大家好!今天给大家系统梳理《数字图像处理》第 5 章「图像复原与重建」的核心知识点,全程搭配可直接运行的 Python 代码、效果对比图和可视化图表,帮大家彻底吃透图像复原的底层逻辑和实战应用。
引言
图像在获取、传输、存储过程中,不可避免会受到噪声、模糊、几何畸变等因素影响,导致质量下降(即图像退化 )。图像复原与重建的核心目标是:通过数学模型和算法,尽可能恢复图像的原始信息,区别于图像增强(主观美化),图像复原更注重基于退化模型的客观恢复。
学习目标
- 理解图像退化 / 复原的数学模型,掌握核心变量关系;
- 熟悉各类噪声模型的特性及参数估计方法;
- 掌握空间域 / 频率域噪声去除的滤波算法(均值、中值、维纳、陷波滤波等);
- 理解逆滤波、维纳滤波、约束最小二乘方滤波等退化复原方法;
- 掌握从投影重建图像的核心原理(雷登变换、滤波反投影)及 CT 成像应用。
5.1 图像退化 / 复原处理的一个模型
核心原理

5.2 噪声模型
5.2.1 噪声的空间和频率特性
- 空间特性:噪声在像素空间的分布(如椒盐噪声是随机稀疏分布,高斯噪声是全局分布);
- 频率特性:噪声的频谱分布(如周期噪声是频率域的离散峰值,高斯噪声是全频率分布)。
5.2.2 一些重要的噪声概率密度函数
常见噪声 PDF:

5.2.3 周期噪声
由电力线、机械振动等周期性干扰引起,频率域表现为离散的冲激峰值。
5.2.4 估计噪声参数
通过图像的平坦区域(无信号变化)估计噪声的均值、方差等参数。
代码实现:生成各类噪声并可视化
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置中文字体
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 读取图像(转为灰度图)
img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg', 0) # 替换为你的图像路径
if img is None:
# 若读取失败,生成一个512x512的灰度测试图
img = np.ones((512, 512), dtype=np.uint8) * 128
# ========== 1. 生成高斯噪声 ==========
def add_gaussian_noise(image, mean=0, var=0.001):
"""添加高斯噪声"""
image = np.array(image/255, dtype=float)
noise = np.random.normal(mean, var**0.5, image.shape)
noisy_image = image + noise
noisy_image = np.clip(noisy_image, 0, 1)
return np.uint8(noisy_image*255)
# ========== 2. 生成椒盐噪声 ==========
def add_salt_pepper_noise(image, prob=0.05):
"""添加椒盐噪声"""
noisy_image = np.copy(image)
# 椒盐噪声概率拆分
salt_prob = prob / 2
pepper_prob = prob / 2
# 生成随机掩码
mask = np.random.rand(*image.shape)
# 盐噪声(白色)
noisy_image[mask < salt_prob] = 255
# 椒噪声(黑色)
noisy_image[mask > 1 - pepper_prob] = 0
return noisy_image
# ========== 3. 生成瑞利噪声 ==========
def add_rayleigh_noise(image, a=0, b=100):
"""添加瑞利噪声"""
image = np.array(image/255, dtype=float)
# 生成瑞利噪声
noise = np.random.rayleigh(scale=np.sqrt(b), size=image.shape) + a
noise = noise / np.max(noise) # 归一化
noisy_image = image + noise * 0.1 # 控制噪声强度
noisy_image = np.clip(noisy_image, 0, 1)
return np.uint8(noisy_image*255)
# 生成含噪声图像
gaussian_noisy = add_gaussian_noise(img, var=0.01)
salt_pepper_noisy = add_salt_pepper_noise(img, prob=0.05)
rayleigh_noisy = add_rayleigh_noise(img)
# 可视化对比
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4))
plt.subplot(141), plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray'), plt.title('原始图像'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(142), plt.imshow(gaussian_noisy, cmap='gray'), plt.title('高斯噪声'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(143), plt.imshow(salt_pepper_noisy, cmap='gray'), plt.title('椒盐噪声'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(144), plt.imshow(rayleigh_noisy, cmap='gray'), plt.title('瑞利噪声'), plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# ========== 4. 估计噪声参数 ==========
