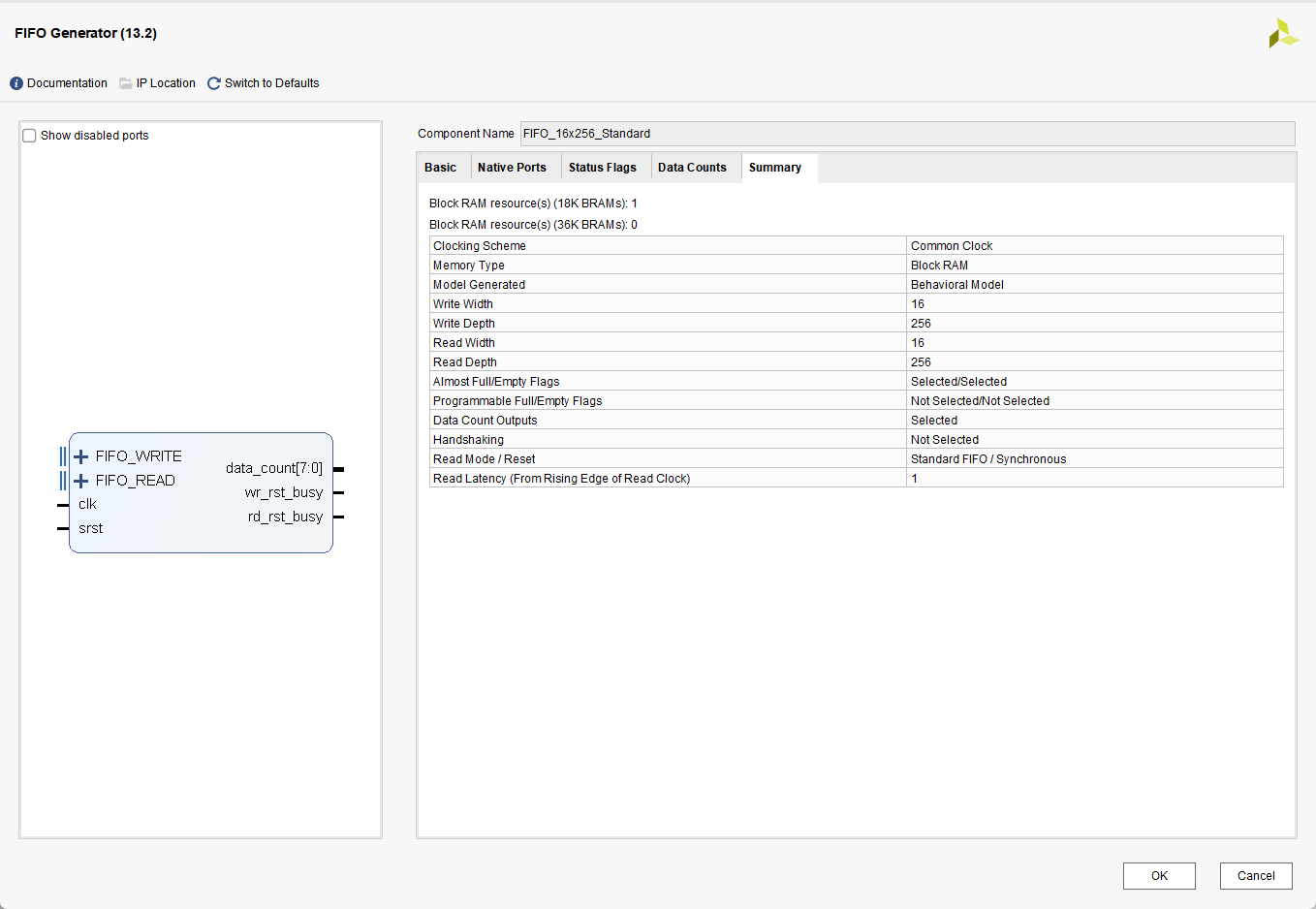
从两种模式配置的总结页面可以看到二者的有
1. 对于FWFT模式 读潜伏期为0 ,而Standard模式 读潜伏期为1
2. 对于FWFT模式,数据深度相比设置的256, 增加至了258。而Standard模式没有发生改变
实验代码
在代码中,对FIFO的一些临界情况,以及普通情况进行了测试,具体如下
C
`timescale 1ns/1ps
module tb_fifo();
reg i_clk ;
reg i_rst ;
initial begin
i_clk = 0;
end
always #5 i_clk = ~i_clk;
reg [15:0] i_din ;
reg i_din_valid ;
reg i_rd_en ;
wire [15:0] w_fifo_fwft_dout ;
wire w_fifo_fwft_empty ;
wire w_fifo_fwft_full ;
wire [8:0] w_fifo_fwft_count ;
wire w_fifo_fwft_wrbusy ;
wire w_fifo_fwft_rdbusy ;
wire w_fifo_fwft_almost_full ;
wire w_fifo_fwft_almost_empty;
wire [15:0] w_fifo_standard_dout ;
wire w_fifo_standard_full ;
wire w_fifo_standard_empty ;
wire [7:0] w_fifo_standard_count ;
wire w_fifo_standard_wrbusy ;
