前言:
书接上回,我们在上一章详细讲解了视觉学习中的数据预处理以及其相应的label的格式类型互转的特性,之后又进一步对数据增强的方法进行进一步的总结,接下来这一章是延续上一章节的数据增强方法进行拓展。
1.像素变换类数据增强锦集
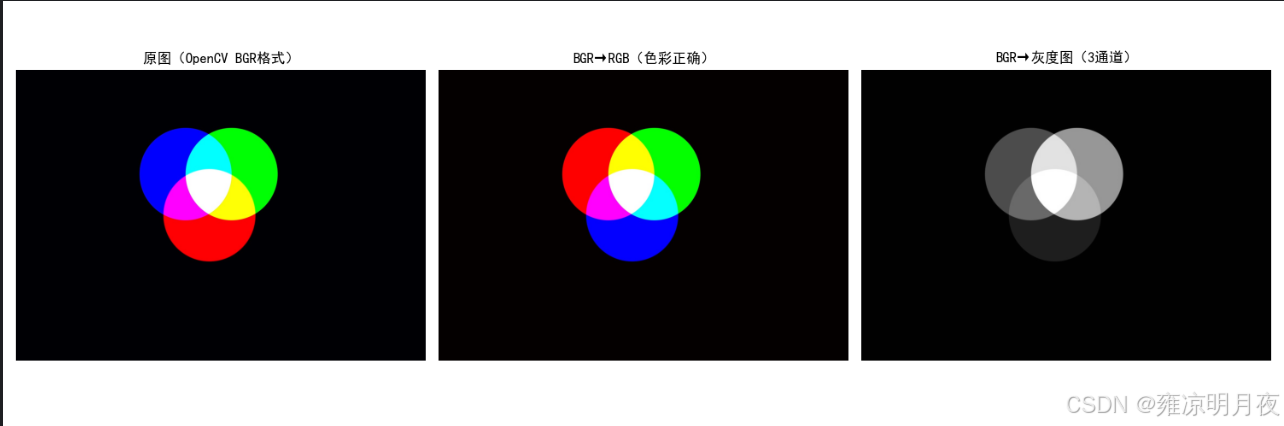
⭐1.BGR<->RGB/BGR->灰度图
核心逻辑:
BGR -> RGB->灰度图
python
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
# ====================== 核心函数:BGR转灰度图 ======================
def bgr2gray(img_bgr: np.ndarray, to_3ch: bool = True) -> np.ndarray:
"""
极简核心:BGR转灰度图(可选转为3通道适配模型输入)
:param img_bgr: OpenCV读取的BGR格式图像(H,W,C)
:param to_3ch: 是否转为3通道(True=模型兼容,False=单通道)
:return: 灰度图(单/3通道)
"""
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 3通道转换(重复单通道数据)
if to_3ch:
return cv2.cvtColor(img_gray, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
return img_gray
# ====================== 核心调用示例 ======================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 配置路径(仅改这里)
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\ok.jpg"
SAVE_DIR = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\pixel_aug_results"
# 2. 加载原图(极简版)
img_bgr = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH)
if img_bgr is None:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"无法读取图片:{IMG_PATH}")
# 3. 核心调用:转灰度图(3通道,适配模型)
img_gray_3ch = bgr2gray(img_bgr, to_3ch=True)
# 可选:转单通道灰度图
# img_gray_1ch = bgr2gray(img_bgr, to_3ch=False)
# 4. 保存结果(仅保留核心保存)
os.makedirs(SAVE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
img_basename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(IMG_PATH))[0]
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_gray_3ch.jpg", img_gray_3ch)
# cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_gray_1ch.jpg", img_gray_1ch) # 单通道保存
print(f"转灰度图完成!保存路径:{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_gray_3ch.jpg")
print("核心要点:")
print("1. to_3ch=True:灰度图转为3通道,可直接输入要求3通道的模型;")
print("2. to_3ch=False:输出单通道灰度图,仅保留亮度信息;")
print("3. 无色彩失真:灰度转换仅丢失色度信息,亮度特征完整保留。")2.全局直方图均衡化
python
cv2.equalizeHist(gray_img) # 仅支持单通道(灰度/Y通道)核心代码:
python
def global_histogram_equalization(img_bgr: np.ndarray) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""
全局直方图均衡化(工业级实现:区分灰度/彩色图)
Args:
img_bgr: BGR格式原图
Returns:
img_gray_eq: 灰度图均衡化结果(3通道)
img_color_eq: 彩色图均衡化结果(仅均衡化亮度通道,保留色彩)
"""
# ========== 1. 灰度图直方图均衡化 ==========
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img_gray_eq = cv2.equalizeHist(img_gray) # 核心API:全局直方图均衡化
img_gray_eq_3ch = cv2.cvtColor(img_gray_eq, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) # 转3通道
print("完成灰度图全局直方图均衡化(提升整体对比度)")
# ========== 2. 彩色图直方图均衡化(关键:仅处理亮度通道) ==========
# 彩色图不能直接均衡化BGR通道(会色彩失真),需转YCrCb空间(Y=亮度,Cr/Cb=色彩)
img_ycrcb = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YCrCb)
# 仅对亮度通道(Y)做均衡化
img_ycrcb[:, :, 0] = cv2.equalizeHist(img_ycrcb[:, :, 0])
# 转回BGR空间
img_color_eq = cv2.cvtColor(img_ycrcb, cv2.COLOR_YCrCb2BGR)
print("完成彩色图全局直方图均衡化(仅均衡化亮度通道,无色彩失真)")
return img_gray_eq_3ch, img_color_eq3.自适应均衡化
cv2.createCLAHE()(区别于全局均衡化的cv2.equalizeHist())
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
def adaptive_histogram_equalization(img_bgr: np.ndarray) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""
自适应区域直方图均衡化(核心方法)
关键参数:
- clipLimit=2.0:限制对比度,避免过度增强放大噪声
- tileGridSize=(8,8):分块大小,将图像分为8×8的小区域分别均衡化
"""
# ========== 1. 灰度图自适应均衡化 ==========
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 创建CLAHE对象(核心API)
clahe = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=2.0, tileGridSize=(8, 8))
img_gray_clahe = clahe.apply(img_gray) # 应用自适应均衡化
img_gray_clahe_3ch = cv2.cvtColor(img_gray_clahe, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
# ========== 2. 彩色图自适应均衡化(仅亮度通道) ==========
img_ycrcb = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YCrCb)
img_ycrcb[:, :, 0] = clahe.apply(img_ycrcb[:, :, 0]) # 仅处理亮度通道
img_color_clahe = cv2.cvtColor(img_ycrcb, cv2.COLOR_YCrCb2BGR)
return img_gray_clahe_3ch, img_color_clahe
# ------------------- 核心调用示例 -------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 加载原图
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\ok.jpg"
img_origin = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
# 2. 核心调用:自适应直方图均衡化
img_gray_clahe, img_color_clahe = adaptive_histogram_equalization(img_origin)
# 3. 保存结果(可选,用于对比)
SAVE_DIR = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\pixel_aug_results"
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/ok_gray_adaptive_hist_eq.jpg", img_gray_clahe)
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/ok_color_adaptive_hist_eq.jpg", img_color_clahe)
print("自适应直方图均衡化完成!")
print("关键差异:")
print("1. 对比全局均衡化:局部明暗不均区域(如部分逆光)会更自然,无过曝/噪声放大;")
print("2. clipLimit越大:对比度增强越明显,但易放大噪声;建议2.0(工业常用);")
print("3. tileGridSize越小:分块越细,局部适配越好,但计算量略增;8×8为最优平衡。")4.随机调节亮度
random_brightness(随机调整亮度)
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import random
def random_brightness(img_bgr: np.ndarray, brightness_range=(0.5, 1.5)) -> np.ndarray:
"""
随机调整亮度(核心方法)
关键约束:
- 亮度因子限制在 0.5~1.5(避免过暗/过曝)
- 像素值强制 clip 到 0~255,防止异常值
"""
# 随机生成亮度因子(0.5~1.5 倍)
brightness = random.uniform(*brightness_range)
# 转为 float 计算(避免 uint8 溢出)
img_float = img_bgr.astype(np.float32)
# 调整亮度(所有通道同比例调整,保留色彩)
img_bright = img_float * brightness
# 限制像素值在 0~255 之间(核心约束)
img_bright = np.clip(img_bright, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
return img_bright
# ------------------- 核心调用示例 -------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 加载原图
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\ok.jpg"
img_origin = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
# 2. 核心调用:随机调整亮度(0.5~1.5 倍)
img_bright = random_brightness(img_origin, brightness_range=(0.5, 1.5))
# 3. 保存结果(用于对比)
SAVE_DIR = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\pixel_aug_results"
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/ok_random_brightness.jpg", img_bright)
print("随机亮度调整完成!")
