在 Unity 开发中,我们经常会遇到这样的场景:
场景中存在大量外观相同、行为相似,但位置、朝向各不相同的对象,例如森林里的树、草地上的草、子弹、NPC 装饰物等。
如果我们为每一个对象都完整地创建一套数据和资源,不仅会造成 内存浪费 ,还会增加 实例化与管理成本 。
而享元模式(Flyweight Pattern)正是为了解决这类问题而存在的。
享元模式的核心思想是:
将"可以共享的内部状态"抽离出来复用,把"不可共享的外部状态"交给使用者维护。
下面我将结合 Unity 的实际开发场景,用一个「森林生成系统」的例子,完整演示享元模式的设计与使用方式。
1.创建享元对象------承载外部状态
Tree 类并不是树的"类型",而是树的一个实例描述。
cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Tree
{
private TreeType treeType; // 共享的内部状态(享元对象)
private Vector3 position; // 外部状态:位置
private Quaternion rotation; // 外部状态:旋转
private float scale; // 外部状态:缩放
private GameObject treeObject; // 实际的游戏对象
public GameObject TreeObject => treeObject;
public Tree(TreeType type, Vector3 pos, Quaternion rot, float scale)
{
this.treeType = type;
this.position = pos;
this.rotation = rot;
this.scale = scale;
}
// 实例化树到场景中
public GameObject Instantiate(Transform parent = null)
{
if (treeType == null) return null;
treeObject = treeType.InstantiateTree(position, rotation, scale, parent);
return treeObject;
}
// 移除树
public void Destroy()
{
if (treeObject != null)
{
GameObject.Destroy(treeObject);
}
}
}2.创建树的类型------真正的享元对象
TreeType 才是享元模式中的核心共享对象。
它保存的是:树的名称,颜色,纹理信息,预制体引用
cs
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class TreeType
{
public string Name { get; } // 树种名称
public Color Color { get; } // 树的主要颜色
public string Texture { get; } // 纹理名称
public GameObject Prefab { get; } // 树的预制体
// 构造函数
public TreeType(string name, Color color, string texture, GameObject prefab)
{
Name = name;
Color = color;
Texture = texture;
Prefab = prefab;
Debug.Log($"创建树种: {name} (颜色: {color}, 纹理: {texture})");
}
// 实例化树的方法
public GameObject InstantiateTree(Vector3 position, Quaternion rotation, float scale, Transform parent)
{
GameObject tree = GameObject.Instantiate(Prefab, position, rotation, parent);
tree.transform.localScale = Vector3.one * scale;
// 可以根据颜色和纹理修改材质
MeshRenderer renderer = tree.GetComponent<MeshRenderer>();
if (renderer != null)
{
// 这里可以设置材质颜色或纹理