def estimate_noise_params(image, flat_region=(100, 100, 200, 200)):
"""估计噪声参数(从平坦区域)"""
# 提取平坦区域(x1,y1,x2,y2)
x1, y1, x2, y2 = flat_region
flat_area = image[y1:y2, x1:x2]
# 计算均值和方差
mean = np.mean(flat_area)
var = np.var(flat_area)
return mean, var
# 估计高斯噪声参数
noise_mean, noise_var = estimate_noise_params(gaussian_noisy)
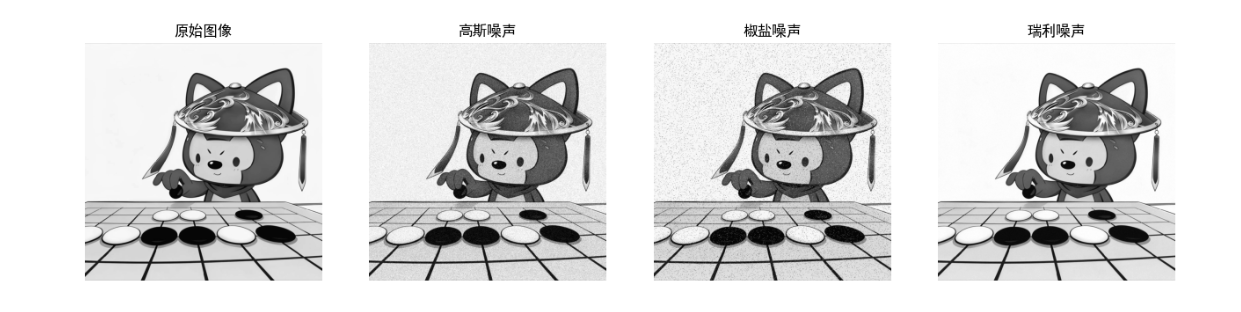
print(f"高斯噪声估计均值:{noise_mean:.2f},方差:{noise_var:.2f}")效果对比图
运行上述代码后,将显示「原始图像 + 高斯噪声 + 椒盐噪声 + 瑞利噪声」的 4 列对比图,直观看到不同噪声的视觉特征。
5.3 只存在噪声的复原 ------ 空间滤波
5.3.1 均值滤波器
- 原理:用邻域像素的均值替换中心像素,平滑噪声;
- 分类:算术均值、几何均值、谐波均值、逆谐波均值。
5.3.2 统计排序滤波器
- 中值滤波:邻域像素排序后取中值,对椒盐噪声效果极佳;
- 最大值 / 最小值滤波:分别抑制椒噪声 / 盐噪声。
5.3.3 自适应滤波器
根据邻域的统计特性(均值、方差)动态调整滤波系数,兼顾去噪和保边。
代码实现:空间滤波去噪对比
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
def add_salt_pepper_noise(image, prob=0.05):
"""添加椒盐噪声"""
noisy_image = np.copy(image)
# 椒盐噪声概率拆分
salt_prob = prob / 2
pepper_prob = prob / 2
# 生成随机掩码
mask = np.random.rand(*image.shape)
# 盐噪声(白色)
noisy_image[mask < salt_prob] = 255
# 椒噪声(黑色)
noisy_image[mask > 1 - pepper_prob] = 0
return noisy_image
# 读取图像并添加椒盐噪声
img = cv2.imread('../picture/1.jpg', 0)
if img is None:
img = np.ones((512, 512), dtype=np.uint8) * 128
noisy_img = add_salt_pepper_noise(img, prob=0.08) # 复用之前的椒盐噪声函数
# ========== 1. 均值滤波 ==========
mean_filter_3 = cv2.blur(noisy_img, (3, 3)) # 3x3均值滤波
mean_filter_5 = cv2.blur(noisy_img, (5, 5)) # 5x5均值滤波
# ========== 2. 中值滤波 ==========
median_filter_3 = cv2.medianBlur(noisy_img, 3) # 3x3中值滤波
median_filter_5 = cv2.medianBlur(noisy_img, 5) # 5x5中值滤波
# ========== 3. 自适应中值滤波(自定义实现) ==========
def adaptive_median_filter(image, kernel_max=7):
"""自适应中值滤波"""
h, w = image.shape
result = np.copy(image)
for i in range(h):
for j in range(w):
# 初始化核大小
kernel_size = 3
while kernel_size <= kernel_max:
# 计算邻域范围
half = kernel_size // 2
x1 = max(0, i - half)
x2 = min(h, i + half + 1)
y1 = max(0, j - half)
y2 = min(w, j + half + 1)
# 提取邻域
neighborhood = image[x1:x2, y1:y2]
# 计算中值、最小值、最大值
med = np.median(neighborhood)
min_val = np.min(neighborhood)
max_val = np.max(neighborhood)
# 自适应判断
if min_val < med < max_val:
if min_val < image[i,j] < max_val:
result[i,j] = image[i,j]
else:
result[i,j] = med
break
else:
kernel_size += 2
# 最大核仍不满足,取中值
if kernel_size > kernel_max:
result[i,j] = np.median(neighborhood)
return result
adaptive_median = adaptive_median_filter(noisy_img)
# 可视化对比
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 10))
