1.结构体概念
在C++中,结构体(struct)是用户自定义的一种复合数据类型,用于将不同类型的数据组合成一个整体。C++的结构体继承了C语言的struct,但功能更强大,几乎与类(class)相同,主要区别在于默认访问权限。
2.结构体定义和使用
语法:
struct 结构体名 { 结构体成员列表 };C++中的结构体定义如下所示:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//结构体定义
struct Student {
int id;
string name;
int age;
};
int main() {
Student s1; // 创建结构体变量
s1.id = 1001;
s1.name = "张三";
s1.age = 20;
// 也可以用聚合初始化(C++推荐)
Student s2 = { 1002, "李四", 21 };
// C++11起支持列表初始化
Student s3{ 1003, "王五", 22 };
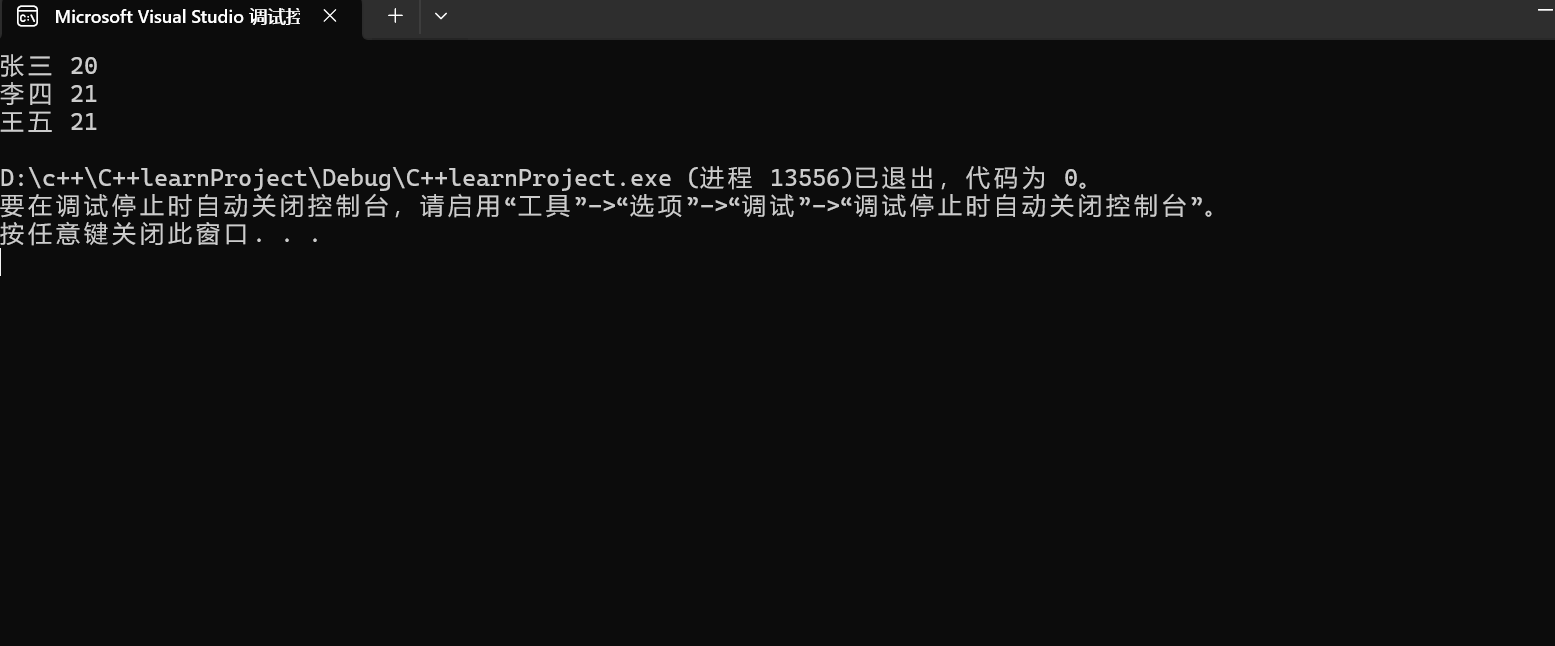
cout << s1.name << " " << s1.age << endl;
cout << s2.name << " " << s2.age << endl;
cout << s3.name << " " << s2.age << endl;
}
3.结构体数组
将自定义的结构体放入到数组中方便维护
struct 结构体名 数组名[元素个数] = { {} , {} , ... {} }
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//结构体定义
struct student
{
//成员列表
string name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
int score; //分数
};
