

我用 Kingbase KES V9R3C15 的 JSON/JSONB 函数有段时间了,来跟大家唠唠~ 这两类函数用法差不多,JSONB 查起来更快,大数据量优先选它🤔 常用的有数组操作的 JSON_ARRAY、JSON_ARRAY_APPEND,构造对象的 JSON_BUILD_OBJECT,提取数据的 JSON_EXTRACT,还有聚合用的 JSON_AGG,增删改查、校验聚合都能覆盖。用之前得先创建 mysql_json 插件,不然会报错❌ path 参数别带 * 通配符,我之前踩过好几个坑。JSON_INSERT、REPLACE、SET 别用混,校验格式靠 JSON_VALID,格式化看 JSON_PRETTY,都挺实用。整体用熟了处理 JSON 数据超省事儿,多跑几个例子就能上手,大家有啥技巧也可以交流呀✅

对于接受 JSON 参数的函数,如果参数不是有效的 JSON 格式,就会发生错误。以 json_doc 表示的参数解析为 JSON,以 val 表示的参数不解析。
返回 JSON 值的函数总是对这些值进行规范化处理,从而对它们进行排序。排序的结果可能随时发生变化,请勿依赖于不同版本之间的一致性。
🚀 下面咋么一起来学习JSON函数,开整......
ARRAY_TO_JSON
用法:
plain
ARRAY_TO_JSON(anyarray [, pretty_bool])
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">anyarray</font>
SQL数组,存放JSON数据。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">pretty_bool</font>
BOOLEAN类型,可选pretty_bool参数默认为false,不添加换行符。如果pretty_bool参数设置为true,换行符将在顶级数组元素之间添加。
功能:
把数组anyarray转换为JSON数组,该行为与TO_JSON相同。
例子:
plain
SELECT ARRAY_TO_JSON('{{1,5},{99,100}}'::int[]);
ARRAY_TO_JSON
------------------
[[1,5],[99,100]]
(1 row)
SELECT ARRAY_TO_JSON('{{1,5},{99,100}}'::int[], false);
ARRAY_TO_JSON
------------------
[[1,5],[99,100]]
(1 row)
SELECT ARRAY_TO_JSON('{{1,5},{99,100}}'::int[], true);
ARRAY_TO_JSON
---------------
[[1,5],
[99,100]]
(1 row)JSON_AGG
JSON_AGG是聚集函数,将传入值包括空值聚集成JSON数组。有关详细信息,请参见 JSON_AGG 。
JSON_ARRAY
用法:
plain
JSON_ARRAY ( [{value_expression} [, ...] ] )
功能:
JSON处理函数,以JSON数组形式返回输入(可为空)。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_ARRAY(1, 'abc', NULL, TRUE, CURTIME());
JSON_ARRAY
----------------------------------
[1, "abc", null, true, "10:26:21"]JSON_ARRAY_APPEND
用法:
plain
JSON_ARRAY_APPEND(json_doc, path, val[, path, val] ...)
功能:
在JSON文档中向指定数组末尾添加值,并返回结果。当任一参数为 NULL,结果即为 NULL。以下情况会发生错误:
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>参数不是有效的JSON文档<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数不是有效的path表达式- 包含 * 或 ** 通配符
如果path选择了一个标量或对象值,该值将被自动封装在一个数组中,并且新值将添加到该数组中。如果path没有识别 JSON 文档中的任何值,则会被忽略。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_ARRAY_APPEND('[1,2,3, [4,5,6]]', '$[0]', '100');
JSON_ARRAY_APPEND
-------------------------------
[[1, "100"], 2, 3, [4, 5, 6]]
(1 row)JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS
用法:
plain
JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(json)
功能:
JSON 处理函数,将 JSON 数组扩展成 JSON 值的集合。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS('[1,true,[1,[2,3]],null,{"f1":1,"f2":[7,8,9]},false,"stringy"]');
JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS
-----------------------
1
true
[1,[2,3]]
null
{"f1":1,"f2":[7,8,9]}
false
"stringy"
(7 rows)JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_TEXT
用法:
plain
JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_TEXT(json)
功能:
JSON处理函数,把一个JSON数组扩展成 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">text</font> 值集合。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_TEXT('["foo","bar"]');
value
-------
foo
bar
(2 rows)
SELECT * FROM JSON_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_TEXT('[1,true,[1,[2,3]],null,{"f1":1,"f2":[7,8,9]},false,"stringy"]');
value
-----------------------
1
true
[1,[2,3]]
{"f1":1,"f2":[7,8,9]}
false
stringy
(7 rows)JSON_ARRAY_INSERT
用法:
plain
JSON_ARRAY_INSERT(json_doc, path, val[, path, val] ...)
功能:
更新一个JSON文档,在文档中插入一个数组,并返回修改后的文档。当任一参数为 NULL,结果即为 NULL。以下情况会发生错误:
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>参数不是有效的 JSON 文档<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数不是有效的path表达式- 包含 * 或 ** 通配符
- 不是以数组元素标识符结尾
如果path没有标识 JSON 文档中的任何数组,则会被忽略。如果path标识了一个数组元素,则会在该元素位置插入相应的值,并将后面的值向右移动。如果path标识的数组位置超过了数组的末尾,则会在数组末尾插入该值。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_ARRAY_INSERT('["a", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, 4]]', '$[1]', 'x');
JSON_ARRAY_INSERT
---------------------------------
["a", "x", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, 4]]
SELECT JSON_ARRAY_INSERT('["a", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, 4]]', '$[100]', 'x');
JSON_ARRAY_INSERT
---------------------------------
["a", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, 4], "x"]
SELECT JSON_ARRAY_INSERT('["a", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, 4]]', '$[1].b[0]', 'x');
JSON_ARRAY_INSERT
---------------------------------
["a", {"b": ["x", 1, 2]}, [3, 4]]
SELECT JSON_ARRAY_INSERT('["a", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, 4]]', '$[2][1]', 'y');
JSON_ARRAY_INSERT
---------------------------------
["a", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, "y", 4]]
SELECT JSON_ARRAY_INSERT('["a", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, 4]]', '$[0]', 'x', '$[2][1]', 'y');
JSON_ARRAY_INSERT
---------------------------------
["x", "a", {"b": [1, 2]}, [3, 4]]JSON_ARRAY_LENGTH
用法:
plain
JSON_ARRAY_LENGTH(json)
功能:
JSON处理函数,返回最外层JSON数组中的元素数量。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_ARRAY_LENGTH('[1,2,3,{"f1":1,"f2":[5,6]},4]');
JSON_ARRAY_LENGTH
-------------------
5
(1 row)JSON_ARRAYAGG
JSON_ARRAYAGG是聚集函数,将输入聚合为JSON数组。有关详细信息,请参见 JSON_ARRAYAGG 。
JSON_BUILD_ARRAY
用法:
plain
JSON_BUILD_ARRAY( VARIADIC "any")
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">VARIADIC "any"</font>
任何类型的可变参数列表。
功能:
JSON处理函数,将可变参数列表构造成一个可能包含不同数据类型的JSON数组。每个参数都按照TO_JSON进行转换。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_BUILD_ARRAY(1,2,'3',4,5);
JSON_BUILD_ARRAY
-------------------
[1, 2, "3", 4, 5]
(1 row)JSON_BUILD_OBJECT
用法:
plain
JSON_BUILD_OBJECT( VARIADIC "any")
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">VARIADIC "any"</font>
可变参数列表,该参数列表由交替出现的键和值构成。
功能:
JSON处理函数,将可变参数列表构造成一个JSON 对象。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_BUILD_OBJECT('foo',1,'bar',2);
JSON_BUILD_OBJECT
------------------------
{"foo" : 1, "bar" : 2}
(1 row)JSON_CONTAINS
用法:
plain
JSON_CONTAINS(target, candidate[, path])
功能:
此功能用于判定 candidate JSON 文档是否作为子集存在于 target JSON 文档中。如果 candidate 文档完全匹配 target 文档的一部分,返回 TRUE。若无匹配,则返回 FALSE。当任意参数为 NULL,或 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数无法正确引用 target 文档中的部分,结果均为 NULL。以下情况会发生错误:
- candidate 或 target 文档不是有效的 JSON 文档
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数不是有效的path表达式- 包含 * 或 ** 通配符
只检查路径上是否存在任何数据,使用 JSON_CONTAINS_PATH 代替。
以下规则定义了限制:
- 候选标量被视为包含于目标标量中,前提是两者可比较且相等。JSON 类型相同的标量值(通过 JSON_TYPE() 确定)是可比较的,此外,INTEGER 和 DECIMAL 类型的值也被认为可比较。
- 只有当候选数组的每个元素都能在目标数组中找到匹配项时,候选数组才被认为是目标数组的子集。
- 候选对象包含于目标对象中,条件是候选对象的每个键能在目标对象中找到同名键,并且与之关联的值也包含于目标键对应的值中。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS('{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}', '1', '$.a');
JSON_CONTAINS
-------------
t
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS('{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}', '1', '$.b');
JSON_CONTAINS
-------------
f
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS('{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}', '{"d": 4}', '$.a');
JSON_CONTAINS
-------------
f
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS('"abc"', '"abc"', '$[0]');
JSON_CONTAINS
-------------
t
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS('{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}', '{"d": 4}', '$.c');
JSON_CONTAINS
-------------
tJSON_CONTAINS_PATH
用法:
plain
JSON_CONTAINS_PATH(json_doc, one_or_all, path[, path] ...)