wire w_fifo_standard_rdbusy ;
wire w_fifo_standard_almost_full ;
wire w_fifo_standard_almost_empty;
initial begin
gen_rst(10);
end
initial begin
i_din = 0;
i_din_valid = 0;
i_rd_en = 0;
wait(~i_rst);
@(posedge i_clk);
//读写一个数据
gen_din(1);
repeat(2) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_rd_en(1);
//读写两个数据
repeat(5) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_din(2);
repeat(2) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_rd_en(2);
//读写255个数据
repeat(5) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_din(255);
repeat(2) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_rd_en(255);
//读写256个数据
repeat(5) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_din(256);
repeat(2) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_rd_en(256);
//读写257个数据
repeat(5) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_din(257);
repeat(2) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_rd_en(257);
//读写258个数据
repeat(5) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_din(258);
repeat(2) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_rd_en(258);
//读写259个数据
repeat(5) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_din(259);
repeat(2) @(posedge i_clk);
gen_rd_en(259);
end
task gen_rst(input [15:0] Tcnt);
begin
i_rst = 1;
repeat(Tcnt) @(posedge i_clk);
i_rst = 0;
end
endtask
task gen_rd_en(input [15:0] Tcnt);
begin
i_rd_en = 1 ;
repeat(Tcnt) @(posedge i_clk);
i_rd_en = 0 ;
end
endtask
task gen_din(input [15:0] data);
integer i;
begin
for(i = 1 ; i <= data ; i = i + 1)