int main() {
//结构体数组
struct student stu[3] =
{
{"张三",18,80 },
{"李四",19,60 },
{"王五",20,70 }
};
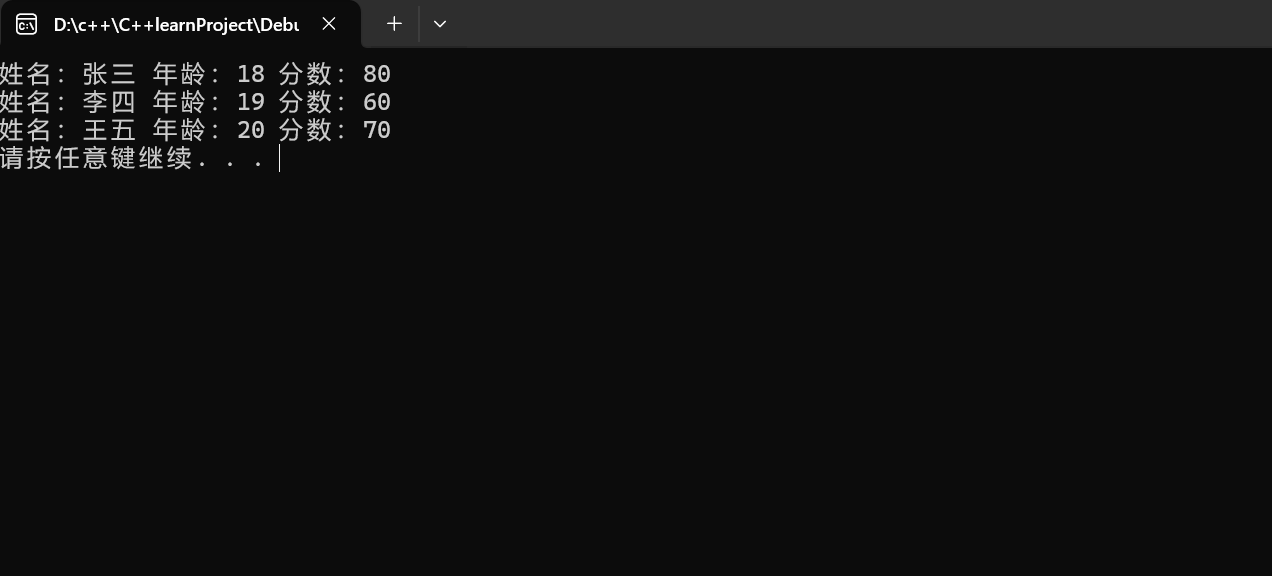
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << stu[i].name << " 年龄:" << stu[i].age << " 分数:" << stu[i].score << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4.结构体指针
通过结构体的指针来访问结构体内的成员变量,利用操作符 -> 可以通过结构体指针访问结构体属性
结构体指针定义
struct 结构体名称 * 指针名称 = 结构体的引用
//完整示例
struct student stu = { "张三",18,100, };
struct student * p= &stu;
//结构体定义
struct student
{
//成员列表
string name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
int score; //分数
};
int main() {
struct student stu = { "张三",18,100, };
struct student* p = &stu;
p->name="李四"; //指针通过 -> 操作符可以访问成员
p->age = 20;
cout << "姓名:" << p->name << " 年龄:" << p->age << " 分数:" << p->score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
5.结构体嵌套