功能:
返回 TRUE 或 FALSE,表示 JSON 文档是否包含给定<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 下的数据。当任一参数为 NULL,结果即为 NULL。以下情况会发生错误:
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>参数不是有效的 JSON 格式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数不是有效的路径表达式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">one_or_all</font>不是 "one "或 "all"
要检查路径上的特定值,请使用 JSON_CONTAINS 代替。
如果文档中不存在指定的路径,则返回值为FALSE。否则,返回值取决于one_or_all参数:
- one :如果文档中至少存在一条路径,返回为 TRUE,否则为 FALSE。
- all :如果文件中存在所有路径,返回为 TRUE,否则为 FALSE。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS_PATH('{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}', 'one', '$.a', '$.e');
JSON_CONTAINS_PATH
-------------------
t
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS_PATH('{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}', 'all', '$.a', '$.e');
JSON_CONTAINS_PATH
-------------------
f
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS_PATH('{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}', 'one', '$.c.d');
JSON_CONTAINS_PATH
-------------------
t
SELECT JSON_CONTAINS_PATH('{"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": {"d": 4}}', 'one', '$.a.d');
JSON_CONTAINS_PATH
-------------------
fJSON_DEPTH
用法:
plain
JSON_DEPTH(json_doc)
功能:
返回 JSON 文档的最大深度。如果参数为 NULL,则返回 NULL。如果参数不是有效的 JSON 格式,则会发生错误。
空数组、空对象以及任何标量值的深度定义为1。非空数组或非空对象,若其所有元素或成员值的深度均为1,则自身的深度为2。对于其他情况,即包含深度大于1的元素或成员的JSON文档,其深度将超过2。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_DEPTH('{}'), JSON_DEPTH('[]'), JSON_DEPTH('true');
JSON_DEPTH|JSON_DEPTH|JSON_DEPTH
----------+----------+----------
1| 1| 1
SELECT JSON_DEPTH('[10, 20]'), JSON_DEPTH('[[], {}]');
JSON_DEPTH|JSON_DEPTH
----------+----------
2| 2
SELECT JSON_DEPTH('[10, {"a": 20}]');
JSON_DEPTH
------------
3JSON_EACH
用法:
plain
JSON_EACH(json)
功能:
JSON处理函数,扩展最外层的JSON对象成为一组键值对。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSON_EACH('{"a":"foo", "b":"bar"}');
key | value
-----+-------
a | "foo"
b | "bar"
(2 rows)JSON_EACH_TEXT
用法:
plain
JSON_EACH_TEXT(json)
功能:
JSON处理函数,扩展最外层的JSON对象成为一组键值对,返回值为 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">text</font> 类型。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSON_EACH_TEXT('{"a":"foo", "b":"bar"}');
key | value
-----+-------
a | foo
b | bar
(2 rows)JSON_EXTRACT
用法:
plain
JSON_EXTRACT(json_doc, path[, path] ...)
功能:
返回 JSON 文档中与<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 参数匹配的部分数据。如果任何参数为 NULL 或在文档中未找到<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 对应的值,则返回 NULL。以下情况会发生错误:
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>参数不是有效的 JSON 格式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数不是有效的path表达式
返回值由<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 参数匹配的所有值组成。如果这些参数可能返回多个值,则匹配值会自动封装为一个数组,并按照产生这些值的<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 顺序排列。否则,返回值就是单个匹配值。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_EXTRACT('[10, 20, [30, 40]]', '$[1]');
JSON_EXTRACT
--------------
20
SELECT JSON_EXTRACT('[10, 20, [30, 40]]', '$[1]', '$[0]');
JSON_EXTRACT
--------------
[20, 10]
SELECT JSON_EXTRACT('[10, 20, [30, 40]]', '$[2][*]');
JSON_EXTRACT
--------------
[30, 40]JSON_EXTRACT_PATH
用法:
plain
JSON_EXTRACT_PATH(from_json, VARIADIC path_elems)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>
JSON类型,指定JSON对象。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">VARIADIC path_elems</font>
指定查找JSON对象的路径。
功能:
JSON处理函数,在指定路径下提取JSON子对象。(这在功能上相当于#>操作符,但在某些情况下,将路径写成可变参数列表会更方便。)
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_EXTRACT_PATH('{"f2":{"f3":1},"f4":{"f5":99,"f6":"foo"}}','f4');
JSON_EXTRACT_PATH
----------------------
{"f5":99,"f6":"foo"}
(1 row)JSON_EXTRACT_PATH_TEXT
用法:
plain
JSON_EXTRACT_PATH_TEXT(from_json, VARIADIC path_elems)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>
JSON类型,指定JSON对象。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">VARIADIC path_elems</font>
指定查找JSON对象的路径。
功能:
JSON处理函数,将指定路径上的JSON子对象提取为文本。(这在功能上等同于#>>操作符。)
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_EXTRACT_PATH_TEXT('{"f2":{"f3":1},"f4":{"f5":99,"f6":"foo"}}','f4', 'f6');
JSON_EXTRACT_PATH_TEXT
------------------------
foo
(1 row)JSON_INSERT
用法:
plain
JSON_INSERT(json_doc, path, val[, path, val] ...)
功能:
更新JSON文档,将其插入文档中的数组中并返回修改后的文档。当任一参数为 NULL,结果即为 NULL。以下情况会发生错误:
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>参数不是有效的 JSON 格式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数不是有效的path表达式- 包含 * 或 ** 通配符
文档中现有path-value将被忽略,不会覆盖现有的文档值。如果文档中的非现有path-value标识了这些类型的值,则会将该值添加到文档中:
- 现有对象中不存在的成员。该成员将被添加到对象中,并与新值相关联。
- 超过现有数组末尾的位置。数组将根据新值进行扩展。如果现有值不是数组,则会自动封装为数组,然后用新值扩展。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_INSERT('{ "a": 1, "b": [2, 3]}', '$.a', 10, '$.c', '[true, false]');
JSON_INSERT
---------------------------------------------
{"a": 1, "b": [2, 3], "c": "[true, false]"}结果中,第三个也是最后一个值呈现为带引号的字符串,不同于第二个值展示的数组形式(在输出中未加引号)。这里并没有对值进行 JSON 类型的转换。若要作为数组插入,必须明确执行转换。如下所示:
plain
SELECT JSON_INSERT('{ "a": 1, "b": [2, 3]}', '$.a', 10, '$.c', CAST('[true, false]' AS JSON));
JSON_INSERT
-------------------------------------------
{"a": 1, "b": [2, 3], "c": [true, false]}JSON_KEYS
用法:
plain
JSON_KEYS(json_doc[, path])
功能:
以 JSON 数组形式返回 JSON 对象的键值,如果给定了<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 参数,则返回给定<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 的顶层键值。如果任何参数为 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">NULL</font>、<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font> 参数不是对象或给定path没有定位到对象,则返回 NULL。以下情况会发生错误:
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>参数不是有效的 JSON 格式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数不是有效的path表达式- 包含 * 或 ** 通配符
如果所选对象为空,则结果数组为空。如果顶级值有嵌套的子对象,则返回值不包括这些子对象中的键。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_KEYS('{"a": 1, "b": {"c": 30}}');
JSON_KEYS
------------
["a", "b"]
SELECT JSON_KEYS('{"a": 1, "b": {"c": 30}}', '$.b');
JSON_KEYS
-----------
["c"]JSON_LENGTH
用法:
plain
JSON_LENGTH(json_doc[, path])
功能:
返回 JSON 文档的长度,如果给定了 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 参数,则返回path标识的文档中值的长度。如果任何参数为 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">NULL</font> 或 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 参数未指定文档中的值,则返回 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">NULL</font>。以下情况会发生错误:
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>参数不是有效的 JSON 格式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数不是有效的path表达式
文档长度的确定方法如下:
- 标量的长度为1。
- 数组的长度是数组元素的数量。
- JSON对象的长度是JSON成员的数量。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_LENGTH('[1, 2, {"a": 3}]');
JSON_LENGTH
-------------
3
SELECT JSON_LENGTH('{"a": 1, "b": {"c": 30}}');
JSON_LENGTH
-------------
2
SELECT JSON_LENGTH('{"a": 1, "b": {"c": 30}}', '$.b');
JSON_LENGTH
-------------
1JSON_MERGE
用法:
plain
JSON_MERGE(json_doc,json_doc[,json_doc]...)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>
JSON 文档。
功能
合并两个或多个 JSON 文档并返回合并的结果。
- 若任何参数为NULL,则返回NULL。
- 若任何参数不是有效的 JSON 文档,则会发生错误。
- 若任何参数为NULL,或者指定的path不存在,则返回NULL。
- 若参数不是有效JSON格式,则返回错误。
- 若所有json_doc都不是JSON对象,返回JSON类型数组
- 若所有json_doc都是JSON对象,返回JSON对象。
示例
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_MERGE('1', '{"a":1}', '{"a":2}');
JSON_MERGE
-------------------------
[1, {"a": 1}, {"a": 2}]
(1 row)JSON_MERGE_PATCH
用法:
plain
JSON_MERGE_PATCH(json_doc, json_doc[, json_doc] ...)