begin
i_din = i;
i_din_valid = 1;
@(posedge i_clk);
end
i_din = 0;
i_din_valid = 0;
end
endtask
FIFO_16x256_FWFT FIFO_16x256_FWFT_U0 (
.clk (i_clk ),// input wire clk
.srst (i_rst ),// input wire srst
.din (i_din ),// input wire [17 : 0] din
.wr_en (i_din_valid ),// input wire wr_en
.rd_en (i_rd_en ),// input wire rd_en
.dout (w_fifo_fwft_dout ),// output wire [17 : 0] dout
.full (w_fifo_fwft_full ),// output wire full
.almost_full (w_fifo_fwft_almost_full ),// output wire almost_full
.empty (w_fifo_fwft_empty ),// output wire empty
.almost_empty (w_fifo_fwft_almost_empty ),// output wire almost_empty
.data_count (w_fifo_fwft_count ),// output wire [10 : 0] data_count
.wr_rst_busy (w_fifo_fwft_wrbusy ),// output wire wr_rst_busy
.rd_rst_busy (w_fifo_fwft_rdbusy ) // output wire rd_rst_busy
);
FIFO_16x256_Standard FIFO_16x256_Standard_U0 (
.clk (i_clk ),// input wire clk
.srst (i_rst ),// input wire srst
.din (i_din ),// input wire [17 : 0] din
.wr_en (i_din_valid ),// input wire wr_en
.rd_en (i_rd_en ),// input wire rd_en
.dout (w_fifo_standard_dout ),// output wire [17 : 0] dout
.full (w_fifo_standard_full ),// output wire full
.almost_full (w_fifo_standard_almost_full ),// output wire almost_full
.empty (w_fifo_standard_empty ),// output wire empty
.almost_empty (w_fifo_standard_almost_empty ),// output wire almost_empty
.data_count (w_fifo_standard_count ),// output wire [9 : 0] data_count
.wr_rst_busy (w_fifo_standard_wrbusy ),// output wire wr_rst_busy