print("关键要点:")
print("1. 亮度因子建议 0.5~1.5:<0.3 过暗丢失细节,>1.8 过曝;")
print("2. 所有通道同比例调整:避免色彩偏移(如仅调R通道导致偏色);")
print("3. 必须 clip 像素值:uint8 范围 0~255,溢出会出现伪色/黑块;")
print("4. 适用场景:模拟强光/弱光下的工业目标(如车间灯光明暗变化)。")5.图像像素取反
核心调用方式:
python# 仅执行像素取反(直接使用) img_bgr = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH) img_inverted = img_bitwise_not(img_bgr) cv2.imwrite("ok_bitwise_not.jpg", img_inverted)
python
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
# ====================== 核心函数:图像像素取反(反色) ======================
def img_bitwise_not(img_bgr: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
"""
极简核心:OpenCV BGR图像像素取反(反色)
:param img_bgr: OpenCV读取的BGR格式图像(H,W,C)
:return: 反色后的BGR图像
"""
# 核心API:cv2.bitwise_not 直接对像素取反(uint8范围0~255,等价于 255 - 像素值)
img_inverted = cv2.bitwise_not(img_bgr)
return img_inverted
# ====================== 极简加载/保存标签(取反无需修改标签,仅拷贝) ======================
def copy_yolo_label(src_label_path: str, dst_label_path: str):
"""复制原标签(取反不改变目标框,无需修正)"""
if os.path.exists(src_label_path):
import shutil
shutil.copy(src_label_path, dst_label_path)
print(f"标签已拷贝:{dst_label_path}")
# ====================== 核心调用示例 ======================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 配置路径(仅改这里)
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\ok.jpg"
LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\ok.txt" # 可选:原YOLO标签
SAVE_DIR = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\pixel_aug_results"
# 2. 加载原图(极简版)
img_bgr = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH)
if img_bgr is None:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"无法读取图片:{IMG_PATH}")
# 3. 核心调用:像素取反
img_inverted = img_bitwise_not(img_bgr)
# 4. 保存结果
os.makedirs(SAVE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
img_basename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(IMG_PATH))[0]
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_bitwise_not.jpg", img_inverted)
# 5. 拷贝标签(取反不改变目标框,直接复用原标签)
if os.path.exists(LABEL_PATH):
copy_yolo_label(LABEL_PATH, f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_bitwise_not.txt")
print(f"像素取反完成!保存路径:{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_bitwise_not.jpg")
print("核心要点:")
print("1. 核心效果:像素值取反(如黑色→白色、红色→青色),增强目标与背景对比度;")
print("2. 标签处理:无需修正YOLO框(仅像素值变化,目标位置/大小不变);")
print("3. 适用场景:深色背景下的浅色目标、黑白对比强烈的工业场景(如印刷字符);")
print("4. 无参数调整:纯像素值反转,无超参需调优。")6.减去像素均值(subtract_mean)
核心调用:
python# 自动计算全局均值并减去 img_bgr = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH) img_sub_mean = subtract_mean(img_bgr, mean=None) cv2.imwrite("ok_sub_mean.jpg", img_sub_mean)作用:像素级归一化操作
1. 消除全局光照偏移的影响
2. 降低数据分布差异,提升模型泛化性
场景:
1. 光照不稳定的工业 / 户外视觉场景(核心场景)
- 工业检测:车间零件 / 包装盒拍摄(灯光明暗、角度导致光照不均);
- 户外视觉:交通摄像头、无人机图像(早晚 / 阴天 / 晴天光照差异大);
- 安防监控:夜间 / 白天的行人 / 车辆检测(全局亮度波动大)。
2. 基于预训练模型的迁移学习(必用场景)
只要你在分类、检测、分割任务中复用「ImageNet 预训练权重」,必须将输入图像减去预训练时的固定均值(如 ImageNet 均值),否则模型的底层特征提取(如边缘、纹理)会完全偏离预期。例:用 ResNet50 做工业零件缺陷分类,第一步预处理就是
subtract_mean(img, mean=[103.939, 116.779, 123.68])
使用必须要做的事情:
- 必须做
clip约束 :减去均值后可能出现负数像素(如暗区像素值 5,均值 10,结果 - 5),需用np.clip(img_sub_mean, 0, 255)限制到 0~255,否则图像会出现伪色、黑块等异常;- 均值选择要匹配场景 :
- 迁移学习:用预训练模型的固定均值(如 ImageNet);
- 自有数据集训练:计算数据集的全局均值(所有图片的通道均值),而非单张图片均值(代码中
np.mean(img_float, axis=(0,1))是单张均值,批量训练需先算全量均值);- 仅像素值变化,标签无需修改:和像素取反、亮度调整一样,减去均值不改变目标的位置 / 大小,YOLO 标签直接拷贝即可。
python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project :Pytorch
@File :subtract_mean.py
@IDE :PyCharm
@Author :wjj
@Date :2025/12/14 18:56
@Description:
"""
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
# ====================== 核心函数:减去像素均值 ======================
def subtract_mean(img_bgr: np.ndarray, mean: list = None) -> np.ndarray:
"""
极简核心:图像减去像素均值(全局/自定义),clip避免像素值异常
:param img_bgr: OpenCV读取的BGR图像(H,W,C)
:param mean: 自定义均值 [B, G, R],None则计算图像全局均值
:return: 减去均值后的BGR图像(uint8)
"""
# 转为float计算,避免uint8溢出(负数/超界)
img_float = img_bgr.astype(np.float32)
# 计算/使用均值
if mean is None:
mean = np.mean(img_float, axis=(0, 1)) # 按通道计算全局均值
print(f"自动计算图像全局均值(B/G/R):{mean.round(2)}")
else:
mean = np.array(mean, dtype=np.float32)
# 核心操作:减去均值 + 约束像素值到0~255
img_sub_mean = img_float - mean
img_sub_mean = np.clip(img_sub_mean, 0, 255) # 避免负数/超255导致图像异常
# 转回uint8(符合OpenCV保存/模型输入要求)
return img_sub_mean.astype(np.uint8)
# ====================== 极简标签处理(直接拷贝) ======================
def copy_yolo_label(src_label_path: str, dst_label_path: str):
"""拷贝原标签(均值减法不改变目标框)"""
if os.path.exists(src_label_path):
import shutil
shutil.copy(src_label_path, dst_label_path)
# ====================== 核心调用示例 ======================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 配置路径
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\ok.jpg"
LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\ok.txt" # 可选
SAVE_DIR = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\pixel_aug_results"
# 2. 加载原图
img_bgr = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH)
if img_bgr is None:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"无法读取图片:{IMG_PATH}")
# 3. 核心调用(两种方式可选)
# 方式1:自动计算全局均值
img_sub_global_mean = subtract_mean(img_bgr, mean=None)
# 方式2:使用自定义均值(如ImageNet均值 [103.939, 116.779, 123.68],适配预训练模型)
# img_sub_custom_mean = subtract_mean(img_bgr, mean=[103.939, 116.779, 123.68])
# 4. 保存结果
os.makedirs(SAVE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
img_basename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(IMG_PATH))[0]
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_sub_global_mean.jpg", img_sub_global_mean)
# cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_sub_custom_mean.jpg", img_sub_custom_mean)
# 5. 拷贝标签(无需修正)
if os.path.exists(LABEL_PATH):
copy_yolo_label(LABEL_PATH, f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_sub_global_mean.txt")
print(f"减去均值完成!保存路径:{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_sub_global_mean.jpg")
print("核心要点:")
print("1. 核心作用:降低光照全局偏移影响,提升模型泛化性;")
print("2. 关键约束:必须clip到0~255,否则负数像素会导致图像偏色/异常;")
print("3. 均值选择:自定义均值(如ImageNet)适配预训练模型,全局均值适配自有数据;")
print("4. 标签处理:仅像素值偏移,目标框不变,直接拷贝原标签。")7.图像锐化增强(拉普拉斯 / 高斯 / 均值)
核心调用:
python# 仅执行高斯锐化(最常用,效果柔和) img_bgr = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH) img_sharpen = image_sharpen(img_bgr, sharpen_type="gaussian", alpha=0.5) cv2.imwrite("ok_gaussian_sharpen.jpg", img_sharpen)其本质作用为:利用 "模糊 / 边缘提取" 的结果反向增强细节。其与去噪的三种模糊效果完全相反。
可以把图像想象成 "一张有纹理的纸":
- 模糊(均值 / 高斯):用手把纸揉平,纹理(细节)变浅(弱化);
- 锐化(均值 / 高斯):把揉平的纸和原纸对比,找出 "变浅的纹理差",再用笔把这些纹理描深(强化);
- 拉普拉斯锐化:直接找到纸的 "轮廓线"(边缘),用笔把轮廓线描粗(强强化)。
场景需求 选模糊(均值 / 高斯) 选锐化(均值 / 高斯 / 拉普拉斯) 图像有颗粒噪声,需降噪 ✅ 均值模糊 ❌ 锐化会放大噪声 低分辨率图,需平滑轮廓 ✅ 高斯模糊 ❌ 锐化会放大像素块 模糊的零件划痕,需清晰 ❌ 模糊会更糊 ✅ 拉普拉斯锐化(强边缘) 印刷字边缘模糊,需柔和增强 ❌ 模糊会更糊 ✅ 高斯锐化(自然无伪影) 纹理对比度低,需强化 ❌ 模糊会降低对比度 ✅ 均值锐化(提升纹理对比)
python
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
# ====================== 核心函数:多类型图像锐化 ======================
def image_sharpen(img_bgr: np.ndarray, sharpen_type: str = "laplacian", alpha: float = 0.5) -> np.ndarray:
"""
极简核心:拉普拉斯/高斯/均值锐化(增强边缘/纹理)
:param img_bgr: OpenCV读取的BGR图像(H,W,C)
:param sharpen_type: 锐化类型 - laplacian/gaussian/mean
:param alpha: 锐化强度(0.3~0.7为宜,过强产生伪影)
:return: 锐化后的BGR图像(uint8)
"""
# 转为float计算,避免uint8溢出
img_float = img_bgr.astype(np.float32)
# 1. 生成模糊/边缘图(不同锐化类型的核心差异)
if sharpen_type == "laplacian":
