聚类常用的是meanshift(均值漂移)与kmeans
具体计算流程不详细写了,有很多大佬都提供了不错的学习做资料(个人的十大算法系列有kmeans,印象中有,读研的时候写的了)。这里为自己对比梳理与代码整理。
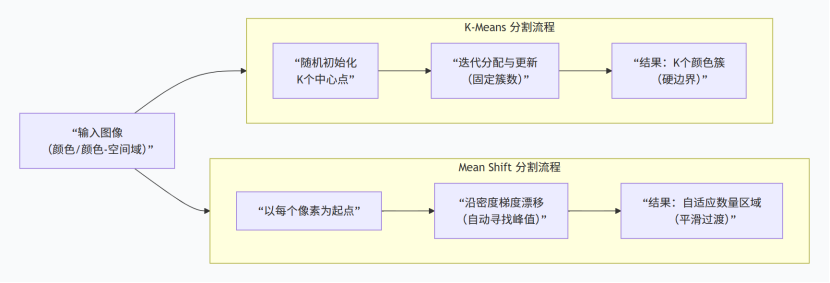

python
def kmeans_segmentation_gray(img_path, n=5):
'''
:param img_path:
:param n: 类中心的个数
:return:
'''
image = cv2.imread(img_path)
(h1, w1) = image.shape[:2]
image_gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
image_gray = image_gray.reshape((image_gray.shape[0] * image_gray.shape[1], 1))
# 创建K-Means聚类器,设定要聚为n类(即分割成n个主色区域)
clt = KMeans(n_clusters = n)
labels = clt.fit_predict(image_gray) # fit_predict返回每个像素所属的聚类标签(0-(n-1))
quant = clt.cluster_centers_.astype("uint8")[labels] # 聚类中心代表每个分区的代表颜色,用聚类中心的颜色值替换每个像素的原始颜色,实现颜色量化
quant = quant.reshape((h1, w1, 1))
# cv2.imshow('image', image)
# cv2.imshow('generated', quant)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
return quant
def kmeans_segmentation_rgb(img_path, n=5):
image = cv2.imread(img_path)
(h1, w1) = image.shape[:2]
# 将3D图像数组(高度, 宽度, 通道)转为2D数组(像素数, 通道)
image_rgb = image.reshape((image.shape[0] * image.shape[1], 3))
clt = KMeans(n_clusters = n)
labels = clt.fit_predict(image_rgb)
quant = clt.cluster_centers_.astype("uint8")[labels]
quant = quant.reshape((h1, w1, 3))
# cv2.imshow('image', image)
# cv2.imshow('generated', quant)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
return quant
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_path = './test/test_img.jpg'
res_gray = kmeans_segmentation_gray(img_path, n=3)
res_rgb = kmeans_segmentation_rgb(img_path, n=3)
cv2.imshow('image', cv2.imread(img_path))
cv2.imshow('res_gray', res_gray)
cv2.imshow('res_rgb', res_rgb)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
python
import cv2
import numpy as np
def mean_shift_segmentation_cv2(image_path, spatial_radius=20, color_radius=20, min_size=100):
"""
使用Mean Shift算法进行图像分割 (OpenCV版本)
参数:
image_path: 输入图像路径
spatial_radius: 空间窗口半径
color_radius: 颜色窗口半径
min_size: 最小区域大小
"""
# 1. 读取图像
image = cv2.imread(image_path)
if image is None:
print(f"错误:无法读取图像 {image_path}")
return
original = image.copy()
original_h, original_w = image.shape[:2]
# 2. 应用Mean Shift滤波
shifted = cv2.pyrMeanShiftFiltering(
image,
sp=spatial_radius,
sr=color_radius,
maxLevel=2
)
# 3. 后处理:移除过小的区域
gray = cv2.cvtColor(shifted, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
_, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# 查找轮廓并过滤小区域
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
mask = np.zeros((original_h, original_w), dtype=np.uint8)
for contour in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
if area > min_size:
cv2.drawContours(mask, [contour], -1, 255, -1)
# 应用掩码得到最终分割结果
segmented = cv2.bitwise_and(shifted, shifted, mask=mask)
# 4. 计算分割区域数量
num_labels, labels_im = cv2.connectedComponents(mask)