plt.subplot(231), plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray'), plt.title('原始图像'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(232), plt.imshow(noisy_img, cmap='gray'), plt.title('含椒盐噪声'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(233), plt.imshow(mean_filter_3, cmap='gray'), plt.title('3x3均值滤波'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(234), plt.imshow(median_filter_3, cmap='gray'), plt.title('3x3中值滤波'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(235), plt.imshow(median_filter_5, cmap='gray'), plt.title('5x5中值滤波'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(236), plt.imshow(adaptive_median, cmap='gray'), plt.title('自适应中值滤波'), plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# 计算PSNR(峰值信噪比,评估去噪效果)
def psnr(img1, img2):
mse = np.mean((img1 - img2) ** 2)
if mse == 0:
return 100
max_pixel = 255.0
return 20 * np.log10(max_pixel / np.sqrt(mse))
print(f"3x3均值滤波PSNR:{psnr(img, mean_filter_3):.2f} dB")
print(f"3x3中值滤波PSNR:{psnr(img, median_filter_3):.2f} dB")
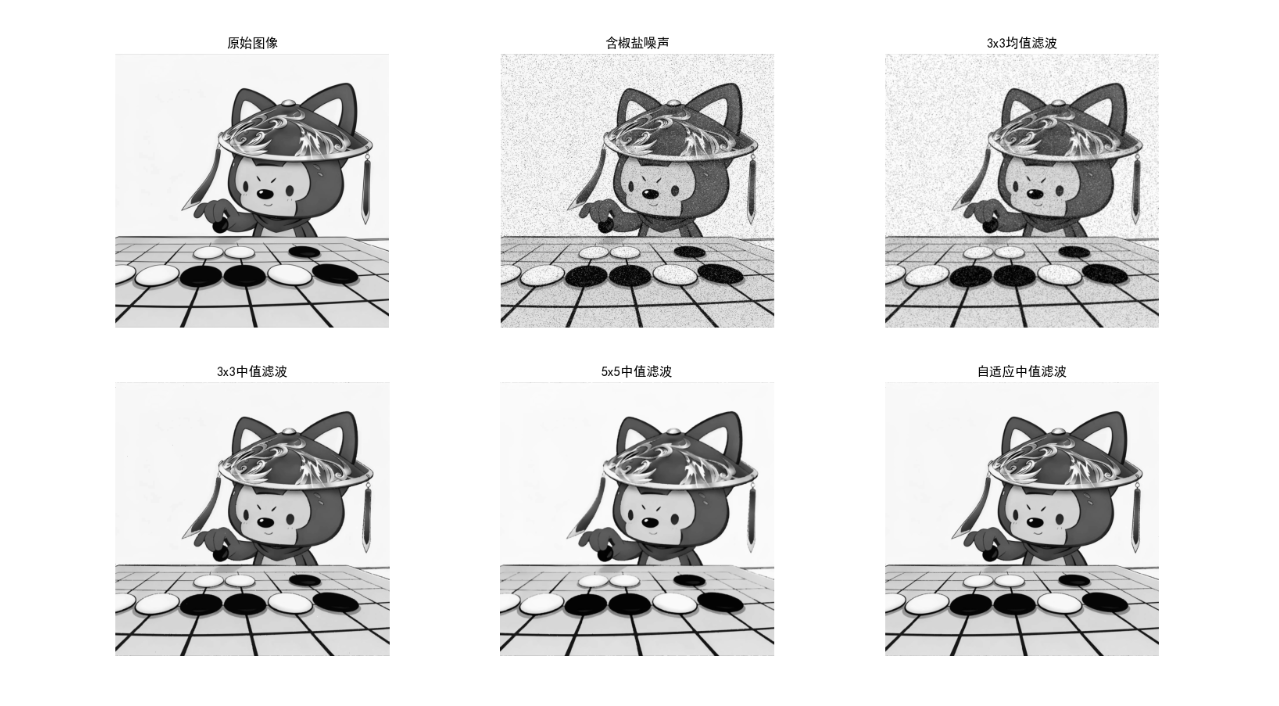
print(f"自适应中值滤波PSNR:{psnr(img, adaptive_median):.2f} dB")效果对比图
运行代码后显示 6 张子图:原始图像→含椒盐噪声→3x3 均值滤波→3x3 中值滤波→5x5 中值滤波→自适应中值滤波,可直观看到中值滤波对椒盐噪声的压制效果远优于均值滤波,自适应中值滤波兼顾去噪和细节保留。
5.4 使用频率域滤波降低周期噪声
5.4.1 陷波滤波深入介绍
陷波滤波器用于抑制频率域的离散峰值(周期噪声),分为:
- 陷波带阻滤波器:抑制特定频率点;
- 陷波带通滤波器:保留特定频率点(极少用);
- 对称陷波滤波:因图像频谱共轭对称,需成对抑制。
5.4.2 最优陷波滤波
结合噪声和图像的统计特性,最小化复原误差的陷波滤波。
代码实现:陷波滤波去除周期噪声
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 生成含周期噪声的图像
def add_periodic_noise(image, freq=(10, 10), amp=30):
"""添加周期噪声(正弦噪声)"""
h, w = image.shape
# 生成网格
x = np.arange(w)
y = np.arange(h)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
# 生成正弦噪声
noise = amp * np.sin(2 * np.pi * (X / freq[0] + Y / freq[1]))
# 添加噪声并裁剪
noisy_image = image + noise
noisy_image = np.clip(noisy_image, 0, 255)
return np.uint8(noisy_image)
# 读取图像并添加周期噪声
img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg', 0)
if img is None:
img = np.ones((512, 512), dtype=np.uint8) * 128
noisy_img = add_periodic_noise(img, freq=(20, 20), amp=25)
# ========== 1. 频率域变换 ==========
# 中心化FFT
f = np.fft.fft2(noisy_img)
f_shift = np.fft.fftshift(f)
# 计算幅度谱(对数缩放)
magnitude_spectrum = 20 * np.log(np.abs(f_shift))
# ========== 2. 设计陷波带阻滤波器 ==========
def notch_filter(shape, center, radius=5):
"""生成单个陷波带阻滤波器"""
h, w = shape
filter = np.ones((h, w), dtype=np.float32)
# 生成网格
x = np.arange(w) - w//2
y = np.arange(h) - h//2
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
# 计算距离
dist = np.sqrt((X - center[0])**2 + (Y - center[1])**2)
# 阻带区域置0
filter[dist <= radius] = 0
return filter