功能:
对两个或多个JSON文档执行合并,并返回合并结果,而不保留具有重复键的成员。如果作为参数传递给此函数的文档中至少有一个无效,则引发错误。
JSON_MERGE_PATCH() 的合并过程如下:
- 如果第一个参数不是对象,则合并的结果与将空对象与第二个参数合并的结果相同。
- 如果第二个参数不是对象,合并的结果就是第二个参数。
- 如果两个参数都是对象,则合并的结果是一个具有以下成员的对象:
第一个对象的所有成员,这些成员在第二个对象中没有具有相同键值的对应成员。
第二个对象的所有成员,这些成员在第一个对象中没有对应的键,且其值不是 JSON 空文字。
键同时存在于第一个和第二个对象中,且第二个对象中的值不是 JSON 空文字的所有成员。这些成员的值是第一个对象中的值与第二个对象中的值递归合并的结果。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PATCH('[1, 2]', '[true, false]');
JSON_MERGE_PATCH
------------------
[true, false]
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PATCH('{"name": "x"}', '{"id": 47}');
JSON_MERGE_PATCH
-------------------------
{"name": "x", "id": 47}
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PATCH('1', 'true');
JSON_MERGE_PATCH
------------------
true
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PATCH('[1, 2]', '{"id": 47}');
JSON_MERGE_PATCH
------------------
{"id": 47}
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PATCH('{ "a": 1, "b":2 }', '{ "a": 3, "c":4 }');
JSON_MERGE_PATCH
--------------------------
{"a": 3, "b": 2, "c": 4}
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PATCH('{ "a": 1, "b":2 }','{ "a": 3, "c":4 }', '{ "a": 5, "d":6 }');
JSON_MERGE_PATCH
----------------------------------
{"a": 5, "b": 2, "c": 4, "d": 6}可以使用此函数删除一个成员,方法是在第二个参数中指定 null 作为同一成员的值,如下所示:
plain
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PATCH('{"a":1, "b":2}', '{"b":null}');
JSON_MERGE_PATCH
------------------
{"a": 1}该示例表明,该函数以递归方式运行;也就是说,成员值不限于标量,其本身也可以是 JSON 文档:
plain
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PATCH('{"a":{"x":1}}', '{"a":{"y":2}}');
JSON_MERGE_PATCH
-------------------------
{"a": {"x": 1, "y": 2}}JSON_MERGE_PATCH()与 JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE()的比较
JSON_MERGE_PATCH()的行为与 JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE()相同,但有以下两个例外:
- JSON_MERGE_PATCH() 会删除第一个对象中与第二个对象中的键相匹配的任何成员,前提是与第二个对象中的键相关联的值不是 JSON 空值。
- 第二个对象中有一个成员的键与第一个对象中的成员相匹配,JSON_MERGE_PATCH() 会用第二个对象中的值替换第一个对象中的值,而 JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE() 则会将第二个值追加到第一个值中。
下面比较了使用这两个函数合并相同的 3 个 JSON 对象(每个对象都有一个匹配键 "a")的结果:
plain
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PATCH('{ "a": 1, "b": 2 }','{ "a": 3, "c": 4 }', '{ "a": 5, "d": 6 }') AS Patch,
JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE('{ "a": 1, "b": 2 }','{ "a": 3, "c": 4 }', '{ "a": 5, "d": 6 }') AS Preserve;
Patch |Preserve
--------------------------------+----------------------------------------
{"a": 5, "b": 2, "c": 4, "d": 6}|{"a": [1, 3, 5], "b": 2, "c": 4, "d": 6}JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE
用法:
plain
JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE(json_doc, json_doc[, json_doc] ...)
功能:
合并两个或多个JSON文档并返回合并结果。当任一参数为 NULL,结果即为 NULL。如果任何参数不是有效的JSON格式,则会发生错误。
合并按照以下规则进行:
- 相邻的数组将被整合成单一数组。
- 相邻的对象会被合并成一个单独的对象
- 标量值会自动被包装进数组,进而与其他数组合并。
- 邻近的数组和对象可以通过将对象封装进数组,再与数组合并的方式结合在一起。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE('[1, 2]', '[true, false]');
JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE
---------------------
[1, 2, true, false]
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE('{"name": "x"}', '{"id": 47}');
JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE
-------------------------
{"name": "x", "id": 47}
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE('1', 'true');
JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE
---------------------
[1, true]
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE('[1, 2]', '{"id": 47}');
JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE
---------------------
[1, 2, {"id": 47}]
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE('{ "a": 1, "b": 2 }','{ "a": 3, "c": 4 }');
JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE
-------------------------------
{"a": [1, 3], "b": 2, "c": 4}
SELECT JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE('{ "a": 1, "b": 2 }','{ "a": 3, "c": 4 }', '{ "a": 5, "d": 6 }');
JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE
------------------------------------------
{"a": [1, 3, 5], "b": 2, "c": 4, "d": 6}JSON_OBJECT
用法:
plain
JSON_OBJECT([key,value[,key,value,...]])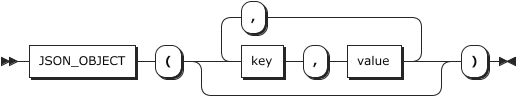
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">key</font>
对象中的键。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">value</font>
对象中的键值。
功能:
JSON处理函数,以JSON对象形式返回输入的键值对(可为空)。当任意键名为NULL或者参数个数为单数时报错。
备注
使用前需要创建mysql_json插件。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json ;
SELECT JSON_OBJECT('id', 87, 'name', 'carrot');
JSON_OBJECT
------------------------------
{"id": 87, "name": "carrot"}
(1 row)JSON_OBJECT_AGG
JSON_OBJECT_AGG是聚集函数,将键值对聚合成JSON对象。有关详细信息,请参见 JSON_OBJECT_AGG 。
JSON_OBJECT_KEYS
用法:
plain
JSON_OBJECT_KEYS(json)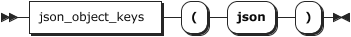
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json</font>
指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON函数,返回外层JSON对象中键的集合。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_OBJECT_KEYS('{"f1":"abc","f2":{"f3":"a", "f4":"b"}}');
JSON_OBJECT_KEYS
------------------
f1
f2
(2 rows)JSON_OBJECTAGG
JSON_OBJECTAGG是聚集函数,将键值对聚合成JSON对象。有关详细信息,请参见 JSON_OBJECTAGG 。
JSON_POPULATE_RECORD
用法:
plain
JSON_POPULATE_RECORD(base, from_json)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">base</font>
定义记录类型。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>
JSON类型,指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON函数,扩展 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font> 中的对象成一个行,它的列匹配由 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">base</font> 定义的记录类型。
例子:
plain
CREATE TYPE subrowtype AS (d int, e text);
CREATE TYPE myrowtype AS (a int, b text[], c subrowtype);
SELECT * FROM JSON_POPULATE_RECORD(null::myrowtype,'{"a":1, "b": ["2", "a b"],"c": {"d":4, "e": "ab c"}}');
a | b | c
---+-----------+------------
1 | {2,"a b"} | (4,"ab c")
(1 row)JSON_POPULATE_RECORDSET
用法:
plain
JSON_POPULATE_RECORDSET(base, from_json)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">base</font>
定义记录类型。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>
JSON类型,指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON函数,扩展 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font> 中最外层的对象数组成一个集合,它的列匹配由 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">base</font> 定义的记录类型。
例子:
plain
CREATE TYPE twoints AS (a int, b int);
SELECT * FROM JSON_POPULATE_RECORDSET(null::twoints, '[{"a":1,"b":2}, {"a":3,"b":4}]');
a | b
---+---
1 | 2
3 | 4
(2 rows)JSON_PRETTY
用法:
plain
JSON_PRETTY(json_val)
功能:
提供与 PHP 及其他编程语言和数据库平台相仿的 JSON 值输出。需提交的值应为 JSON 值,或是能恰当表示 JSON 值的字符串。值内多余的空白字符与换行不会干扰输出结果。遇到 NULL 值时,函数将直接返回 NULL。若提供的值非 JSON 文档格式,或无法成功解析为 JSON,函数执行将中断,并抛出错误提示。
该函数的输出格式遵循以下规则:
- 数组元素与对象成员各自占据独立行,相较于其父级元素或多级嵌套,每层缩进增加两个前导空格。
- 逗号分隔符置于换行符前,用于区隔数组元素或对象成员。
- 物件成员的键与值间以冒号加空格(': ')隔开。
- 空对象与空数组在单行展示,且括号间不插入空格。
- 字符串标量及键名内特殊字符的转义遵循与 JSON_QUOTE 相同规则。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_PRETTY('123'); # 标量
JSON_PRETTY
-------------
123
SELECT JSON_PRETTY('{"a":"10","b":"15","x":"25"}'); # 数组
JSON_PRETTY
---------------------------------------------
{
"a": "10",
"b": "15",
"x": "25"
}
SELECT JSON_PRETTY
('["a",1,{"key1":"value1"},"5","77",{"key2":["value3","valueX","valueY"]},"j", "2"]');
JSON_PRETTY
--------------------------
[
"a",
1,
{
"key1": "value1"
},
"5",
"77",
{
"key2": [
"value3",
"valueX",
"valueY"
]
},
"j",
"2"
]
(1 row)JSON_QUOTE
用法:
plain
JSON_QUOTE(string)
功能:
使用双引号字符将字符串封装为 JSON 值,并转义内部引号和其他字符,然后将结果作为JSON格式字符串返回。如果参数为 NULL,则返回 NULL。
该函数通常用于生成一个有效的 JSON 字符串常量,以便包含在 JSON 文档中。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_QUOTE('null'), JSON_QUOTE('"null"');
JSON_QUOTE|JSON_QUOTE
----------+----------
"null" |"\"null\""
SELECT JSON_QUOTE('[1, 2, 3]');
JSON_QUOTE
--------------
"[1, 2, 3]"JSON_REMOVE
用法
plain
JSON_REMOVE(json_doc,path[, path]...)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>
要查询的JSON文档。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>
指定删除路径,可以指定多个路径。
功能
从JSON文档中删除数据并返回结果。
返回值说明
- NULL: json_doc,path参数中任何一个为NULL,则返回NULL;
- JSON基本类型/标量:更新结果为JSON基本类型/标量,则返回JSON基本类型/标量;
- JSON类型数组:更新结果为JSON数组,则返回JSON基本JSON数组;
- JSON对象;更新结果为JSON对象,则返回JSON基本JSON对象;
注:如果json_doc参数不是有效的 JSON 文档,或者任何path参数不是有效的path表达式,或者是$或包含*或**通配符,则会发生错误。
例子
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_REMOVE('12345', '$[0]', '$[1]');
JSON_REMOVE
-------------
12345
(1 row)JSON_REPLACE
用法:
plain
JSON_REPLACE(json_doc, path, val[, path, val] ...)
