python
复制代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 定义生成器网络
class Generator(nn.Module):
"""
生成器网络:将随机噪声转换为伪造的图像
输入:随机噪声向量(维度为latent_dim)
输出:生成的图像(1 x 28 x 28)
"""
def __init__(self, latent_dim):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(latent_dim, 256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.BatchNorm1d(256),
nn.Linear(256, 512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.BatchNorm1d(512),
nn.Linear(512, 1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.BatchNorm1d(1024),
nn.Linear(1024, 28 * 28),
nn.Tanh()
)
def forward(self, z):
"""
前向传播
参数:
z: 随机噪声向量
返回:
生成的图像,形状为 [batch_size, 1, 28, 28]
"""
img = self.model(z)
img = img.view(img.size(0), 1, 28, 28)
return img
# 定义判别器网络
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
"""
判别器网络:判断输入的图像是真实的还是生成的
输入:图像(1 x 28 x 28)
输出:图像为真实的概率(0-1之间的标量)
"""
def __init__(self):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(28 * 28, 1024),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Dropout(0.3),
nn.Linear(1024, 512),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Dropout(0.3),
nn.Linear(512, 256),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2),
nn.Dropout(0.3),
nn.Linear(256, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, img):
"""
前向传播
参数:
img: 输入图像,形状为 [batch_size, 1, 28, 28]
返回:
图像为真实的概率,形状为 [batch_size, 1]
"""
img_flat = img.view(img.size(0), -1)
validity = self.model(img_flat)
return validity
def train_gan(epochs=100, batch_size=64, latent_dim=100, sample_interval=200):
"""
训练GAN模型
参数:
epochs: 训练轮数
batch_size: 批次大小
latent_dim: 随机噪声向量的维度
sample_interval: 生成并保存样本的间隔
"""
# 设置设备(GPU或CPU)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"使用设备: {device}")
# 加载MNIST数据集
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.5], [0.5])
])
dataset = datasets.MNIST(root="./data", train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
# 初始化生成器和判别器
generator = Generator(latent_dim).to(device)
discriminator = Discriminator().to(device)
# 定义损失函数和优化器
adversarial_loss = nn.BCELoss()
optimizer_G = optim.Adam(generator.parameters(), lr=0.0002, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