# 拉普拉斯锐化:提取边缘后叠加到原图
laplacian = cv2.Laplacian(img_float, cv2.CV_32F, ksize=3) # 3×3核提取边缘
img_sharpen = img_float + alpha * laplacian
elif sharpen_type == "gaussian":
# 高斯锐化:原图 - 高斯模糊图 → 增强细节
img_blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(img_float, (3, 3), 1.0) # 3×3高斯核,sigma=1
img_sharpen = img_float + alpha * (img_float - img_blur)
elif sharpen_type == "mean":
# 均值锐化:原图 - 均值模糊图 → 增强对比度
img_blur = cv2.blur(img_float, (3, 3)) # 3×3均值核
img_sharpen = img_float + alpha * (img_float - img_blur)
else:
raise ValueError(f"无效锐化类型:{sharpen_type},可选laplacian/gaussian/mean")
# 2. 约束像素值到0~255,避免伪影/溢出
img_sharpen = np.clip(img_sharpen, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
return img_sharpen
# ====================== 极简标签处理(直接拷贝) ======================
def copy_yolo_label(src_label_path: str, dst_label_path: str):
"""拷贝原标签(锐化不改变目标框)"""
if os.path.exists(src_label_path):
import shutil
shutil.copy(src_label_path, dst_label_path)
# ====================== 核心调用示例 ======================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 配置路径
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy.jpg"
LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\ok.txt" # 可选
SAVE_DIR = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out"
# 2. 加载原图
img_bgr = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH)
if img_bgr is None:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"无法读取图片:{IMG_PATH}")
# 3. 核心调用:三种锐化(按需选一种)
img_laplacian = image_sharpen(img_bgr, sharpen_type="laplacian", alpha=0.5) # 拉普拉斯(边缘最强)
img_gaussian = image_sharpen(img_bgr, sharpen_type="gaussian", alpha=0.5) # 高斯(最柔和)
img_mean = image_sharpen(img_bgr, sharpen_type="mean", alpha=0.5) # 均值(对比度增强)
# 4. 保存结果
os.makedirs(SAVE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
img_basename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(IMG_PATH))[0]
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_laplacian_sharpen.jpg", img_laplacian)
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_gaussian_sharpen.jpg", img_gaussian)
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_mean_sharpen.jpg", img_mean)
# 5. 拷贝标签(无需修正)
if os.path.exists(LABEL_PATH):
copy_yolo_label(LABEL_PATH, f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_laplacian_sharpen.txt")
print("三种锐化完成!保存路径:", SAVE_DIR)
print("核心要点:")
print("1. 锐化强度alpha:0.3~0.7为宜,>0.8易产生锯齿/伪影,<0.2效果不明显;")
print("2. 类型选择:")
print(" - laplacian:边缘增强最强(适合模糊的目标边缘,如远距离小目标);")
print(" - gaussian:锐化最柔和(适合低分辨率/运动模糊图像,无明显伪影);")
print(" - mean:对比度增强(适合纹理模糊的目标,如印刷字符/零件纹理);")
print("3. 适用场景:低分辨率、运动模糊、边缘模糊的工业目标(如包装盒文字、零件划痕);")
print("4. 标签处理:仅增强纹理,目标框不变,直接拷贝原标签。")8.Sobel 边缘融合增强
本质:
Sobel 边缘提取 + 边缘融合到原图核心逻辑(强化目标边缘特征)
python# 仅执行双方向Sobel边缘融合(最常用) img_bgr = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH) img_sobel = sobel_edge_to_image(img_bgr, edge_dir="both", alpha=0.5) cv2.imwrite("ok_sobel_both.jpg", img_sobel)
- Sobel 算子是 "边缘提取刀",高斯算子是 "降噪洗菜盆",二者都是底层工具;
- Sobel 边缘融合增强是 "用刀 + 盆(可选)做一道边缘更清晰的菜",是上层应用流程;
python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project :Pytorch
@File :sobel_.py
@IDE :PyCharm
@Author :wjj
@Date :2025/12/14 19:23
@Description:
"""
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
# ====================== 核心函数:Sobel边缘提取+融合到原图 ======================
def sobel_edge_to_image(img_bgr: np.ndarray, edge_dir: str = "both", alpha: float = 0.5) -> np.ndarray:
"""
极简核心:Sobel边缘提取 + 边缘图融合到原图(强化边缘特征)
:param img_bgr: OpenCV读取的BGR图像(H,W,C)
:param edge_dir: 边缘检测方向 - x(垂直)/y(水平)/both(双方向)
:param alpha: 边缘融合强度(0.3~0.8为宜,过强掩盖原图细节)
:return: 融合边缘后的BGR图像(uint8)
"""
# 1. 转为灰度图(Sobel仅支持单通道)
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY).astype(np.float32)
# 2. Sobel边缘提取(核心API:cv2.Sobel,一阶导数边缘检测)
if edge_dir == "x":
# x方向:检测垂直边缘(如文字竖线、零件竖边)
sobel_edge = cv2.Sobel(img_gray, cv2.CV_32F, dx=1, dy=0, ksize=3)
elif edge_dir == "y":
# y方向:检测水平边缘(如文字横线、零件横边)
sobel_edge = cv2.Sobel(img_gray, cv2.CV_32F, dx=0, dy=1, ksize=3)
elif edge_dir == "both":
# 双方向:合并x/y边缘(最常用,完整边缘)
sobel_x = cv2.Sobel(img_gray, cv2.CV_32F, dx=1, dy=0, ksize=3)
sobel_y = cv2.Sobel(img_gray, cv2.CV_32F, dx=0, dy=1, ksize=3)
sobel_edge = cv2.addWeighted(sobel_x, 0.5, sobel_y, 0.5, 0)
else:
raise ValueError(f"无效边缘方向:{edge_dir},可选x/y/both")
# 3. 边缘图归一化(0~255)+ 转为3通道(匹配原图)
sobel_edge = np.clip(cv2.normalize(sobel_edge, None, 0, 255, cv2.NORM_MINMAX), 0, 255)
sobel_edge_3ch = cv2.cvtColor(sobel_edge.astype(np.uint8), cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
# 4. 边缘图融合到原图(核心:原图为主,边缘图为辅)
img_float = img_bgr.astype(np.float32)
edge_float = sobel_edge_3ch.astype(np.float32)
img_fused = (1 - alpha) * img_float + alpha * edge_float # 加权融合
img_fused = np.clip(img_fused, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
return img_fused
# ====================== 极简标签处理(直接拷贝) ======================
def copy_yolo_label(src_label_path: str, dst_label_path: str):
"""拷贝原标签(边缘融合不改变目标框)"""
if os.path.exists(src_label_path):
import shutil
shutil.copy(src_label_path, dst_label_path)
# ====================== 核心调用示例 ======================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 配置路径
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy.jpg"
LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\perspective_data\ok.txt" # 可选
SAVE_DIR = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\sobel"
# 2. 加载原图
img_bgr = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH)
if img_bgr is None:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"无法读取图片:{IMG_PATH}")
# 3. 核心调用(按需选方向)
img_sobel_x = sobel_edge_to_image(img_bgr, edge_dir="x", alpha=0.5) # 垂直边缘
img_sobel_y = sobel_edge_to_image(img_bgr, edge_dir="y", alpha=0.5) # 水平边缘
img_sobel_both = sobel_edge_to_image(img_bgr, edge_dir="both", alpha=0.5) # 双方向(最常用)
# 4. 保存结果
os.makedirs(SAVE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
img_basename = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(IMG_PATH))[0]
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_sobel_x.jpg", img_sobel_x)
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_sobel_y.jpg", img_sobel_y)
cv2.imwrite(f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_sobel_both.jpg", img_sobel_both)
# 5. 拷贝标签(无需修正)
if os.path.exists(LABEL_PATH):
copy_yolo_label(LABEL_PATH, f"{SAVE_DIR}/{img_basename}_sobel_both.txt")
print("Sobel边缘融合完成!保存路径:", SAVE_DIR)
print("核心要点:")
print("1. 边缘方向选择:")
print(" - x方向:强化垂直边缘(如包装盒竖边、文字竖线);")
print(" - y方向:强化水平边缘(如包装盒横边、文字横线);")
print(" - both:完整强化所有边缘(工业场景首选);")
print("2. 强度alpha:0.3~0.8为宜,>0.8会掩盖原图纹理,<0.3边缘增强不明显;")
print("3. 适用场景:边缘模糊的工业目标(如低分辨率零件边缘、印刷字符轮廓);")
print("4. 核心差异:Sobel是一阶导数边缘(柔和),拉普拉斯是二阶(锐利),Sobel更适合工业模糊图。")2.图像融合 / 拼接类数据增强锦集
1.MixUp 数据增强
核心:将两张图按照一定的权重进行融合为一张图
核心代码:
python# 仅执行MixUp融合(λ=0.5) img1 = cv2.imread(IMG1_PATH) img2 = cv2.imread(IMG2_PATH) bboxes1 = load_yolo_bboxes(LABEL1_PATH) bboxes2 = load_yolo_bboxes(LABEL2_PATH) img_mix, bboxes_mix = mix_up_images(img1, img2, bboxes1, bboxes2, lambda_=0.5)
python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project :Pytorch
@File :mixup.py
@IDE :PyCharm
@Author :wjj
@Date :2025/12/14 19:41
@Description:mixup(新增带Box可视化功能)
"""
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
import random