功能:
替换 JSON 文档中的现有值并返回结果。当任一参数为 NULL,结果即为 NULL。以下情况会发生错误:
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>参数不是有效的 JSON 格式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数不是有效的path表达式- 包含 * 或 ** 通配符
文档中现有path-value对会用新值覆盖现有文档值。文档中不存在的path-value将被忽略,并且无效。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_REPLACE('{ "a": 1, "b": [2, 3]}', '$.a', 10, '$.c', '[true, false]');
JSON_REPLACE
-------------------------
{"a": 10, "b": [2, 3]}JSON_SEARCH
用法:
plain
JSON_SEARCH(json_doc, one_or_all, search_str[, escape_char[, path] ...])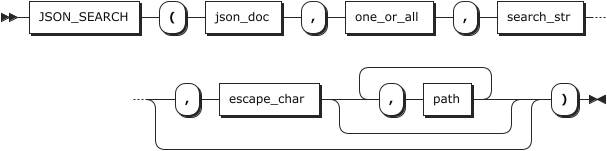
功能:
返回给定字符串在 JSON 文档中的路径。如果 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>、<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">search_str</font> 或 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 参数为空,文档中不存在path或未找到 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">search_str</font>,则返回 NULL。以下情况会发生错误:
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>不是有效的 JSON 格式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>不是有效的path表达式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">one_or_all</font>不是 "one "或 "all"<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">escape_char</font>不是常量表达式
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">one_or_all</font> 参数对搜索的影响如下:
- one:搜索在第一个匹配后终止,并返回一个路径字符串。
- all:搜索会返回所有匹配的路径字符串,不会包含重复的路径。如果有多个字符串,则会自动封装为一个数组。数组元素的顺序未定义。
在 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">search_str</font> 参数内,<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">%</font> 与 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">_</font> 字符的功能等同于 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">LIKE</font> 运算符中的作用。<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">%</font> 能匹配任意数量的字符,包括零字符,而 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">_</font> 则精确匹配单个字符。
为了在搜索字符串中指定 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">%</font> 或 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">_</font> ,需使用转义字符进行前缀标记。若 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">escape_char</font> 参数缺省或为 NULL,默认转义字符为 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">\</font> 。反之, <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">escape_char</font> 必须是空常量或单一字符。
值得注意的是,<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">JSON_SEARCH()</font> 的转义字符要求在编译阶段就被评估为常量,而不仅仅是执行时的常量。这与 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">LIKE</font> 的行为有别。举例来说,在预备语句中运用 JSON_SEARCH() 并通过 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">?</font> 参数传入 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">escape_char</font> ,虽然该参数值在执行时可能是常量,但未必满足编译时的常量要求。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]', 'one', 'abc');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[0]"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]', 'all', 'abc');
JSON_SEARCH
---------------------
["$[0]", "$[2].x"]
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]', 'all', 'ghi');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '10');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[1][0].k"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '10', NULL, '$');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[1][0].k"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '10', NULL, '$[*]');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[1][0].k"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '10', NULL, '$**.k');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[1][0].k"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '10', NULL, '$[*][0].k');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[1][0].k"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '10', NULL, '$[1]');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[1][0].k"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '10', NULL, '$[1][0]');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[1][0].k"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', 'abc', NULL, '$[2]');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[2].x"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '%a%');
JSON_SEARCH
---------------------
["$[0]", "$[2].x"]
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '%b%');
JSON_SEARCH
-------------------------------
["$[0]", "$[2].x", "$[3].y"]
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '%b%', NULL, '$[0]');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[0]"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '%b%', NULL, '$[2]');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[2].x"
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '%b%', NULL, '$[1]');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '%b%', '', '$[1]');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_SEARCH('["abc", [{"k": "10"}, "def"],
{"x":"abc"}, {"y":"bcd"}]','all', '%b%', '', '$[3]');
JSON_SEARCH
--------------
"$[3].y"
(1 row)JSON_SET
用法:
plain
JSON_SET(json_doc, path, val[, path, val] ...)
功能:
插入或更新 JSON 文档中的数据并返回结果。如果 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font> 或 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 为空,或 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 未找到对象,则返回 NULL。以下情况会发生错误:
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_doc</font>参数不是有效的JSON格式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>参数不是有效的path表达式- 包含 * 或 ** 通配符
文档中现有path-value会用新值覆盖现有文档值。如果文档中的非现有path标识了这些类型的值,则path-value会将该值添加到文档中:
- 现有对象中不存在的成员。该成员将被添加到对象中,并与新值相关联。
- 超过现有数组末尾的位置。数组将根据新值进行扩展。如果现有值不是数组,则会自动封装为数组,然后用新值扩展。
否则,文档中不存在的path-value将被忽略,也不会产生任何影响。
JSON_SET、JSON_INSERT 和 JSON_REPLACE 函数是相关的:
- JSON_SET 可替换现有值并添加非现有值。
- JSON_INSERT 插入值而不替换现有值。
- JSON_REPLACE 只替换现有值。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_SET('{ "a": 1, "b": [2, 3]}', '$.a', 10, '$.c', '[true, false]');
JSON_SET
-----------------------------------------------
{"a": 10, "b": [2, 3], "c": "[true, false]"}
SELECT JSON_INSERT('{ "a": 1, "b": [2, 3]}', '$.a', 10, '$.c', '[true, false]');
JSON_INSERT
----------------------------------------------
{"a": 1, "b": [2, 3], "c": "[true, false]"}
SELECT JSON_REPLACE('{ "a": 1, "b": [2, 3]}', '$.a', 10, '$.c', '[true, false]');
JSON_REPLACE
-------------------------
{"a": 10, "b": [2, 3]}JSON_STRIP_NULLS
用法:
plain
JSON_STRIP_NULLS(from_json)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>
JSON类型,指定JSON数据。
功能:
JSON函数,返回 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>,其中所有具有空值的对象域都被过滤掉,其他空值不动。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_STRIP_NULLS('[{"f1":1,"f2":null},2,null,3]');
JSON_STRIP_NULLS
---------------------
[{"f1":1},2,null,3]
(1 row)JSON_TABLE
用法:
plain
JSON_TABLE(expr, path COLUMNS (column_list) [AS] alias)
功能:
从JSON文档中提取数据,并作为具有指定列的关系表返回。
此函数的完整语法如下:
plain
JSON_TABLE(
expr,
path COLUMNS (column_list)
) [AS] alias
column_list:
column[, column][, ...]