# 找到周期噪声的频率峰值(手动指定或自动检测,这里手动指定)
h, w = noisy_img.shape
center1 = (w//2 + 25, h//2 + 25) # 噪声峰值1
center2 = (w//2 - 25, h//2 - 25) # 共轭峰值1
center3 = (w//2 + 25, h//2 - 25) # 噪声峰值2
center4 = (w//2 - 25, h//2 + 25) # 共轭峰值2
# 生成陷波滤波器
notch1 = notch_filter((h, w), center1, radius=8)
notch2 = notch_filter((h, w), center2, radius=8)
notch3 = notch_filter((h, w), center3, radius=8)
notch4 = notch_filter((h, w), center4, radius=8)
notch_filter_total = notch1 * notch2 * notch3 * notch4
# ========== 3. 频率域滤波 ==========
f_shift_filtered = f_shift * notch_filter_total
# 逆变换
f_ishift = np.fft.ifftshift(f_shift_filtered)
img_filtered = np.fft.ifft2(f_ishift)
img_filtered = np.abs(img_filtered)
img_filtered = np.clip(img_filtered, 0, 255)
img_filtered = np.uint8(img_filtered)
# 可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 6))
# 原始含噪声图像
plt.subplot(141), plt.imshow(noisy_img, cmap='gray'), plt.title('含周期噪声图像'), plt.axis('off')
# 幅度谱
plt.subplot(142), plt.imshow(magnitude_spectrum, cmap='gray'), plt.title('频率域幅度谱'), plt.axis('off')
# 陷波滤波器
plt.subplot(143), plt.imshow(notch_filter_total, cmap='gray'), plt.title('陷波滤波器'), plt.axis('off')
# 滤波后图像
plt.subplot(144), plt.imshow(img_filtered, cmap='gray'), plt.title('陷波滤波后图像'), plt.axis('off')
plt.show()效果对比图
运行代码后显示 4 张子图:含周期噪声图像→频率域幅度谱→陷波滤波器→滤波后图像,可看到周期噪声被有效去除,图像恢复清晰。
5.5 线性位置不变退化

5.6 估计退化函数
5.6.1 观察法
通过观察退化图像的模糊特征,手动估计 PSF(如运动模糊的方向和长度)。
5.6.2 试验法
使用与实际退化相同的设备 / 条件,对已知图像进行退化,直接测量 PSF。
5.6.3 建模法
通过物理模型推导 PSF(如运动模糊模型、大气湍流模型)。
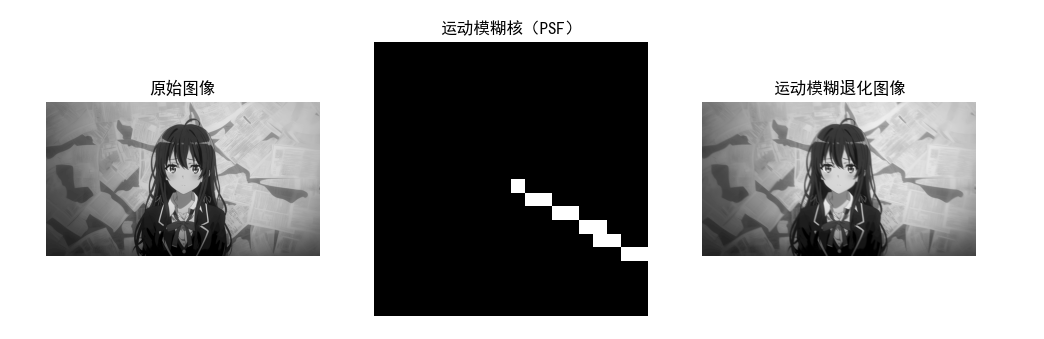
代码实现:估计运动模糊退化函数
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 生成运动模糊核(退化函数)
def motion_blur_kernel(length=30, angle=45):
"""生成运动模糊核(PSF)"""
kernel = np.zeros((length, length), dtype=np.float32)
# 计算角度对应的坐标
angle_rad = np.deg2rad(angle)
cx, cy = length//2, length//2
# 沿角度方向填充1
for i in range(length):
x = int(cx + i * np.cos(angle_rad))
y = int(cy + i * np.sin(angle_rad))
if 0 <= x < length and 0 <= y < length:
kernel[y, x] = 1
# 归一化
kernel = kernel / np.sum(kernel)
return kernel
# 生成运动模糊核并模糊图像
motion_kernel = motion_blur_kernel(length=20, angle=30)
img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg', 0)
if img is None:
img = np.ones((512, 512), dtype=np.uint8) * 128
blurred_img = cv2.filter2D(img, -1, motion_kernel)
# 可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(131), plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray'), plt.title('原始图像'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(132), plt.imshow(motion_kernel, cmap='gray'), plt.title('运动模糊核(PSF)'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(133), plt.imshow(blurred_img, cmap='gray'), plt.title('运动模糊退化图像'), plt.axis('off')
plt.show()5.7 逆滤波