# ====================== 核心函数:MixUp图像+标签融合 ======================
def mix_up_images(img1: np.ndarray, img2: np.ndarray, bboxes1: np.ndarray, bboxes2: np.ndarray,
lambda_: float = None) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""
极简核心:两张图像MixUp融合 + YOLO标签合并(检测场景)
:param img1: 第一张BGR图像(H,W,C)
:param img2: 第二张BGR图像(需和img1同尺寸)
:param bboxes1: 第一张图YOLO归一化框 [x,y,w,h],shape=(n,4)
:param bboxes2: 第二张图YOLO归一化框 [x,y,w,h],shape=(m,4)
:param lambda_: 融合系数(0~1),None则随机生成(0.3~0.7)
:return: mix_up后的图像、合并后的YOLO框(n+m,4)
"""
# 1. 确保两张图尺寸一致(MixUp前提)
if img1.shape != img2.shape:
img2 = cv2.resize(img2, (img1.shape[1], img1.shape[0]))
# 2. 随机生成融合系数λ(0.3~0.7避免某张图占比过高)
if lambda_ is None:
lambda_ = random.uniform(0.3, 0.7)
# 3. 图像加权融合(核心:img1*λ + img2*(1-λ))
img1_float = img1.astype(np.float32)
img2_float = img2.astype(np.float32)
img_mix = lambda_ * img1_float + (1 - lambda_) * img2_float
img_mix = np.clip(img_mix, 0, 255).astype(np.uint8)
# 4. 标签合并(检测任务:保留两张图的所有框,无需加权)
# 分类任务需加权类别概率,检测任务直接合并框即可
bboxes_mix = np.vstack([bboxes1, bboxes2]) if len(bboxes1) > 0 and len(bboxes2) > 0 else (
bboxes1 if len(bboxes1) > 0 else bboxes2)
return img_mix, bboxes_mix
# ====================== 新增:可视化MixUp结果(带Box) ======================
def visualize_mix_up(img_mix: np.ndarray, bboxes_mix: np.ndarray, class_ids: list, save_path: str):
"""
将合并后的YOLO框绘制到MixUp图像上,保存带框的可视化结果
:param img_mix: MixUp融合后的BGR图像
:param bboxes_mix: 合并后的YOLO归一化框 [x,y,w,h]
:param class_ids: 框对应的类别ID列表
:param save_path: 可视化结果保存路径
"""
img_vis = img_mix.copy()
h, w = img_vis.shape[:2]
# 定义不同类别的框颜色(区分img1和img2的框)
class_colors = {0: (0, 255, 0), 1: (0, 0, 255)} # class0绿色,class1红色
# 遍历所有框,绘制到图像上
for cls, box in zip(class_ids, bboxes_mix):
# YOLO归一化框 → 像素坐标
x_center, y_center, box_w, box_h = box
x_center_pix = x_center * w
y_center_pix = y_center * h
box_w_pix = box_w * w
box_h_pix = box_h * h
# 计算框的左上角/右下角坐标
x1 = int(x_center_pix - box_w_pix / 2)
y1 = int(y_center_pix - box_h_pix / 2)
x2 = int(x_center_pix + box_w_pix / 2)
y2 = int(y_center_pix + box_h_pix / 2)
# 绘制矩形框 + 类别标签
color = class_colors.get(cls, (255, 0, 0)) # 默认蓝色
cv2.rectangle(img_vis, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
cv2.putText(img_vis, f"cls{cls}", (x1, y1 - 5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2)
# 保存可视化结果
cv2.imwrite(save_path, img_vis)
print(f"带Box的MixUp可视化结果已保存:{save_path}")
# ====================== 极简加载/保存YOLO标签 ======================
def load_yolo_bboxes(label_path: str) -> np.ndarray:
"""仅加载YOLO归一化框"""
bboxes = []
if os.path.exists(label_path):
with open(label_path) as f:
for line in f:
parts = line.strip().split()
if len(parts) >= 5: bboxes.append([float(x) for x in parts[1:5]])
return np.array(bboxes, dtype=np.float32)
def save_yolo_bboxes(label_path: str, class_ids: list, bboxes: np.ndarray):
"""保存MixUp后的YOLO标签(合并两张图的类别+框)"""
# class_ids需和bboxes长度匹配(如img1的框对应class0,img2的框对应class1)
with open(label_path, "w") as f:
for cls, box in zip(class_ids, bboxes):
f.write(f"{cls} {box[0]:.6f} {box[1]:.6f} {box[2]:.6f} {box[3]:.6f}\n")
# ====================== 核心调用示例 ======================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 配置两张图/标签路径(MixUp需至少两张图)
IMG1_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy.jpg"
LABEL1_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy.txt" # class 0
IMG2_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy1.jpg"
LABEL2_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy1.txt" # class 1
SAVE_DIR = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out"
# 2. 加载两张图+标签
img1 = cv2.imread(IMG1_PATH)
img2 = cv2.imread(IMG2_PATH)
bboxes1 = load_yolo_bboxes(LABEL1_PATH)
bboxes2 = load_yolo_bboxes(LABEL2_PATH)
# 3. 核心调用:MixUp融合
img_mix, bboxes_mix = mix_up_images(img1, img2, bboxes1, bboxes2, lambda_=0.5)
# 4. 准备合并后的类别ID(img1的框→class0,img2的框→class1)
class_ids = [0] * len(bboxes1) + [1] * len(bboxes2)
# 5. 保存结果(原融合图 + 带Box的可视化图)
os.makedirs(SAVE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
# 保存纯融合图
mix_img_path = f"{SAVE_DIR}/mix_up_result.jpg"
cv2.imwrite(mix_img_path, img_mix)
# 保存带Box的可视化图
vis_img_path = f"{SAVE_DIR}/mix_up_result_with_box.jpg"
visualize_mix_up(img_mix, bboxes_mix, class_ids, vis_img_path)
# 6. 保存标签
save_yolo_bboxes(f"{SAVE_DIR}/mix_up_result.txt", class_ids, bboxes_mix)
print(f"\nMixUp完成!融合系数λ=0.5,合并后框数:{len(bboxes_mix)}")
print("生成文件列表:")
print(f"1. 纯融合图像:{mix_img_path}")
print(f"2. 带Box可视化图像:{vis_img_path}")
print(f"3. 合并后标签文件:{SAVE_DIR}/mix_up_result.txt")
print("\n核心要点:")
print("1. 核心作用:提升模型泛化性,缓解过拟合(尤其小样本工业场景);")
print("2. 关键约束:两张图需同尺寸(自动resize适配),λ取0.3~0.7效果最优;")
print("3. 标签处理:检测任务直接合并框,分类任务需加权类别概率;")
print("4. 可视化说明:class0(img1)框为绿色,class1(img2)框为红色,便于区分来源;")
print("5. 区别于普通融合:MixUp是随机λ加权,且标签需同步融合,非简单拼接。")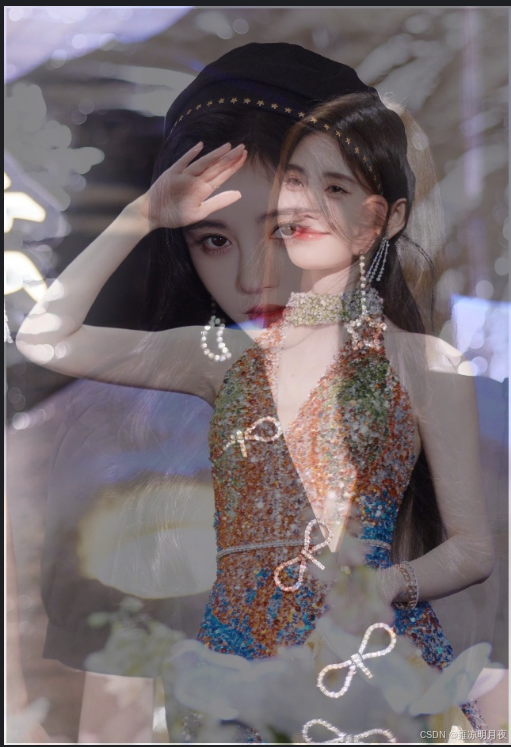
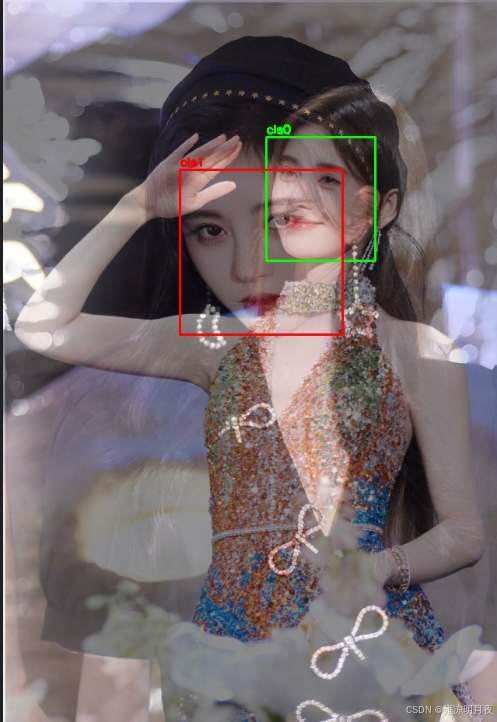

2.mosaic数据增强
本质:将四张图组合到一起,形成新的图,遵循"随机采样+策略约束",裁剪面积要求,保证有效的box留存率。本质就是在数据集中随机选4张图片再组合起来,形成新的图片增加box的密度。
python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project :Pytorch
@File :mosaic.py
@IDE :PyCharm
@Author :wjj
@Date :2025/12/14 22:00
@Description:Mosaic增强:4图固定位置+保留所有Box(修复NameError)
"""
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
# ====================== 单张图预处理:resize+Box坐标转换 ======================
def process_single_image(img_path, label_path, target_region_size):
"""
处理单张图:
1. resize到目标区域尺寸(最终图的1/4)
2. 转换Box坐标为区域内像素坐标
3. 返回:处理后的图、区域内Box像素坐标、类别ID
"""
region_w, region_h = target_region_size
# 加载图像并resize到区域尺寸
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img is None:
img = np.ones((region_h, region_w, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 128 # 灰色填充
img = cv2.resize(img, (region_w, region_h))
# 加载标签并转换为区域内像素坐标
box_pix = [] # 区域内像素坐标:[x1, y1, x2, y2]
class_ids = []
if os.path.exists(label_path):
with open(label_path, "r") as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if not line:
continue
parts = line.split()
try:
if len(parts) >= 5:
cls_id = int(parts[0])
# 归一化坐标→区域内像素坐标
xc, yc, bw, bh = [float(p) for p in parts[1:5]]
x1 = int((xc - bw / 2) * region_w)
y1 = int((yc - bh / 2) * region_h)
x2 = int((xc + bw / 2) * region_w)
y2 = int((yc + bh / 2) * region_h)
# 确保Box在区域内
x1 = max(0, x1)
y1 = max(0, y1)
x2 = min(region_w - 1, x2)
y2 = min(region_h - 1, y2)
box_pix.append([x1, y1, x2, y2])
class_ids.append(cls_id)
except (ValueError, IndexError):
print(f"警告:标签文件{label_path}无效行:{line}")
continue
return img, box_pix, class_ids
# ====================== 核心Mosaic拼接:固定4图位置+保留所有Box ======================
def fixed_position_mosaic(img_paths, label_paths, target_size=(640, 640)):
"""
固定位置Mosaic:
- 图0 → 左上区域(0~w/2, 0~h/2)
- 图1 → 右上区域(w/2~w, 0~h/2)
- 图2 → 左下区域(0~w/2, h/2~h)
- 图3 → 右下区域(w/2~w, h/2~h)
强制保留所有图的Box,转换为最终图的归一化坐标
"""
assert len(img_paths) == 4 and len(label_paths) == 4, "必须传入4张图/标签"
final_w, final_h = target_size
region_w = final_w // 2
region_h = final_h // 2
# 步骤1:创建最终Mosaic大图
mosaic_img = np.zeros((final_h, final_w, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 步骤2:处理每张图并拼接,同时转换Box坐标到最终图
all_final_boxes = [] # 最终图的归一化Box
all_class_ids = [] # 最终图的类别ID
box_counts_per_img = [0, 0, 0, 0] # 记录每张图的Box数量
# 图0 → 左上区域
img0, boxes0, cls0 = process_single_image(img_paths[0], label_paths[0], (region_w, region_h))
mosaic_img[0:region_h, 0:region_w] = img0