column:
name FOR ORDINALITY
| name type PATH string path [on_empty] [on_error]
| name type EXISTS PATH string path
| NESTED [PATH] path COLUMNS (column_list)
on_empty:
{NULL | DEFAULT json_string | ERROR} ON EMPTY
on_error:
{NULL | DEFAULT json_string | ERROR} ON ERRORexpr:
这是一个返回JSON数据的表达式。可以是常量(<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">\{"a":1\}</font>)、列或函数。
path: 应用于数据源的 JSON 路径表达式用于定位和提取 JSON 数据中的具体值。这个表达式所指向的 JSON 值被称为"行源"。行源是 JSON 数据中的一个片段,它可以是一个对象或者一个数组元素,它会被转换成关系数据库中的一行数据。
alias 是必需的。
此函数以不区分大小写的方式比较列名。
JSON_TABLE()支持四种类型的列,如下所示:
- name FOR ORDINALITY:这种列类型用于计数,其类型为 UNSIGNED INT,并从 1 开始递增。它类似于 AUTO_INCREMENT 列,用于唯一标识由 NESTED PATH 子句产生的具有相同父级值的行。
- name type PATH string_path [ on_empty ] [ on_error ]:此类型列用于提取 JSON 中的标量数据,并转换为指定的列类型。on_empty 子句处理缺失值情况,on_error 处理无法转换数据类型的情况,如尝试将字符串转换为整数。
- name type EXISTS PATH path:此列检查给定路径是否存在数据,存在则返回 1,不存在则返回 0。类型通常是某种 INT 类型。
- NESTED [PATH] path COLUMNS ( column_list ):将嵌套的对象或数组与父级数据在同一行展示。多层嵌套可以通过多个 PATH 选项投影到同一行。
on empty:决定函数在数据丢失时的处理方式(取决于类型)。
- NULL ON EMPTY:默认行为,列值设为 NULL。
- DEFAULT json_string ON EMPTY:提供的 json_string 作为替代值。
- ERROR ON EMPTY:抛出错误。
on_error:如果使用,on_error将采用以下值之一:
- NULL ON ERROR:默认行为,列值设为 NULL。
- DEFAULT json string ON ERROR:使用 json_string 替换无法转换的对象或数组。
- ERROR ON ERROR:抛出错误。
对于值的截断,如将超出精度的数值存入固定精度的列,系统会发出警告,但不会受 ON ERROR 设置的影响。即便有多处截断,也只会发出一次警告。
当传递给该函数的表达式和路径解析为 JSON null 时,JSON_TABLE() 将根据 SQL 标准返回 SQL NULL,如下所示:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSON_TABLE(
'[ {"c1": null} ]','$[*]' COLUMNS( c1 INT PATH '$.c1' ERROR ON ERROR )
) as jt;
c1
-------
(1 row)下面的查询演示了 ON EMPTY 和 ON ERROR 的使用。对于路径"$.a",{"b":1} 对应的行为空,而尝试将 [1,2] 保存为标量会产生错误:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSON_TABLE(
'[{"a":"3"},{"a":2},{"b":1},{"a":0},{"a":[1,2]}]','$[*]'
COLUMNS(rowid FOR ORDINALITY,
ac VARCHAR(100) PATH '$.a' DEFAULT '111' ON EMPTY DEFAULT '999' ON ERROR,
aj JSON PATH '$.a' DEFAULT '{"x": 333}' ON EMPTY,
bx INT EXISTS PATH '$.b')) AS tt;
rowid|ac |aj |bx
-----+------+----------+--
1|3 |"3" | 0
2|2 |2 | 0
3|111 |{"x": 333}| 1
4|0 |0 | 0
5|[1, 2]|[1, 2] | 0
(5 rows)所有 JSON 和 JSON 路径表达式都会进行有效性检查;表达式无效会导致错误。
COLUMNS 关键字前面的路径的每个匹配都映射到结果表中的单行。例如,下面的查询结果如下所示:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSON_TABLE(
'[{"x":2,"y":"8"},{"x":"3","y":"7"},{"x":"4","y":6}]',
'$[*]' COLUMNS(xval VARCHAR(100) PATH '$.x',yval VARCHAR(100) PATH '$.y')
) AS jt1;
xval | yval
-----+-----
2 | 8
3 | 7
4 | 6
(3 rows)表达式<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">'$[*]'</font>匹配数组中的每个元素。通过修改路径,可以过滤结果中的行。例如,使用<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">'$[1]'</font>可将提取 JSON 数组的第二个元素,如下所示:
plain
SELECT * FROM
JSON_TABLE('[{"x":2,"y":"8"},{"x":"3","y":"7"},{"x":"4","y":6}]','$[1]'
COLUMNS(xval VARCHAR(100) PATH '$.x', yval VARCHAR(100) PATH '$.y')) AS jt1;
xval | yval
-----+-------
3 | 7
(1 row)在列定义中," " 将整个匹配传递给列; " "将整个匹配传递给列;" "将整个匹配传递给列;".x "和"$.y "只传递该匹配中分别与键 x 和键 y 对应的值。
NESTED PATH 在 JSON_TABLE 的 COLUMNS 子句中,为每一项匹配生成记录集。若无匹配项,则关联列设为空,实现顶层与 NESTED PATH 间的外部连接效果。通过 WHERE 子句设定条件,可模拟内部连接行为,如下所示:
plain
SELECT * FROM
JSON_TABLE('[ {"a": 1, "b": [11,111]}, {"a": 2, "b": [22,222]}, {"a":3}]',
'$[*]' COLUMNS(a INT PATH '$.a',
NESTED PATH '$.b[*]' COLUMNS (b INT PATH '$'))) AS jt
WHERE b IS NOT NULL;
a | b
---+-----
1 | 11
1 | 111
2 | 22
2 | 222
(4 rows)在同一个 COLUMNS 子句里,多个 NESTED [PATH] 会逐一处理。处理期间,其它同级路径的列值会被置为 NULL。因此,整个 COLUMNS 子句产生的记录数,等于各 NESTED [PATH] 所产记录数的总和,而非它们的乘积。简单说,就是每次只展开一个嵌套路径,其余的保持为空,最终的记录数是各个路径独立产生记录数量的加总。如下所示:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSON_TABLE
('[{"a": 1, "b": [11,111]}, {"a": 2, "b": [22,222]}]','$[*]' COLUMNS(
a INT PATH '$.a',NESTED PATH '$.b[*]' COLUMNS (b1 INT PATH '$'),
NESTED PATH '$.b[*]' COLUMNS (b2 INT PATH '$')))AS jt;
a | b1 | b2
---+-----+-----
1 | 11 |
1 | 111 |
1 | | 11
1 | | 111
2 | 22 |
2 | 222 |
2 | | 22
2 | | 222
(8 rows)FOR ORDINALITY 列对 COLUMNS 子句生成的记录进行枚举,可用于区分嵌套路径的父记录,尤其是当父记录中的值相同时,如下所示:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSON_TABLE(
'[{"a": "a_val","b": [{"c": "c_val", "l": [1,2]}]},
{"a": "a_val","b": [{"c": "c_val","l": [11]}, {"c": "c_val", "l": [22]}]}]',
'$[*]' COLUMNS(top_ord FOR ORDINALITY,apath VARCHAR(10) PATH '$.a',
NESTED PATH '$.b[*]' COLUMNS (bpath VARCHAR(10) PATH '$.c',ord FOR ORDINALITY,
NESTED PATH '$.l[*]' COLUMNS (lpath varchar(10) PATH '$')))) as jt;
top_ord | apath | bpath | ord | lpath
---------+-------+-------+-----+-------
1 | a_val | c_val | 1 | 1
1 | a_val | c_val | 1 | 2
2 | a_val | c_val | 1 | 11
2 | a_val | c_val | 2 | 22
(4 rows)源文件生成了一个双元素的数组,每个元素能产出两行数据。在所有生成的数据行中,apath和bpath的值一致,这表明我们无法仅凭这些值判断lpath是否源自同一父节点。ord列的值对应top_ord为1的行,意味着这两个值源于同一实体。而其他两值由于在ord列上的差异,显示它们来自不同实体。
一般而言,若一个派生表需引用FROM子句中前一表的列,直接联结此派生表是不被允许的。按照SQL标准,禁止在调用JSON_TABLE()前使用这种依赖关系。简言之,在处理数据库查询时,如果后续表依赖于前面表的数据,直接做联结操作是不符合规则的,尤其在使用JSON_TABLE()函数时更是如此。
创建表t1,并使用以下语句插入:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
CREATE TABLE t1 (c1 INT, c2 CHAR(1), c3 JSONB);
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES
ROW(1, 'z', JSON_OBJECT('a', 23, 'b', 27, 'c', 1)),
ROW(1, 'y', JSON_OBJECT('a', 44, 'b', 22, 'c', 11)),
ROW(2, 'x', JSON_OBJECT('b', 1, 'c', 15)),
ROW(3, 'w', JSON_OBJECT('a', 5, 'b', 6, 'c', 7)),
ROW(5, 'v', JSON_OBJECT('a', 123, 'c', 1111))
;然后,可以执行连接,例如在这个连接中,JSON_TABLE() 充当派生表,同时引用先前引用表中的一列:
plain
SELECT c1, c2, JSON_EXTRACT(c3, '$.*')
FROM t1 AS m
JOIN
JSON_TABLE(
m.c3,
'$.*'
COLUMNS(
at VARCHAR(10) PATH '$.a' DEFAULT '1' ON EMPTY,
bt VARCHAR(10) PATH '$.b' DEFAULT '2' ON EMPTY,
ct VARCHAR(10) PATH '$.c' DEFAULT '3' ON EMPTY
)
) AS tt
ON m.c1 > tt.at;
c1 | c2 | JSON_EXTRACT
----+----+--------------
2 | x | [1, 15]
2 | x | [1, 15]
3 | w | [5, 6, 7]
3 | w | [5, 6, 7]
3 | w | [5, 6, 7]
5 | v | [123, 1111]
5 | v | [123, 1111]
(7 rows)JSON_TO_RECORD
用法:
plain
JSON_TO_RECORD(json)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json</font>
JSON类型,指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON函数,从一个JSON对象构建一个任意的记录,正如所有返回 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">record</font> 的函数一样,调用者必须用一个 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">AS</font> 子句显式的定义记录的结构。
例子:
plain
CREATE TYPE myrowtype AS (a int, b text);
SELECT * FROM JSON_TO_RECORD('{"a":1,"b":[1,2,3],"c":[1,2,3],"e":"bar","r": {"a": 123, "b": "a b c"}}') AS x(a int,b text, c int[], d text, r myrowtype);
a | b | c | d | r
---+---------+---------+---+---------------
1 | [1,2,3] | {1,2,3} | | (123,"a b c")
(1 row)JSON_TO_RECORDSET
用法:
plain
JSON_TO_RECORDSET(json)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json</font>
JSON类型,指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON函数,从一个JSON对象数组构建一个任意的记录集合,正如所有返回 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">record</font> 的函数一样,调用者必须用一个 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">AS</font> 子句显式的定义记录的结构。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSON_TO_RECORDSET('[{"a":1,"b":"foo"},{"a":"2","c":"bar"}]')AS x(a int, b text);
a | b
---+-----
1 | foo
2 |
(2 rows)JSON_TYPE
用法
plain
JSON_TYPE(json_val)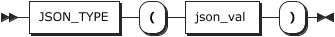
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json_val</font>
待测试的字符串,可以为列名;字符串符合JSON结构。
功能
返回JSON值类型。
返回值说明
- JSON类型:OBJECT,ARRAY,BOOLEAN,NULL
- 数字类型:INTEGER,DOUBLE,DECIMAL,UNSIGNED INTEGER
- 字符串类型:STRING
注:如果参数不符合JSON结构,则返回错误。
示例
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_TYPE('123456789012345678901234567890');
JSON_TYPE
-----------
DOUBLE
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_TYPE('"a"');
JSON_TYPE
-----------
STRING
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_TYPE('[]');
JSON_TYPE
-----------
ARRAY
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_TYPE('[1,"a", true, null]');