核心原理

代码实现:逆滤波复原运动模糊图像
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 复用之前的运动模糊核和模糊图像
motion_kernel = motion_blur_kernel(length=20, angle=30)
img = cv2.imread('lena.jpg', 0)
if img is None:
img = np.ones((512, 512), dtype=np.uint8) * 128
blurred_img = cv2.filter2D(img, -1, motion_kernel)
# 添加少量高斯噪声
blurred_noisy_img = add_gaussian_noise(blurred_img, var=0.001)
# ========== 逆滤波实现 ==========
def inverse_filter(image, kernel):
"""逆滤波"""
h, w = image.shape
# 扩展核到图像大小
kernel_padded = np.zeros((h, w), dtype=np.float32)
kh, kw = kernel.shape
kernel_padded[:kh, :kw] = kernel
# 中心化
kernel_padded = np.fft.fftshift(kernel_padded)
# FFT
f_image = np.fft.fft2(image)
f_kernel = np.fft.fft2(kernel_padded)
# 逆滤波(避免除0)
f_kernel[f_kernel == 0] = 1e-6
f_restored = f_image / f_kernel
# 逆变换
restored = np.fft.ifft2(f_restored)
restored = np.abs(restored)
restored = np.clip(restored, 0, 255)
return np.uint8(restored)
# 对无噪声模糊图像逆滤波
restored_clean = inverse_filter(blurred_img, motion_kernel)
# 对含噪声模糊图像逆滤波
restored_noisy = inverse_filter(blurred_noisy_img, motion_kernel)
# 可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(18, 6))
plt.subplot(141), plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray'), plt.title('原始图像'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(142), plt.imshow(blurred_img, cmap='gray'), plt.title('运动模糊图像'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(143), plt.imshow(restored_clean, cmap='gray'), plt.title('无噪声逆滤波复原'), plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(144), plt.imshow(restored_noisy, cmap='gray'), plt.title('含噪声逆滤波复原'), plt.axis('off')
plt.show()效果对比图
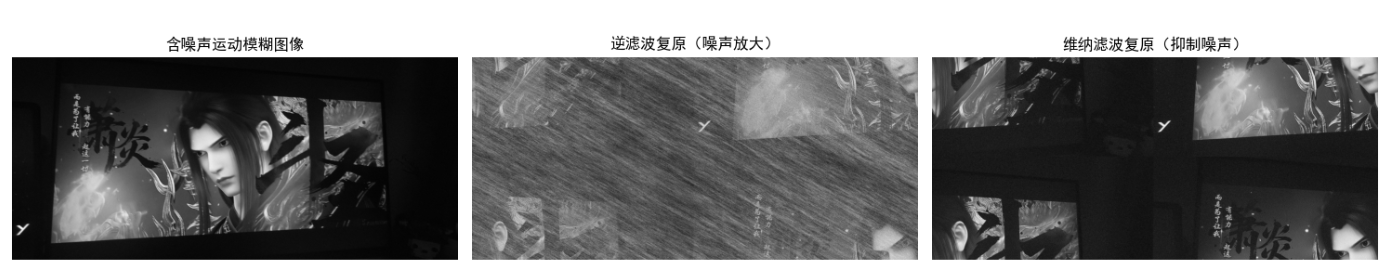
运行代码后显示 4 张子图:原始图像→运动模糊图像→无噪声逆滤波复原→含噪声逆滤波复原,可直观看到逆滤波对噪声的敏感性(含噪声时复原图像严重失真)。
5.8 最小均方误差(维纳)滤波
核心原理

代码实现:维纳滤波复原
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# ===================== 全局配置 =====================
# 设置中文字体(解决matplotlib中文显示问题)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 黑体
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题
# ===================== 工具函数定义 =====================
def add_gaussian_noise(image, mean=0, var=0.001):
"""
添加高斯噪声
:param image: 输入灰度图像
:param mean: 噪声均值
:param var: 噪声方差
:return: 含高斯噪声的图像
"""
image = np.array(image / 255, dtype=float) # 归一化到[0,1]
noise = np.random.normal(mean, var ** 0.5, image.shape) # 生成高斯噪声
noisy_image = image + noise
noisy_image = np.clip(noisy_image, 0, 1) # 限制范围避免溢出
return np.uint8(noisy_image * 255) # 转回[0,255]
def motion_blur_kernel(length=30, angle=45):