num_regions = num_labels - 1 if num_labels > 1 else 0
# 5. 创建边界叠加图
boundaries = cv2.Canny(mask, 30, 100)
overlay = original.copy()
overlay[boundaries > 0] = [0, 0, 255] # 红色边界 (BGR格式)
# 6. 创建网格显示 (2行3列)
# 第一行:原始图像,Mean Shift结果,二值掩码
row1 = np.hstack([original, shifted, cv2.cvtColor(mask, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)])
# 第二行:最终分割结果,边界叠加,区域统计文本图
# 创建文本信息图
text_img = np.zeros((original_h, original_w, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
text_img[:] = [240, 240, 240] # 浅灰色背景
# 添加文本信息
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
line_height = 30
start_y = 40
info_lines = [
f"Mean Shift report",
f"original_w_h: {original_w} x {original_h}",
f"spatial_radius(sp): {spatial_radius}",
f"color_radius(sr): {color_radius}",
f"num_regions: {num_regions}",
f"min_size: {min_size}",
"",
"press any key to continue..."
]
for i, line in enumerate(info_lines):
y_pos = start_y + i * line_height
cv2.putText(text_img, line, (20, y_pos), font, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
row2 = np.hstack([segmented, overlay, text_img])
# 7. 垂直拼接两行
display = np.vstack([row1, row2])
# 8. 显示结果
cv2.imshow(f"Mean Shift (sp={spatial_radius}, sr={color_radius})", display)
# 9. 打印控制台信息
print("=" * 50)
print("Mean Shift 图像分割报告")
print("=" * 50)
print(f"图像尺寸: {original_w} x {original_h}")
print(f"参数设置: sp={spatial_radius}, sr={color_radius}")
print(f"分割区域数量: {num_regions}")
print(f"最小区域大小: {min_size} 像素")
print("\n显示说明:")
print("第一行: [原始图像] | [Mean Shift滤波] | [区域掩码]")
print("第二行: [最终结果] | [边界叠加] | [参数信息]")
print("=" * 50)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# cv2.imshow("original", original)
# cv2.imshow("shifted result", shifted)
# cv2.imshow("mask", mask)
# cv2.imshow("segmented result", segmented)
# cv2.imshow("overlay", overlay)
print("\n按 's' 键保存结果,其他任意键退出...")
key = cv2.waitKey(0)
if key == ord('s') or key == ord('S'):
# 保存结果
cv2.imwrite("mean_shift_original.jpg", original)
cv2.imwrite("mean_shift_filtered.jpg", shifted)
cv2.imwrite("mean_shift_mask.jpg", mask)
cv2.imwrite("mean_shift_segmented.jpg", segmented)
cv2.imwrite("mean_shift_overlay.jpg", overlay)
cv2.imwrite("mean_shift_display.jpg", display)
print("结果已保存为JPG文件")
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
return {
'original': original,
'shifted': shifted,
'mask': mask,
'segmented': segmented,
'num_regions': num_regions
}
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 示例1:使用默认参数
result = mean_shift_segmentation_cv2(
image_path='./test/test_img.jpg',
spatial_radius=15, # 调整空间平滑度
color_radius=20, # 调整颜色敏感度
min_size=100 # 最小区域大小
)
# result2 = mean_shift_segmentation_cv2(
# image_path='./test/test_img.jpg',
# spatial_radius=10, # 更小的空间半径 -> 更多细节
# color_radius=15, # 更小的颜色半径 -> 更多颜色区分
# min_size=50 # 更小的最小区域
# )效果对比暂时不放辣,后续更新。