Material newMaterial = new Material(renderer.sharedMaterial);
newMaterial.color = Color;
renderer.material = newMaterial;
}
return tree;
}
}3.创建享元工厂------统一管理共享对象
TreeFactory 的职责是:
-
管理所有已经创建的
TreeType -
保证同一类型只会被创建一次
-
对外提供统一获取接口
cs
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class TreeFactory
{
private static Dictionary<string, TreeType> treeTypes = new Dictionary<string, TreeType>();
// 获取或创建树种 - 新增prefab参数
public static TreeType GetTreeType(string name, Color color, string texture, GameObject prefab = null)
{
string key = $"{name}_{color}_{texture}";
if (!treeTypes.ContainsKey(key))
{
// 如果不存在,创建新的享元对象
if (prefab == null)
{
Debug.LogError($"首次创建树种 '{name}' 时必须提供预制体!");
return null;
}
treeTypes[key] = new TreeType(name, color, texture, prefab);
Debug.Log($"✓ 创建新的树种类型: {name}");
}
else
{
Debug.Log($"✓ 重用现有的树种类型: {name}");
}
return treeTypes[key];
}
// 获取已创建的树种数量
public static int GetTreeTypeCount()
{
return treeTypes.Count;
}
// 获取特定类型的树种
public static TreeType GetExistingTreeType(string name, Color color, string texture)
{
string key = $"{name}_{color}_{texture}";
if (treeTypes.ContainsKey(key))
{
return treeTypes[key];
}
return null;
}
public static void Clear()
{
treeTypes.Clear();
Debug.Log("已清除所有树种类型");
}
}4.创建一片森林
-
创建 1000 棵树
-
实际只创建 2 个 TreeType
-
每棵树位置、旋转、缩放都不同
cs
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Forest : MonoBehaviour
{
public GameObject treePrefab; // 树的预制体
public int treeCount = 1000; // 要创建的树数量
public Vector2 areaSize = new Vector2(200, 200); // 森林区域大小
public Transform forestParent; // 所有树的父对象(可选)
private List<Tree> trees = new List<Tree>();
void Start()
{
CreateForest();
}
void CreateForest()
{
Debug.Log("=== 开始创建森林 ===");
// 确保有预制体
if (treePrefab == null)
{
Debug.LogError("请先指定树的预制体!");
return;
}
// 创建两种树型配置
TreeType pineTreeType = null;
TreeType oakTreeType = null;
// 创建1000棵树,但只有2种树种
for (int i = 0; i < treeCount; i++)
{
TreeType treeType;
// 随机选择树种(只有2种类型)
if (UnityEngine.Random.value > 0.5f)