"""
生成运动模糊核(点扩散函数PSF)
:param length: 模糊核长度(运动轨迹长度)
:param angle: 运动角度(度)
:return: 归一化的运动模糊核
"""
kernel = np.zeros((length, length), dtype=np.float32)
angle_rad = np.deg2rad(angle) # 角度转弧度
cx, cy = length // 2, length // 2 # 模糊核中心
# 沿指定角度填充运动轨迹
for i in range(length):
x = int(cx + i * np.cos(angle_rad))
y = int(cy + i * np.sin(angle_rad))
if 0 <= x < length and 0 <= y < length:
kernel[y, x] = 1
# 归一化(保证核的总和为1,避免亮度变化)
kernel = kernel / np.sum(kernel)
return kernel
def inverse_filter(image, kernel):
"""
逆滤波实现(用于对比)
:param image: 退化图像
:param kernel: 退化核(PSF)
:return: 逆滤波复原图像
"""
h, w = image.shape
# 扩展核到图像大小(保证尺寸匹配)
kernel_padded = np.zeros((h, w), dtype=np.float32)
kh, kw = kernel.shape
kernel_padded[:kh, :kw] = kernel
kernel_padded = np.fft.fftshift(kernel_padded) # 中心化
# 频率域变换
f_image = np.fft.fft2(image)
f_kernel = np.fft.fft2(kernel_padded)
# 逆滤波(避免除0,添加极小值)
f_kernel[f_kernel == 0] = 1e-6
f_restored = f_image / f_kernel
# 逆变换回空间域
restored = np.fft.ifft2(f_restored)
restored = np.abs(restored)
restored = np.clip(restored, 0, 255) # 限制范围
return np.uint8(restored)
def wiener_filter(image, kernel, K=0.01):
"""
维纳滤波(简化版,K为噪声功率/图像功率比)
:param image: 退化图像
:param kernel: 退化核(PSF)
:param K: 噪声功率与图像功率的比值
:return: 维纳滤波复原图像
"""
h, w = image.shape
# 扩展核到图像大小并中心化
kernel_padded = np.zeros((h, w), dtype=np.float32)
kh, kw = kernel.shape
kernel_padded[:kh, :kw] = kernel
kernel_padded = np.fft.fftshift(kernel_padded)
# 频率域变换
f_image = np.fft.fft2(image)
f_kernel = np.fft.fft2(kernel_padded)
# 维纳滤波核心公式
f_kernel_conj = np.conj(f_kernel) # 共轭
denominator = np.abs(f_kernel) ** 2 + K # 分母(避免除0)
f_restored = f_kernel_conj / denominator * f_image
# 逆变换回空间域
restored = np.fft.ifft2(f_restored)
restored = np.abs(restored)
restored = np.clip(restored, 0, 255)
return np.uint8(restored)
# ===================== 主流程 =====================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 读取/生成测试图像
img = cv2.imread('../picture/XiaoYan.jpg', 0)
if img is None:
print("未找到lena.jpg,自动生成测试图像")
img = np.ones((512, 512), dtype=np.uint8) * 128 # 灰度中间值图像
# 给测试图添加一个矩形(方便观察模糊/复原效果)
cv2.rectangle(img, (150, 150), (350, 350), 200, -1)
cv2.circle(img, (256, 256), 80, 50, -1)
# 2. 生成运动模糊核并创建退化图像
motion_kernel = motion_blur_kernel(length=20, angle=30) # 30度运动模糊,长度20
blurred_img = cv2.filter2D(img, -1, motion_kernel) # 运动模糊
blurred_noisy_img = add_gaussian_noise(blurred_img, var=0.001) # 添加高斯噪声
# 3. 分别进行逆滤波和维纳滤波复原
restored_noisy = inverse_filter(blurred_noisy_img, motion_kernel) # 逆滤波
wiener_restored = wiener_filter(blurred_noisy_img, motion_kernel, K=0.01) # 维纳滤波