box_counts_per_img[0] = len(boxes0)
# 转换Box到最终图坐标
for (x1, y1, x2, y2), cls in zip(boxes0, cls0):
xc = (x1 + x2) / 2 / final_w
yc = (y1 + y2) / 2 / final_h
bw = (x2 - x1) / final_w
bh = (y2 - y1) / final_h
all_final_boxes.append([xc, yc, bw, bh])
all_class_ids.append(cls)
# 图1 → 右上区域
img1, boxes1, cls1 = process_single_image(img_paths[1], label_paths[1], (region_w, region_h))
mosaic_img[0:region_h, region_w:final_w] = img1
box_counts_per_img[1] = len(boxes1)
# 转换Box到最终图坐标(x坐标+region_w)
for (x1, y1, x2, y2), cls in zip(boxes1, cls1):
x1_final = x1 + region_w
x2_final = x2 + region_w
xc = (x1_final + x2_final) / 2 / final_w
yc = (y1 + y2) / 2 / final_h
bw = (x2_final - x1_final) / final_w
bh = (y2 - y1) / final_h
all_final_boxes.append([xc, yc, bw, bh])
all_class_ids.append(cls)
# 图2 → 左下区域
img2, boxes2, cls2 = process_single_image(img_paths[2], label_paths[2], (region_w, region_h))
mosaic_img[region_h:final_h, 0:region_w] = img2
box_counts_per_img[2] = len(boxes2)
# 转换Box到最终图坐标(y坐标+region_h)
for (x1, y1, x2, y2), cls in zip(boxes2, cls2):
y1_final = y1 + region_h
y2_final = y2 + region_h
xc = (x1 + x2) / 2 / final_w
yc = (y1_final + y2_final) / 2 / final_h
bw = (x2 - x1) / final_w
bh = (y2_final - y1_final) / final_h
all_final_boxes.append([xc, yc, bw, bh])
all_class_ids.append(cls)
# 图3 → 右下区域
img3, boxes3, cls3 = process_single_image(img_paths[3], label_paths[3], (region_w, region_h))
mosaic_img[region_h:final_h, region_w:final_w] = img3
box_counts_per_img[3] = len(boxes3)
# 转换Box到最终图坐标(x+region_w, y+region_h)
for (x1, y1, x2, y2), cls in zip(boxes3, cls3):
x1_final = x1 + region_w
x2_final = x2 + region_w
y1_final = y1 + region_h
y2_final = y2 + region_h
xc = (x1_final + x2_final) / 2 / final_w
yc = (y1_final + y2_final) / 2 / final_h
bw = (x2_final - x1_final) / final_w
bh = (y2_final - y1_final) / final_h
all_final_boxes.append([xc, yc, bw, bh])
all_class_ids.append(cls)
# 转换为numpy数组
all_final_boxes = np.array(all_final_boxes, dtype=np.float32)
return mosaic_img, all_final_boxes, all_class_ids, box_counts_per_img
# ====================== 可视化:绘制所有Box ======================
def visualize_mosaic_with_all_boxes(mosaic_img, boxes, class_ids, box_counts_per_img, save_path):
"""
修复NameError,正确统计每张图的Box数量
:param mosaic_img: 最终拼接图
:param boxes: 所有Box的归一化坐标
:param class_ids: 所有Box的类别ID
:param box_counts_per_img: 每张图的Box数量列表 [img0, img1, img2, img3]
:param save_path: 可视化图保存路径
"""
img_vis = mosaic_img.copy()
final_h, final_w = img_vis.shape[:2]
# 不同图的Box用不同颜色区分
colors = [
(0, 255, 0), # 图0(左上)→ 绿色
(0, 0, 255), # 图1(右上)→ 红色
(255, 0, 0), # 图2(左下)→ 蓝色
(255, 255, 0) # 图3(右下)→ 黄色
]
# 按图的索引遍历Box
box_idx = 0
for img_idx in range(4):
color = colors[img_idx]
# 取当前图的Box数量
curr_box_num = box_counts_per_img[img_idx]
if curr_box_num == 0:
continue
# 遍历当前图的所有Box
for _ in range(curr_box_num):
if box_idx >= len(boxes):
break
box = boxes[box_idx]
cls = class_ids[box_idx]
# 转换为像素坐标
xc, yc, bw, bh = box
x1 = int((xc - bw / 2) * final_w)
y1 = int((yc - bh / 2) * final_h)
x2 = int((xc + bw / 2) * final_w)
y2 = int((yc + bh / 2) * final_h)
# 绘制Box和标注
cv2.rectangle(img_vis, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), color, 2)
cv2.putText(img_vis, f"img{img_idx}_cls{cls}", (x1, y1 - 5),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 2)
box_idx += 1
# 保存可视化图
cv2.imwrite(save_path, img_vis)
print(f"带所有Box的Mosaic图已保存:{save_path}")
print(
f"各图Box数量:img0={box_counts_per_img[0]}, img1={box_counts_per_img[1]}, img2={box_counts_per_img[2]}, img3={box_counts_per_img[3]}")
# ====================== 保存YOLO标签 ======================
def save_yolo_labels(label_path, class_ids, boxes):
with open(label_path, "w") as f:
for cls, box in zip(class_ids, boxes):
xc, yc, bw, bh = box
f.write(f"{cls} {xc:.6f} {yc:.6f} {bw:.6f} {bh:.6f}\n")
print(f"包含所有Box的YOLO标签已保存:{label_path}")
# ====================== 主函数 ======================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 配置4张图/标签路径(替换为你的实际路径)
IMG_PATHS = [
r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy.jpg",
r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy1.jpg",
r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy2.jpg",
r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy3.jpg",
]
LABEL_PATHS = [
r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy.txt",
r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy1.txt",
r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy2.txt",
r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy3.txt"
]
SAVE_DIR = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out"
FINAL_SIZE = (640, 640) # 最终Mosaic图尺寸
# 2. 创建保存目录
os.makedirs(SAVE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
# 3. 执行固定位置Mosaic(强制保留所有图和Box)
mosaic_img, all_boxes, all_classes, box_counts = fixed_position_mosaic(IMG_PATHS, LABEL_PATHS, FINAL_SIZE)
# 4. 保存纯Mosaic图
mosaic_img_path = os.path.join(SAVE_DIR, "mosaic_fixed_position1.jpg")
cv2.imwrite(mosaic_img_path, mosaic_img)
print(f"纯Mosaic图已保存:{mosaic_img_path}")
# 5. 保存带所有Box的可视化图(修复参数传递)
vis_img_path = os.path.join(SAVE_DIR, "mosaic_with_all_boxes1.jpg")
visualize_mosaic_with_all_boxes(mosaic_img, all_boxes, all_classes, box_counts, vis_img_path)
# 6. 保存包含所有Box的YOLO标签
label_path = os.path.join(SAVE_DIR, "mosaic_all_boxes1.txt")
save_yolo_labels(label_path, all_classes, all_boxes)
# 7. 最终统计
print(f"\n=== 固定位置Mosaic增强完成 ===")
print(f"最终图尺寸:{FINAL_SIZE}")
print(f"总Box数量:{len(all_boxes)}(4张图的Box全部保留)")
print(f"保存路径:{SAVE_DIR}")
print(f"核心特性:")
print(f"1. 图0→左上,图1→右上,图2→左下,图3→右下,位置固定;")
print(f"2. 每张图的Box全部转换为最终图坐标,无遗漏;")
print(f"3. 可视化图中不同图的Box用不同颜色区分,便于验证;")
print(f"4. 标签文件包含所有Box,可直接用于YOLO训练。")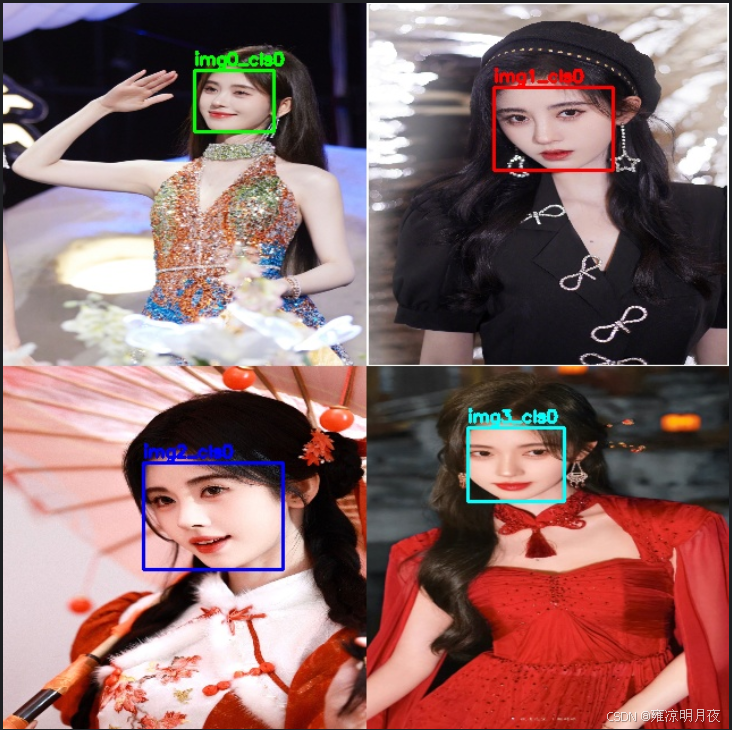
3.paste_img1box_to_img2数据增强
本质:把 img1 中某个 Box 对应的像素区域裁剪出来,粘贴到 img2 的指定位置,同时将该 Box 的坐标从 img1 的归一化坐标转换为 img2 的归一化坐标,生成新标签。
步骤 核心操作 公式 / 逻辑 1. Box 解析 归一化→像素坐标 x1 = (xc - bw/2)*w1,y1 = (yc - bh/2)*h12. 裁剪区域 从 img1 裁剪 Box 区域 crop_img = img1[y1:y2, x1:x2]3. 粘贴位置 避免越界 paste_x ∈ [0, w2-crop_w],paste_y ∈ [0, h2-crop_h]4. 图像粘贴 覆盖 img2 对应区域 img2[paste_y:paste_y+crop_h, paste_x:paste_x+crop_w] = crop_img5. 坐标转换 像素→归一化(img2) new_xc = (paste_x + paste_x+crop_w)/2 /w2
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
def paste_img1box_to_img2(
img1_path: str, # 源图(要裁剪Box的图)路径
img2_path: str, # 目标图(要粘贴的图)路径
label1_path: str, # 源图标签路径(包含Box信息)
box_idx: int = 0, # 选择源图的第几个Box(默认第0个)
paste_pos: tuple = None, # 粘贴位置 (x, y),None则随机位置
save_path: str = "paste_result.jpg", # 结果保存路径
label_save_path: str = "paste_result.txt" # 新标签保存路径
):
"""
将img1的指定Box区域粘贴到img2,并生成新的标签(Box坐标转换为img2的归一化坐标)
:return: 粘贴后的图像、新的归一化Box坐标、新标签
"""
# ========== 步骤1:读取并预处理图像 ==========
# 读取源图img1和目标图img2
img1 = cv2.imread(img1_path)
img2 = cv2.imread(img2_path)
if img1 is None:
raise ValueError(f"源图{img1_path}读取失败!")
if img2 is None:
raise ValueError(f"目标图{img2_path}读取失败!")
h1, w1 = img1.shape[:2] # 源图尺寸
h2, w2 = img2.shape[:2] # 目标图尺寸
# ========== 步骤2:解析img1的Box(归一化→像素坐标) ==========
box1_norm = None # 源图Box的归一化坐标 [xc, yc, bw, bh]
box1_pix = None # 源图Box的像素坐标 [x1, y1, x2, y2]
cls1 = None # 源图Box的类别ID
with open(label1_path, "r") as f:
lines = [line.strip() for line in f if line.strip()]
if box_idx >= len(lines):
raise IndexError(f"源图标签仅{len(lines)}个Box,无法选择第{box_idx}个!")
