文章目录
- [一. 力扣 [1926. 迷宫中离入口最近的出口](https://leetcode.cn/problems/nearest-exit-from-entrance-in-maze/description/)](#一. 力扣 1926. 迷宫中离入口最近的出口)
-
- [1. 题目](#1. 题目)
- [2. 算法原理](#2. 算法原理)
- [3. 代码](#3. 代码)
- [二. 力扣 [433. 最小基因变化](https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-genetic-mutation/description/)](#二. 力扣 433. 最小基因变化)
-
- [1. 题目](#1. 题目)
- [2. 算法原理](#2. 算法原理)
- [3. 代码](#3. 代码)
- [三. 力扣 [127. 单词接龙](https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-ladder/description/)](#三. 力扣 127. 单词接龙)
-
- [1. 题目](#1. 题目)
- [2. 算法原理](#2. 算法原理)
- [3. 代码](#3. 代码)
- [四. 力扣 [542. 01 矩阵](https://leetcode.cn/problems/01-matrix/description/)](#四. 力扣 542. 01 矩阵)
-
- [1. 题目解析](#1. 题目解析)
- [2. 算法原理](#2. 算法原理)
- [3. 代码](#3. 代码)
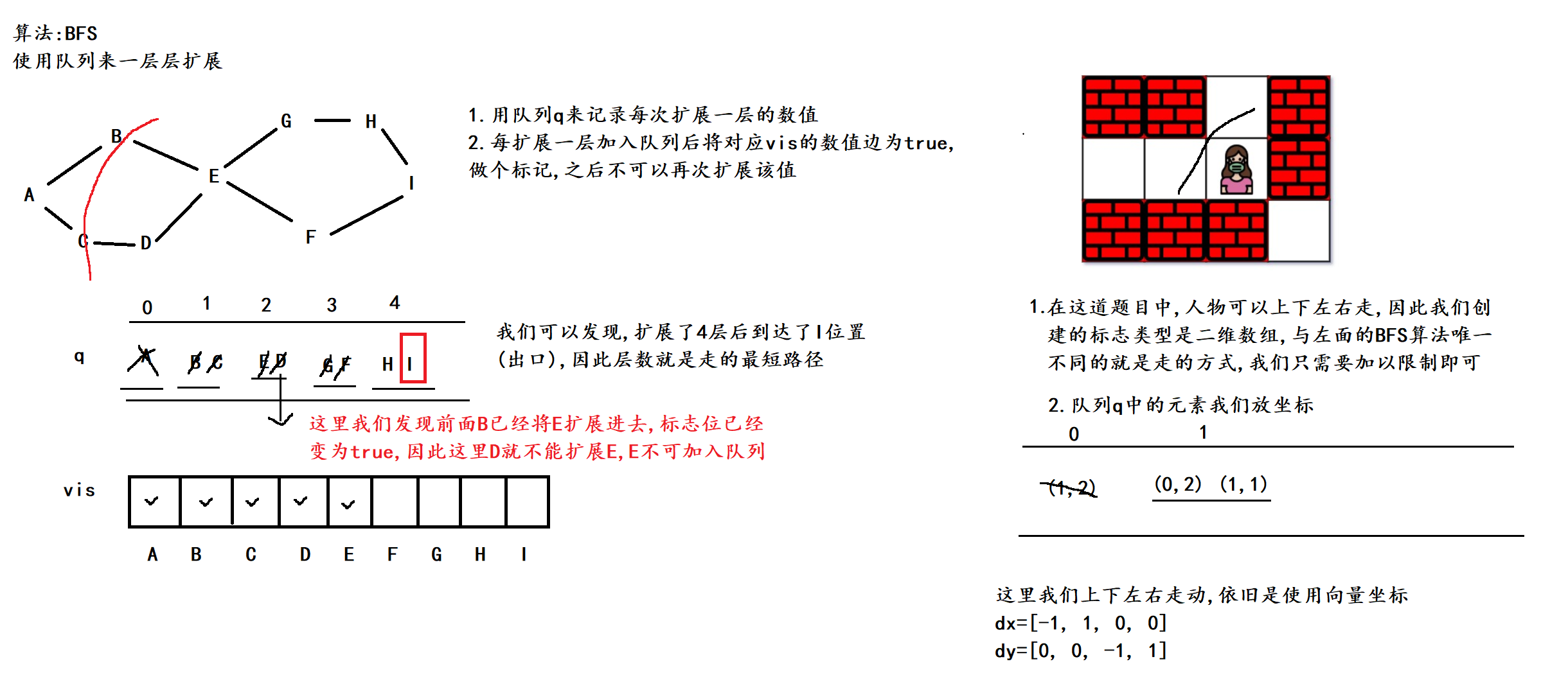
一. 力扣 1926. 迷宫中离入口最近的出口
1. 题目
这道题可是把小编害惨了,因为写完上一篇BFS解决洪水问题后,我就去切换动态规划换换脑子,这一换就出问题了,导致BFS解决的方法忘光了,这里给大家劝解,做一个系列题目的时候最好就做完,不然到时候忘记太快,会花费更多时间...