.rd_rst_busy (w_fifo_standard_rdbusy ) // output wire rd_rst_busy
);
endmodule实验分析
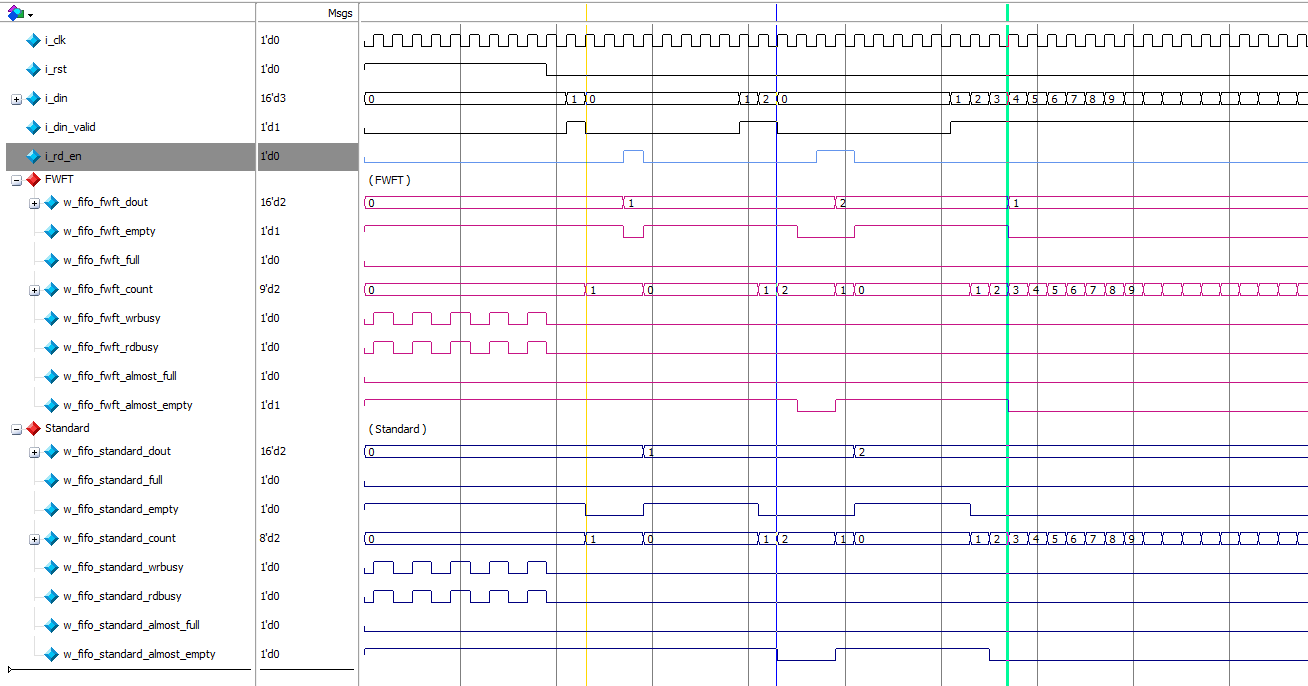
i_din_valid 作为两个FIFO的写入使能,可以观察到写入一个数据后,对于Standard模式 empty信号立即拉低,而对于FWFT模式empty信号并不会立即拉低。当写入三个数据后,FWFT模式下的empty信号才拉低,也可以理解为FWFT模式下,写入数据后延迟两个时钟周期empty才会拉低
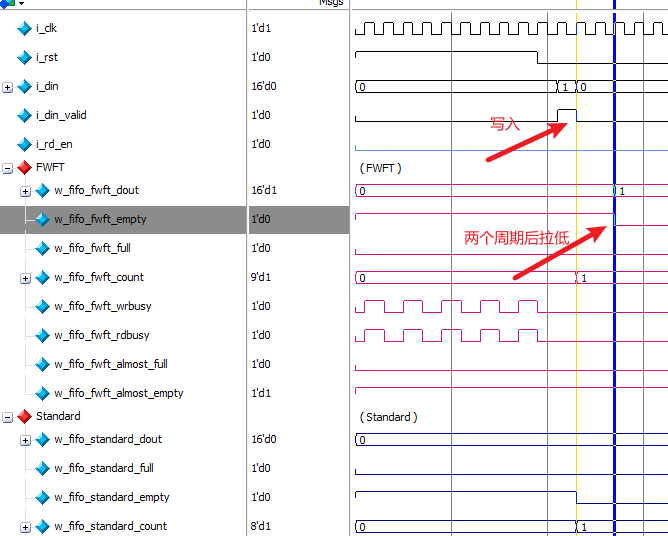
将读写的周期加大后,可以看到确实如此。
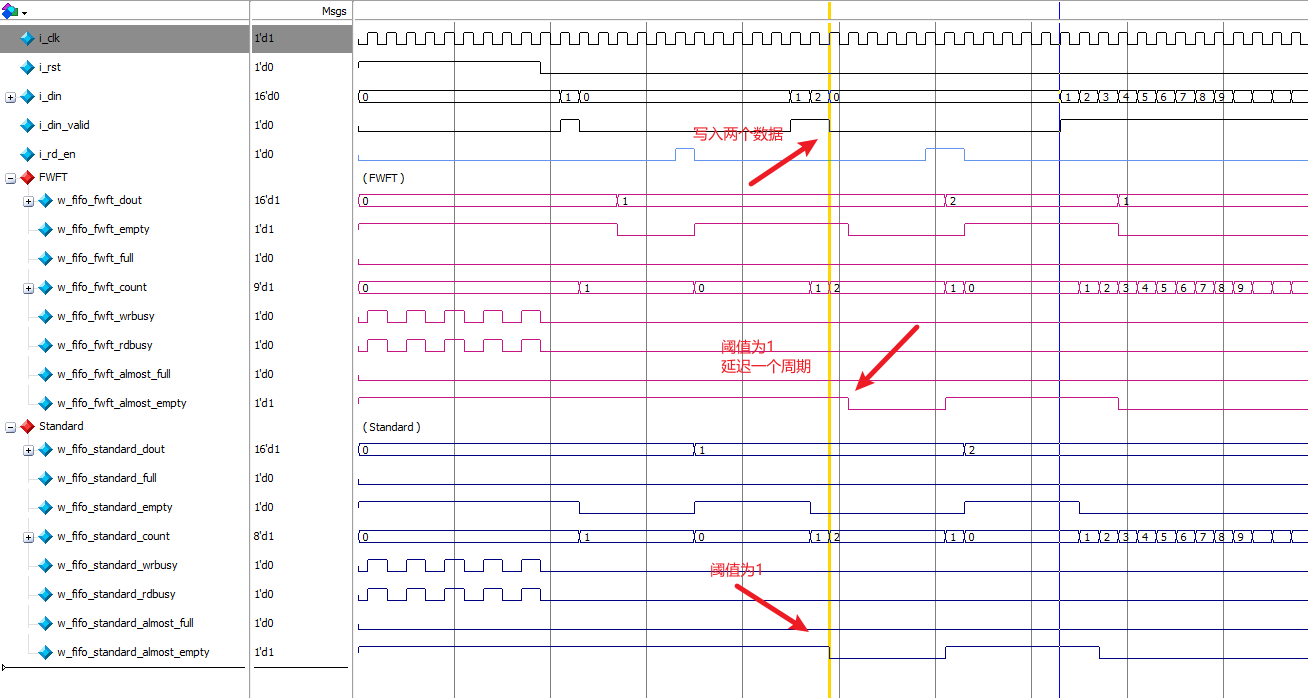
写入两个数据后,对于Standard模式,almost_empty 会拉低,说明几乎空信号 最低的阈值是1。对于FWFT模式,almost_empty 在延迟一个周期后才会拉低,说明几乎空信号 最低的阈值也是1,或者可以理解为在连续写入的过程中,FWFT模式下,几乎空信号 最低的阈值是2
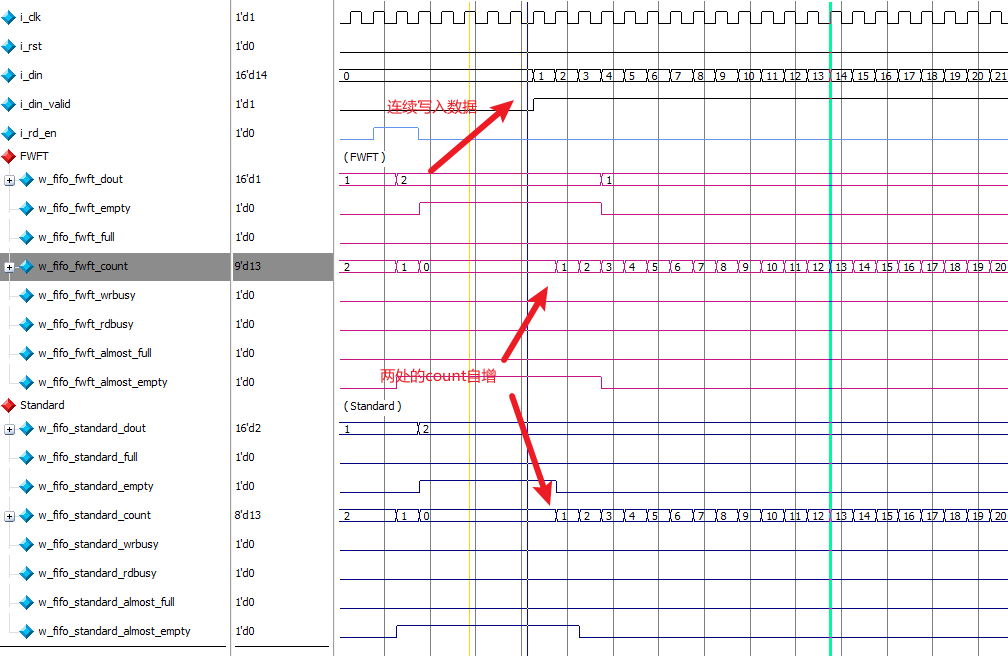
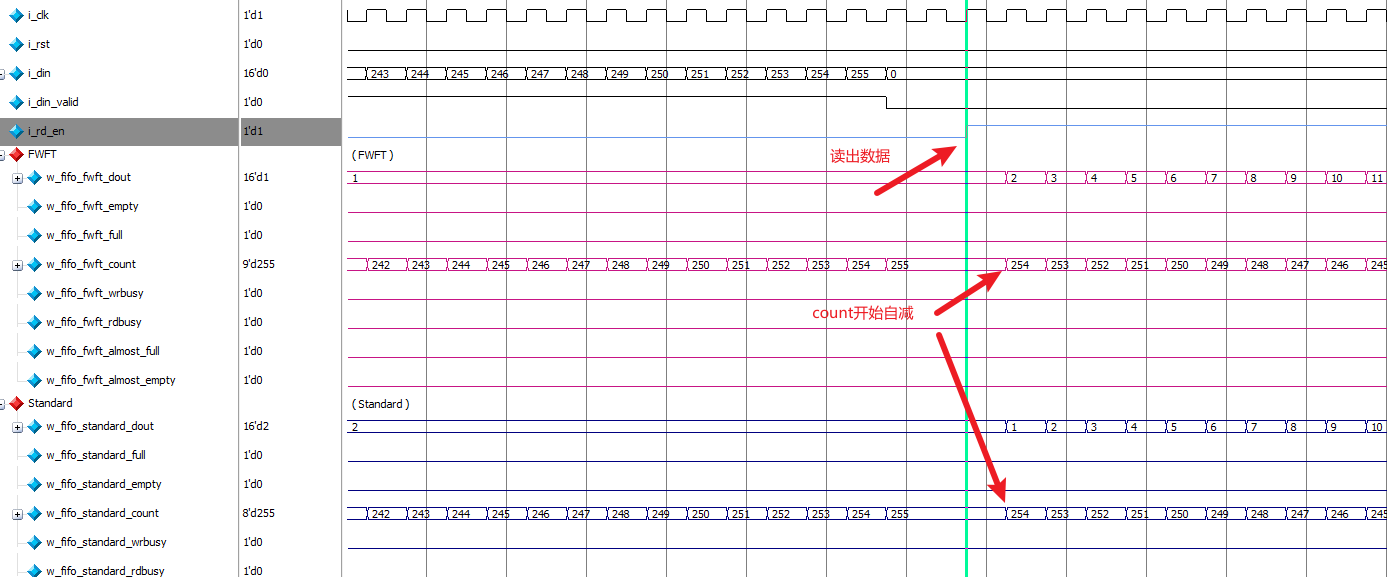
对于count信号 ,两种模式下写入时都会开始自增,读出数据时开始自减。
同时也可以看到在FWFT模式下,dout 输出与i_rd_en 读使能是同步的
而在Standard模式下,dout 输出与i_rd_en 读使能相差一个时钟周期。
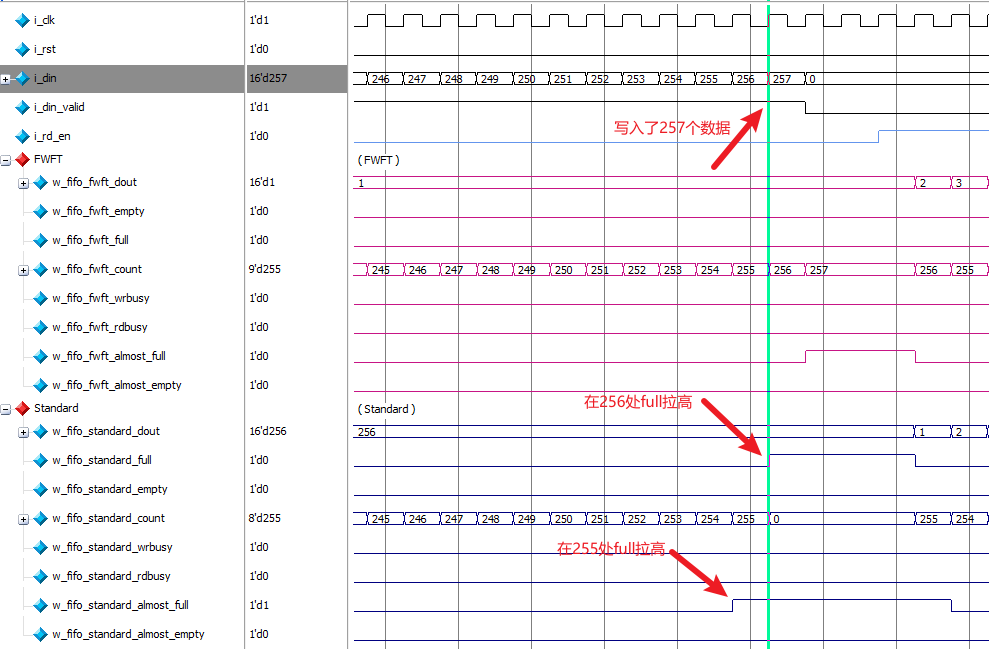