JSON_TYPE
-----------
ARRAY
(1 row)JSON_TYPEOF
用法:
plain
JSON_TYPEOF(json)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">json</font>
JSON类型,指定JSON数据。
功能:
JSON函数,以文本字符串形式返回顶级JSON值的类型。可能类型是: <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">object</font> 、 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">array</font> 、 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">string</font> 、 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">number</font> 、 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">boolean</font> 以及 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">null</font> 。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_TYPEOF('-123.4');
JSON_TYPEOF
-------------
number
(1 row)JSON_UNQUOTE
用法:
plain
JSON_UNQUOTE(json_val)
功能:
取消 JSON 值的引号,并以 utf8mb4 字符串形式返回结果。如果参数为 NULL,则返回 NULL。如果值以双引号开始和结束,但不是有效的 JSON 字符串文字,则会发生错误。
除非启用了 NO_BACKSLASH_ESCAPES SQL 模式,否则在字符串中,某些序列具有特殊含义。每个序列都以反斜线(<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">\</font>)开头,称为转义字符。JSON_UNQUOTE() 特殊字符转义序列如下表所示:
| 转义序列 | 序列转义的字符 |
|---|---|
| " | 双引号(")字符 |
| \b | 退格字符 |
| \f | 换页字符 |
| \n | 换行符 |
| \r | 回车符 |
| \t | 制表符 |
| </font> | 反斜线 () 字符 |
| \uXXXX | Unicode值为XXXX的UTF-8字节 |
对于所有其他转义序列,反斜杠将被忽略。也就是说,转义字符被解释为未转义字符。例如,<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">\x</font> 就是 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">x</font>。例如,<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">\b</font> 被解释为退格,但 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">\B</font> 被解释为 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">B</font>。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT '"abc"', JSON_UNQUOTE('"abc"');
?column? | JSON_UNQUOTE
----------+--------------
"abc" | abc
(1 row)
SELECT '[1, 2, 3]', JSON_UNQUOTE('[1, 2, 3]');
?column? | JSON_UNQUOTE
-----------+--------------
[1, 2, 3] | [1, 2, 3]
(1 row)JSON_VALID
用法:
plain
JSON_VALID(val)
功能:
合法json格式返回true,非法json格式返回false。如果参数为 NULL,则返回 NULL。
例子:
plain
CREATE EXTENSION mysql_json;
SELECT JSON_VALID('{"a": 1}');
JSON_VALID
------------
t
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_VALID('hello'), JSON_VALID('"hello"');
JSON_VALID | JSON_VALID
------------+------------
f | t
(1 row)JSON_VALUE
用法:
plain
JSON_VALUE(json_doc, path)
功能:
从文档给定<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 中提取值,并返回提取值,可选择将其转换为所需类型。完整语法如下所示:
plain
JSON_VALUE(json_doc, path [RETURNING type] [on_empty] [on_error])
on_empty:
{NULL | ERROR | DEFAULT value} ON EMPTY
on_error:
{NULL | ERROR | DEFAULT value} ON ERRORjson_doc 是一个有效的 JSON 格式。如果为空,函数将返回 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">NULL</font>。
path 是指向文档中某个位置的 JSON 路径。它必须是一个字符串。
type 是以下数据类型之一:
未通过 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">RETURNING</font> 子句指定,<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">JSON_VALUE()</font> 函数的返回类型是 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">VARCHAR(512)</font>。未指定字符集,<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">JSON_VALUE()</font> 使用二进制排序规格和 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">utf8mb4</font>,区分大小写。如果将 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">utf8mb4</font> 指定为结果的字符集,则服务器将使用此字符集的默认排序规则,该排序规则不区分大小写。
当指定路径上的数据由JSON空文本组成或解析为JSON空文本时,该函数返回 null。
on_empty 如果指定,当在给定路径找不到数据时,此子句采用以下值之一:
- NULL ON EMPTY:函数返回 NULL
- DEFAULT value ON EMPTY:返回值,其值必须与返回类型的值相匹配。
- ERROR ON EMPTY:函数抛出错误。
如果使用了 on_error,则在发生错误时,on_error 会取以下值之一,并给出相应的结果:
- NULL ON ERROR:JSON_VALUE() 返回 NULL。
- DEFAULT value ON EMPTY:返回值,其值必须与返回类型的值相匹配。
- ERROR ON ERROR:抛出错误。
ON EMPTY (如果使用)必须位于 ON ERROR 子句之前。指定顺序错误会导致语法错误。
错误处理
一般来说,JSON_VALUE() 会按以下方式处理错误:
- 检查所有JSON输入的有效性。如果其中任何一个无效,则会抛出SQL错误,而不会触发ON error子句。
- 每当发生以下任何事件时,都会触发ON ERROR:
试图提取一个对象或数组,例如从一个解析到 JSON 文档中多个位置的路径中提取的对象或数组。
转换错误,例如试图将 <font style="color:rgb(68, 73, 80);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">asdf</font> 转换为未指定值。
数值截断。
- 即使指定了 NULL ON ERROR 或 DEFAULT ... ON ERROR,转换错误始终会触发警告。
- 当源 JSON 文档(expr )在指定位置(path )不包含数据时,就会触发
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">ON EMPTY</font>子句。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSON_VALUE('{"fname": "Joe", "lname": "Palmer"}', '$.fname');
JSON_VALUE
------------
Joe
(1 row)
SELECT JSON_VALUE('{"item": "shoes", "price": "49.95"}', '$.price' RETURNING DECIMAL(4,2)) AS price;
price
-------
49.95
(1 row)语句 SELECT JSON_VALUE(json_doc, path RETURNING type) 相当于下面的语句:
plain
SELECT CAST(
JSON_UNQUOTE(JSON_EXTRACT(json_doc, path) )
AS type
);JSON_VALUE() 简化了在 JSON 列上创建索引的过程,在许多情况下无需先创建生成列,然后在生成列上创建索引。在创建具有 JSON 列的表 t1 时,可以在使用 JSON_VALUE() 对该列进行操作的表达式上创建索引,如下所示:
plain
CREATE TABLE t1(
j JSON,
INDEX i1 ( (JSON_VALUE(j, '$.id' RETURNING UNSIGNED)) )
);下面的 EXPLAIN 输出显示,在 WHERE 子句中使用索引表达式对 t1 进行的查询使用了这样创建的索引:
plain
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE JSON_VALUE(j, '$.id' RETURNING UNSIGNED) = 123;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Bitmap Heap Scan on t1 (cost=4.21..14.42 rows=7 width=32)
Recheck Cond: (JSON_VALUE(j, '$."id"' RETURNING uint8) = 123)
-> Bitmap Index Scan on i1 (cost=0.00..4.21 rows=7 width=0)
Index Cond: (JSON_VALUE(j, '$."id"' RETURNING uint8) = 123)
(4 rows)ROW_TO_JSON
用法:
plain
ROW_TO_JSON(record [, pretty_bool])
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">record</font>
SQL组合值(行)。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">pretty_bool</font>
BOOLEAN类型,可选pretty_bool参数默认为false,不添加换行符。如果pretty_bool参数设置为true,换行符将在顶级元素之间添加。
功能:
将行作为JSON对象返回。
例子:
plain
SELECT ROW_TO_JSON(ROW(1,'foo'));
ROW_TO_JSON
---------------------
{"f1":1,"f2":"foo"}
(1 row)TO_JSON
用法:
plain
TO_JSON(anyelement)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">anyelement</font>
指定JSON数据。
功能:
将anyelement转换为JSON格式的数据。数组和组合会被(递归)转换成数组和对象;对于不是数组和组合的值,如果有从该类型到JSON的转换,转换函数将被用来执行该转换 ;否则将产生一个标量值。对于任何不是数字、布尔、空值的标量类型,将使用文本表示,并根据需要进行转义,使其成为有 效的JSON字符串值。
例子:
plain
SELECT TO_JSON('Fred said "Hi."'::text);
TO_JSON
--------------------
"Fred said \"Hi.\""
(1 row)JSONB_AGG
JSONB_AGG是聚集函数,将传入值包括空值聚集成JSON数组。有关详细信息,请参见 JSONB_AGG 。
JSONB_ARRAY_ELEMENTS
用法:
plain
JSONB_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(jsonb)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数组。
功能:
JSON 处理函数,将 JSON 数组扩展成 JSON 值的集合。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSONB_ARRAY_ELEMENTS('["a","b"]');
value
-------
"a"
"b"
(2 rows)JSONB_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_TEXT
用法:
plain
JSONB_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_TEXT(jsonb)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数组。
功能:
JSON处理函数,把一个JSON数组扩展成text值集合。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSONB_ARRAY_ELEMENTS_TEXT('["foo","bar"]');
value
-------
foo
bar
(2 rows)JSONB_ARRAY_LENGTH
用法:
plain
JSONB_ARRAY_LENGTH(jsonb)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数组。
功能:
JSON处理函数,返回最外层JSON数组中的元素数量。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_ARRAY_LENGTH('[1,2,3,{"f1":1,"f2":[5,6]},4]');
JSONB_ARRAY_LENGTH
--------------------
5
(1 row)JSONB_BUILD_ARRAY
用法:
plain
JSONB_BUILD_ARRAY( VARIADIC "any")
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">VARIADIC "any"</font>
任何类型的可变参数列表。
功能:
JSON处理函数,将可变参数列表构造成一个可能包含不同数据类型的JSON数组。每个参数都按照TO_JSONB进行转换。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_BUILD_ARRAY(1,2,'3',4,5);
JSONB_BUILD_ARRAY
-------------------
[1, 2, "3", 4, 5]
(1 row)JSONB_BUILD_OBJECT
用法:
plain
JSONB_BUILD_OBJECT( VARIADIC "any")
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">VARIADIC "any"</font>
可变参数列表,该参数列表由交替出现的键和值构成。
功能:
JSON处理函数,将可变参数列表构造成一个JSON 对象。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_BUILD_OBJECT('foo',1,'bar',2);