{
// 松树 - 共享的享元对象
if (pineTreeType == null)
{
pineTreeType = TreeFactory.GetTreeType(
"松树",
Color.green,
"pine_texture",
treePrefab // 传入预制体
);
}
treeType = pineTreeType;
}
else
{
// 橡树 - 共享的享元对象
if (oakTreeType == null)
{
oakTreeType = TreeFactory.GetTreeType(
"橡树",
new Color(0.2f, 0.8f, 0.3f),
"oak_texture",
treePrefab // 传入预制体
);
}
treeType = oakTreeType;
}
// 每棵树有不同的位置、旋转和缩放(外部状态)
Vector3 randomPosition = new Vector3(
UnityEngine.Random.Range(-areaSize.x / 2, areaSize.x / 2),
0,
UnityEngine.Random.Range(-areaSize.y / 2, areaSize.y / 2)
);
Quaternion randomRotation = Quaternion.Euler(
0,
UnityEngine.Random.Range(0, 360),
0
);
float randomScale = UnityEngine.Random.Range(0.8f, 1.5f);
// 创建树对象(此时还没有实例化游戏对象)
Tree tree = new Tree(treeType, randomPosition, randomRotation, randomScale);
trees.Add(tree);
}
Debug.Log($"=== 创建完成 ===");
Debug.Log($"总共创建了 {trees.Count} 棵树");
Debug.Log($"但只创建了 {TreeFactory.GetTreeTypeCount()} 种树种类型");
Debug.Log($"节省了 {trees.Count - TreeFactory.GetTreeTypeCount()} 个重复对象的创建!");
// 实际实例化所有树到场景中
InstantiateAllTrees();
}
void InstantiateAllTrees()
{
Debug.Log("开始实例化树到场景中...");
// 创建森林父对象(如果指定)
Transform parent = forestParent;
if (parent == null)
{
GameObject forestContainer = new GameObject("ForestContainer");
parent = forestContainer.transform;
}
foreach (Tree tree in trees)
{
tree.Instantiate(parent);
}
Debug.Log($"已实例化 {trees.Count} 棵树到场景中");
}
// 清空森林
void ClearForest()
{
foreach (Tree tree in trees)
{
tree.Destroy();
}
trees.Clear();
TreeFactory.Clear(); // 如果需要添加清除方法
}
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
// 绘制森林区域
Gizmos.color = new Color(0, 1, 0, 0.1f);
Gizmos.DrawCube(transform.position + Vector3.up * 0.1f,
new Vector3(areaSize.x, 0.1f, areaSize.y));
}
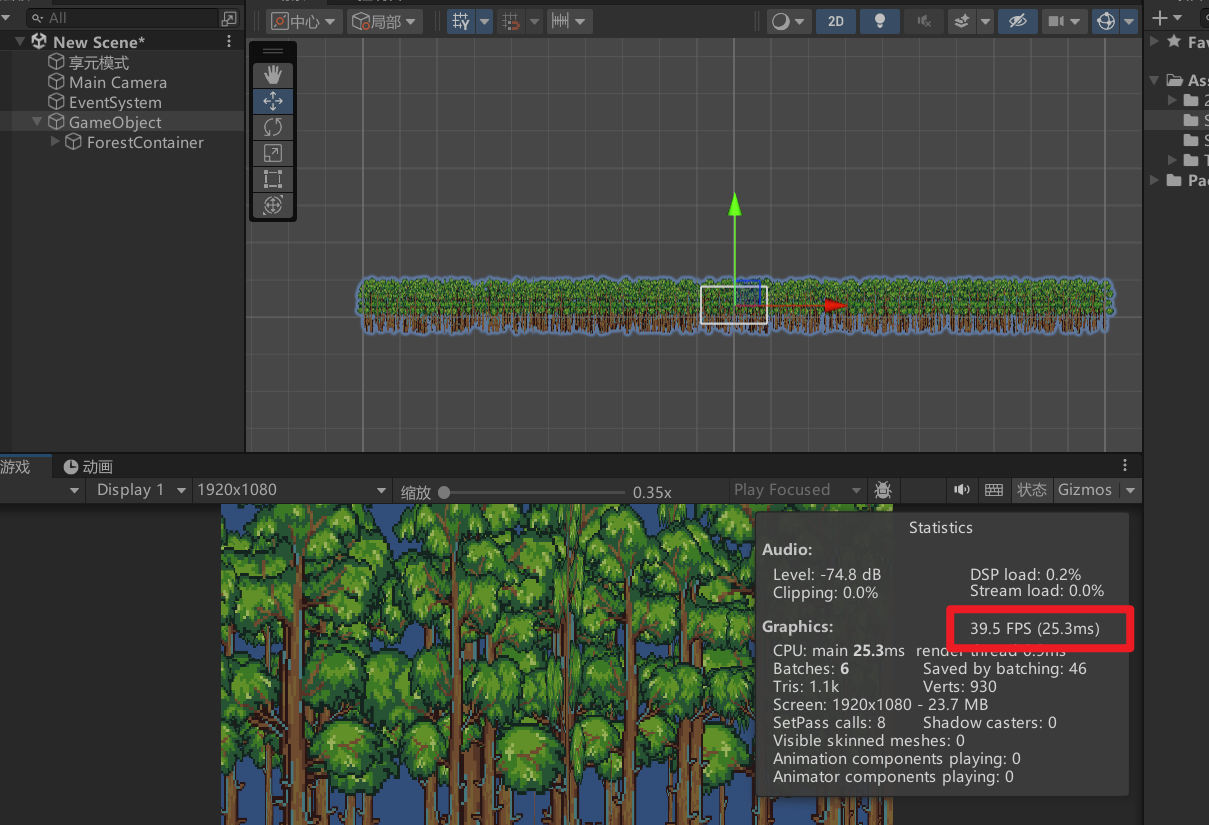
}5.运行效果对比
使用享元
可以看到帧率最高能达到120帧。

不使用享元
可以看到帧率直接下降了一半多,提升还是很显著的。
总结
在 Unity 中,享元模式非常适合应用在:
-
大规模场景物体(树、草、岩石)
-
特效实例(同类型粒子)
-
子弹、道具、装饰物
-
UI 中的重复元素
一句话总结就是:
当你发现"很多对象看起来一样,只是位置或状态不同"时,享元模式几乎一定值得考虑。