在结构体中,一个结构体中的成员可以是另一个结构体,例如每个老师辅导一个学员,一个老师的结构体中,记录一个学生的结构体
//学生结构体定义
struct student
{
//成员列表
string name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
int score; //分数
};
//教师结构体定义
struct teacher
{
//成员列表
int id; //职工编号
string name; //教师姓名
int age; //教师年龄
struct student stu; //子结构体 学生
};
int main() {
struct teacher t1;
t1.id = 1001;
t1.name = "李老师";
t1.age = 36;
t1.stu.name = "李四";
t1.stu.age = 19;
t1.stu.score = 95;
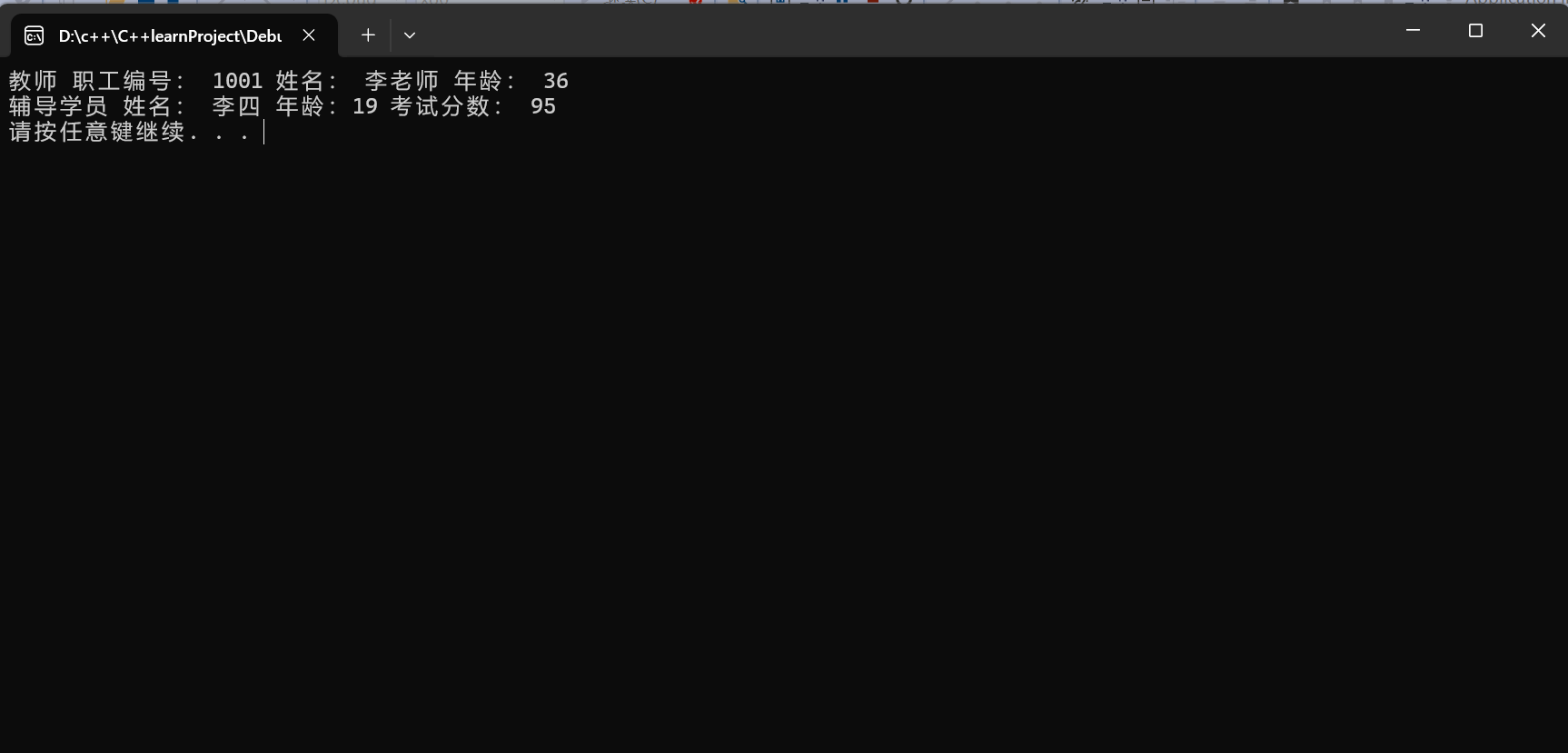
cout << "教师 职工编号: " << t1.id << " 姓名: " << t1.name << " 年龄: " << t1.age << endl;
cout << "辅导学员 姓名: " << t1.stu.name << " 年龄:" << t1.stu.age << " 考试分数: " << t1.stu.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
6.结构体作为函数参数
在C++的函数中,传递方式有两种:
值传递
地址传递
在C++中可以将结构体作为参数进行传递
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//结构体定义
struct student
{
//成员列表
string name; //姓名
int age; //年龄
int score; //分数
};
//结构体值传递