# 解析指定Box
parts = lines[box_idx].split()
if len(parts) < 5:
raise ValueError(f"源图标签行格式错误:{lines[box_idx]}")
cls1 = int(parts[0])
xc, yc, bw, bh = [float(p) for p in parts[1:5]]
# 归一化坐标→像素坐标(x1,y1=左上,x2,y2=右下)
x1 = int((xc - bw/2) * w1)
y1 = int((yc - bh/2) * h1)
x2 = int((xc + bw/2) * w1)
y2 = int((yc + bh/2) * h1)
# 确保Box在img1范围内
x1 = max(0, x1)
y1 = max(0, y1)
x2 = min(w1-1, x2)
y2 = min(h1-1, y2)
box1_norm = [xc, yc, bw, bh]
box1_pix = [x1, y1, x2, y2]
# ========== 步骤3:裁剪img1的Box区域 ==========
crop_img = img1[y1:y2, x1:x2] # 裁剪Box对应的像素区域
crop_h, crop_w = crop_img.shape[:2]
if crop_h == 0 or crop_w == 0:
raise ValueError(f"源图Box裁剪区域为空!Box像素坐标:{box1_pix}")
# ========== 步骤4:确定img2上的粘贴位置(避免越界) ==========
if paste_pos is None:
# 随机位置(确保裁剪区域完全在img2内)
paste_x = np.random.randint(0, w2 - crop_w)
paste_y = np.random.randint(0, h2 - crop_h)
else:
paste_x, paste_y = paste_pos
# 强制修正越界位置
paste_x = max(0, min(paste_x, w2 - crop_w))
paste_y = max(0, min(paste_y, h2 - crop_h))
# ========== 步骤5:将裁剪区域粘贴到img2 ==========
img2_pasted = img2.copy()
img2_pasted[paste_y:paste_y+crop_h, paste_x:paste_x+crop_w] = crop_img
# ========== 步骤6:转换Box坐标为img2的归一化坐标 ==========
# 粘贴后的Box像素坐标(img2上)
new_x1 = paste_x
new_y1 = paste_y
new_x2 = paste_x + crop_w
new_y2 = paste_y + crop_h
# 像素坐标→归一化坐标
new_xc = (new_x1 + new_x2) / 2 / w2
new_yc = (new_y1 + new_y2) / 2 / h2
new_bw = (new_x2 - new_x1) / w2
new_bh = (new_y2 - new_y1) / h2
new_box_norm = [new_xc, new_yc, new_bw, new_bh]
# ========== 步骤7:保存结果 ==========
# 保存粘贴后的图像
cv2.imwrite(save_path, img2_pasted)
print(f"粘贴后的图像已保存:{save_path}")
# 保存新标签(格式:cls xc yc bw bh)
with open(label_save_path, "w") as f:
f.write(f"{cls1} {new_xc:.6f} {new_yc:.6f} {new_bw:.6f} {new_bh:.6f}\n")
print(f"新标签已保存:{label_save_path}")
return img2_pasted, new_box_norm, cls1
# ------------------- 调用示例 -------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 配置路径
IMG1_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy2.jpg" # 源图(要裁剪的图)
IMG2_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy1.jpg" # 目标图(要粘贴的背景图)
LABEL1_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy2.txt" # 源图标签
SAVE_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\paste_result.jpg"
LABEL_SAVE_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\paste_label.txt"
# 执行粘贴操作:将img1的第0个Box粘贴到img2的(100, 100)位置
try:
pasted_img, new_box, cls = paste_img1box_to_img2(
img1_path=IMG1_PATH,
img2_path=IMG2_PATH,
label1_path=LABEL1_PATH,
box_idx=0, # 选择img1的第0个Box
paste_pos=(100, 100), # 粘贴到img2的(100,100)位置
save_path=SAVE_PATH,
label_save_path=LABEL_SAVE_PATH
)
print(f"粘贴完成!")
print(f"新Box归一化坐标:xc={new_box[0]:.6f}, yc={new_box[1]:.6f}, bw={new_box[2]:.6f}, bh={new_box[3]:.6f}")
print(f"Box类别:{cls}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"执行失败:{e}")
3.局部增强/裁剪类数据增强锦集
1.sliding_crop
本质:从一张大图中按固定步长滑动裁剪出多个子图,同时将Box坐标转换到对应的子图中,是目标检测中扩充数据/处理大图的常用手段。
「按固定窗口 + 步长遍历大图→裁剪子图→转换原图 Box 到子图坐标」
python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project :Pytorch
@File :sliding_crop.py
@IDE :PyCharm
@Author :wjj
@Date :2025/12/15 16:43
@Description: Sliding Crop (Fix encoding & window calculation)
"""
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
from typing import List, Tuple, Dict
def sliding_crop(
img_path: str,
label_path: str,
crop_size: Tuple[int, int] = (640, 640), # Crop window size (w, h)
stride: Tuple[int, int] = (320, 320), # Sliding stride (x, y)
save_dir: str = "sliding_crop_album", # Album save dir
keep_partial_box: bool = True, # Keep box if center in window
filter_empty: bool = True, # Filter sub-img without box
class_names: List[str] = None # Class names (optional)
) -> List[Dict]:
"""
Sliding crop large image to sub-images, convert box coords to sub-img normalized coords
:return: Crop results list (sub-img path, label path, box num, etc.)
"""
# ========== Initialization ==========
os.makedirs(save_dir, exist_ok=True)
crop_w, crop_h = crop_size
stride_x, stride_y = stride
result_list = []
# ========== Read image & label ==========
# Read large image
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img is None:
raise ValueError(f"Failed to read image: {img_path}!")
img_h, img_w = img.shape[:2]
# Auto adjust oversize crop window
if crop_w >= img_w or crop_h >= img_h:
print(
f"Warning: Crop window ({crop_w}x{crop_h}) ≥ image size ({img_w}x{img_h}), auto adjust to 1/2 of image size")
crop_w = img_w // 2
crop_h = img_h // 2
stride_x = crop_w // 2
stride_y = crop_h // 2
print(f"Adjusted: Crop window ({crop_w}x{crop_h}), stride ({stride_x}x{stride_y})")
# Parse label (normalized → pixel coords, GBK encoding for Windows)
original_boxes = []
try:
with open(label_path, "r", encoding='gbk') as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if not line:
continue
parts = line.split()
if len(parts) < 5:
print(f"Warning: Invalid label line {line}, skip")
continue
try:
cls_id = int(parts[0])
xc, yc, bw, bh = [float(p) for p in parts[1:5]]
# Normalized → pixel coords
x1 = int((xc - bw / 2) * img_w)
y1 = int((yc - bh / 2) * img_h)
x2 = int((xc + bw / 2) * img_w)
y2 = int((yc + bh / 2) * img_h)
# Fix out-of-bounds
x1 = max(0, x1)
y1 = max(0, y1)
x2 = min(img_w - 1, x2)
y2 = min(img_h - 1, y2)
original_boxes.append((x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_id))
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to parse label line {line}: {e}")
continue
except FileNotFoundError:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Label file {label_path} not found!")
# ========== Calculate sliding window positions ==========
# X direction starts
x_starts = []
x = 0
while x + crop_w <= img_w:
x_starts.append(x)
x += stride_x
if x_starts and x_starts[-1] + crop_w < img_w:
x_starts.append(img_w - crop_w)
if not x_starts:
x_starts = [0]
# Y direction starts
y_starts = []
y = 0
while y + crop_h <= img_h:
y_starts.append(y)
y += stride_y
if y_starts and y_starts[-1] + crop_h < img_h:
y_starts.append(img_h - crop_h)
if not y_starts:
y_starts = [0]
# ========== Crop sub-images ==========
crop_idx = 0
for y_start in y_starts:
for x_start in x_starts:
x_end = x_start + crop_w
y_end = y_start + crop_h
# Crop sub-image
sub_img = img[y_start:y_end, x_start:x_end]
sub_img_h, sub_img_w = sub_img.shape[:2]
if sub_img_h != crop_h or sub_img_w != crop_w:
# Pad black border to keep size
sub_img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(
sub_img, 0, crop_h - sub_img_h, 0, crop_w - sub_img_w,
cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=(0, 0, 0)
)
# Filter boxes in current window
sub_boxes = []
for (bx1, by1, bx2, by2, cls_id) in original_boxes:
box_cx = (bx1 + bx2) / 2
box_cy = (by1 + by2) / 2
if keep_partial_box:
in_window = (x_start <= box_cx <= x_end) and (y_start <= box_cy <= y_end)
else:
in_window = (x_start <= bx1) and (bx2 <= x_end) and (y_start <= by1) and (by2 <= y_end)
if not in_window:
continue
# Convert to sub-image normalized coords
sub_bx1 = bx1 - x_start
sub_by1 = by1 - y_start
sub_bx2 = bx2 - x_start
sub_by2 = by2 - y_start
# Fix out-of-bounds in sub-image
sub_bx1 = max(0, sub_bx1)
sub_by1 = max(0, sub_by1)
sub_bx2 = min(crop_w - 1, sub_bx2)
sub_by2 = min(crop_h - 1, sub_by2)
# Pixel → normalized
sub_xc = (sub_bx1 + sub_bx2) / 2 / crop_w
sub_yc = (sub_by1 + sub_by2) / 2 / crop_h
sub_bw = (sub_bx2 - sub_bx1) / crop_w
sub_bh = (sub_by2 - sub_by1) / crop_h
sub_boxes.append((sub_xc, sub_yc, sub_bw, sub_bh, cls_id))
# Filter empty sub-images
if filter_empty and len(sub_boxes) == 0:
continue
# Save sub-image and label
sub_img_name = f"crop_{crop_idx:04d}_x{x_start}_y{y_start}.jpg"
sub_label_name = f"crop_{crop_idx:04d}_x{x_start}_y{y_start}.txt"
sub_img_path = os.path.join(save_dir, sub_img_name)
sub_label_path = os.path.join(save_dir, sub_label_name)
cv2.imwrite(sub_img_path, sub_img)
# Save label with GBK encoding
with open(sub_label_path, "w", encoding='gbk') as f:
for (xc, yc, bw, bh, cls_id) in sub_boxes:
f.write(f"{cls_id} {xc:.6f} {yc:.6f} {bw:.6f} {bh:.6f}\n")
# Record result
result_info = {
"crop_idx": crop_idx,
"window_pos": (x_start, y_start, x_end, y_end),
"sub_img_path": sub_img_path,
"sub_label_path": sub_label_path,
"box_num": len(sub_boxes)
}
result_list.append(result_info)
print(f"Crop completed {sub_img_path} | Box count: {len(sub_boxes)}")
crop_idx += 1
# ========== Generate summary file (GBK encoding) ==========
album_summary_path = os.path.join(save_dir, "sliding_crop_summary.txt")
with open(album_summary_path, "w", encoding='gbk') as f:
f.write("Sliding Crop Album Summary\n")
f.write(f"Original image path: {img_path}\n")
f.write(f"Original image size: {img_w}x{img_h}\n")
f.write(f"Crop window size: {crop_w}x{crop_h}\n")
f.write(f"Sliding stride: {stride_x}x{stride_y}\n")
f.write(f"Generated sub-images: {len(result_list)}\n")
f.write("-" * 50 + "\n")
for info in result_list:
f.write(
f"Index {info['crop_idx']} | Window pos {info['window_pos']} | Sub-img {info['sub_img_path']} | Box count {info['box_num']}\n")
print(f"\nSliding crop completed!")