2. 算法原理
3. 代码
java
int[] dx = new int[]{-1, 1, 0, 0};
int[] dy = new int[]{0, 0, -1, 1};
public int nearestExit(char[][] maze, int[] entrance) {
int m = maze.length;
int n = maze[0].length;
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[m][n];
vis[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = true;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(entrance[0]);
q.offer(entrance[1]);
int count = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
count++;
while (size > 0) {
int a = q.poll();
int b = q.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = dx[i] + a;
int y = dy[i] + b;
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && maze[x][y] == '.' && !vis[x][y]) {
if (x == 0 || x == m - 1 || y == 0 || y == n - 1) {
return count;
}
q.offer(x);
q.offer(y);
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
size -= 2;
}
}
return -1;
}二. 力扣 433. 最小基因变化
1. 题目
2. 算法原理
3. 代码
java
char[] chs = { 'A', 'C', 'G', 'T' };
public int minMutation(String startGene, String endGene, String[] bank) {
Set<String> hash = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> vis = new HashSet<>();
for (String s : bank) {
vis.add(s);
}
int n = startGene.length();
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(startGene);
hash.add(startGene);
int ret = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
ret++;
while (size > 0) {
String s = q.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append(s.substring(0, i));
stringBuilder.append(chs[j]);
if (i < n - 1) {
stringBuilder.append(s.substring(i + 1, n));
}
String tmp = stringBuilder.toString();
if (!hash.contains(tmp) && vis.contains(tmp)) {
if (tmp.equals(endGene)) {
return ret;
}
q.offer(tmp);
}
hash.add(tmp);
}
}
size--;
}
}
return -1;
}三. 力扣 127. 单词接龙
1. 题目
2. 算法原理
这道题和上一道题(最小基因变化)的题解原理很相似, 因此我们这里就简单叙述一下
3. 代码
java
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
Set<String> hash = new HashSet<>();
Set<String> vis = new HashSet<>();
for (String s : wordList) {
vis.add(s);
}
if (!vis.contains(endWord)) {
return 0;
}
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<>();
hash.add(beginWord);
q.offer(beginWord);
int ret = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
ret++;
while (size-- > 0) {
String ss = q.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length(); i++) {
char[] ch = ss.toCharArray();
for (char j = 'a'; j <= 'z'; j++) {
ch[i] = j;
String s = new String(ch);
if (!hash.contains(s) && vis.contains(s)) {
if (s.equals(endWord)) {
return ret;
}
q.offer(s);
}
hash.add(s);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
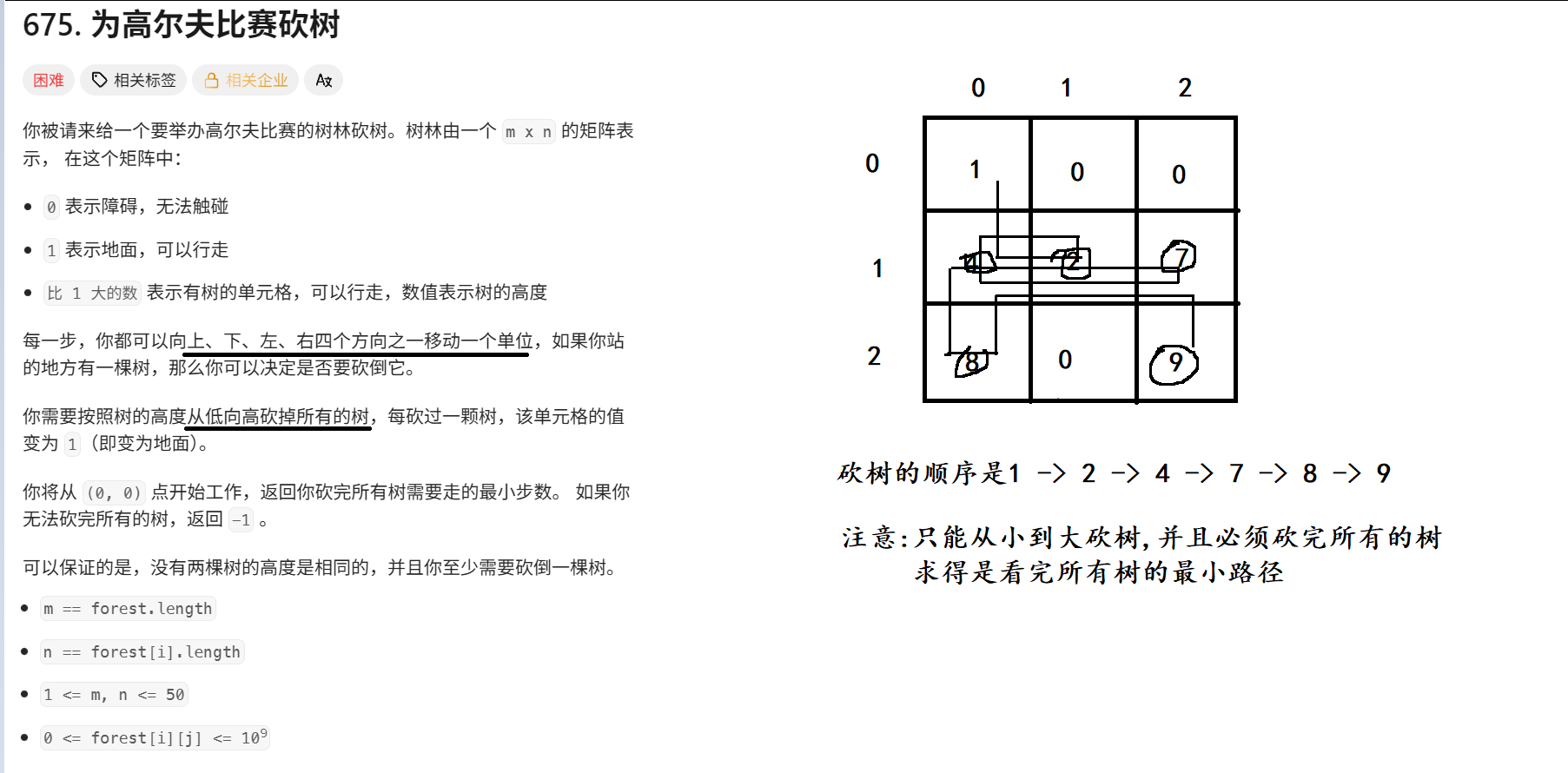
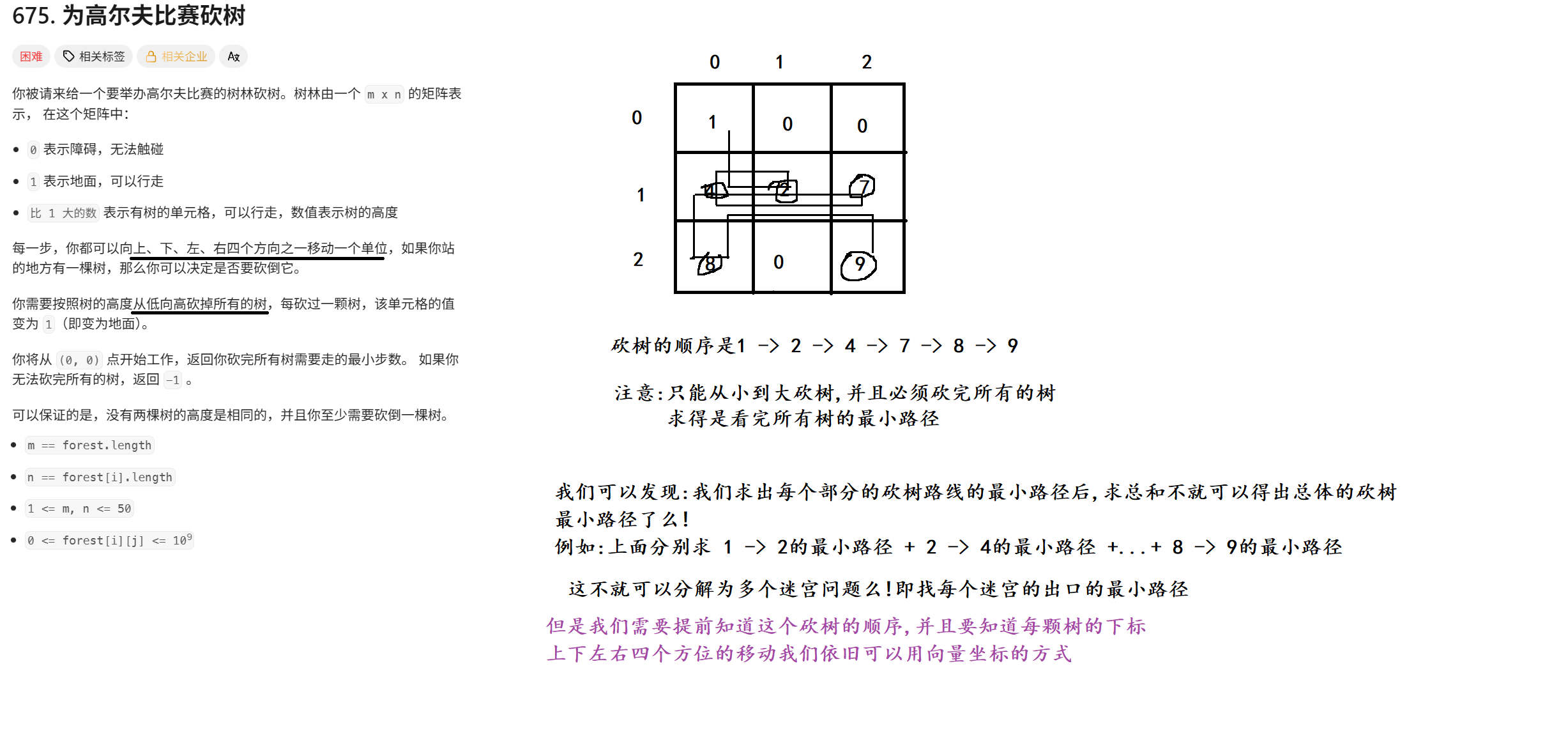
}四. 力扣 542. 01 矩阵
1. 题目解析