void printStudent1(student stu)
{
stu.age = 18;
}
//结构体地址传递
void printStudent2(student* stu)
{
stu->age = 18;
}
int main() {
student stu = { "李四",20,96 };
//值传递
printStudent1(stu);
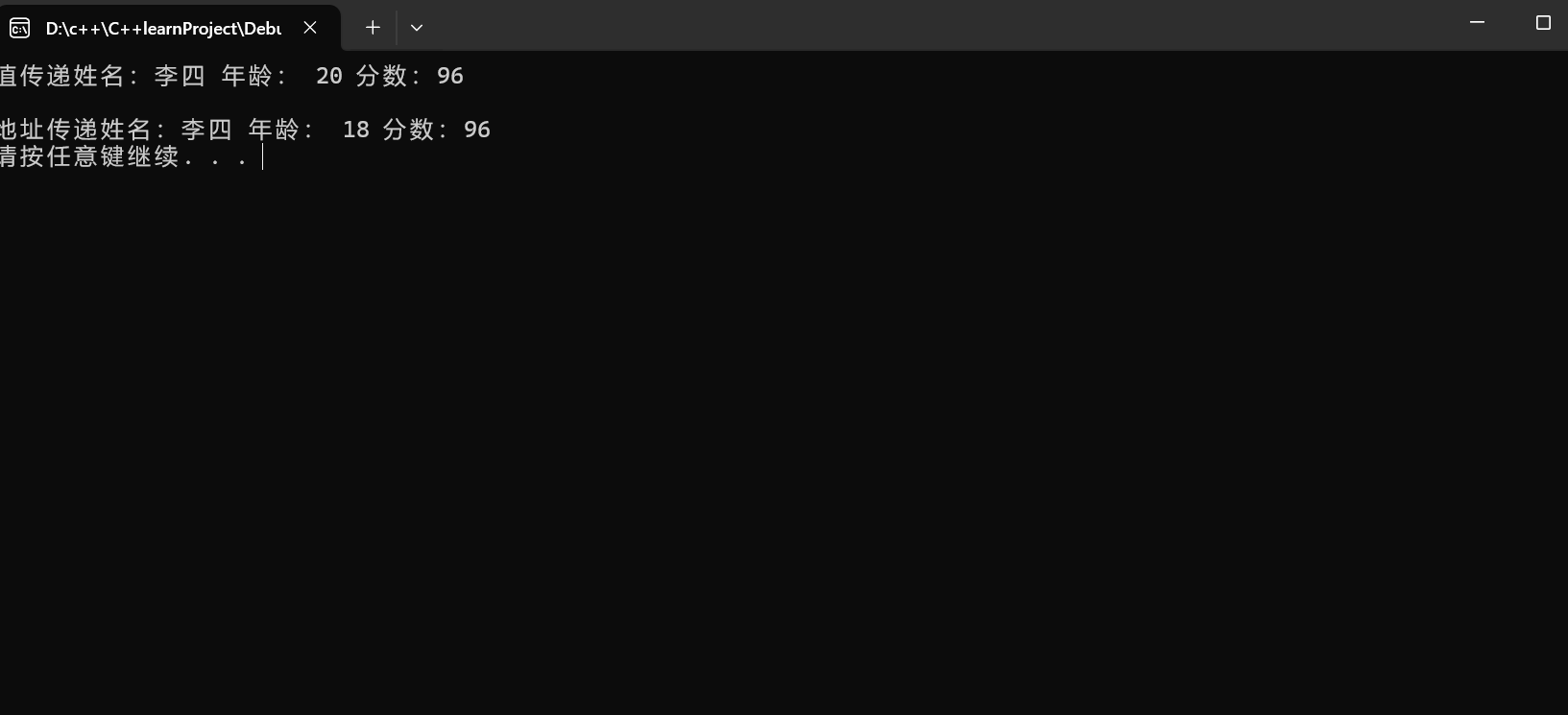
cout << "值传递姓名:" << stu.name << " 年龄: " << stu.age << " 分数:" << stu.score << endl;
cout << endl;
//地址传递
printStudent2(&stu);
cout << "地址传递姓名:" << stu.name << " 年龄: " << stu.age << " 分数:" << stu.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
7.结构体中的的const
const主要用于保证数据的不可变性、防止误操作、提升代码安全性和可读性。
当结构体变量不需要修改时,用const修饰整个对象。防止任何成员被意外更改。
结构体作为函数参数传递时,尤其是地址传递(指针),用const修饰指针,防止函数内部误操作修改原数据。
struct Student {
string name;
int age;
int score;
};
void printStudent(const Student* s) { // const防止误修改
// s->age = 100; // 错误:编译器报错
cout << "姓名:" << s->name << " 年龄:" << s->age << endl;
}
int main() {
Student s = {"张三", 20, 90};
printStudent(&s); // 原数据不变
}