JSONB_BUILD_OBJECT
----------------------
{"bar": 2, "foo": 1}
(1 row)JSONB_CONCAT
用法:
plain
JSONB_CONCAT(jsonb, jsonb)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSONB对象。
功能:
JSON处理函数,将两个JSONB对象连接起来,形成一个新的JSONB对象。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_CONCAT('{"d": "test", "a": [1, 2]}', '{"g": "test2", "c": {"c1":1, "c2":2}}');
JSONB_CONCAT
-------------------------------------------------------------------
{"a": [1, 2], "c": {"c1": 1, "c2": 2}, "d": "test", "g": "test2"}
(1 row)JSONB_EACH
用法:
plain
JSONB_EACH(jsonb)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON处理函数,扩展最外层的JSON对象成为一组键值对。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSONB_EACH('{"a":"foo", "b":"bar"}');
key | value
-----+-------
a | "foo"
b | "bar"
(2 rows)JSONB_EACH_TEXT
用法:
plain
JSONB_EACH_TEXT(jsonb)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON处理函数,扩展最外层的JSON对象成为一组键值对,返回值为text类型。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSONB_EACH_TEXT('{"a":"foo", "b":"bar"}');
key | value
-----+-------
a | foo
b | bar
(2 rows)JSONB_EXTRACT_PATH
用法:
plain
JSONB_EXTRACT_PATH(from_json, VARIADIC path_elems)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON对象。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">VARIADIC path_elems</font>
指定查找JSON对象的路径。
功能:
JSON处理函数,在指定路径下提取JSON子对象。(这在功能上相当于#>操作符,但在某些情况下,将路径写成可变参数列表会更方便。)
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_EXTRACT_PATH('{"f2":{"f3":1},"f4":{"f5":99,"f6":"foo"}}','f4');
JSONB_EXTRACT_PATH
-------------------------
{"f5": 99, "f6": "foo"}
(1 row)JSONB_EXTRACT_PATH_TEXT
用法:
plain
JSONB_EXTRACT_PATH_TEXT(from_json, VARIADIC path_elems)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON对象。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">VARIADIC path_elems</font>
指定查找JSON对象的路径。
功能:
JSON处理函数,将指定路径上的JSON子对象提取为文本。(这在功能上等同于#>>操作符。)
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_EXTRACT_PATH_TEXT('{"f2":{"f3":1},"f4":{"f5":99,"f6":"foo"}}','f4', 'f6');
JSONB_EXTRACT_PATH_TEXT
-------------------------
foo
(1 row)JSONB_INSERT
用法:
plain
JSONB_INSERT(target jsonb, path, new_value [, insert_after])
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font>
JSONB类型,待插入JSON数据。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>
指定查找JSON数据的路径。出现在 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 中的负整数表示从JSONB数组的末尾开始计数。如果最后一个路径是超出范围的数组下标,则如果下标为 负,则将新值添加到数组的开头;如果下标为正,则将新值添加到数组的结尾。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">new_value</font>
JSONB类型,待插入到 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font> 中的新数据。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">insert_after</font>
BOOLEAN类型,指定是否将 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">new_value</font> 插入到指定路径之后。如果 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 指定的 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font> 节在一个JSONB数组中, <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">new_value</font> 将被插入到目标之前( <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">insert_after</font> 默认为false) 或者之后( <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">insert_after</font> 为true)。如果 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 指定的 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font> 在一个JSONB对象内,则只有当 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font> 不存在时才插入 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">new_value</font>。
功能:
JSON处理函数,返回被插入了 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">new_value</font> 的 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font> 。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_INSERT('{"a": [0,1,2]}', '{a,1}', '"new_value"');
JSONB_INSERT
-------------------------------
{"a": [0, "new_value", 1, 2]}
(1 row)
SELECT JSONB_INSERT('{"a":[0,1,2]}','{a,1}','"new_value"', true);
JSONB_INSERT
-------------------------------
{"a": [0, 1, "new_value", 2]}
(1 row)JSONB_OBJECT
用法1:
plain
JSONB_OBJECT(text[])<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">text[]</font>
文本数组。

功能:
JSONB处理函数,从文本数组中构造JSON对象。该数组必须是具有偶数个成员的一维数组(成员被当做交替出现的键值对),或者是一个二维数组(每一个内部数组只有两个元素,可以被看做键值对,所有的值均被转换为JSON字符串)。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_OBJECT('{a, 1, b, "def", c, 3.5}');
JSONB_OBJECT
------------------------------------
{"a": "1", "b": "def", "c": "3.5"}
(1 row)
SELECT JSONB_OBJECT('{{a,1},{b, "def"},{c, 3.5}}');
JSONB_OBJECT
------------------------------------
{"a": "1", "b": "def", "c": "3.5"}
(1 row)用法2:
plain
JSONB_OBJECT(keys, values text)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">keys</font>
JSON属性key键数组。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">values</font>
JSON属性value值数组。
功能:
JSON处理函数,从文本数组中构造JSON对象。从两个独立的数组得到键值对。在其他方面和一个参数的形式相同。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_OBJECT('{a,b}', '{1,2}');
JSONB_OBJECT
----------------------
{"a": "1", "b": "2"}
(1 row)JSONB_OBJECT_AGG
JSONB_OBJECT_AGG是聚集函数,将键值对聚合成JSON对象。有关详细信息,请参见 JSONB_OBJECT_AGG 。
JSONB_OBJECT_KEYS
用法:
plain
JSONB_OBJECT_KEYS(jsonb)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON函数,返回外层JSON对象中键的集合。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSONB_OBJECT_KEYS('{"a1":"aaa","a2":{"b1":"bbb","b2":"abc"}}');
JSONB_OBJECT_KEYS
-------------------
a1
a2
(2 rows)JSONB_PATH_EXISTS
用法:
plain
JSONB_PATH_EXISTS(target, path [, vars [, silent]])
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数据。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>
JSONPATH类型,指定JSONPATH表达式。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">vars</font>
JSONB类型,如果指定了vars参数,则它必须是一个JSON对象,并且它的字段提供要替换到JSONPATH表达式中的名称值。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">silent</font>
BOOLEAN类型,如果指定了silent参数并为true,函数会抑制与@?和@@操作符相同的错误。
功能:
JSON函数,检查JSON路径是否返回指定JSON值的任何项。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_PATH_EXISTS('{"a":[1,2,3,4,5]}', '$.a[*] ?(@ >= $min && @ <= $max)', '{"min":2,"max":4}');
JSONB_PATH_EXISTS
-------------------
t
(1 row)JSONB_PATH_MATCH
用法:
plain
JSONB_PATH_MATCH(target, path [, vars [, silent]])
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数据。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>
JSONPATH类型,指定JSONPATH表达式。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">vars</font>
JSONB类型,如果指定了vars参数,则它必须是一个JSON对象,并且它的字段提供要替换到JSONPATH表达式中的名称值。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">silent</font>
BOOLEAN类型,如果指定了silent参数并为true,函数会抑制与@?和@@操作符相同的错误。
功能:
JSON函数,返回指定JSON值的JSON路径谓词检查的结果。只考虑结果的第一项。如果结果不是布尔值,则返回NULL。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_PATH_MATCH('{"a":[1,2,3,4,5]}', 'exists($.a[*] ? (@ >= $min && @ <= $max))', '{"min":2,"max":4}');
JSONB_PATH_MATCH
------------------
t
(1 row)JSONB_PATH_QUERY
用法:
plain
JSONB_PATH_QUERY(target, path [, vars [, silent]])
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数据。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>
JSONPATH类型,指定JSONPATH表达式。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">vars</font>
JSONB类型,如果指定了vars参数,则它必须是一个JSON对象,并且它的字段提供要替换到JSONPATH表达式中的名称值。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">silent</font>
BOOLEAN类型,如果指定了silent参数并为true,函数会抑制与@?和@@操作符相同的错误。
功能:
JSON函数,获取指定JSON值的JSON路径返回的所有项。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSONB_PATH_QUERY('{"a":[1,2,3,4,5]}', '$.a[*] ? (@ >= $min && @ <= $max)', '{"min":2,"max":4}');
JSONB_PATH_QUERY
------------------
2
3
4
(3 rows)JSONB_PATH_QUERY_ARRAY
用法:
plain
JSONB_PATH_QUERY_ARRAY(target, path [, vars [, silent]])
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数据。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>
JSONPATH类型,指定JSONPATH表达式。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">vars</font>