2. 算法原理
这里特别要注意, 说我们砍的是 > 1 的树, 数值为1的元素是平路, 当时小编就是把1也给砍了, 浪费了很长时间~
3. 代码
java
int[] dx = { 0, 0, 1, -1};
int[] dy = { 1, -1, 0, 0};
int m, n;
public int cutOffTree(List<List<Integer>> f) {
m = f.size();
n = f.get(0).size();
List<int[]> init = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (f.get(i).get(j) > 1) {
init.add(new int[] { i, j });
}
}
}
// 排序
Collections.sort(init, (a, b) -> {
return f.get(a[0]).get(a[1]) - f.get(b[0]).get(b[1]);
});
int ret = 0;
int bx = 0;
int by = 0;
for (int[] tree : init) {
int ex = tree[0];
int ey = tree[1];
int step = maze(f, bx, by, ex, ey);
if (step == -1) {
return -1;
}
ret += step;
bx = ex;
by = ey;
}
return ret;
}
int maze(List<List<Integer>> f, int bx, int by, int ex, int ey) {
if (bx == ex && by == ey) {
return 0;
}
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[m][n];
vis[bx][by] = true;
q.offer(new int[]{bx, by});
int ret = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
ret++;
while (size-- > 0) {
int[] tmp = q.poll();
int a = tmp[0];
int b = tmp[1];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int x = a + dx[i];
int y = b + dy[i];
if (x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n && !vis[x][y] && f.get(x).get(y) != 0 ) {
if (x == ex && y == ey) {
return ret;
}
q.offer(new int[]{x,y});
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}