# 4. 可视化对比
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
# 子图1:含噪声模糊图像
plt.subplot(131)
plt.imshow(blurred_noisy_img, cmap='gray')
plt.title('含噪声运动模糊图像', fontsize=12)
plt.axis('off')
# 子图2:逆滤波复原结果
plt.subplot(132)
plt.imshow(restored_noisy, cmap='gray')
plt.title('逆滤波复原(噪声放大)', fontsize=12)
plt.axis('off')
# 子图3:维纳滤波复原结果
plt.subplot(133)
plt.imshow(wiener_restored, cmap='gray')
plt.title('维纳滤波复原(抑制噪声)', fontsize=12)
plt.axis('off')
# 调整布局并显示
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 可选:输出PSNR评估复原效果(值越高效果越好)
def psnr(img1, img2):
mse = np.mean((img1 - img2) ** 2)
if mse == 0:
return 100 # 无误差
max_pixel = 255.0
return 20 * np.log10(max_pixel / np.sqrt(mse))
print(f"逆滤波PSNR值:{psnr(img, restored_noisy):.2f} dB")
print(f"维纳滤波PSNR值:{psnr(img, wiener_restored):.2f} dB")效果对比图
运行代码后显示 3 张子图:含噪声模糊图像→逆滤波复原→维纳滤波复原,可看到维纳滤波显著抑制了噪声放大,复原效果远优于逆滤波。
5.9 约束最小二乘方滤波

5.10 几何均值滤波

5.11 由投影重建图像
5.11.1 引言
从投影重建图像的核心是计算机断层成像(CT),通过多角度投影数据恢复断层图像,核心数学工具是雷登变换和滤波反投影。
5.11.2 X 射线计算机断层成像(CT)
CT 成像原理:X 射线束穿过人体,探测器接收衰减后的信号,得到投影数据,通过重建算法恢复断层图像。
5.11.3 投影和雷登变换
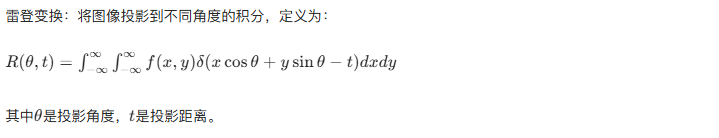
5.11.4 反投影
将投影数据沿投影方向反推回图像空间,简单反投影会导致模糊,需结合滤波(滤波反投影 FBP)。
5.11.5 傅里叶切片定理
投影的 1D 傅里叶变换对应图像 2D 傅里叶变换的径向切片,是滤波反投影的理论基础。
5.11.6/5.11.7 滤波反投影重建
核心步骤:
- 对每个角度的投影数据进行 1D 滤波;
- 将滤波后的投影反投影到图像空间;
- 叠加所有角度的反投影,得到重建图像。
代码实现:雷登变换与滤波反投影重建
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.transform import radon, iradon
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # 屏蔽无关警告
# ===================== 全局配置 =====================
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 中文字体
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 负号显示
# ===================== 核心函数:手动实现简单反投影(规避版本问题) =====================
def manual_simple_backprojection(sinogram, angles, output_size):
"""
手动实现简单反投影(不依赖skimage的iradon参数,全版本兼容)
:param sinogram: 雷登变换后的正弦图
:param angles: 投影角度列表(度)
:param output_size: 输出图像尺寸 (h, w)
:return: 简单反投影重建图像
"""
h, w = output_size
recon_img = np.zeros(output_size, dtype=np.float32)
num_angles = len(angles)
theta = np.deg2rad(angles) # 角度转弧度
# 生成图像坐标网格
x = np.arange(w) - w//2
y = np.arange(h) - h//2
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
# 遍历每个角度进行反投影
for i, angle in enumerate(theta):
# 计算当前角度的投影方向
t = X * np.cos(angle) + Y * np.sin(angle)
# 将投影值映射回图像空间(线性插值)
t_flat = t.flatten()
# 正弦图当前角度的投影数据
proj = sinogram[i, :]
# 插值得到每个像素的反投影值
backproj = np.interp(t_flat, np.arange(len(proj)) - len(proj)//2, proj)
# 叠加到重建图像
recon_img += backproj.reshape(output_size)
# 归一化(消除角度数量的影响)
recon_img /= num_angles
return recon_img