JSONB类型,如果指定了vars参数,则它必须是一个JSON对象,并且它的字段提供要替换到JSONPATH表达式中的名称值。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">silent</font>
BOOLEAN类型,如果指定了silent参数并为true,函数会抑制与@?和@@操作符相同的错误。
功能:
JSON函数,获取指定JSON值的JSON路径返回的所有项,并将结果包装到数组中。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSONB_PATH_QUERY_ARRAY('{"a":[1,2,3,4,5]}', '$.a[*] ? (@ >= $min && @ <= $max)', '{"min":2,"max":4}');
JSONB_PATH_QUERY_ARRAY
------------------------
[2, 3, 4]
(1 row)JSONB_PATH_QUERY_FIRST
用法:
plain
JSONB_PATH_QUERY_FIRST(target, path [, vars [, silent]])
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数据。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>
JSONPATH类型,指定JSONPATH表达式。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">vars</font>
JSONB类型,如果指定了vars参数,则它必须是一个JSON对象,并且它的字段提供要替换到JSONPATH表达式中的名称值。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">silent</font>
BOOLEAN类型,如果指定了silent参数并为true,函数会抑制与@?和@@操作符相同的错误。
功能:
JSON函数,获取指定JSON值的JSON路径返回的第一个JSON项。在没有结果时返回NULL。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSONB_PATH_QUERY_FIRST('{"a":[1,2,3,4,5]}', '$.a[*] ? (@ >= $min && @ <= $max)', '{"min":2,"max":4}');
JSONB_PATH_QUERY_FIRST
------------------------
2
(1 row)JSONB_POPULATE_RECORD
用法:
plain
JSONB_POPULATE_RECORD(base,from_json)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">base</font>
定义记录类型。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON函数,扩展 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font> 中的对象成一个行,它的列匹配由 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">base</font> 定义的记录类型。
例子:
plain
CREATE TYPE subrowtype AS (d int, e text);
CREATE TYPE myrowtype AS (a int, b text[], c subrowtype);
SELECT * FROM JSONB_POPULATE_RECORD(null::myrowtype,'{"a":1, "b": ["2", "a b"],"c": {"d":4, "e": "ab c"}}');
a | b | c
---+-------------+-------------
1 | {2, "a b"} |(4, "ab c")
(1 row)JSONB_POPULATE_RECORDSET
用法:
plain
JSONB_POPULATE_RECORDSET(base, from_json)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">base</font>
定义记录类型。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON函数,扩展 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font> 中最外层的对象数组成一个集合,它的列匹配由 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">base</font> 定义的记录类型。
例子:
plain
CREATE TYPE twoints AS (a int, b int);
SELECT * FROM JSONB_POPULATE_RECORDSET(null::twoints, '[{"a":1,"b":2}, {"a":3,"b":4}]');
a | b
---+---
1 | 2
3 | 4
(2 rows)JSONB_PRETTY
用法:
plain
JSONB_PRETTY(from_json)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数据。
功能:
JSON函数,把 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font> 处理成一段带缩进的JSON文本。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_PRETTY('[{"f1":1,"f2":null},2,null,3]');
JSONB_PRETTY
--------------------
[
{
"f1": 1,
"f2": null
},
2,
null,
3
]
(1 row)JSONB_SET
用法:
plain
JSONB_SET(target, path, new_value [, create_missing])
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font>
JSONB类型,待设置新值的JSON数据。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font>
指定查找JSON数据的路径。正如面向路径的操作符一样,出现在 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 中的负整数表示从JSON数组的末尾开始数。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">new_value</font>
JSONB类型,待设置的新值。
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">create_missing</font>
BOOLEAN类型,如果指定的项不存在并且 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">create_missing</font> 为true(默认为true),则加上 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">new_value</font> ;如果最后一个路径是超出范围的数组 索引,并且 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">create_missing</font> 为true,那么如果索引为负,新值将添加到数组的开头,如果索引为正,则添加到数组的结尾。
功能:
JSON函数,返回 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">target</font> ,将 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">path</font> 指定的节点用 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">new_value</font> 替换。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_SET('[{"f1":1,"f2":null},2,null,3]', '{0,f1}', '[2,3,4]', false);
JSONB_SET
---------------------------------------------
[{"f1": [2, 3, 4], "f2": null}, 2, null, 3]
(1 row)JSONB_STRIP_NULLS
用法:
plain
JSONB_STRIP_NULLS(from_json)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数据。
功能:
JSON函数,返回 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">from_json</font>,其中所有具有空值的对象域都被过滤掉,其他空值不动。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_STRIP_NULLS('[{"f1":1,"f2":null},2,null,3]');
JSONB_STRIP_NULLS
-------------------------
[{"f1": 1}, 2, null, 3]
(1 row)JSONB_TO_RECORD
用法:
plain
JSONB_TO_RECORD(jsonb)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON对象。
功能:
JSON函数,从一个JSON对象构建一个任意的记录,正如所有返回 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">record</font> 的函数一样,调用者必须用一个 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">AS</font> 子句显式的定义记录的结构。
例子:
plain
CREATE TYPE myrowtype AS (a int, b text);
SELECT * FROM JSONB_TO_RECORD('{"a":1,"b":[1,2,3],"c":[1,2,3],"e":"bar","r": {"a": 123, "b": "a b c"}}') AS x(a int,b text, c int[], d text, r myrowtype);
a | b | c | d | r
---+-----------+---------+---+---------------
1 | [1, 2, 3] | {1,2,3} | | (123,"a b c")
(1 row)JSONB_TO_RECORDSET
用法:
plain
JSONB_TO_RECORDSET(jsonb)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON对象数组。
功能:
JSON函数,从一个JSON对象数组构建一个任意的记录集合,正如所有返回 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">record</font> 的函数一样,调用者必须用一个 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">AS</font> 子句显式的定义记录的结构。
例子:
plain
SELECT * FROM JSONB_TO_RECORDSET('[{"a":1,"b":"foo"},{"a":"2","c":"bar"}]')AS x(a int, b text);
a | b
---+-----
1 | foo
2 |
(2 rows)JSONB_TYPEOF
用法:
plain
JSONB_TYPEOF(jsonb)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">jsonb</font>
JSONB类型,指定JSON数据。
功能:
JSON函数,以文本字符串形式返回顶层JSON值的类型。可能类型是: <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">object</font> 、 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">array</font> 、 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">string</font> 、 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">number</font> 、 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">boolean</font> 以及 <font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">null</font> 。
例子:
plain
SELECT JSONB_TYPEOF('-123.4');
JSONB_TYPEOF
--------------
number
(1 row)TO_JSONB
用法:
plain
TO_JSONB(anyelement)
<font style="color:rgb(28, 30, 33);background-color:rgb(246, 247, 248);">anyelement</font>
任意类型的SQL值。
功能:
JSON函数,将任何SQL值转换为JSONB。数组和组合会被(递归)转换成数组和对象;对于不是数组和组合的值,如果有从该类型到JSONB的cast转换函数,那么转换函数将被用来执行该转换;否则将产生一个标量JSONB值。对于任何不是数字、布尔、空值的标量类型都将使用文本表达替代,并根据需要进行转义,使其成为有 效的JSON字符串值。
例子:
plain
SELECT TO_JSONB('Fred said "Hi."'::text);
TO_JSONB
---------------------
"Fred said \"Hi.\""
(1 row)📝Kingbase JSON/JSONB函数使用总结
用了这么久Kingbase KES V9R3C15的JSON相关函数,真的踩过不少坑也摸透了些门道😮💨 简单跟大家唠唠这些函数到底咋用、有啥坑要避。
首先说核心啊,这些函数分JSON和JSONB两类,大部分用法都差不多,JSONB好像更适合做索引、查询更快?反正我平时处理大数据量的时候都优先用JSONB🤔 比如JSONB_CONCAT拼接对象、JSONB_SET修改值,用着都挺顺手。
常用的那些函数里,数组相关的JSON_ARRAY、JSON_ARRAY_APPEND必须提一嘴,之前想往JSON数组里加元素,一开始不知道path咋写,试了半天才明白$[0]这种写法😅 还有JSON_ARRAY_LENGTH查数组长度,外层数组元素个数直接就能出来,不用自己循环计数了,省事儿!
对象操作的话,JSON_BUILD_OBJECT、JSON_OBJECT这些用来构造对象超方便,键值对传进去就行,就是要注意参数个数得是偶数,不然会报错⚠️ 之前手滑少写个值,报得我一脸懵。提取数据的时候JSON_EXTRACT、JSON_EXTRACT_PATH_TEXT很实用,想拿哪个路径的值,直接指定path就行,文本类型用后者更直接。
还有聚合函数像JSON_AGG、JSONB_AGG,把查询结果聚合成JSON数组,做报表统计的时候简直是救星🌟 比如统计每个用户的订单,直接聚合起来返回,前端处理也方便。
坑的话也得说说,很多函数用之前要先创建mysql_json插件,不然会报错❌ 还有path参数不能带*或者**通配符,之前没注意,踩了好几个坑才记住。另外JSON_INSERT和JSON_REPLACE、JSON_SET的区别得分清,insert不替换现有值,replace只替换,set是又替换又新增,别用混了!
对了,JSON_VALID用来校验JSON格式真的好用,接收用户输入的时候先过一遍,避免存进去无效数据。还有JSON_PRETTY,格式化输出JSON看着舒服多了,调试的时候再也不用对着一堆挤在一起的字符串头疼了🤯
整体来说,这些函数覆盖了JSON数据的增删改查、聚合、校验各种场景,用熟了处理JSON数据效率能提不少✅ 就是一开始参数和path写法得慢慢试,多跑几个例子就懂了,大家有啥好用的技巧也可以跟我交流交流呀!
