用双向语义理解模型解锁自回归文本生成
1.自回归文本生成模型选择
1.1 什么是语言模型(Language Model)?
语言模型的目标是计算一个句子的概率。简单来说,就是让计算机学会"说人话"。
在数学上,给定序列 w1,w2,...,wnw_1, w_2, ..., w_nw1,w2,...,wn,其概率表示为:
P(w1,w2,...,wn)=P(w1)×P(w2∣w1)×P(w3∣w1,w2)×...×P(wn∣w1,...,wn−1)P(w_1, w_2, ..., w_n) = P(w_1) \times P(w_2|w_1) \times P(w_3|w_1,w_2) \times ... \times P(w_n|w_1,...,w_{n-1})P(w1,w2,...,wn)=P(w1)×P(w2∣w1)×P(w3∣w1,w2)×...×P(wn∣w1,...,wn−1)
这意味着模型需要根据已经出现的字,预测下一个字出现的概率。
1.2 为什么选择 BERT?
在 NLP 历史上,有三个代表性阶段:
- RNN/LSTM 时代: 适合处理序列,但训练慢,长程记忆差。
- GPT 时代(自回归): 专门为生成设计,采用单向 Transformer。
- BERT 时代(自编码): 采用双向 Transformer,语义理解极强。
本任务的独特性:
现在的任务是用 BERT 的肉身(强大的语义理解能力) 去做 GPT 的工作(自回归生成)。这就像是让一个善于"阅读理解"的专家去练习"命题作文"。
2. 核心技术解决路径
2.1 BERT 的先天缺陷:双向性
BERT 在预训练时使用的是 Masked LM(填空题),它通过 wi−1w_{i-1}wi−1 和 wi+1w_{i+1}wi+1 来预测 wiw_iwi。在生成任务中,如果我们直接输入全句,模型会产生"信息泄露"------它会直接看到后面的字,导致 Loss 迅速降为 0,但模型什么也没学会。
2.2 解决路线:因果掩码 (Causal Masking)
为了解决这个问题,我们必须在 BERT 的内部强行插入一个规则:第 iii 个字只能看到它之前的字,不能看后面的。
通过一个下三角矩阵(Lower Triangular Matrix),我们将那些"超前"的注意力权重(Attention Weights)设为负无穷(或者在 PyTorch 掩码中设为 False),这样在 Softmax 之后,模型就不会给未来的字分配任何权重。
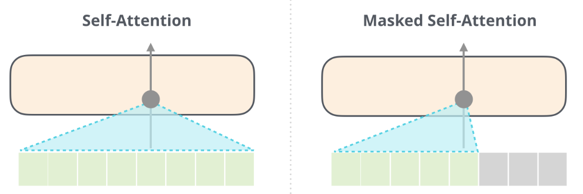
在 Mask Attention 机制中,为确保文本生成遵循 "左到右" 的时序逻辑,需先将不可见的未来位置对应分数设为 -inf (负无穷),进而形成仅下三角区域有效、上三角区域屏蔽的下三角矩阵。

将注意力分数矩阵中不可关注位置的值设为 -inf (负无穷)后,按行执行 SoftMax 运算时,这些 -inf 会被映射为 0 概率,而需要被关注的位置则会通过 SoftMax 归一化得到有效概率值,参与后续的注意力权重计算。

3. 代码逻辑分块详细拆解
模块一:构建字表与语料预处理
模型不认识汉字,只认识数字。我们需要建立"字 <-> 索引"的映射。
python
def build_vocab(vocab_path):
"""
Args:
vocab_path: 词表文件路径。
逻辑:
1. 初始化填充符 <pad>。
2. 遍历词表文件,将每个字映射到一个唯一的整数 ID。
"""
vocab = {"<pad>" : 0}
with open(vocab_path, encoding="utf-8") as f:
for index, line in enumerate(f):
char = line[:-1]
vocab[char] = index + 1
return vocab模块二:样本构造(滑窗法)
为了让模型学会预测,我们需要给它输入序列 ,并要求它预测目标序列 ( 整体后移一位)。
python
def build_sample(vocab, window_size, corpus):
"""
Args:
window_size: 每次看多少个字。
corpus: 整个语料库字符串。
逻辑:
随机截取一段文本,长度为 window_size。
x = [我, 是, 中, 国]
y = [是, 中, 国, 人] # 目标是预测下一个字
"""
start_index = random.randint(0, len(corpus) -1 - window_size)
end_index = start_index + window_size
sampling_window = corpus[start_index:end_index]
target = corpus[start_index + 1 : end_index + 1] # 错位对齐
# 转换为数字列表
x = [vocab.get(char, vocab["<UNK>"]) for char in sampling_window]
y = [vocab.get(char, vocab["<UNK>"]) for char in target]
return x, y模块三:模型定义(改造 BERT)
这是整段代码的灵魂。我们手动管理 BERT 的层,并注入因果掩码。(因为硬件性能原因)
python
class LanguageModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim = 768, vocab = None, use_bert_layers = 1):
super(LanguageModel, self).__init__()
# 1. 加载预训练权重,获取 BERT 的核心组件
full_bert = BertModel.from_pretrained(r"F:\bert-base-chinese")
self.bert_embeddings = full_bert.embeddings
self.bert_encoder_layers = nn.Sequential(*full_bert.encoder.layer[:use_bert_layers])
# 2. 输出层:将 BERT 的 768 维向量映射回词表大小
self.classify = nn.Linear(input_dim, len(vocab))
self.loss = nn.functional.cross_entropy
def generate_causal_mask(self, seq_len, device):
"""
核心逻辑:生成下三角掩码
[[1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1]]
这确保了位置 0 只能看位置 0,位置 1 只能看 [0, 1]
"""
mask = torch.tril(torch.ones((seq_len, seq_len), device=device)).bool()
return mask.unsqueeze(0)
def forward(self, x, y = None):
embeddings_output = self.bert_embeddings(x)
causal_mask = self.generate_causal_mask(x.shape[1], x.device)
# 3. 逐层通过 BERT Encoder,并强制注入掩码
encoder_output = embeddings_output
for layer_module in self.bert_encoder_layers:
encoder_output = layer_module(
hidden_states = encoder_output,
attention_mask = causal_mask # 关键:强制单向关注
)[0]
y_pred = self.classify(encoder_output)