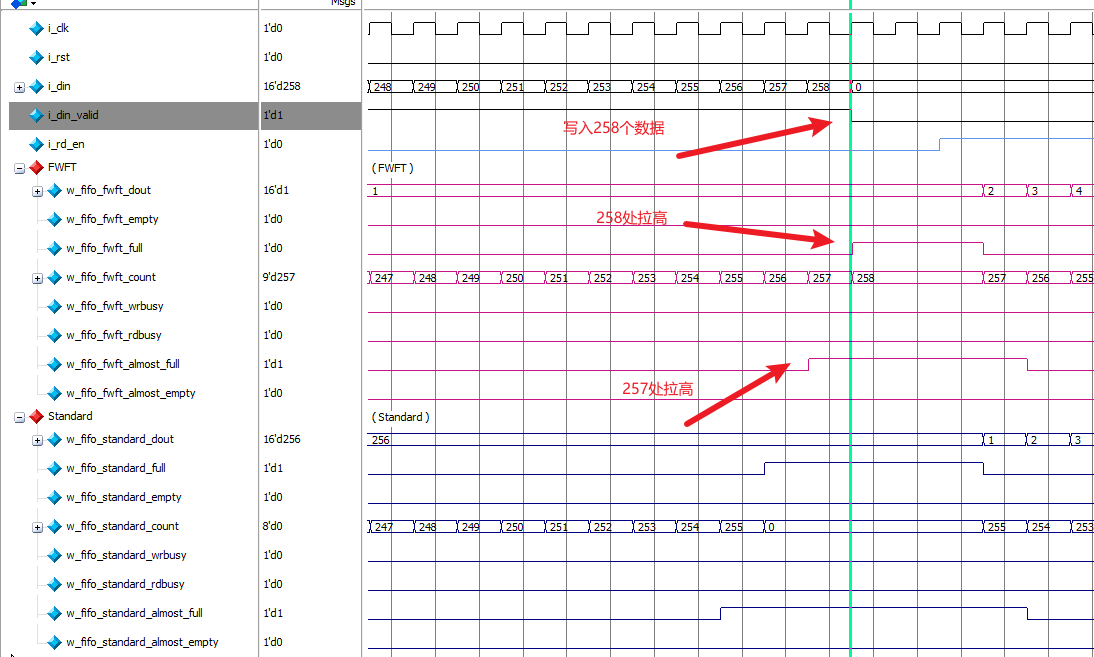
配置完成时,在IP的总结页面上可以看到Standard模式下最大的数据深度为256 ,在波形图中可以看到当写入257个数据时,full信号 在256处被拉高了,而almost_full信号 在255处被拉高。
在FWFT模式下最大的数据深度为258 ,在波形图中可以看到当写入258个数据时,full信号 在258处被拉高了,而almost_full信号 在257处被拉高。
两种模式下,full信号 都是在写入数据最大深度后立即拉低,almost_full信号阈值都是1
总结
| 信号 | FWFT模式 | Standard模式 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 读潜伏期 | 0 | 1 | 一般详细的数值可以看配置界面的总结部分 |
| dout | 用户可以提前看到下一个数据的值,数据相较读使能没有延迟 | 需要等待读使能的触发,数据相较读使能延迟一个时钟周期 | 无 |
| full | 在写入数据最大深度后立即拉低 | 在写入数据最大深度后立即拉低 | 无 |
| empty | 写入数据后 ,延迟两个时钟周期拉低或写入三个数据后拉低 | 数据写入后,信号立即拉低 | 无 |
| almost_full | 阈值为1,写入最大数据深度-1时拉高 | 阈值为1,写入最大数据深度-1时拉高 | 无 |
| almost_empty | 阈值为1,写入两个数据后延迟一个周期后才会拉低或连续写入下,阈值为2 | 阈值为1,写入两个数据后信号拉低 | 无 |
| data_cout | 写时自增,读时自减 | 写时自增,读时自减 | 无 |