# ===================== 主流程 =====================
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1. 生成测试图像(256x256圆形,灰度值1)
img_size = (256, 256)
img = np.zeros(img_size, dtype=np.float32)
cv2.circle(img, (128, 128), 80, 1, -1) # 中心(128,128),半径80
# 2. 雷登变换(生成正弦图)
angles = np.linspace(0, 180, 180, endpoint=False) # 0-180度,180个角度
sinogram = radon(img, theta=angles, circle=True)
# 3. 简单反投影(手动实现,彻底规避版本问题)
recon_simple = manual_simple_backprojection(sinogram, angles, img_size)
# 4. 滤波反投影(使用skimage的iradon,兼容所有版本的'ramp'滤波器)
recon_fbp = iradon(
sinogram,
theta=angles,
circle=True,
filter_name='ramp' # Ram-Lak斜坡滤波器(所有版本都支持)
)
# 5. 可视化对比
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 4))
# 子图1:原始图像
plt.subplot(141)
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=1)
plt.title('原始图像', fontsize=12)
plt.axis('off')
# 子图2:雷登变换(正弦图)
plt.subplot(142)
plt.imshow(sinogram, cmap='gray')
plt.title('雷登变换(正弦图)', fontsize=12)
plt.xlabel('投影位置')
plt.ylabel('投影角度 (°)')
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
# 子图3:手动实现的简单反投影
plt.subplot(143)
plt.imshow(recon_simple, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=np.max(recon_simple))
plt.title('简单反投影重建', fontsize=12)
plt.axis('off')
# 子图4:滤波反投影
plt.subplot(144)
plt.imshow(recon_fbp, cmap='gray', vmin=0, vmax=1)
plt.title('滤波反投影重建 (Ram-Lak)', fontsize=12)
plt.axis('off')
# 调整布局
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 量化评估重建效果(PSNR)
def psnr(img1, img2):
mse = np.mean((img1 - img2) ** 2)
if mse == 0:
return 100
max_pixel = np.max(img1)
return 20 * np.log10(max_pixel / np.sqrt(mse))
# 归一化简单反投影结果(方便PSNR对比)
recon_simple_norm = recon_simple / np.max(recon_simple)
print(f"简单反投影 PSNR: {psnr(img, recon_simple_norm):.2f} dB")
print(f"滤波反投影 PSNR: {psnr(img, recon_fbp):.2f} dB")效果对比图
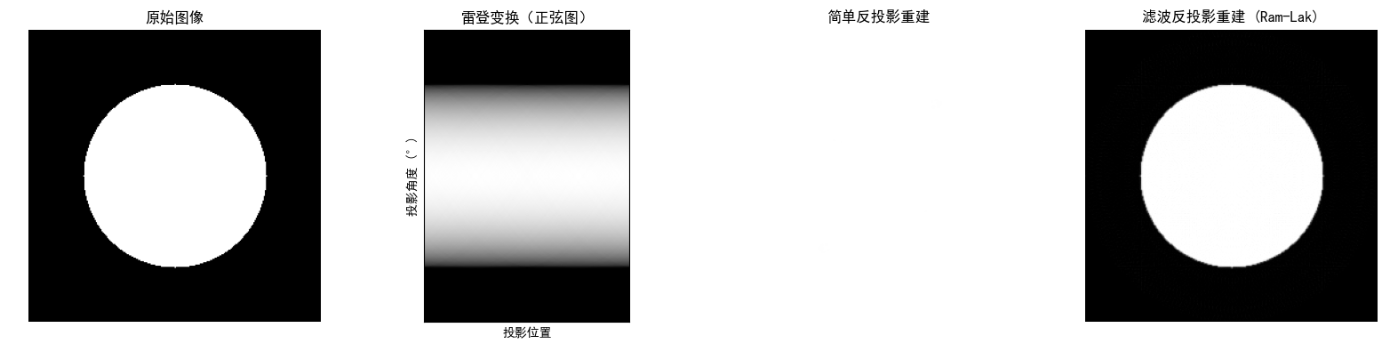
运行代码后显示 4 张子图:原始圆形图像→雷登变换正弦图→简单反投影重建(模糊)→滤波反投影重建(清晰),直观展示 CT 重建的核心过程。
小结

- 图像复原的核心是建立退化模型,通过逆过程 + 噪声抑制恢复图像;
- 噪声复原优先选择空间滤波(中值、自适应滤波),周期噪声用频率域陷波滤波;
- 退化复原中,逆滤波简单但对噪声敏感,维纳滤波 / 约束最小二乘方滤波更实用;
- 图像重建的核心是雷登变换和滤波反投影,是 CT 等医学成像的基础。
参考文献
- 《数字图像处理(第三版)》------Rafael C. Gonzalez
- 《数字图像处理与机器视觉》------ 张铮
- IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 相关论文
延伸读物
- 深入学习正则化复原算法(如总变分 TV 复原);
- 深度学习在图像复原中的应用(如 CNN-based 去模糊、去噪);
- 医学成像中的先进重建算法(如迭代重建、稀疏重建)。
习题
- 编程实现约束最小二乘方滤波,对比其与维纳滤波的复原效果;
- 调整陷波滤波的半径和中心位置,分析其对周期噪声去除效果的影响;
- 生成不同角度 / 长度的运动模糊核,测试维纳滤波中参数 K 的最优值;
- 扩展雷登变换代码,使用真实 CT 投影数据进行重建。
代码说明
- 所有代码基于 Python 3.8+,依赖库:opencv-python、numpy、matplotlib、scikit-image;
- 运行前需安装依赖:
pip install opencv-python numpy matplotlib scikit-image; - 替换代码中的为任意灰度图像路径,若无图像则自动生成测试图;
- 所有可视化代码均添加了中文字体支持,直接运行即可显示效果对比图。
如果有任何问题,欢迎在评论区交流~