if y is not None:
# 训练模式:计算预测分布与真实字 ID 的差距
return self.loss(y_pred.view(-1, y_pred.shape[-1]), y.view(-1))
else:
# 预测模式:输出最后一个字的概率分布
return torch.softmax(y_pred, dim = -1)模块四:生成策略(推理阶段)
生成时,模型会输出几万个字的概率,我们需要选择一个字作为结果。
python
def sampling_strategy(y_prob_distribution):
"""
逻辑:
混合策略:90% 时间用最稳妥的(Greedy),10% 时间加点随机性(Sampling)。
这样生成的句子既通顺,又不会一直在几个字之间死循环。
"""
if random.random() > 0.1:
return int(torch.argmax(y_prob_distribution))
else:
y_prob_distribution = y_prob_distribution.cpu().numpy()
return np.random.choice(list(range(len(y_prob_distribution))), p = y_prob_distribution)4. 总结:这套方案是如何解决问题的?
- 特征提取: 我们利用了 BERT 在海量中文数据上练就的"语感"(Embedding 和底层 Transformer 权重)。
- 打破禁忌: 通过
generate_causal_mask改变了 BERT 的计算逻辑,使其符合"自回归"要求。 - 循环生成: 在
generate_sentence函数中,通过while循环不断将新生成的字喂回模型,实现了从"预测一个字"到"生成一段话"的跨越。
最终效果: 你的模型不仅学会了字的排列组合,还通过 BERT 的上下文建模能力,学到了比普通 RNN 更深刻的语义逻辑。
5. 完整整合后的代码
- vocab.txt 就是 bert 的 vocab
- corpus 是一个预料,后续给百度云盘吧,着急的,问我吧
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import math
import random
import os
import re
from transformers import BertModel
#计算文本ppl
def calc_perplexity(sentence, model, vocab, window_size):
"""
计算文本的困惑度(Perplexity, PPL)
PPL是语言模型的评估指标,值越低表示模型对文本的预测越准确
Args:
sentence (str): 待评估的文本
model (LanguageModel): 训练好的语言模型
vocab (dict): 字表字典
window_size (int): 输入窗口大小(与训练一致)
Returns:
float: 文本的困惑度值
计算公式:
PPL = 2^(-1/N * Σ(log2 P(w_i | w_1...w_{i-1})))
其中N为文本长度,P(w_i)为模型预测第i个字符的概率
说明:
- 对每个字符,用其前面的字符(最多window_size个)预测当前字符
- 取log10后转换为log2计算(因最终结果用2为底)
"""
prob = 0
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for i in range(1, len(sentence)):
start = max(0, i - window_size)
window = sentence[start:i]
x = [vocab.get(char, vocab["<UNK>"]) for char in window]
x = torch.LongTensor([x])
target = sentence[i]
target_index = vocab.get(target, vocab["<UNK>"])
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x = x.cuda()
pred_prob_distribute = model(x)[0][-1]
target_prob = pred_prob_distribute[target_index]
prob += math.log(target_prob, 10)
return 2 ** (prob * ( -1 / len(sentence)))
class LanguageModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim = 768, vocab = None, use_bert_layers = 1):
"""
Args:
input_dim: BERT隐藏层维度(固定768)
vocab: 字表字典
use_bert_layers: 使用BERT的前N层(1≤N≤12)
"""
super(LanguageModel, self).__init__()
# 加载完整BERT预训练模型
full_bert = BertModel.from_pretrained(r"F:\bert-base-chinese")
self.bert_embeddings = full_bert.embeddings
self.bert_encoder_layers = nn.Sequential(*full_bert.encoder.layer[:use_bert_layers])
self.classify = nn.Linear(input_dim, len(vocab))
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.1)
self.loss = nn.functional.cross_entropy
# 生成 mask 掩码
def generate_causal_mask(self, seq_len, device):
"""
生成因果掩码(下三角矩阵)
:param seq_len: 序列长度
:param device: 设备
:return: [1, seq_len, seq_len]的掩码矩阵
"""
mask = torch.tril(torch.ones((seq_len, seq_len), device=device)).bool()
return mask.unsqueeze(0) # 增加batch维度
def forward(self, x, y = None):
batch_size, seq_len = x.shape
device = x.device
embeddings_output = self.bert_embeddings(x)
# 2. 生成因果掩码(阻止看到未来token)
causal_mask = self.generate_causal_mask(seq_len, device) # [1, seq_len, seq_len]
encoder_output = embeddings_output
# 取出每层BERT编码器进行前向计算
for layer_module in self.bert_encoder_layers:
encoder_output = layer_module(
hidden_states = encoder_output,
attention_mask = causal_mask
)[0]
encoder_output = self.dropout(encoder_output)
y_pred = self.classify(encoder_output)
if y is not None:
return self.loss(y_pred.view(-1, y_pred.shape[-1]), y.view(-1))