print(f"Album save directory: {save_dir}")
print(f"Generated sub-images count: {len(result_list)}")
print(f"Summary file: {album_summary_path}")
return result_list
# ------------------- Test Example -------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Config
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy1.jpg"
LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy1.txt"
SAVE_DIR = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\sliding_crop_album"
CROP_SIZE = (640, 640) # Reasonable size for model input
STRIDE = (320, 320) # 50% overlap
# Run sliding crop
try:
crop_results = sliding_crop(
img_path=IMG_PATH,
label_path=LABEL_PATH,
crop_size=CROP_SIZE,
stride=STRIDE,
save_dir=SAVE_DIR,
keep_partial_box=True,
filter_empty=True
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Sliding crop failed: {e}")实现效果1->4的核心对比:





裁剪后的子图能实现数据增强:
- 样本数量扩充:从 1 张原图→4 张子图,直接增加训练样本量,降低模型过拟合风险;
- 目标位置多样性:子图中目标的「相对位置」和原图不同(比如原图中目标在中间,子图中目标在左上角 / 右下角),模型能学习到「目标出现在图像任意位置」的特征,避免对目标位置过拟合;
- 目标聚焦增强:如果原图中目标占比小(比如小目标),裁剪后的子图会让目标在画面中占比更高,模型更容易捕捉目标的细节特征;
- 抗截断鲁棒性:50% 重叠的裁剪方式,会让跨窗口的目标在不同子图中被「部分保留」(比如目标一半在 A 子图、一半在 B 子图),模型能学习到「目标被截断时的特征」,提升检测的鲁棒性。
2.copy_paste
本质:在同一张图内复制指定类别目标,随机粘贴到空白区域
同图内复制指定类别目标→随机粘贴到空白区域
支持翻转 / 旋转 / 缩放增强,且通过掩码避免目标重叠。
python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project :Pytorch
@File :copy_paste.py
@IDE :PyCharm
@Author :wjj
@Date :2025/12/15 17:12
@Description:
"""
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
import random
from typing import List, Tuple
def copy_paste(
img_path: str,
label_path: str,
target_cls: int, # 要复制的目标类别ID(如0)
paste_num: int = 3, # 复制粘贴的数量(默认3个)
save_path: str = "copy_paste_aug.jpg",
new_label_path: str = "copy_paste_aug.txt",
aug_prob: float = 0.5, # 目标增强(翻转/旋转/缩放)的概率
scale_range: Tuple = (0.8, 1.2), # 缩放范围
rotate_range: Tuple = (-15, 15) # 旋转角度范围(±15°)
):
"""
同图内复制指定类别目标,随机粘贴到空白区域(避免重叠),支持目标增强
:param target_cls: 要增强的稀有目标类别ID
:param paste_num: 复制粘贴的目标数量
"""
# ========== 1. 读取图片和标签 ==========
# 读取原图
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img is None:
raise ValueError(f"读取图片失败: {img_path}")
img_h, img_w = img.shape[:2]
img_copy = img.copy() # 用于粘贴的画布
# 解析标签:分离目标类别 + 转换为像素坐标
original_boxes = [] # 所有目标:[(x1,y1,x2,y2,cls_id), ...]
target_boxes = [] # 指定类别的目标:[(x1,y1,x2,y2), ...]
with open(label_path, "r", encoding='gbk') as f:
for line in f:
parts = line.strip().split()
if len(parts) < 5:
continue
cls_id = int(parts[0])
xc, yc, bw, bh = [float(p) for p in parts[1:5]]
# 归一化→像素坐标
x1 = int((xc - bw / 2) * img_w)
y1 = int((yc - bh / 2) * img_h)
x2 = int((xc + bw / 2) * img_w)
y2 = int((yc + bh / 2) * img_h)
original_boxes.append((x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_id))
# 筛选指定类别的目标
if cls_id == target_cls:
target_boxes.append((x1, y1, x2, y2))
# 校验:指定类别是否有目标
if len(target_boxes) == 0:
raise ValueError(f"图片中无类别ID为 {target_cls} 的目标!")
# ========== 2. 生成空白区域掩码(避免粘贴重叠) ==========
# 初始化掩码:0=空白,1=已有目标
mask = np.zeros((img_h, img_w), dtype=np.uint8)
for (x1, y1, x2, y2, _) in original_boxes:
mask[y1:y2, x1:x2] = 1 # 已有目标区域标记为1
# ========== 3. 复制指定类别目标并增强 ==========
# 随机选一个指定类别目标作为复制模板(若有多个,随机选)
src_x1, src_y1, src_x2, src_y2 = random.choice(target_boxes)
src_crop = img[src_y1:src_y2, src_x1:src_x2] # 复制的目标像素区域
src_h, src_w = src_crop.shape[:2]
# 存储粘贴后的新目标坐标(用于生成新标签)
new_boxes = []
# ========== 4. 随机粘贴到空白区域 ==========
paste_count = 0
max_attempts = paste_num * 10 # 最大尝试次数(避免死循环)
attempts = 0
while paste_count < paste_num and attempts < max_attempts:
attempts += 1
# -------- 4.1 对复制的目标做增强(翻转/旋转/缩放) --------
aug_crop = src_crop.copy()
# 随机水平翻转
if random.random() < aug_prob:
aug_crop = cv2.flip(aug_crop, 1)
# 随机缩放
scale = random.uniform(*scale_range)
aug_w = int(src_w * scale)
aug_h = int(src_h * scale)
aug_crop = cv2.resize(aug_crop, (aug_w, aug_h))
# 随机旋转(带黑边,避免裁剪)
if random.random() < aug_prob:
angle = random.uniform(*rotate_range)
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((aug_w / 2, aug_h / 2), angle, 1)
aug_crop = cv2.warpAffine(aug_crop, M, (aug_w, aug_h), borderValue=(0, 0, 0))
# -------- 4.2 随机选择空白粘贴位置 --------
# 确保粘贴位置在图片内,且目标完整放下
paste_x = random.randint(0, img_w - aug_w)
paste_y = random.randint(0, img_h - aug_h)
# 检查粘贴区域是否为空白(掩码全0)
paste_mask = mask[paste_y:paste_y + aug_h, paste_x:paste_x + aug_w]
if np.sum(paste_mask) == 0: # 无重叠,可粘贴
# 粘贴目标到画布
img_copy[paste_y:paste_y + aug_h, paste_x:paste_x + aug_w] = aug_crop
# 更新掩码(标记为已有目标)
mask[paste_y:paste_y + aug_h, paste_x:paste_x + aug_w] = 1
# 记录新目标坐标(像素→归一化)
new_xc = (paste_x + aug_w / 2) / img_w
new_yc = (paste_y + aug_h / 2) / img_h
new_bw = aug_w / img_w
new_bh = aug_h / img_h
new_boxes.append((target_cls, new_xc, new_yc, new_bw, new_bh))
paste_count += 1
print(f"成功粘贴第 {paste_count} 个目标 → 位置: ({paste_x}, {paste_y})")
if paste_count < paste_num:
print(f"警告:仅成功粘贴 {paste_count} 个目标(剩余位置有重叠)")
# ========== 5. 生成新标签(原目标 + 新粘贴目标) ==========
with open(new_label_path, "w", encoding='gbk') as f:
# 写入原目标
for (x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_id) in original_boxes:
xc = (x1 + x2) / 2 / img_w
yc = (y1 + y2) / 2 / img_h
bw = (x2 - x1) / img_w
bh = (y2 - y1) / img_h
f.write(f"{cls_id} {xc:.6f} {yc:.6f} {bw:.6f} {bh:.6f}\n")
# 写入新粘贴的目标
for (cls_id, xc, yc, bw, bh) in new_boxes:
f.write(f"{cls_id} {xc:.6f} {yc:.6f} {bw:.6f} {bh:.6f}\n")
# ========== 6. 保存增强后的图片 ==========
cv2.imwrite(save_path, img_copy)
print(f"\nCopy-Paste 增强完成!")