optimizer_D = optim.Adam(discriminator.parameters(), lr=0.0002, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
# 训练循环
for epoch in range(epochs):
for i, (imgs, _) in enumerate(dataloader):
# 配置输入
real_imgs = imgs.to(device)
batch_size = real_imgs.size(0)
# 创建标签
real = torch.ones(batch_size, 1).to(device)
fake = torch.zeros(batch_size, 1).to(device)
# ---------------------
# 训练判别器
# ---------------------
optimizer_D.zero_grad()
# 计算真实图像的损失
real_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(real_imgs), real)
# 生成假图像
z = torch.randn(batch_size, latent_dim).to(device)
gen_imgs = generator(z)
# 计算假图像的损失
fake_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_imgs.detach()), fake)
# 总判别器损失
d_loss = (real_loss + fake_loss) / 2
d_loss.backward()
optimizer_D.step()
# ---------------------
# 训练生成器
# ---------------------
optimizer_G.zero_grad()
# 生成假图像
z = torch.randn(batch_size, latent_dim).to(device)
gen_imgs = generator(z)
# 生成器希望判别器认为生成的图像是真实的
g_loss = adversarial_loss(discriminator(gen_imgs), real)
g_loss.backward()
optimizer_G.step()
# 打印训练进度
if i % 50 == 0:
print(
f"[Epoch {epoch}/{epochs}] [Batch {i}/{len(dataloader)}] "
f"[D loss: {d_loss.item():.4f}] [G loss: {g_loss.item():.4f}]"
)
# 定期保存生成的图像
if i % sample_interval == 0:
save_images(gen_imgs, epoch, i)
# 训练完成后,生成最终样本
print("\n训练完成!生成最终样本...")
z = torch.randn(25, latent_dim).to(device)
gen_imgs = generator(z)
save_images(gen_imgs, epochs, 0, final=True)
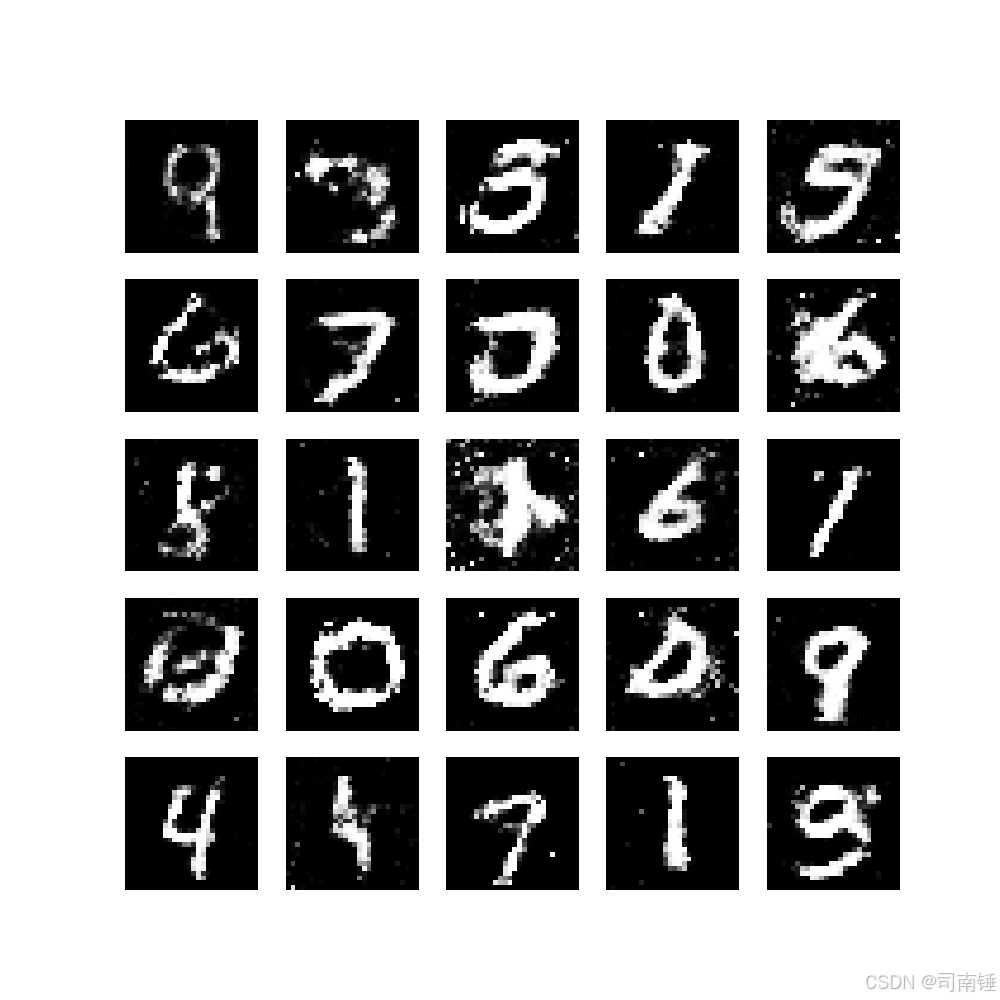
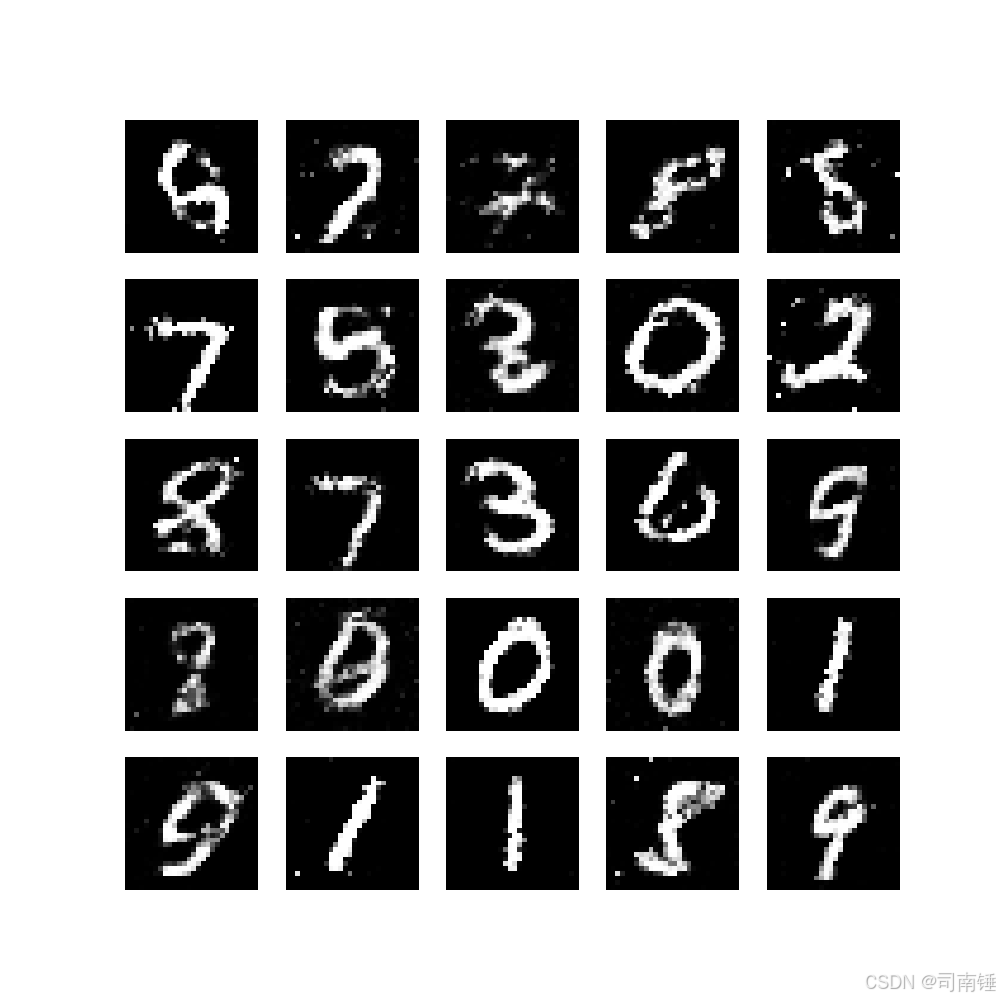
def save_images(images, epoch, batch_idx, final=False):
"""
保存生成的图像
参数:
images: 生成的图像张量
epoch: 当前轮数
batch_idx: 当前批次索引
final: 是否为最终样本
"""
images = images.detach().cpu().numpy()
images = 0.5 * images + 0.5 # 反归一化到[0, 1]范围
fig, axes = plt.subplots(5, 5, figsize=(10, 10))
for i, ax in enumerate(axes.flat):
if i < images.shape[0]:
ax.imshow(images[i, 0], cmap='gray')
ax.axis('off')
if final:
plt.savefig(f'gan_final_samples.png')
print(f"最终样本已保存为: gan_final_samples.png")
else:
plt.savefig(f'gan_epoch{epoch}_batch{batch_idx}.png')
plt.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 训练GAN模型
train_gan(epochs=20, batch_size=64, latent_dim=100, sample_interval=200)