else:
return torch.softmax(y_pred, dim = -1)
def build_vocab(vocab_path):
vocab = {"<pad>" : 0} #特殊填充符号
with open(vocab_path, encoding="utf-8") as f:
for index, line in enumerate(f):
char = line[:-1] #去掉结尾换行符
vocab[char] = index + 1
return vocab
def load_corpus(corpus_path):
corpus = ""
with open(corpus_path, encoding = "gbk") as f:
for line in f:
corpus += line.strip()
return corpus
def build_model(vocab, char_dim, encoder_layers):
model = LanguageModel(char_dim, vocab, encoder_layers)
return model
def build_sample(vocab, window_size, corpus):
start_index = random.randint(0, len(corpus) -1 - window_size)
end_index = start_index + window_size
sampling_window = corpus[start_index:end_index]
target = corpus[start_index + 1 : end_index + 1] #目标文本比输入文本向后移动一个字
x = [vocab.get(char, vocab["<UNK>"]) for char in sampling_window]
y = [vocab.get(char, vocab["<UNK>"]) for char in target]
return x, y
def build_dataset(sample_length, vocab, window_size, corpus):
dataset_x = []
dataset_y = []
for i in range(sample_length):
x, y = build_sample(vocab, window_size, corpus)
dataset_x.append(x)
dataset_y.append(y)
return torch.LongTensor(dataset_x), torch.LongTensor(dataset_y)
def sampling_strategy(y_prob_distribution):
if random.random() > 0.1:
strategy = "greedy"
else:
strategy = "sampling"
if strategy == "greedy":
return int(torch.argmax(y_prob_distribution))
elif strategy == "sampling":
y_prob_distribution = y_prob_distribution.cpu().numpy()
sampling_text = np.random.choice(list(range(len(y_prob_distribution))), p = y_prob_distribution)
return sampling_text
def generate_sentence(openings_text, model, vocab, window_size):
# 解码,idx到字的映射
ix_to_char = {ix:char for char, ix in vocab.items()}
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# 一个个字进行预测
pred_char = ""
# 生成了换行符,或生成文本超过30字则终止迭代
while pred_char != "\n" and len(openings_text) <=30:
openings_text += pred_char
x = [vocab.get(char, vocab["<UNK>"]) for char in openings_text[-window_size:]]
x = torch.LongTensor([x])
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x = x.cuda()
y = model(x)[0][-1]
index = sampling_strategy(y)
pred_char = ix_to_char[index]
return openings_text
def train(corpus_path, save_weight = True):
epoch_num = 20 #训练轮数
batch_size = 64 #每次训练样本个数
train_sample = 50000 #每轮训练总共训练的样本总数
char_dim = 768 #每个字的维度
window_size = 10 #样本文本长度
encoder_layers = 3
vocab = build_vocab("vocab.txt") #建立字表
corpus = load_corpus(corpus_path) #加载语料
model = build_model(vocab, char_dim, encoder_layers) #建立模型
if torch.cuda.is_available():
model = model.cuda()
# 学习率变小
optim = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr = 0.0001) #优化器
print("文本词表模型加载完成,开始训练...")
for epoch in range(epoch_num):
model.train()
watch_loss = []
for batch in range(int(train_sample / batch_size)):
x, y = build_dataset(batch_size, vocab, window_size, corpus)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
x = x.cuda()
y = y.cuda()
optim.zero_grad()
loss = model(x, y)
loss.backward()
optim.step()
watch_loss.append(loss.item())
print("============第{}轮训练完成,平均损失:{:.4f}============".format(epoch + 1, np.mean(watch_loss)))
print("===============================================")
print(generate_sentence("让他在半年之前,就不能做出", model, vocab, window_size))
print(generate_sentence("科学技术是第一生产力,", model, vocab, window_size))
if not save_weight:
return
else:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "nnlm_model.pth")
print("模型权重保存完成!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
train("corpus.txt", False)