print(f"增强后图片保存至: {save_path}")
print(f"新标签保存至: {new_label_path}")
print(f"原目标数量: {len(original_boxes)} | 新增目标数量: {len(new_boxes)}")
return img_copy, new_boxes
# ------------------- 测试示例 -------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 配置参数(仅需修改以下5项)
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy1.jpg"
LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy1.txt"
TARGET_CLS = 0 # 要增强的目标类别ID(根据你的标签修改)
SAVE_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\copy_paste_aug.jpg"
NEW_LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\copy_paste_aug.txt"
# 核心调用
try:
copy_paste(
img_path=IMG_PATH,
label_path=LABEL_PATH,
target_cls=TARGET_CLS,
paste_num=3, # 复制粘贴3个目标
save_path=SAVE_PATH,
new_label_path=NEW_LABEL_PATH
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"执行失败: {e}")修改前后对比:


| 模块 | 实现逻辑 |
|---|---|
| 目标筛选 | 解析标签后筛选指定target_cls的目标,仅复制该类别(解决稀有目标增强) |
| 重叠避免 | 生成掩码矩阵,标记已有目标区域,仅在掩码为 0 的空白区域粘贴 |
| 目标增强 | 复制的目标随机做:水平翻转(50% 概率)、缩放(0.8~1.2 倍)、小角度旋转 |
| 坐标转换 | 粘贴后自动将像素坐标转换为 YOLO 格式的归一化坐标,生成新标签 |
| 鲁棒性 | 限制最大尝试次数,避免因空白区域不足导致死循环,同时提示实际粘贴数量 |
3.pyr_up/pyr_down
本质:很简单,就是我们常见的将原图放大或缩小达到增加数据样本的作用。
上采样(小目标增强):
- 建议仅用 1~2 次:1 次缩放后目标尺寸 ×2,小目标细节更清晰;2 次后可能模糊,需结合实际图像质量判断;
- 适用场景:原图中小目标占比 < 5%,检测模型难以捕捉的场景。
下采样(大目标适配):
- 无次数限制(建议 1~3 次):每次缩小为原来的 1/2,适配模型输入尺寸(如 640×640);
- 适用场景:原图中大目标占比 > 80%,超出模型检测范围的场景。
验证方法:
- 运行代码后,打开缩放后的图片,对比标注框是否与目标位置匹配;
- 检查新标签文件的归一化坐标,确保数值在 0~1 范围内(无越界)
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
def pyr_scale(
img_path: str,
label_path: str,
scale_type: str = "up", # "up"放大/"down"缩小
scale_times: int = 1, # 缩放次数(up建议1次)
save_path: str = "pyr_scaled.jpg",
new_label_path: str = "pyr_scaled.txt"
):
# 1. 读取原图
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
orig_h, orig_w = img.shape[:2]
scaled_img = img.copy()
# 2. 解析原标签(归一化→像素坐标)
orig_boxes = []
with open(label_path, "r", encoding='gbk') as f:
for line in f:
parts = line.strip().split()
if len(parts) < 5: continue
cls_id = int(parts[0])
xc, yc, bw, bh = [float(p) for p in parts[1:5]]
x1 = int((xc - bw/2) * orig_w)
y1 = int((yc - bh/2) * orig_h)
x2 = int((xc + bw/2) * orig_w)
y2 = int((yc + bh/2) * orig_h)
orig_boxes.append((x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_id))
# 3. 执行图像缩放(pyrUp/pyrDown)
scale_factor = 1.0
for _ in range(scale_times):
if scale_type == "up":
scaled_img = cv2.pyrUp(scaled_img)
scale_factor *= 2
else:
scaled_img = cv2.pyrDown(scaled_img)
scale_factor /= 2
scaled_h, scaled_w = scaled_img.shape[:2]
# 4. 缩放标注框并生成新标签
with open(new_label_path, "w", encoding='gbk') as f:
for (x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_id) in orig_boxes:
# 像素坐标缩放 + 修正越界
new_x1 = max(0, int(x1 * scale_factor))
new_y1 = max(0, int(y1 * scale_factor))
new_x2 = min(scaled_w-1, int(x2 * scale_factor))
new_y2 = min(scaled_h-1, int(y2 * scale_factor))
# 像素→归一化坐标
new_xc = (new_x1 + new_x2)/2 / scaled_w
new_yc = (new_y1 + new_y2)/2 / scaled_h
new_bw = (new_x2 - new_x1)/scaled_w
new_bh = (new_y2 - new_y1)/scaled_h
f.write(f"{cls_id} {new_xc:.6f} {new_yc:.6f} {new_bw:.6f} {new_bh:.6f}\n")
# 5. 保存结果
cv2.imwrite(save_path, scaled_img)
print(f"完成!原图尺寸:{orig_w}x{orig_h} → 缩放后:{scaled_w}x{scaled_h}")
print(f"缩放后图片:{save_path} | 新标签:{new_label_path}")
# ------------------- 极简验证调用 -------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 仅需修改这6行路径/参数即可验证
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy1.jpg"
LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy1.txt"
SCALE_TYPE = "up" # 测试放大(改"down"测试缩小)
SCALE_TIMES = 1 # 仅缩放1次(避免模糊)
SAVE_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\pyr_up.jpg"
NEW_LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\pyr_up.txt"
pyr_scale(
img_path=IMG_PATH,
label_path=LABEL_PATH,
scale_type=SCALE_TYPE,
scale_times=SCALE_TIMES,
save_path=SAVE_PATH,
new_label_path=NEW_LABEL_PATH
)图片与原图一致,仅变大/变小罢了。
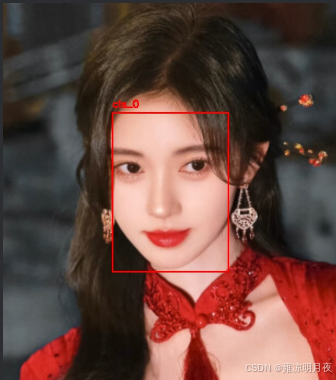
4.cut_box
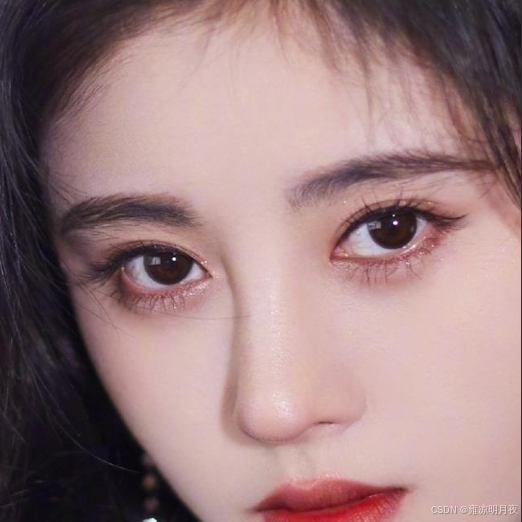
本质:
「裁剪小目标周边区域 + 放大」
图片变化:
- 原图 → 裁剪「目标 + 周边 100 像素」的局部区域 → 放大 2 倍,小目标特征被强化(更清晰);
- 对比
IMG_PATH(原图)和SAVE_PATH(裁剪放大图),能直观看到小目标从 "模糊小点" 变成 "清晰区域"。Label 变化:
- 原标签:目标坐标是「相对于整张原图」的归一化值;
- 新标签:目标坐标是「相对于裁剪放大后局部图」的归一化值,框的占比会显著变大(因为图片尺寸变小,目标占比提升)
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
def cut_box(
img_path: str,
label_path: str,
target_cls: int = 0, # 要增强的小目标类别ID
expand_pixel: int = 100, # 目标周边保留像素(默认100)
scale_factor: int = 2, # 放大倍数(强化小目标特征)
save_path: str = "cut_box_aug.jpg",
new_label_path: str = "cut_box_aug.txt"
):
# 1. 读取原图
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img is None:
raise ValueError(f"读取图片失败: {img_path}")
img_h, img_w = img.shape[:2]
# 2. 解析标签(归一化→像素坐标),筛选指定类别小目标
target_box = None
with open(label_path, "r", encoding='gbk') as f:
for line in f:
parts = line.strip().split()
if len(parts) < 5: continue
cls_id = int(parts[0])
if cls_id != target_cls: continue # 仅处理指定类别
xc, yc, bw, bh = [float(p) for p in parts[1:5]]
# 归一化→像素坐标
x1 = int((xc - bw/2) * img_w)
y1 = int((yc - bh/2) * img_h)
x2 = int((xc + bw/2) * img_w)
y2 = int((yc + bh/2) * img_h)
target_box = (x1, y1, x2, y2)
break # 仅处理第一个指定类别目标(验证用)
if target_box is None:
raise ValueError(f"未找到类别ID为 {target_cls} 的目标!")
x1, y1, x2, y2 = target_box
# 3. 裁剪目标周边区域(保留expand_pixel像素)
crop_x1 = max(0, x1 - expand_pixel)
crop_y1 = max(0, y1 - expand_pixel)
crop_x2 = min(img_w - 1, x2 + expand_pixel)
crop_y2 = min(img_h - 1, y2 + expand_pixel)
cut_img = img[crop_y1:crop_y2, crop_x1:crop_x2] # 裁剪区域
# 4. 放大裁剪区域(强化小目标特征)
cut_h, cut_w = cut_img.shape[:2]
scaled_cut = cv2.resize(cut_img, (cut_w * scale_factor, cut_h * scale_factor))
scaled_h, scaled_w = scaled_cut.shape[:2]
# 5. 重新计算目标框坐标(相对于放大后的裁剪图)
rel_x1 = x1 - crop_x1
rel_y1 = y1 - crop_y1
rel_x2 = x2 - crop_x1
rel_y2 = y2 - crop_y1
# 放大后像素坐标(用于绘制框)
new_x1 = int(rel_x1 * scale_factor)
new_y1 = int(rel_y1 * scale_factor)
new_x2 = int(rel_x2 * scale_factor)
new_y2 = int(rel_y2 * scale_factor)
# 归一化坐标(保存到标签)
new_xc = (new_x1 + new_x2) / 2 / scaled_w
new_yc = (new_y1 + new_y2) / 2 / scaled_h
new_bw = (new_x2 - new_x1) / scaled_w
new_bh = (new_y2 - new_y1) / scaled_h
# ========== 新增:在放大后的图片上绘制label框 ==========
# 绘制红色矩形框(线宽2,醒目)
cv2.rectangle(scaled_cut, (new_x1, new_y1), (new_x2, new_y2), (0, 0, 255), 2)
# 可选:添加类别文字标注
cv2.putText(scaled_cut, f"cls_{target_cls}", (new_x1, new_y1-10),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# 6. 保存结果(带框的图片+新标签)
cv2.imwrite(save_path, scaled_cut)
with open(new_label_path, "w", encoding='gbk') as f:
f.write(f"{target_cls} {new_xc:.6f} {new_yc:.6f} {new_bw:.6f} {new_bh:.6f}\n")
# 输出关键信息(对比用)
print(f"裁剪区域:({crop_x1},{crop_y1})→({crop_x2},{crop_y2})")
print(f"裁剪后尺寸:{cut_w}x{cut_h} → 放大后:{scaled_w}x{scaled_h}")
print(f"绘制框坐标:({new_x1},{new_y1})→({new_x2},{new_y2})")
print(f"完成!带框图片:{save_path} | 新标签:{new_label_path}")
# ------------------- 极简验证调用 -------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 仅需修改以下6行参数即可验证
IMG_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\jjy3.jpg"
LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\jjy\jjy3.txt"
TARGET_CLS = 0 # 要增强的小目标类别ID
EXPAND_PIXEL = 100 # 目标周边保留100像素
SAVE_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\cut_box_aug.jpg"
NEW_LABEL_PATH = r"C:\Users\Excub\workspace\Pytorch\12.08_cv\out\cut_box_aug.txt"
cut_box(
img_path=IMG_PATH,
label_path=LABEL_PATH,
target_cls=TARGET_CLS,
expand_pixel=EXPAND_PIXEL,
save_path=SAVE_PATH,
new_label_path=NEW_LABEL_PATH
)成品图片:


总结:
本章节承接上一份文章,继续总结了常见的数据增强的方法,并配上了相应的案例和实例仅供大家学习参考,如有不对的地方,欢迎大家指出!感谢!